Songtao Jiang
Knowing or Guessing? Robust Medical Visual Question Answering via Joint Consistency and Contrastive Learning
Aug 26, 2025Abstract:In high-stakes medical applications, consistent answering across diverse question phrasings is essential for reliable diagnosis. However, we reveal that current Medical Vision-Language Models (Med-VLMs) exhibit concerning fragility in Medical Visual Question Answering, as their answers fluctuate significantly when faced with semantically equivalent rephrasings of medical questions. We attribute this to two limitations: (1) insufficient alignment of medical concepts, leading to divergent reasoning patterns, and (2) hidden biases in training data that prioritize syntactic shortcuts over semantic understanding. To address these challenges, we construct RoMed, a dataset built upon original VQA datasets containing 144k questions with variations spanning word-level, sentence-level, and semantic-level perturbations. When evaluating state-of-the-art (SOTA) models like LLaVA-Med on RoMed, we observe alarming performance drops (e.g., a 40\% decline in Recall) compared to original VQA benchmarks, exposing critical robustness gaps. To bridge this gap, we propose Consistency and Contrastive Learning (CCL), which integrates two key components: (1) knowledge-anchored consistency learning, aligning Med-VLMs with medical knowledge rather than shallow feature patterns, and (2) bias-aware contrastive learning, mitigating data-specific priors through discriminative representation refinement. CCL achieves SOTA performance on three popular VQA benchmarks and notably improves answer consistency by 50\% on the challenging RoMed test set, demonstrating significantly enhanced robustness. Code will be released.
CAPO: Reinforcing Consistent Reasoning in Medical Decision-Making
Jun 15, 2025
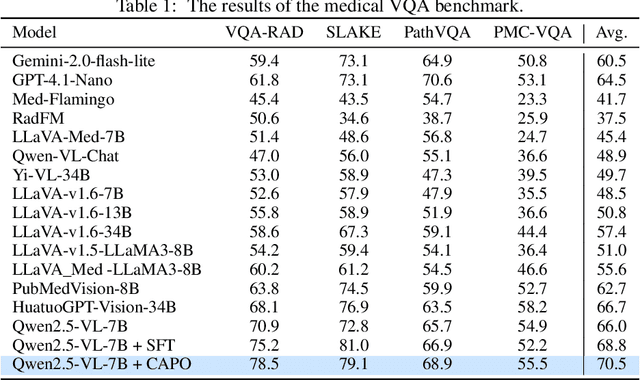
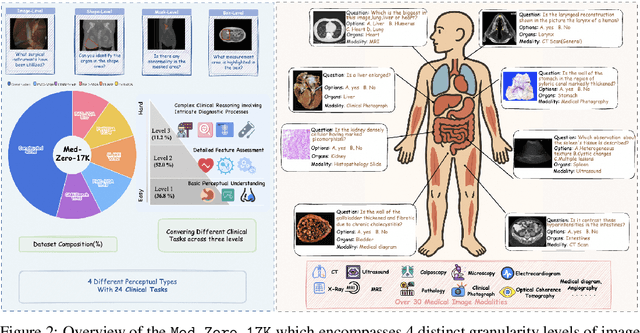
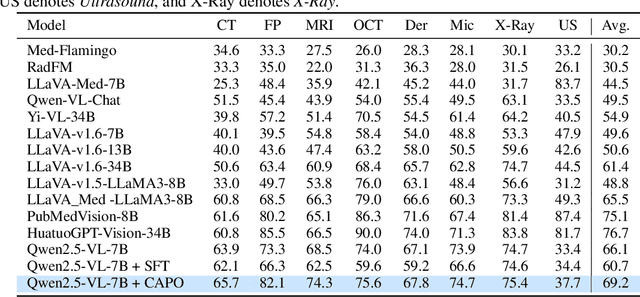
Abstract:In medical visual question answering (Med-VQA), achieving accurate responses relies on three critical steps: precise perception of medical imaging data, logical reasoning grounded in visual input and textual questions, and coherent answer derivation from the reasoning process. Recent advances in general vision-language models (VLMs) show that large-scale reinforcement learning (RL) could significantly enhance both reasoning capabilities and overall model performance. However, their application in medical domains is hindered by two fundamental challenges: 1) misalignment between perceptual understanding and reasoning stages, and 2) inconsistency between reasoning pathways and answer generation, both compounded by the scarcity of high-quality medical datasets for effective large-scale RL. In this paper, we first introduce Med-Zero-17K, a curated dataset for pure RL-based training, encompassing over 30 medical image modalities and 24 clinical tasks. Moreover, we propose a novel large-scale RL framework for Med-VLMs, Consistency-Aware Preference Optimization (CAPO), which integrates rewards to ensure fidelity between perception and reasoning, consistency in reasoning-to-answer derivation, and rule-based accuracy for final responses. Extensive experiments on both in-domain and out-of-domain scenarios demonstrate the superiority of our method over strong VLM baselines, showcasing strong generalization capability to 3D Med-VQA benchmarks and R1-like training paradigms.
OmniV-Med: Scaling Medical Vision-Language Model for Universal Visual Understanding
Apr 20, 2025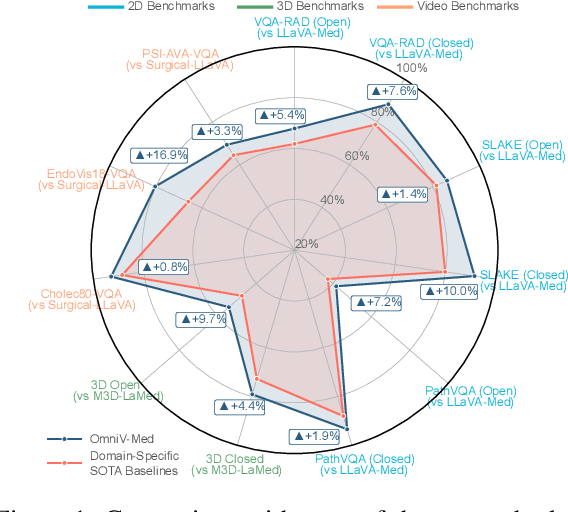
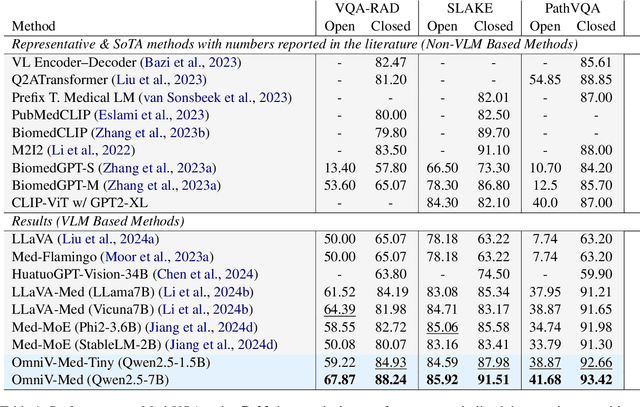
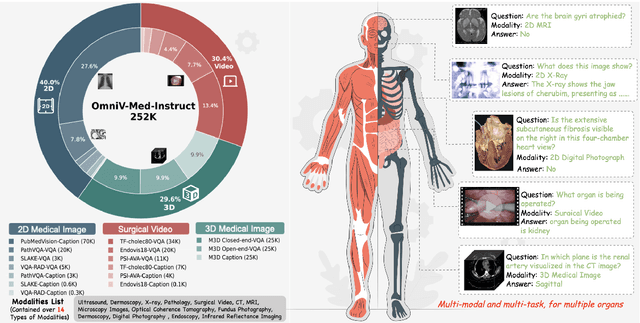
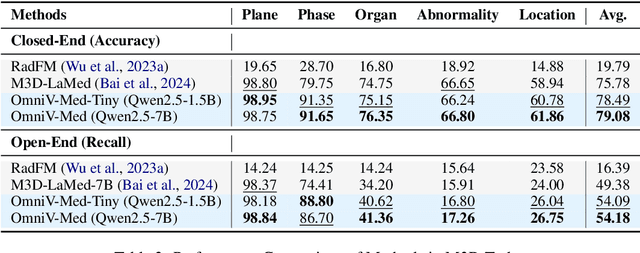
Abstract:The practical deployment of medical vision-language models (Med-VLMs) necessitates seamless integration of textual data with diverse visual modalities, including 2D/3D images and videos, yet existing models typically employ separate encoders for different modalities. To address this limitation, we present OmniV-Med, a unified framework for multimodal medical understanding. Our technical contributions are threefold: First, we construct OmniV-Med-Instruct, a comprehensive multimodal medical dataset containing 252K instructional samples spanning 14 medical image modalities and 11 clinical tasks. Second, we devise a rotary position-adaptive encoder that processes multi-resolution 2D/3D images and videos within a unified architecture, diverging from conventional modality-specific encoders. Third, we introduce a medical-aware token pruning mechanism that exploits spatial-temporal redundancy in volumetric data (e.g., consecutive CT slices) and medical videos, effectively reducing 60\% of visual tokens without performance degradation. Empirical evaluations demonstrate that OmniV-Med-7B achieves state-of-the-art performance on 7 benchmarks spanning 2D/3D medical imaging and video understanding tasks. Notably, our lightweight variant (OmniV-Med-1.5B) attains comparable performance while requiring only 8 RTX3090 GPUs for training and supporting efficient long-video inference. Data, code and model will be released.
Modality-Fair Preference Optimization for Trustworthy MLLM Alignment
Oct 20, 2024



Abstract:Direct Preference Optimization (DPO) is effective for aligning large language models (LLMs), but when applied to multimodal models (MLLMs), it often favors text over image information, leading to unreliable outputs and visual hallucinations. To address this, we propose Modality-Fair Preference Optimization (MFPO) to balance text and image preferences. First, we found that the lack of image-related rewards in preference data biases optimization toward text, so we created automated, fine-grained image preference data to correct this. Then, we designed a learning objective to ensure the model captures both text and image preferences while maintaining high-quality outputs. Finally, we use a multi-stage alignment approach to stabilize training and improve learning across both modalities. Extensive experiments demonstrate that MFPO significantly enhances MLLM trustworthiness. On models like LLaVA-v1.5 (7B, 13B), our approach reduces hallucinations substantially. On the 7B model, MFPO outperforms GPT-4V and achieves a nearly 40\% improvement over previous methods on Object HalBench, as well as achieving state-of-the-art performance on both Object HalBench and AMBER when combined with the latest LLaVA-v1.6. Code will be released.
MoE-TinyMed: Mixture of Experts for Tiny Medical Large Vision-Language Models
Apr 16, 2024



Abstract:Mixture of Expert Tuning (MoE-Tuning) has effectively enhanced the performance of general MLLMs with fewer parameters, yet its application in resource-limited medical settings has not been fully explored. To address this gap, we developed MoE-TinyMed, a model tailored for medical applications that significantly lowers parameter demands. In evaluations on the VQA-RAD, SLAKE, and Path-VQA datasets, MoE-TinyMed outperformed LLaVA-Med in all Med-VQA closed settings with just 3.6B parameters. Additionally, a streamlined version with 2B parameters surpassed LLaVA-Med's performance in PathVQA, showcasing its effectiveness in resource-limited healthcare settings.
Joint Visual and Text Prompting for Improved Object-Centric Perception with Multimodal Large Language Models
Apr 06, 2024



Abstract:Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) such as GPT-4V and Gemini Pro face challenges in achieving human-level perception in Visual Question Answering (VQA), particularly in object-oriented perception tasks which demand fine-grained understanding of object identities, locations or attributes, as indicated by empirical findings. This is mainly due to their limited capability to effectively integrate complex visual cues with textual information and potential object hallucinations. In this paper, we present a novel approach, Joint Visual and Text Prompting (VTPrompt), that employs fine-grained visual information to enhance the capability of MLLMs in VQA, especially for object-oriented perception. VTPrompt merges visual and text prompts to extract key concepts from textual questions and employs a detection model to highlight relevant objects as visual prompts in images. The processed images alongside text prompts are subsequently fed into MLLMs to produce more accurate answers. Our experiments with GPT-4V and Gemini Pro, on three benchmarks, i.e., MME , MMB and POPE, demonstrate significant improvements. Particularly, our method led to a score improvement of up to 183.5 for GPT-4V on MME and enhanced MMB performance by 8.17\% for GPT-4V and 15.69\% for Gemini Pro.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge