Zhiqi Ma
Learning to Efficiently Adapt Foundation Models for Self-Supervised Endoscopic 3D Scene Reconstruction from Any Cameras
Mar 20, 2025

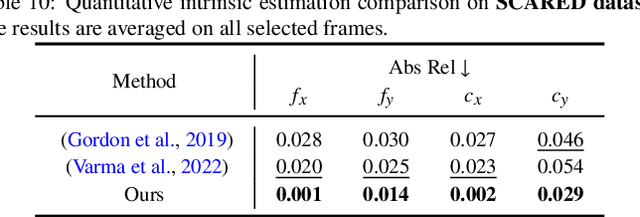
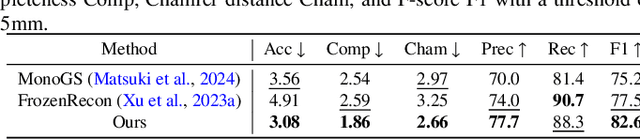
Abstract:Accurate 3D scene reconstruction is essential for numerous medical tasks. Given the challenges in obtaining ground truth data, there has been an increasing focus on self-supervised learning (SSL) for endoscopic depth estimation as a basis for scene reconstruction. While foundation models have shown remarkable progress in visual tasks, their direct application to the medical domain often leads to suboptimal results. However, the visual features from these models can still enhance endoscopic tasks, emphasizing the need for efficient adaptation strategies, which still lack exploration currently. In this paper, we introduce Endo3DAC, a unified framework for endoscopic scene reconstruction that efficiently adapts foundation models. We design an integrated network capable of simultaneously estimating depth maps, relative poses, and camera intrinsic parameters. By freezing the backbone foundation model and training only the specially designed Gated Dynamic Vector-Based Low-Rank Adaptation (GDV-LoRA) with separate decoder heads, Endo3DAC achieves superior depth and pose estimation while maintaining training efficiency. Additionally, we propose a 3D scene reconstruction pipeline that optimizes depth maps' scales, shifts, and a few parameters based on our integrated network. Extensive experiments across four endoscopic datasets demonstrate that Endo3DAC significantly outperforms other state-of-the-art methods while requiring fewer trainable parameters. To our knowledge, we are the first to utilize a single network that only requires surgical videos to perform both SSL depth estimation and scene reconstruction tasks. The code will be released upon acceptance.
M2oE: Multimodal Collaborative Expert Peptide Model
Nov 20, 2024Abstract:Peptides are biomolecules comprised of amino acids that play an important role in our body. In recent years, peptides have received extensive attention in drug design and synthesis, and peptide prediction tasks help us better search for functional peptides. Typically, we use the primary sequence and structural information of peptides for model encoding. However, recent studies have focused more on single-modal information (structure or sequence) for prediction without multi-modal approaches. We found that single-modal models are not good at handling datasets with less information in that particular modality. Therefore, this paper proposes the M2oE multi-modal collaborative expert peptide model. Based on previous work, by integrating sequence and spatial structural information, employing expert model and Cross-Attention Mechanism, the model's capabilities are balanced and improved. Experimental results indicate that the M2oE model performs excellently in complex task predictions.
Flare-Aware Cross-modal Enhancement Network for Multi-spectral Vehicle Re-identification
May 23, 2023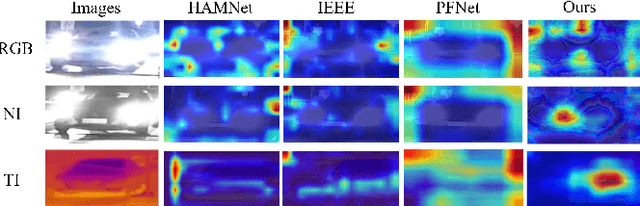
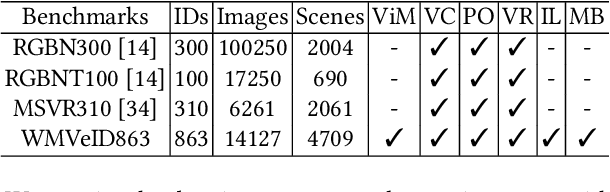
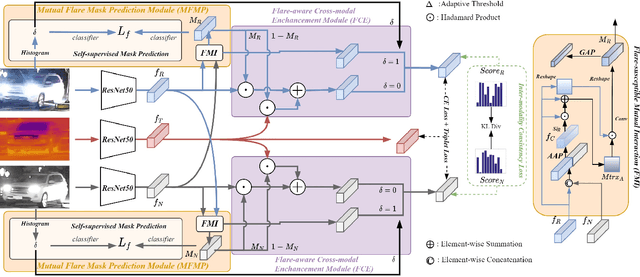
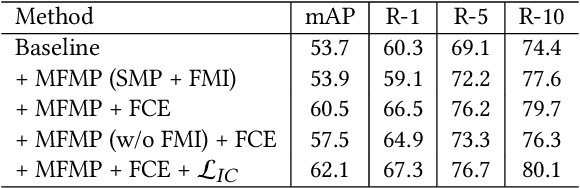
Abstract:Multi-spectral vehicle re-identification aims to address the challenge of identifying vehicles in complex lighting conditions by incorporating complementary visible and infrared information. However, in harsh environments, the discriminative cues in RGB and NIR modalities are often lost due to strong flares from vehicle lamps or sunlight, and existing multi-modal fusion methods are limited in their ability to recover these important cues. To address this problem, we propose a Flare-Aware Cross-modal Enhancement Network that adaptively restores flare-corrupted RGB and NIR features with guidance from the flare-immunized thermal infrared spectrum. First, to reduce the influence of locally degraded appearance due to intense flare, we propose a Mutual Flare Mask Prediction module to jointly obtain flare-corrupted masks in RGB and NIR modalities in a self-supervised manner. Second, to use the flare-immunized TI information to enhance the masked RGB and NIR, we propose a Flare-Aware Cross-modal Enhancement module that adaptively guides feature extraction of masked RGB and NIR spectra with prior flare-immunized knowledge from the TI spectrum. Third, to extract common informative semantic information from RGB and NIR, we propose an Inter-modality Consistency loss that enforces semantic consistency between the two modalities. Finally, to evaluate the proposed FACENet in handling intense flare, we introduce a new multi-spectral vehicle re-ID dataset, called WMVEID863, with additional challenges such as motion blur, significant background changes, and particularly intense flare degradation. Comprehensive experiments on both the newly collected dataset and public benchmark multi-spectral vehicle re-ID datasets demonstrate the superior performance of the proposed FACENet compared to state-of-the-art methods, especially in handling strong flares. The code and dataset will be released soon.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge