Xuesong Li
RnG: A Unified Transformer for Complete 3D Modeling from Partial Observations
Mar 01, 2026Abstract:Human perceive the 3D world through 2D observations from limited viewpoints. While recent feed-forward generalizable 3D reconstruction models excel at recovering 3D structures from sparse images, their representations are often confined to observed regions, leaving unseen geometry un-modeled. This raises a key, fundamental challenge: Can we infer a complete 3D structure from partial 2D observations? We present RnG (Reconstruction and Generation), a novel feed-forward Transformer that unifies these two tasks by predicting an implicit, complete 3D representation. At the core of RnG, we propose a reconstruction-guided causal attention mechanism that separates reconstruction and generation at the attention level, and treats the KV-cache as an implicit 3D representation. Then, arbitrary poses can efficiently query this cache to render high-fidelity, novel-view RGBD outputs. As a result, RnG not only accurately reconstructs visible geometry but also generates plausible, coherent unseen geometry and appearance. Our method achieves state-of-the-art performance in both generalizable 3D reconstruction and novel view generation, while operating efficiently enough for real-time interactive applications. Project page: https://npucvr.github.io/RnG
Probing and Bridging Geometry-Interaction Cues for Affordance Reasoning in Vision Foundation Models
Feb 24, 2026Abstract:What does it mean for a visual system to truly understand affordance? We argue that this understanding hinges on two complementary capacities: geometric perception, which identifies the structural parts of objects that enable interaction, and interaction perception, which models how an agent's actions engage with those parts. To test this hypothesis, we conduct a systematic probing of Visual Foundation Models (VFMs). We find that models like DINO inherently encode part-level geometric structures, while generative models like Flux contain rich, verb-conditioned spatial attention maps that serve as implicit interaction priors. Crucially, we demonstrate that these two dimensions are not merely correlated but are composable elements of affordance. By simply fusing DINO's geometric prototypes with Flux's interaction maps in a training-free and zero-shot manner, we achieve affordance estimation competitive with weakly-supervised methods. This final fusion experiment confirms that geometric and interaction perception are the fundamental building blocks of affordance understanding in VFMs, providing a mechanistic account of how perception grounds action.
A Kung Fu Athlete Bot That Can Do It All Day: Highly Dynamic, Balance-Challenging Motion Dataset and Autonomous Fall-Resilient Tracking
Feb 14, 2026Abstract:Current humanoid motion tracking systems can execute routine and moderately dynamic behaviors, yet significant gaps remain near hardware performance limits and algorithmic robustness boundaries. Martial arts represent an extreme case of highly dynamic human motion, characterized by rapid center-of-mass shifts, complex coordination, and abrupt posture transitions. However, datasets tailored to such high-intensity scenarios remain scarce. To address this gap, we construct KungFuAthlete, a high-dynamic martial arts motion dataset derived from professional athletes' daily training videos. The dataset includes ground and jump subsets covering representative complex motion patterns. The jump subset exhibits substantially higher joint, linear, and angular velocities compared to commonly used datasets such as LAFAN1, PHUMA, and AMASS, indicating significantly increased motion intensity and complexity. Importantly, even professional athletes may fail during highly dynamic movements. Similarly, humanoid robots are prone to instability and falls under external disturbances or execution errors. Most prior work assumes motion execution remains within safe states and lacks a unified strategy for modeling unsafe states and enabling reliable autonomous recovery. We propose a novel training paradigm that enables a single policy to jointly learn high-dynamic motion tracking and fall recovery, unifying agile execution and stabilization within one framework. This framework expands robotic capability from pure motion tracking to recovery-enabled execution, promoting more robust and autonomous humanoid performance in real-world high-dynamic scenarios.
Adaptive and Balanced Re-initialization for Long-timescale Continual Test-time Domain Adaptation
Feb 06, 2026Abstract:Continual test-time domain adaptation (CTTA) aims to adjust models so that they can perform well over time across non-stationary environments. While previous methods have made considerable efforts to optimize the adaptation process, a crucial question remains: Can the model adapt to continually changing environments over a long time? In this work, we explore facilitating better CTTA in the long run using a re-initialization (or reset) based method. First, we observe that the long-term performance is associated with the trajectory pattern in label flip. Based on this observed correlation, we propose a simple yet effective policy, Adaptive-and-Balanced Re-initialization (ABR), towards preserving the model's long-term performance. In particular, ABR performs weight re-initialization using adaptive intervals. The adaptive interval is determined based on the change in label flip. The proposed method is validated on extensive CTTA benchmarks, achieving superior performance.
Quality-Driven and Diversity-Aware Sample Expansion for Robust Marine Obstacle Segmentation
Dec 16, 2025Abstract:Marine obstacle detection demands robust segmentation under challenging conditions, such as sun glitter, fog, and rapidly changing wave patterns. These factors degrade image quality, while the scarcity and structural repetition of marine datasets limit the diversity of available training data. Although mask-conditioned diffusion models can synthesize layout-aligned samples, they often produce low-diversity outputs when conditioned on low-entropy masks and prompts, limiting their utility for improving robustness. In this paper, we propose a quality-driven and diversity-aware sample expansion pipeline that generates training data entirely at inference time, without retraining the diffusion model. The framework combines two key components:(i) a class-aware style bank that constructs high-entropy, semantically grounded prompts, and (ii) an adaptive annealing sampler that perturbs early conditioning, while a COD-guided proportional controller regulates this perturbation to boost diversity without compromising layout fidelity. Across marine obstacle benchmarks, augmenting training data with these controlled synthetic samples consistently improves segmentation performance across multiple backbones and increases visual variation in rare and texture-sensitive classes.
Structural Energy-Guided Sampling for View-Consistent Text-to-3D
Aug 23, 2025Abstract:Text-to-3D generation often suffers from the Janus problem, where objects look correct from the front but collapse into duplicated or distorted geometry from other angles. We attribute this failure to viewpoint bias in 2D diffusion priors, which propagates into 3D optimization. To address this, we propose Structural Energy-Guided Sampling (SEGS), a training-free, plug-and-play framework that enforces multi-view consistency entirely at sampling time. SEGS defines a structural energy in a PCA subspace of intermediate U-Net features and injects its gradients into the denoising trajectory, steering geometry toward the intended viewpoint while preserving appearance fidelity. Integrated seamlessly into SDS/VSD pipelines, SEGS significantly reduces Janus artifacts, achieving improved geometric alignment and viewpoint consistency without retraining or weight modification.
3D Gaussian Representations with Motion Trajectory Field for Dynamic Scene Reconstruction
Aug 10, 2025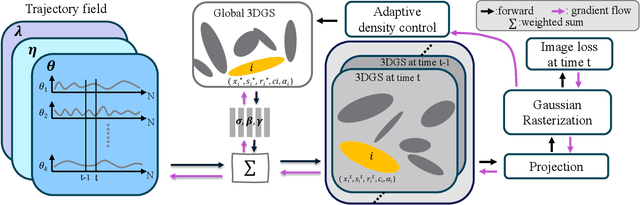
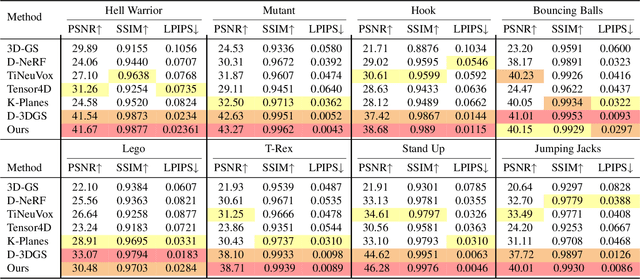
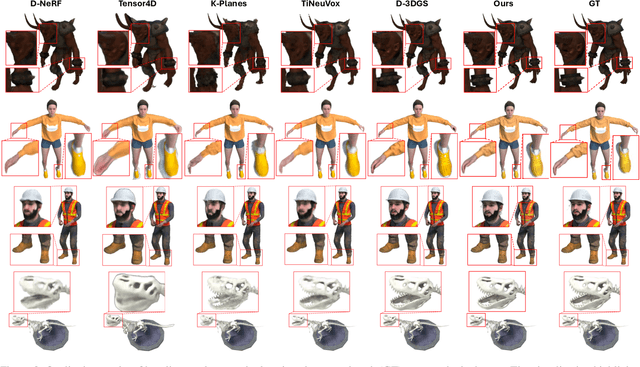

Abstract:This paper addresses the challenge of novel-view synthesis and motion reconstruction of dynamic scenes from monocular video, which is critical for many robotic applications. Although Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF) and 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) have demonstrated remarkable success in rendering static scenes, extending them to reconstruct dynamic scenes remains challenging. In this work, we introduce a novel approach that combines 3DGS with a motion trajectory field, enabling precise handling of complex object motions and achieving physically plausible motion trajectories. By decoupling dynamic objects from static background, our method compactly optimizes the motion trajectory field. The approach incorporates time-invariant motion coefficients and shared motion trajectory bases to capture intricate motion patterns while minimizing optimization complexity. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our approach achieves state-of-the-art results in both novel-view synthesis and motion trajectory recovery from monocular video, advancing the capabilities of dynamic scene reconstruction.
Vibration-Based Energy Metric for Restoring Needle Alignment in Autonomous Robotic Ultrasound
Aug 09, 2025Abstract:Precise needle alignment is essential for percutaneous needle insertion in robotic ultrasound-guided procedures. However, inherent challenges such as speckle noise, needle-like artifacts, and low image resolution make robust needle detection difficult, particularly when visibility is reduced or lost. In this paper, we propose a method to restore needle alignment when the ultrasound imaging plane and the needle insertion plane are misaligned. Unlike many existing approaches that rely heavily on needle visibility in ultrasound images, our method uses a more robust feature by periodically vibrating the needle using a mechanical system. Specifically, we propose a vibration-based energy metric that remains effective even when the needle is fully out of plane. Using this metric, we develop a control strategy to reposition the ultrasound probe in response to misalignments between the imaging plane and the needle insertion plane in both translation and rotation. Experiments conducted on ex-vivo porcine tissue samples using a dual-arm robotic ultrasound-guided needle insertion system demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed approach. The experimental results show the translational error of 0.41$\pm$0.27 mm and the rotational error of 0.51$\pm$0.19 degrees.
Speckle2Self: Self-Supervised Ultrasound Speckle Reduction Without Clean Data
Jul 09, 2025



Abstract:Image denoising is a fundamental task in computer vision, particularly in medical ultrasound (US) imaging, where speckle noise significantly degrades image quality. Although recent advancements in deep neural networks have led to substantial improvements in denoising for natural images, these methods cannot be directly applied to US speckle noise, as it is not purely random. Instead, US speckle arises from complex wave interference within the body microstructure, making it tissue-dependent. This dependency means that obtaining two independent noisy observations of the same scene, as required by pioneering Noise2Noise, is not feasible. Additionally, blind-spot networks also cannot handle US speckle noise due to its high spatial dependency. To address this challenge, we introduce Speckle2Self, a novel self-supervised algorithm for speckle reduction using only single noisy observations. The key insight is that applying a multi-scale perturbation (MSP) operation introduces tissue-dependent variations in the speckle pattern across different scales, while preserving the shared anatomical structure. This enables effective speckle suppression by modeling the clean image as a low-rank signal and isolating the sparse noise component. To demonstrate its effectiveness, Speckle2Self is comprehensively compared with conventional filter-based denoising algorithms and SOTA learning-based methods, using both realistic simulated US images and human carotid US images. Additionally, data from multiple US machines are employed to evaluate model generalization and adaptability to images from unseen domains. \textit{Code and datasets will be released upon acceptance.
Semantic Scene Graph for Ultrasound Image Explanation and Scanning Guidance
Jun 24, 2025Abstract:Understanding medical ultrasound imaging remains a long-standing challenge due to significant visual variability caused by differences in imaging and acquisition parameters. Recent advancements in large language models (LLMs) have been used to automatically generate terminology-rich summaries orientated to clinicians with sufficient physiological knowledge. Nevertheless, the increasing demand for improved ultrasound interpretability and basic scanning guidance among non-expert users, e.g., in point-of-care settings, has not yet been explored. In this study, we first introduce the scene graph (SG) for ultrasound images to explain image content to ordinary and provide guidance for ultrasound scanning. The ultrasound SG is first computed using a transformer-based one-stage method, eliminating the need for explicit object detection. To generate a graspable image explanation for ordinary, the user query is then used to further refine the abstract SG representation through LLMs. Additionally, the predicted SG is explored for its potential in guiding ultrasound scanning toward missing anatomies within the current imaging view, assisting ordinary users in achieving more standardized and complete anatomical exploration. The effectiveness of this SG-based image explanation and scanning guidance has been validated on images from the left and right neck regions, including the carotid and thyroid, across five volunteers. The results demonstrate the potential of the method to maximally democratize ultrasound by enhancing its interpretability and usability for ordinaries.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge