Zhongliang Jiang
Vibration-Based Energy Metric for Restoring Needle Alignment in Autonomous Robotic Ultrasound
Aug 09, 2025Abstract:Precise needle alignment is essential for percutaneous needle insertion in robotic ultrasound-guided procedures. However, inherent challenges such as speckle noise, needle-like artifacts, and low image resolution make robust needle detection difficult, particularly when visibility is reduced or lost. In this paper, we propose a method to restore needle alignment when the ultrasound imaging plane and the needle insertion plane are misaligned. Unlike many existing approaches that rely heavily on needle visibility in ultrasound images, our method uses a more robust feature by periodically vibrating the needle using a mechanical system. Specifically, we propose a vibration-based energy metric that remains effective even when the needle is fully out of plane. Using this metric, we develop a control strategy to reposition the ultrasound probe in response to misalignments between the imaging plane and the needle insertion plane in both translation and rotation. Experiments conducted on ex-vivo porcine tissue samples using a dual-arm robotic ultrasound-guided needle insertion system demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed approach. The experimental results show the translational error of 0.41$\pm$0.27 mm and the rotational error of 0.51$\pm$0.19 degrees.
Tactile-Guided Robotic Ultrasound: Mapping Preplanned Scan Paths for Intercostal Imaging
Jul 27, 2025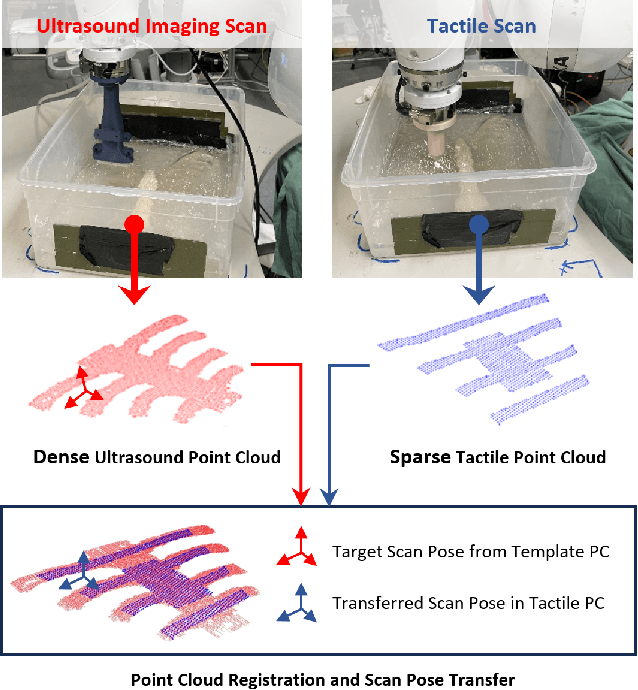
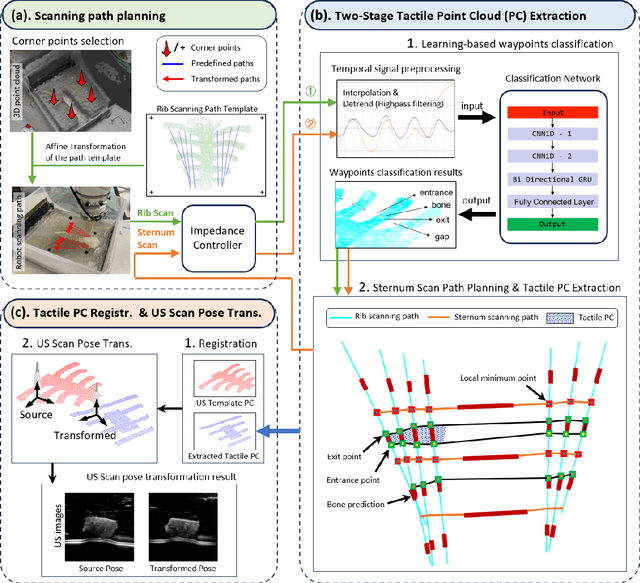
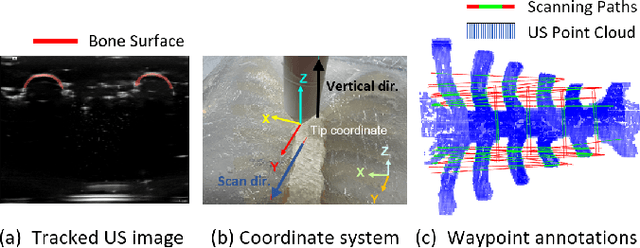
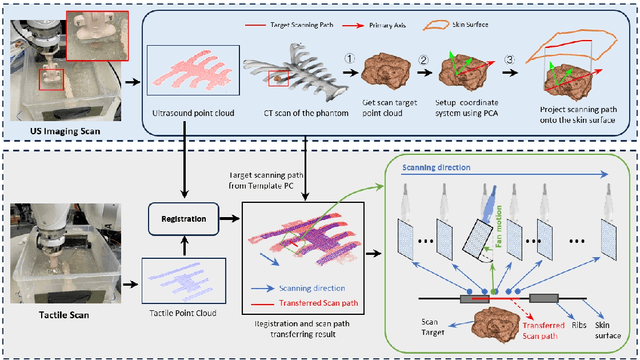
Abstract:Medical ultrasound (US) imaging is widely used in clinical examinations due to its portability, real-time capability, and radiation-free nature. To address inter- and intra-operator variability, robotic ultrasound systems have gained increasing attention. However, their application in challenging intercostal imaging remains limited due to the lack of an effective scan path generation method within the constrained acoustic window. To overcome this challenge, we explore the potential of tactile cues for characterizing subcutaneous rib structures as an alternative signal for ultrasound segmentation-free bone surface point cloud extraction. Compared to 2D US images, 1D tactile-related signals offer higher processing efficiency and are less susceptible to acoustic noise and artifacts. By leveraging robotic tracking data, a sparse tactile point cloud is generated through a few scans along the rib, mimicking human palpation. To robustly map the scanning trajectory into the intercostal space, the sparse tactile bone location point cloud is first interpolated to form a denser representation. This refined point cloud is then registered to an image-based dense bone surface point cloud, enabling accurate scan path mapping for individual patients. Additionally, to ensure full coverage of the object of interest, we introduce an automated tilt angle adjustment method to visualize structures beneath the bone. To validate the proposed method, we conducted comprehensive experiments on four distinct phantoms. The final scanning waypoint mapping achieved Mean Nearest Neighbor Distance (MNND) and Hausdorff distance (HD) errors of 3.41 mm and 3.65 mm, respectively, while the reconstructed object beneath the bone had errors of 0.69 mm and 2.2 mm compared to the CT ground truth.
Intelligent Virtual Sonographer (IVS): Enhancing Physician-Robot-Patient Communication
Jul 17, 2025Abstract:The advancement and maturity of large language models (LLMs) and robotics have unlocked vast potential for human-computer interaction, particularly in the field of robotic ultrasound. While existing research primarily focuses on either patient-robot or physician-robot interaction, the role of an intelligent virtual sonographer (IVS) bridging physician-robot-patient communication remains underexplored. This work introduces a conversational virtual agent in Extended Reality (XR) that facilitates real-time interaction between physicians, a robotic ultrasound system(RUS), and patients. The IVS agent communicates with physicians in a professional manner while offering empathetic explanations and reassurance to patients. Furthermore, it actively controls the RUS by executing physician commands and transparently relays these actions to the patient. By integrating LLM-powered dialogue with speech-to-text, text-to-speech, and robotic control, our system enhances the efficiency, clarity, and accessibility of robotic ultrasound acquisition. This work constitutes a first step toward understanding how IVS can bridge communication gaps in physician-robot-patient interaction, providing more control and therefore trust into physician-robot interaction while improving patient experience and acceptance of robotic ultrasound.
Speckle2Self: Self-Supervised Ultrasound Speckle Reduction Without Clean Data
Jul 09, 2025



Abstract:Image denoising is a fundamental task in computer vision, particularly in medical ultrasound (US) imaging, where speckle noise significantly degrades image quality. Although recent advancements in deep neural networks have led to substantial improvements in denoising for natural images, these methods cannot be directly applied to US speckle noise, as it is not purely random. Instead, US speckle arises from complex wave interference within the body microstructure, making it tissue-dependent. This dependency means that obtaining two independent noisy observations of the same scene, as required by pioneering Noise2Noise, is not feasible. Additionally, blind-spot networks also cannot handle US speckle noise due to its high spatial dependency. To address this challenge, we introduce Speckle2Self, a novel self-supervised algorithm for speckle reduction using only single noisy observations. The key insight is that applying a multi-scale perturbation (MSP) operation introduces tissue-dependent variations in the speckle pattern across different scales, while preserving the shared anatomical structure. This enables effective speckle suppression by modeling the clean image as a low-rank signal and isolating the sparse noise component. To demonstrate its effectiveness, Speckle2Self is comprehensively compared with conventional filter-based denoising algorithms and SOTA learning-based methods, using both realistic simulated US images and human carotid US images. Additionally, data from multiple US machines are employed to evaluate model generalization and adaptability to images from unseen domains. \textit{Code and datasets will be released upon acceptance.
UltraAD: Fine-Grained Ultrasound Anomaly Classification via Few-Shot CLIP Adaptation
Jun 24, 2025Abstract:Precise anomaly detection in medical images is critical for clinical decision-making. While recent unsupervised or semi-supervised anomaly detection methods trained on large-scale normal data show promising results, they lack fine-grained differentiation, such as benign vs. malignant tumors. Additionally, ultrasound (US) imaging is highly sensitive to devices and acquisition parameter variations, creating significant domain gaps in the resulting US images. To address these challenges, we propose UltraAD, a vision-language model (VLM)-based approach that leverages few-shot US examples for generalized anomaly localization and fine-grained classification. To enhance localization performance, the image-level token of query visual prototypes is first fused with learnable text embeddings. This image-informed prompt feature is then further integrated with patch-level tokens, refining local representations for improved accuracy. For fine-grained classification, a memory bank is constructed from few-shot image samples and corresponding text descriptions that capture anatomical and abnormality-specific features. During training, the stored text embeddings remain frozen, while image features are adapted to better align with medical data. UltraAD has been extensively evaluated on three breast US datasets, outperforming state-of-the-art methods in both lesion localization and fine-grained medical classification. The code will be released upon acceptance.
Semantic Scene Graph for Ultrasound Image Explanation and Scanning Guidance
Jun 24, 2025Abstract:Understanding medical ultrasound imaging remains a long-standing challenge due to significant visual variability caused by differences in imaging and acquisition parameters. Recent advancements in large language models (LLMs) have been used to automatically generate terminology-rich summaries orientated to clinicians with sufficient physiological knowledge. Nevertheless, the increasing demand for improved ultrasound interpretability and basic scanning guidance among non-expert users, e.g., in point-of-care settings, has not yet been explored. In this study, we first introduce the scene graph (SG) for ultrasound images to explain image content to ordinary and provide guidance for ultrasound scanning. The ultrasound SG is first computed using a transformer-based one-stage method, eliminating the need for explicit object detection. To generate a graspable image explanation for ordinary, the user query is then used to further refine the abstract SG representation through LLMs. Additionally, the predicted SG is explored for its potential in guiding ultrasound scanning toward missing anatomies within the current imaging view, assisting ordinary users in achieving more standardized and complete anatomical exploration. The effectiveness of this SG-based image explanation and scanning guidance has been validated on images from the left and right neck regions, including the carotid and thyroid, across five volunteers. The results demonstrate the potential of the method to maximally democratize ultrasound by enhancing its interpretability and usability for ordinaries.
Manipulating Elasto-Plastic Objects With 3D Occupancy and Learning-Based Predictive Control
May 22, 2025Abstract:Manipulating elasto-plastic objects remains a significant challenge due to severe self-occlusion, difficulties of representation, and complicated dynamics. This work proposes a novel framework for elasto-plastic object manipulation with a quasi-static assumption for motions, leveraging 3D occupancy to represent such objects, a learned dynamics model trained with 3D occupancy, and a learning-based predictive control algorithm to address these challenges effectively. We build a novel data collection platform to collect full spatial information and propose a pipeline for generating a 3D occupancy dataset. To infer the 3D occupancy during manipulation, an occupancy prediction network is trained with multiple RGB images supervised by the generated dataset. We design a deep neural network empowered by a 3D convolution neural network (CNN) and a graph neural network (GNN) to predict the complex deformation with the inferred 3D occupancy results. A learning-based predictive control algorithm is introduced to plan the robot actions, incorporating a novel shape-based action initialization module specifically designed to improve the planner efficiency. The proposed framework in this paper can successfully shape the elasto-plastic objects into a given goal shape and has been verified in various experiments both in simulation and the real world.
Learning to Efficiently Adapt Foundation Models for Self-Supervised Endoscopic 3D Scene Reconstruction from Any Cameras
Mar 20, 2025

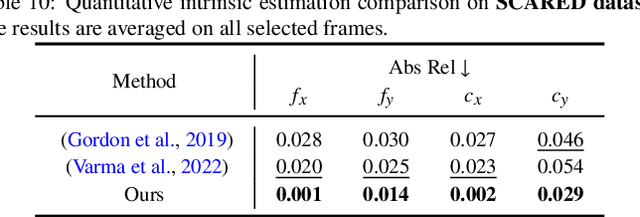
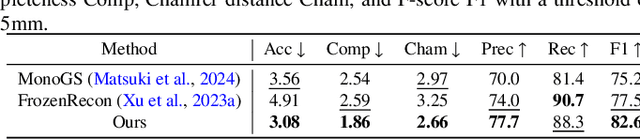
Abstract:Accurate 3D scene reconstruction is essential for numerous medical tasks. Given the challenges in obtaining ground truth data, there has been an increasing focus on self-supervised learning (SSL) for endoscopic depth estimation as a basis for scene reconstruction. While foundation models have shown remarkable progress in visual tasks, their direct application to the medical domain often leads to suboptimal results. However, the visual features from these models can still enhance endoscopic tasks, emphasizing the need for efficient adaptation strategies, which still lack exploration currently. In this paper, we introduce Endo3DAC, a unified framework for endoscopic scene reconstruction that efficiently adapts foundation models. We design an integrated network capable of simultaneously estimating depth maps, relative poses, and camera intrinsic parameters. By freezing the backbone foundation model and training only the specially designed Gated Dynamic Vector-Based Low-Rank Adaptation (GDV-LoRA) with separate decoder heads, Endo3DAC achieves superior depth and pose estimation while maintaining training efficiency. Additionally, we propose a 3D scene reconstruction pipeline that optimizes depth maps' scales, shifts, and a few parameters based on our integrated network. Extensive experiments across four endoscopic datasets demonstrate that Endo3DAC significantly outperforms other state-of-the-art methods while requiring fewer trainable parameters. To our knowledge, we are the first to utilize a single network that only requires surgical videos to perform both SSL depth estimation and scene reconstruction tasks. The code will be released upon acceptance.
Robotic CBCT Meets Robotic Ultrasound
Feb 17, 2025Abstract:The multi-modality imaging system offers optimal fused images for safe and precise interventions in modern clinical practices, such as computed tomography - ultrasound (CT-US) guidance for needle insertion. However, the limited dexterity and mobility of current imaging devices hinder their integration into standardized workflows and the advancement toward fully autonomous intervention systems. In this paper, we present a novel clinical setup where robotic cone beam computed tomography (CBCT) and robotic US are pre-calibrated and dynamically co-registered, enabling new clinical applications. This setup allows registration-free rigid registration, facilitating multi-modal guided procedures in the absence of tissue deformation. First, a one-time pre-calibration is performed between the systems. To ensure a safe insertion path by highlighting critical vasculature on the 3D CBCT, SAM2 segments vessels from B-mode images, using the Doppler signal as an autonomously generated prompt. Based on the registration, the Doppler image or segmented vessel masks are then mapped onto the CBCT, creating an optimally fused image with comprehensive detail. To validate the system, we used a specially designed phantom, featuring lesions covered by ribs and multiple vessels with simulated moving flow. The mapping error between US and CBCT resulted in an average deviation of 1.72+-0.62 mm. A user study demonstrated the effectiveness of CBCT-US fusion for needle insertion guidance, showing significant improvements in time efficiency, accuracy, and success rate. Needle intervention performance improved by approximately 50% compared to the conventional US-guided workflow. We present the first robotic dual-modality imaging system designed to guide clinical applications. The results show significant performance improvements compared to traditional manual interventions.
Gaze-Guided Robotic Vascular Ultrasound Leveraging Human Intention Estimation
Feb 07, 2025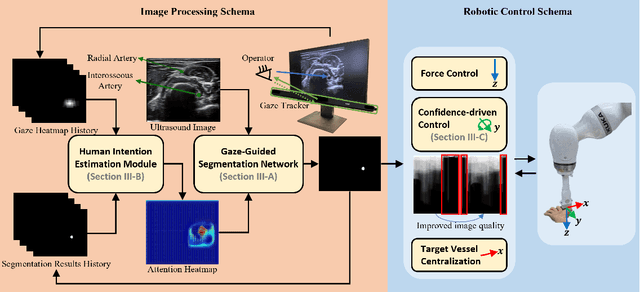
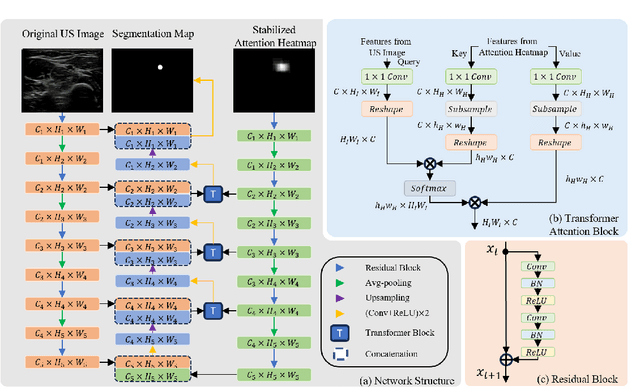
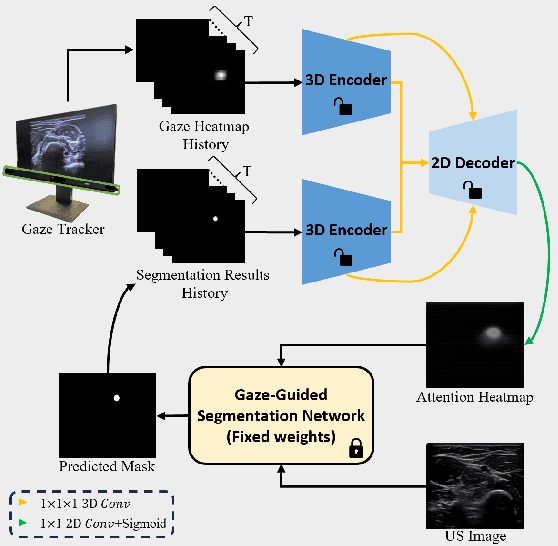
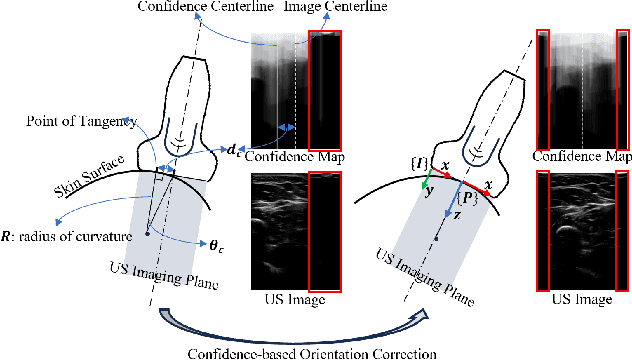
Abstract:Medical ultrasound has been widely used to examine vascular structure in modern clinical practice. However, traditional ultrasound examination often faces challenges related to inter- and intra-operator variation. The robotic ultrasound system (RUSS) appears as a potential solution for such challenges because of its superiority in stability and reproducibility. Given the complex anatomy of human vasculature, multiple vessels often appear in ultrasound images, or a single vessel bifurcates into branches, complicating the examination process. To tackle this challenge, this work presents a gaze-guided RUSS for vascular applications. A gaze tracker captures the eye movements of the operator. The extracted gaze signal guides the RUSS to follow the correct vessel when it bifurcates. Additionally, a gaze-guided segmentation network is proposed to enhance segmentation robustness by exploiting gaze information. However, gaze signals are often noisy, requiring interpretation to accurately discern the operator's true intentions. To this end, this study proposes a stabilization module to process raw gaze data. The inferred attention heatmap is utilized as a region proposal to aid segmentation and serve as a trigger signal when the operator needs to adjust the scanning target, such as when a bifurcation appears. To ensure appropriate contact between the probe and surface during scanning, an automatic ultrasound confidence-based orientation correction method is developed. In experiments, we demonstrated the efficiency of the proposed gaze-guided segmentation pipeline by comparing it with other methods. Besides, the performance of the proposed gaze-guided RUSS was also validated as a whole on a realistic arm phantom with an uneven surface.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge