Lulu Zhao
RecGPT Technical Report
Jul 30, 2025



Abstract:Recommender systems are among the most impactful applications of artificial intelligence, serving as critical infrastructure connecting users, merchants, and platforms. However, most current industrial systems remain heavily reliant on historical co-occurrence patterns and log-fitting objectives, i.e., optimizing for past user interactions without explicitly modeling user intent. This log-fitting approach often leads to overfitting to narrow historical preferences, failing to capture users' evolving and latent interests. As a result, it reinforces filter bubbles and long-tail phenomena, ultimately harming user experience and threatening the sustainability of the whole recommendation ecosystem. To address these challenges, we rethink the overall design paradigm of recommender systems and propose RecGPT, a next-generation framework that places user intent at the center of the recommendation pipeline. By integrating large language models (LLMs) into key stages of user interest mining, item retrieval, and explanation generation, RecGPT transforms log-fitting recommendation into an intent-centric process. To effectively align general-purpose LLMs to the above domain-specific recommendation tasks at scale, RecGPT incorporates a multi-stage training paradigm, which integrates reasoning-enhanced pre-alignment and self-training evolution, guided by a Human-LLM cooperative judge system. Currently, RecGPT has been fully deployed on the Taobao App. Online experiments demonstrate that RecGPT achieves consistent performance gains across stakeholders: users benefit from increased content diversity and satisfaction, merchants and the platform gain greater exposure and conversions. These comprehensive improvement results across all stakeholders validates that LLM-driven, intent-centric design can foster a more sustainable and mutually beneficial recommendation ecosystem.
Manipulating Elasto-Plastic Objects With 3D Occupancy and Learning-Based Predictive Control
May 22, 2025Abstract:Manipulating elasto-plastic objects remains a significant challenge due to severe self-occlusion, difficulties of representation, and complicated dynamics. This work proposes a novel framework for elasto-plastic object manipulation with a quasi-static assumption for motions, leveraging 3D occupancy to represent such objects, a learned dynamics model trained with 3D occupancy, and a learning-based predictive control algorithm to address these challenges effectively. We build a novel data collection platform to collect full spatial information and propose a pipeline for generating a 3D occupancy dataset. To infer the 3D occupancy during manipulation, an occupancy prediction network is trained with multiple RGB images supervised by the generated dataset. We design a deep neural network empowered by a 3D convolution neural network (CNN) and a graph neural network (GNN) to predict the complex deformation with the inferred 3D occupancy results. A learning-based predictive control algorithm is introduced to plan the robot actions, incorporating a novel shape-based action initialization module specifically designed to improve the planner efficiency. The proposed framework in this paper can successfully shape the elasto-plastic objects into a given goal shape and has been verified in various experiments both in simulation and the real world.
CareBot: A Pioneering Full-Process Open-Source Medical Language Model
Dec 23, 2024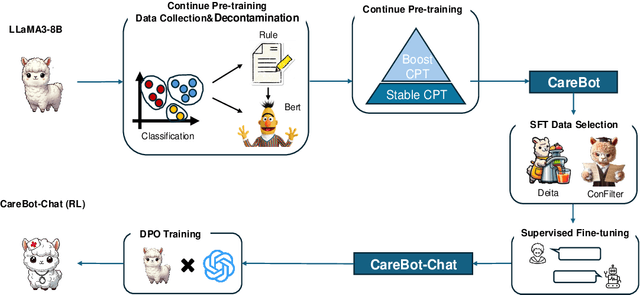
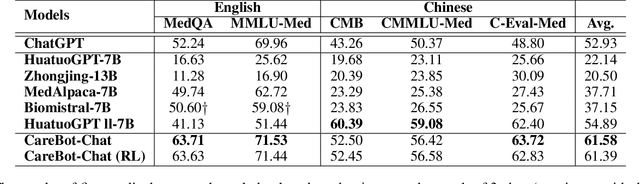
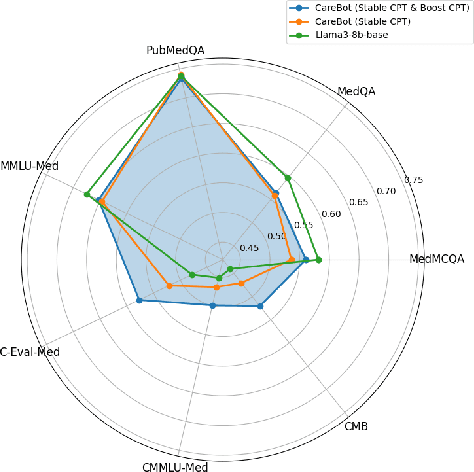
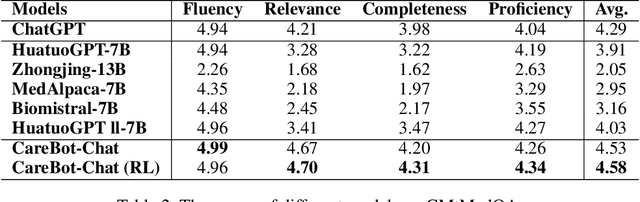
Abstract:Recently, both closed-source LLMs and open-source communities have made significant strides, outperforming humans in various general domains. However, their performance in specific professional domains such as medicine, especially within the open-source community, remains suboptimal due to the complexity of medical knowledge. In this paper, we propose CareBot, a bilingual medical LLM, which leverages a comprehensive approach integrating continuous pre-training (CPT), supervised fine-tuning (SFT), and reinforcement learning with human feedback (RLHF). Our novel two-stage CPT method, comprising Stable CPT and Boost CPT, effectively bridges the gap between general and domain-specific data, facilitating a smooth transition from pre-training to fine-tuning and enhancing domain knowledge progressively. We also introduce DataRater, a model designed to assess data quality during CPT, ensuring that the training data is both accurate and relevant. For SFT, we develope a large and diverse bilingual dataset, along with ConFilter, a metric to enhance multi-turn dialogue quality, which is crucial to improving the model's ability to handle more complex dialogues. The combination of high-quality data sources and innovative techniques significantly improves CareBot's performance across a range of medical applications. Our rigorous evaluations on Chinese and English benchmarks confirm CareBot's effectiveness in medical consultation and education. These advancements not only address current limitations in medical LLMs but also set a new standard for developing effective and reliable open-source models in the medical domain. We will open-source the datasets and models later, contributing valuable resources to the research community.
B-STaR: Monitoring and Balancing Exploration and Exploitation in Self-Taught Reasoners
Dec 23, 2024



Abstract:In the absence of extensive human-annotated data for complex reasoning tasks, self-improvement -- where models are trained on their own outputs -- has emerged as a primary method for enhancing performance. However, the critical factors underlying the mechanism of these iterative self-improving methods remain poorly understood, such as under what conditions self-improvement is effective, and what are the bottlenecks in the current iterations. In this work, we identify and propose methods to monitor two pivotal factors in this iterative process: (1) the model's ability to generate sufficiently diverse responses (exploration); and (2) the effectiveness of external rewards in distinguishing high-quality candidates from lower-quality ones (exploitation). Using mathematical reasoning as a case study, we begin with a quantitative analysis to track the dynamics of exploration and exploitation, discovering that a model's exploratory capabilities rapidly deteriorate over iterations, and the effectiveness of exploiting external rewards diminishes as well. Motivated by these findings, we introduce B-STaR, a Self-Taught Reasoning framework that autonomously adjusts configurations across iterations to Balance exploration and exploitation, thereby optimizing the self-improving effectiveness based on the current policy model and available rewards. Our experiments on mathematical reasoning, coding, and commonsense reasoning demonstrate that B-STaR not only enhances the model's exploratory capabilities throughout training but also achieves a more effective balance between exploration and exploitation, leading to superior performance.
Smaller Language Models Are Better Instruction Evolvers
Dec 15, 2024



Abstract:Instruction tuning has been widely used to unleash the complete potential of large language models. Notably, complex and diverse instructions are of significant importance as they can effectively align models with various downstream tasks. However, current approaches to constructing large-scale instructions predominantly favour powerful models such as GPT-4 or those with over 70 billion parameters, under the empirical presumption that such larger language models (LLMs) inherently possess enhanced capabilities. In this study, we question this prevalent assumption and conduct an in-depth exploration into the potential of smaller language models (SLMs) in the context of instruction evolution. Extensive experiments across three scenarios of instruction evolution reveal that smaller language models (SLMs) can synthesize more effective instructions than LLMs. Further analysis demonstrates that SLMs possess a broader output space during instruction evolution, resulting in more complex and diverse variants. We also observe that the existing metrics fail to focus on the impact of the instructions. Thus, we propose Instruction Complex-Aware IFD (IC-IFD), which introduces instruction complexity in the original IFD score to evaluate the effectiveness of instruction data more accurately. Our source code is available at: \href{https://github.com/HypherX/Evolution-Analysis}{https://github.com/HypherX/Evolution-Analysis}
MoSLD: An Extremely Parameter-Efficient Mixture-of-Shared LoRAs for Multi-Task Learning
Dec 12, 2024Abstract:Recently, LoRA has emerged as a crucial technique for fine-tuning large pre-trained models, yet its performance in multi-task learning scenarios often falls short. In contrast, the MoE architecture presents a natural solution to this issue. However, it introduces challenges such as mutual interference of data across multiple domains and knowledge forgetting of various tasks. Additionally, MoE significantly increases the number of parameters, posing a computational cost challenge. Therefore, in this paper, we propose MoSLD, a mixture-of-shared-LoRAs model with a dropout strategy. MoSLD addresses these challenges by sharing the upper projection matrix in LoRA among different experts, encouraging the model to learn general knowledge across tasks, while still allowing the lower projection matrix to focus on the unique features of each task. The application of dropout alleviates the imbalanced update of parameter matrix and mitigates parameter overfitting in LoRA. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our model exhibits excellent performance in both single-task and multi-task scenarios, with robust out-of-domain generalization capabilities.
Aqulia-Med LLM: Pioneering Full-Process Open-Source Medical Language Models
Jun 18, 2024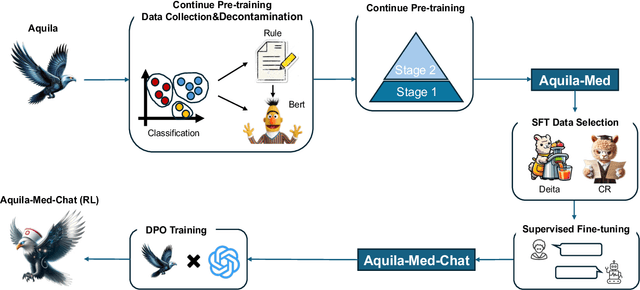
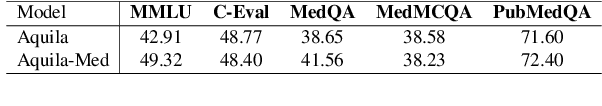
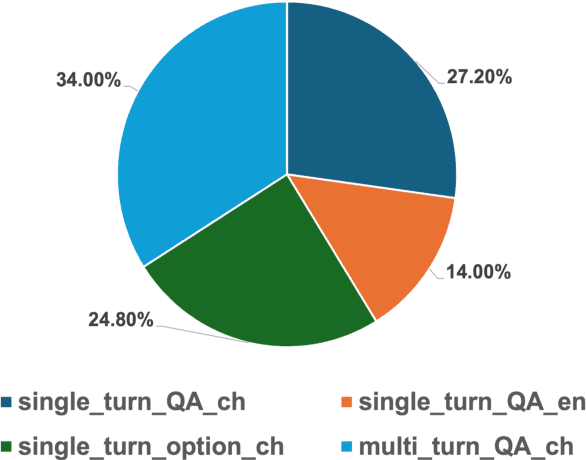
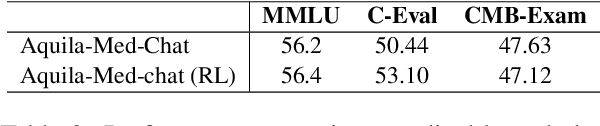
Abstract:Recently, both closed-source LLMs and open-source communities have made significant strides, outperforming humans in various general domains. However, their performance in specific professional fields such as medicine, especially within the open-source community, remains suboptimal due to the complexity of medical knowledge. We propose Aquila-Med, a bilingual medical LLM based on Aquila, addressing these challenges through continue pre-training, supervised fine-tuning (SFT), and reinforcement learning from human feedback (RLHF). We construct a large-scale Chinese and English medical dataset for continue pre-training and a high-quality SFT dataset, covering extensive medical specialties. Additionally, we develop a high-quality Direct Preference Optimization (DPO) dataset for further alignment. Aquila-Med achieves notable results across single-turn, multi-turn dialogues, and medical multiple-choice questions, demonstrating the effectiveness of our approach. We open-source the datasets and the entire training process, contributing valuable resources to the research community. Our models and datasets will released at https://huggingface.co/BAAI/AquilaMed-RL.
Graph Convolutional Network with Connectivity Uncertainty for EEG-based Emotion Recognition
Oct 22, 2023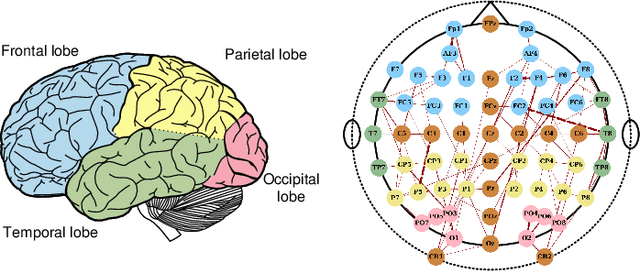
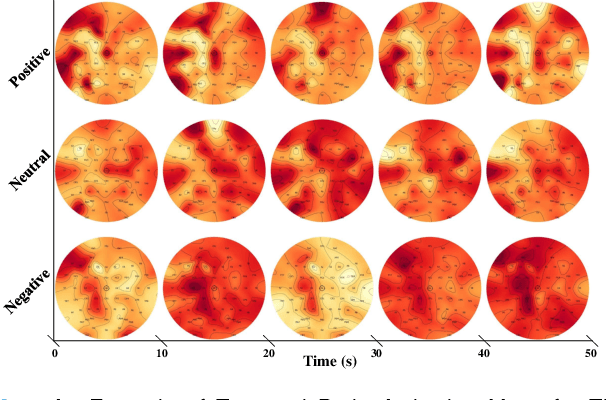
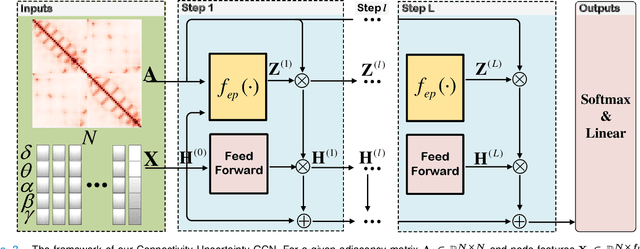

Abstract:Automatic emotion recognition based on multichannel Electroencephalography (EEG) holds great potential in advancing human-computer interaction. However, several significant challenges persist in existing research on algorithmic emotion recognition. These challenges include the need for a robust model to effectively learn discriminative node attributes over long paths, the exploration of ambiguous topological information in EEG channels and effective frequency bands, and the mapping between intrinsic data qualities and provided labels. To address these challenges, this study introduces the distribution-based uncertainty method to represent spatial dependencies and temporal-spectral relativeness in EEG signals based on Graph Convolutional Network (GCN) architecture that adaptively assigns weights to functional aggregate node features, enabling effective long-path capturing while mitigating over-smoothing phenomena. Moreover, the graph mixup technique is employed to enhance latent connected edges and mitigate noisy label issues. Furthermore, we integrate the uncertainty learning method with deep GCN weights in a one-way learning fashion, termed Connectivity Uncertainty GCN (CU-GCN). We evaluate our approach on two widely used datasets, namely SEED and SEEDIV, for emotion recognition tasks. The experimental results demonstrate the superiority of our methodology over previous methods, yielding positive and significant improvements. Ablation studies confirm the substantial contributions of each component to the overall performance.
Seen to Unseen: Exploring Compositional Generalization of Multi-Attribute Controllable Dialogue Generation
Jun 17, 2023Abstract:Existing controllable dialogue generation work focuses on the single-attribute control and lacks generalization capability to out-of-distribution multiple attribute combinations. In this paper, we explore the compositional generalization for multi-attribute controllable dialogue generation where a model can learn from seen attribute values and generalize to unseen combinations. We propose a prompt-based disentangled controllable dialogue generation model, DCG. It learns attribute concept composition by generating attribute-oriented prompt vectors and uses a disentanglement loss to disentangle different attributes for better generalization. Besides, we design a unified reference-free evaluation framework for multiple attributes with different levels of granularities. Experiment results on two benchmarks prove the effectiveness of our method and the evaluation metric.
Domain-Oriented Prefix-Tuning: Towards Efficient and Generalizable Fine-tuning for Zero-Shot Dialogue Summarization
Apr 09, 2022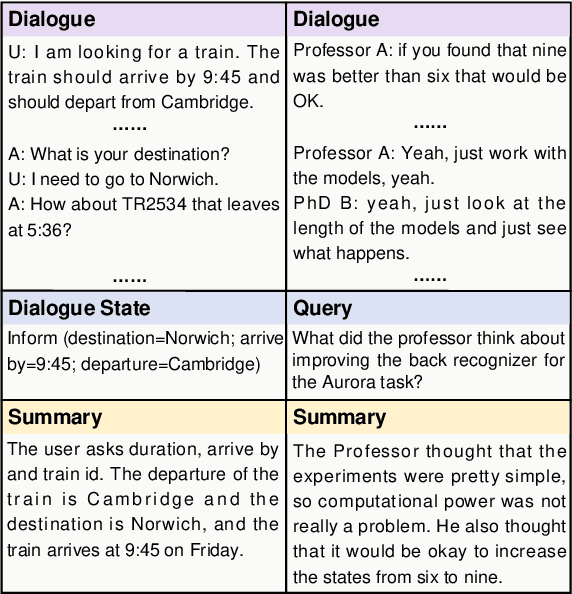
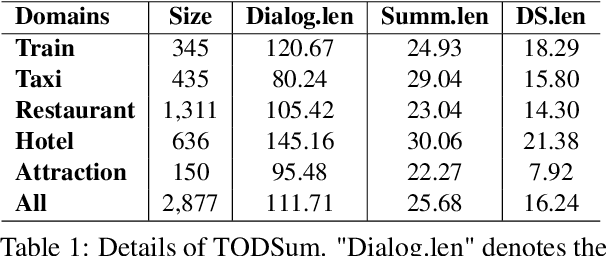
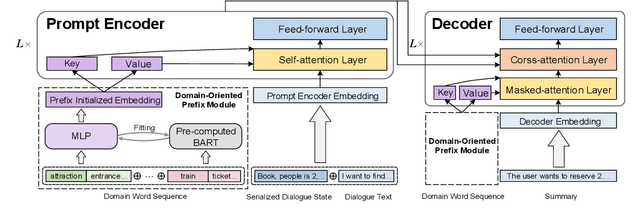
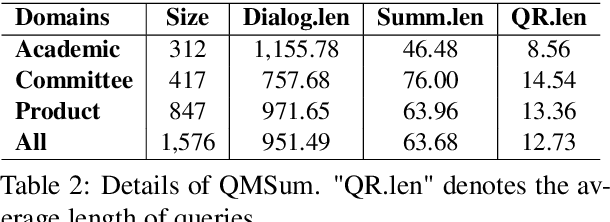
Abstract:The most advanced abstractive dialogue summarizers lack generalization ability on new domains and the existing researches for domain adaptation in summarization generally rely on large-scale pre-trainings. To explore the lightweight fine-tuning methods for domain adaptation of dialogue summarization, in this paper, we propose an efficient and generalizable Domain-Oriented Prefix-tuning model, which utilizes a domain word initialized prefix module to alleviate domain entanglement and adopts discrete prompts to guide the model to focus on key contents of dialogues and enhance model generalization. We conduct zero-shot experiments and build domain adaptation benchmarks on two multi-domain dialogue summarization datasets, TODSum and QMSum. Adequate experiments and qualitative analysis prove the effectiveness of our methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge