Dianye Huang
Vibration-Based Energy Metric for Restoring Needle Alignment in Autonomous Robotic Ultrasound
Aug 09, 2025Abstract:Precise needle alignment is essential for percutaneous needle insertion in robotic ultrasound-guided procedures. However, inherent challenges such as speckle noise, needle-like artifacts, and low image resolution make robust needle detection difficult, particularly when visibility is reduced or lost. In this paper, we propose a method to restore needle alignment when the ultrasound imaging plane and the needle insertion plane are misaligned. Unlike many existing approaches that rely heavily on needle visibility in ultrasound images, our method uses a more robust feature by periodically vibrating the needle using a mechanical system. Specifically, we propose a vibration-based energy metric that remains effective even when the needle is fully out of plane. Using this metric, we develop a control strategy to reposition the ultrasound probe in response to misalignments between the imaging plane and the needle insertion plane in both translation and rotation. Experiments conducted on ex-vivo porcine tissue samples using a dual-arm robotic ultrasound-guided needle insertion system demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed approach. The experimental results show the translational error of 0.41$\pm$0.27 mm and the rotational error of 0.51$\pm$0.19 degrees.
Tactile-Guided Robotic Ultrasound: Mapping Preplanned Scan Paths for Intercostal Imaging
Jul 27, 2025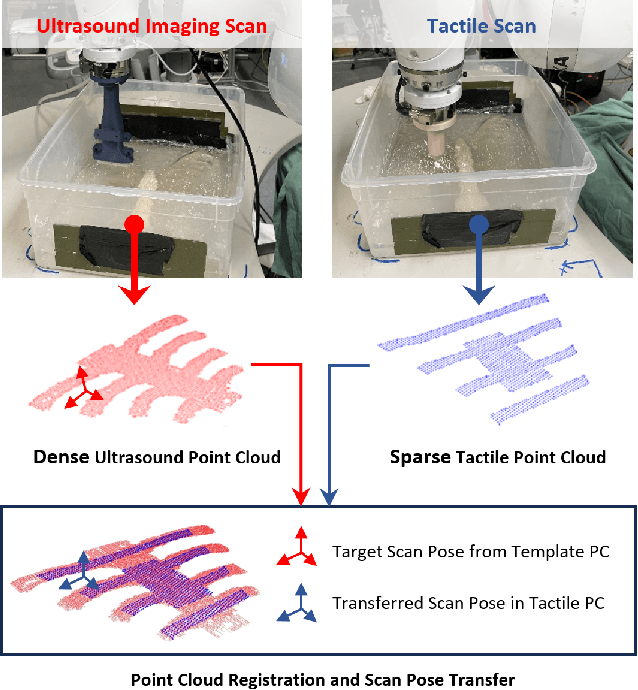
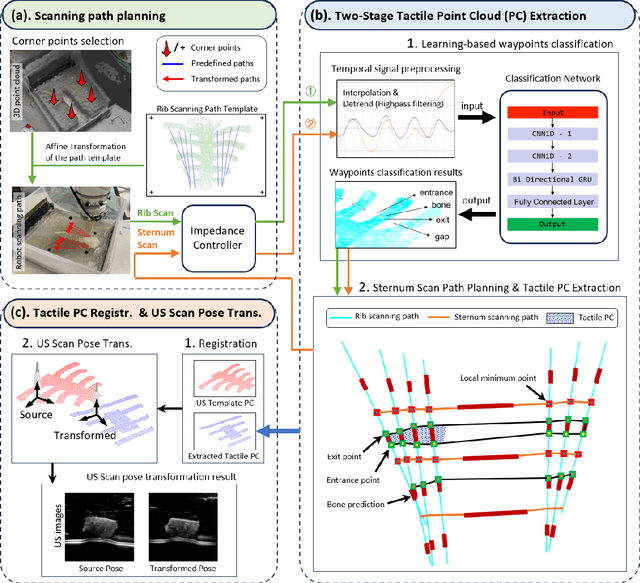
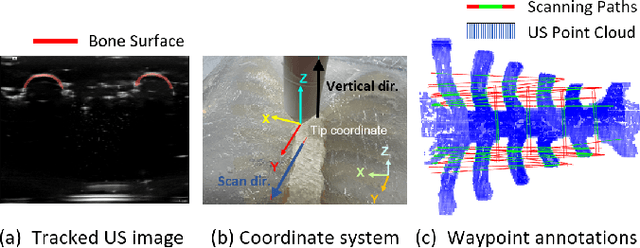
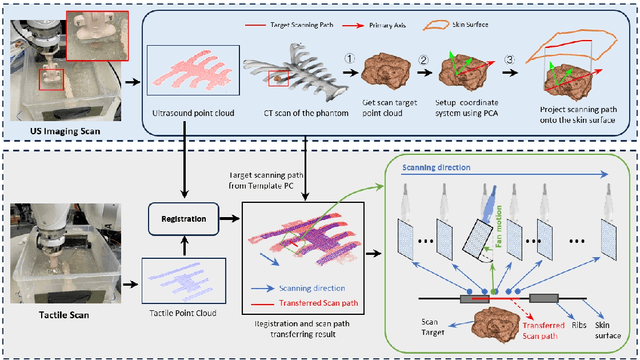
Abstract:Medical ultrasound (US) imaging is widely used in clinical examinations due to its portability, real-time capability, and radiation-free nature. To address inter- and intra-operator variability, robotic ultrasound systems have gained increasing attention. However, their application in challenging intercostal imaging remains limited due to the lack of an effective scan path generation method within the constrained acoustic window. To overcome this challenge, we explore the potential of tactile cues for characterizing subcutaneous rib structures as an alternative signal for ultrasound segmentation-free bone surface point cloud extraction. Compared to 2D US images, 1D tactile-related signals offer higher processing efficiency and are less susceptible to acoustic noise and artifacts. By leveraging robotic tracking data, a sparse tactile point cloud is generated through a few scans along the rib, mimicking human palpation. To robustly map the scanning trajectory into the intercostal space, the sparse tactile bone location point cloud is first interpolated to form a denser representation. This refined point cloud is then registered to an image-based dense bone surface point cloud, enabling accurate scan path mapping for individual patients. Additionally, to ensure full coverage of the object of interest, we introduce an automated tilt angle adjustment method to visualize structures beneath the bone. To validate the proposed method, we conducted comprehensive experiments on four distinct phantoms. The final scanning waypoint mapping achieved Mean Nearest Neighbor Distance (MNND) and Hausdorff distance (HD) errors of 3.41 mm and 3.65 mm, respectively, while the reconstructed object beneath the bone had errors of 0.69 mm and 2.2 mm compared to the CT ground truth.
Semantic Scene Graph for Ultrasound Image Explanation and Scanning Guidance
Jun 24, 2025Abstract:Understanding medical ultrasound imaging remains a long-standing challenge due to significant visual variability caused by differences in imaging and acquisition parameters. Recent advancements in large language models (LLMs) have been used to automatically generate terminology-rich summaries orientated to clinicians with sufficient physiological knowledge. Nevertheless, the increasing demand for improved ultrasound interpretability and basic scanning guidance among non-expert users, e.g., in point-of-care settings, has not yet been explored. In this study, we first introduce the scene graph (SG) for ultrasound images to explain image content to ordinary and provide guidance for ultrasound scanning. The ultrasound SG is first computed using a transformer-based one-stage method, eliminating the need for explicit object detection. To generate a graspable image explanation for ordinary, the user query is then used to further refine the abstract SG representation through LLMs. Additionally, the predicted SG is explored for its potential in guiding ultrasound scanning toward missing anatomies within the current imaging view, assisting ordinary users in achieving more standardized and complete anatomical exploration. The effectiveness of this SG-based image explanation and scanning guidance has been validated on images from the left and right neck regions, including the carotid and thyroid, across five volunteers. The results demonstrate the potential of the method to maximally democratize ultrasound by enhancing its interpretability and usability for ordinaries.
Robotic CBCT Meets Robotic Ultrasound
Feb 17, 2025Abstract:The multi-modality imaging system offers optimal fused images for safe and precise interventions in modern clinical practices, such as computed tomography - ultrasound (CT-US) guidance for needle insertion. However, the limited dexterity and mobility of current imaging devices hinder their integration into standardized workflows and the advancement toward fully autonomous intervention systems. In this paper, we present a novel clinical setup where robotic cone beam computed tomography (CBCT) and robotic US are pre-calibrated and dynamically co-registered, enabling new clinical applications. This setup allows registration-free rigid registration, facilitating multi-modal guided procedures in the absence of tissue deformation. First, a one-time pre-calibration is performed between the systems. To ensure a safe insertion path by highlighting critical vasculature on the 3D CBCT, SAM2 segments vessels from B-mode images, using the Doppler signal as an autonomously generated prompt. Based on the registration, the Doppler image or segmented vessel masks are then mapped onto the CBCT, creating an optimally fused image with comprehensive detail. To validate the system, we used a specially designed phantom, featuring lesions covered by ribs and multiple vessels with simulated moving flow. The mapping error between US and CBCT resulted in an average deviation of 1.72+-0.62 mm. A user study demonstrated the effectiveness of CBCT-US fusion for needle insertion guidance, showing significant improvements in time efficiency, accuracy, and success rate. Needle intervention performance improved by approximately 50% compared to the conventional US-guided workflow. We present the first robotic dual-modality imaging system designed to guide clinical applications. The results show significant performance improvements compared to traditional manual interventions.
Invisible Needle Detection in Ultrasound: Leveraging Mechanism-Induced Vibration
Mar 21, 2024



Abstract:In clinical applications that involve ultrasound-guided intervention, the visibility of the needle can be severely impeded due to steep insertion and strong distractors such as speckle noise and anatomical occlusion. To address this challenge, we propose VibNet, a learning-based framework tailored to enhance the robustness and accuracy of needle detection in ultrasound images, even when the target becomes invisible to the naked eye. Inspired by Eulerian Video Magnification techniques, we utilize an external step motor to induce low-amplitude periodic motion on the needle. These subtle vibrations offer the potential to generate robust frequency features for detecting the motion patterns around the needle. To robustly and precisely detect the needle leveraging these vibrations, VibNet integrates learning-based Short-Time-Fourier-Transform and Hough-Transform modules to achieve successive sub-goals, including motion feature extraction in the spatiotemporal space, frequency feature aggregation, and needle detection in the Hough space. Based on the results obtained on distinct ex vivo porcine and bovine tissue samples, the proposed algorithm exhibits superior detection performance with efficient computation and generalization capability.
Robot-Assisted Deep Venous Thrombosis Ultrasound Examination using Virtual Fixture
Jan 04, 2024Abstract:Deep Venous Thrombosis (DVT) is a common vascular disease with blood clots inside deep veins, which may block blood flow or even cause a life-threatening pulmonary embolism. A typical exam for DVT using ultrasound (US) imaging is by pressing the target vein until its lumen is fully compressed. However, the compression exam is highly operator-dependent. To alleviate intra- and inter-variations, we present a robotic US system with a novel hybrid force motion control scheme ensuring position and force tracking accuracy, and soft landing of the probe onto the target surface. In addition, a path-based virtual fixture is proposed to realize easy human-robot interaction for repeat compression operation at the lesion location. To ensure the biometric measurements obtained in different examinations are comparable, the 6D scanning path is determined in a coarse-to-fine manner using both an external RGBD camera and US images. The RGBD camera is first used to extract a rough scanning path on the object. Then, the segmented vascular lumen from US images are used to optimize the scanning path to ensure the visibility of the target object. To generate a continuous scan path for developing virtual fixtures, an arc-length based path fitting model considering both position and orientation is proposed. Finally, the whole system is evaluated on a human-like arm phantom with an uneven surface.
Machine Learning in Robotic Ultrasound Imaging: Challenges and Perspectives
Jan 04, 2024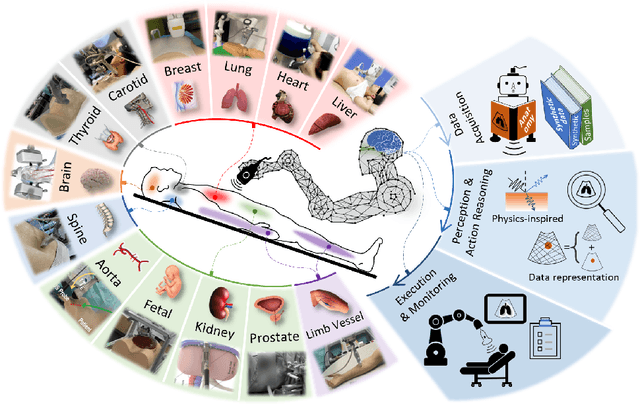
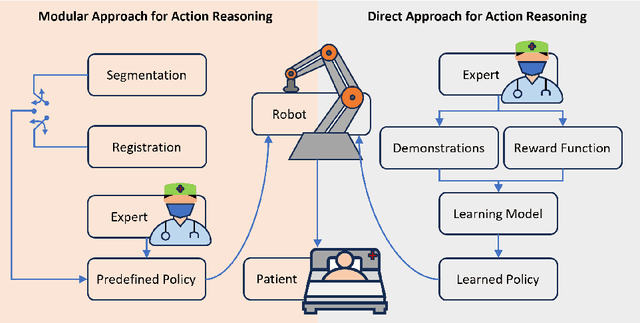
Abstract:This article reviews the recent advances in intelligent robotic ultrasound (US) imaging systems. We commence by presenting the commonly employed robotic mechanisms and control techniques in robotic US imaging, along with their clinical applications. Subsequently, we focus on the deployment of machine learning techniques in the development of robotic sonographers, emphasizing crucial developments aimed at enhancing the intelligence of these systems. The methods for achieving autonomous action reasoning are categorized into two sets of approaches: those relying on implicit environmental data interpretation and those using explicit interpretation. Throughout this exploration, we also discuss practical challenges, including those related to the scarcity of medical data, the need for a deeper understanding of the physical aspects involved, and effective data representation approaches. Moreover, we conclude by highlighting the open problems in the field and analyzing different possible perspectives on how the community could move forward in this research area.
SG-Bot: Object Rearrangement via Coarse-to-Fine Robotic Imagination on Scene Graphs
Sep 21, 2023Abstract:Object rearrangement is pivotal in robotic-environment interactions, representing a significant capability in embodied AI. In this paper, we present SG-Bot, a novel rearrangement framework that utilizes a coarse-to-fine scheme with a scene graph as the scene representation. Unlike previous methods that rely on either known goal priors or zero-shot large models, SG-Bot exemplifies lightweight, real-time, and user-controllable characteristics, seamlessly blending the consideration of commonsense knowledge with automatic generation capabilities. SG-Bot employs a three-fold procedure--observation, imagination, and execution--to adeptly address the task. Initially, objects are discerned and extracted from a cluttered scene during the observation. These objects are first coarsely organized and depicted within a scene graph, guided by either commonsense or user-defined criteria. Then, this scene graph subsequently informs a generative model, which forms a fine-grained goal scene considering the shape information from the initial scene and object semantics. Finally, for execution, the initial and envisioned goal scenes are matched to formulate robotic action policies. Experimental results demonstrate that SG-Bot outperforms competitors by a large margin.
Motion Magnification in Robotic Sonography: Enabling Pulsation-Aware Artery Segmentation
Jul 07, 2023Abstract:Ultrasound (US) imaging is widely used for diagnosing and monitoring arterial diseases, mainly due to the advantages of being non-invasive, radiation-free, and real-time. In order to provide additional information to assist clinicians in diagnosis, the tubular structures are often segmented from US images. To improve the artery segmentation accuracy and stability during scans, this work presents a novel pulsation-assisted segmentation neural network (PAS-NN) by explicitly taking advantage of the cardiac-induced motions. Motion magnification techniques are employed to amplify the subtle motion within the frequency band of interest to extract the pulsation signals from sequential US images. The extracted real-time pulsation information can help to locate the arteries on cross-section US images; therefore, we explicitly integrated the pulsation into the proposed PAS-NN as attention guidance. Notably, a robotic arm is necessary to provide stable movement during US imaging since magnifying the target motions from the US images captured along a scan path is not manually feasible due to the hand tremor. To validate the proposed robotic US system for imaging arteries, experiments are carried out on volunteers' carotid and radial arteries. The results demonstrated that the PAS-NN could achieve comparable results as state-of-the-art on carotid and can effectively improve the segmentation performance for small vessels (radial artery).
MonoGraspNet: 6-DoF Grasping with a Single RGB Image
Sep 26, 2022



Abstract:6-DoF robotic grasping is a long-lasting but unsolved problem. Recent methods utilize strong 3D networks to extract geometric grasping representations from depth sensors, demonstrating superior accuracy on common objects but perform unsatisfactorily on photometrically challenging objects, e.g., objects in transparent or reflective materials. The bottleneck lies in that the surface of these objects can not reflect back accurate depth due to the absorption or refraction of light. In this paper, in contrast to exploiting the inaccurate depth data, we propose the first RGB-only 6-DoF grasping pipeline called MonoGraspNet that utilizes stable 2D features to simultaneously handle arbitrary object grasping and overcome the problems induced by photometrically challenging objects. MonoGraspNet leverages keypoint heatmap and normal map to recover the 6-DoF grasping poses represented by our novel representation parameterized with 2D keypoints with corresponding depth, grasping direction, grasping width, and angle. Extensive experiments in real scenes demonstrate that our method can achieve competitive results in grasping common objects and surpass the depth-based competitor by a large margin in grasping photometrically challenging objects. To further stimulate robotic manipulation research, we additionally annotate and open-source a multi-view and multi-scene real-world grasping dataset, containing 120 objects of mixed photometric complexity with 20M accurate grasping labels.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge