Ruizhe Chen
Towards Proactive Personalization through Profile Customization for Individual Users in Dialogues
Dec 17, 2025Abstract:The deployment of Large Language Models (LLMs) in interactive systems necessitates a deep alignment with the nuanced and dynamic preferences of individual users. Current alignment techniques predominantly address universal human values or static, single-turn preferences, thereby failing to address the critical needs of long-term personalization and the initial user cold-start problem. To bridge this gap, we propose PersonalAgent, a novel user-centric lifelong agent designed to continuously infer and adapt to user preferences. PersonalAgent constructs and dynamically refines a unified user profile by decomposing dialogues into single-turn interactions, framing preference inference as a sequential decision-making task. Experiments show that PersonalAgent achieves superior performance over strong prompt-based and policy optimization baselines, not only in idealized but also in noisy conversational contexts, while preserving cross-session preference consistency. Furthermore, human evaluation confirms that PersonalAgent excels at capturing user preferences naturally and coherently. Our findings underscore the importance of lifelong personalization for developing more inclusive and adaptive conversational agents. Our code is available here.
Datasets and Recipes for Video Temporal Grounding via Reinforcement Learning
Jul 24, 2025Abstract:Video Temporal Grounding (VTG) aims to localize relevant temporal segments in videos given natural language queries. Despite recent progress with large vision-language models (LVLMs) and instruction-tuning, existing approaches often suffer from limited temporal awareness and poor generalization. In this work, we introduce a two-stage training framework that integrates supervised fine-tuning with reinforcement learning (RL) to improve both the accuracy and robustness of VTG models. Our approach first leverages high-quality curated cold start data for SFT initialization, followed by difficulty-controlled RL to further enhance temporal localization and reasoning abilities. Comprehensive experiments on multiple VTG benchmarks demonstrate that our method consistently outperforms existing models, particularly in challenging and open-domain scenarios. We conduct an in-depth analysis of training strategies and dataset curation, highlighting the importance of both high-quality cold start data and difficulty-controlled RL. To facilitate further research and industrial adoption, we release all intermediate datasets, models, and code to the community.
CAPO: Reinforcing Consistent Reasoning in Medical Decision-Making
Jun 15, 2025
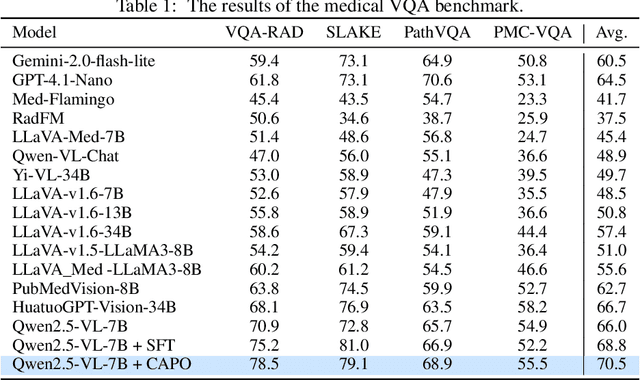
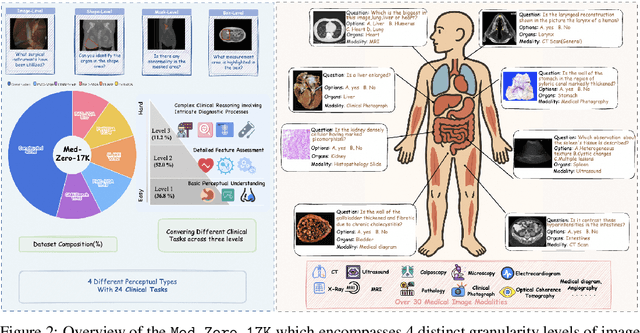
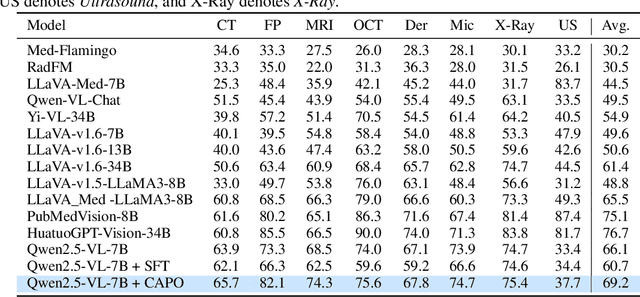
Abstract:In medical visual question answering (Med-VQA), achieving accurate responses relies on three critical steps: precise perception of medical imaging data, logical reasoning grounded in visual input and textual questions, and coherent answer derivation from the reasoning process. Recent advances in general vision-language models (VLMs) show that large-scale reinforcement learning (RL) could significantly enhance both reasoning capabilities and overall model performance. However, their application in medical domains is hindered by two fundamental challenges: 1) misalignment between perceptual understanding and reasoning stages, and 2) inconsistency between reasoning pathways and answer generation, both compounded by the scarcity of high-quality medical datasets for effective large-scale RL. In this paper, we first introduce Med-Zero-17K, a curated dataset for pure RL-based training, encompassing over 30 medical image modalities and 24 clinical tasks. Moreover, we propose a novel large-scale RL framework for Med-VLMs, Consistency-Aware Preference Optimization (CAPO), which integrates rewards to ensure fidelity between perception and reasoning, consistency in reasoning-to-answer derivation, and rule-based accuracy for final responses. Extensive experiments on both in-domain and out-of-domain scenarios demonstrate the superiority of our method over strong VLM baselines, showcasing strong generalization capability to 3D Med-VQA benchmarks and R1-like training paradigms.
Med-U1: Incentivizing Unified Medical Reasoning in LLMs via Large-scale Reinforcement Learning
Jun 14, 2025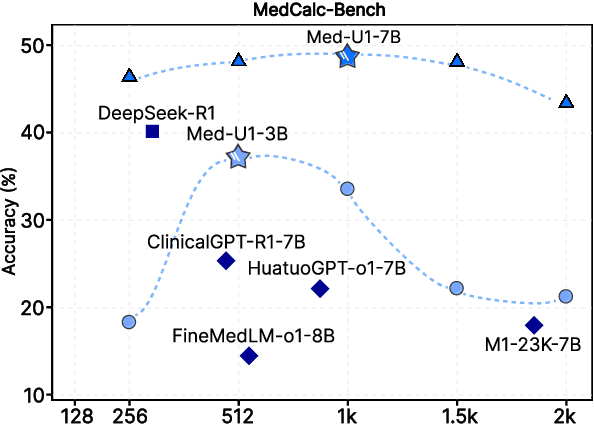
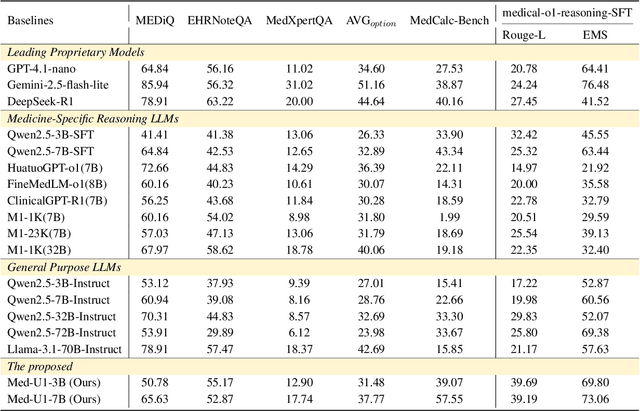
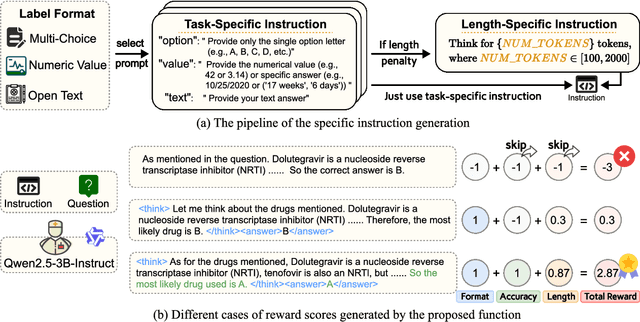
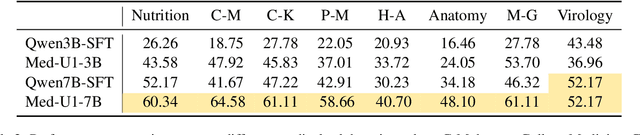
Abstract:Medical Question-Answering (QA) encompasses a broad spectrum of tasks, including multiple choice questions (MCQ), open-ended text generation, and complex computational reasoning. Despite this variety, a unified framework for delivering high-quality medical QA has yet to emerge. Although recent progress in reasoning-augmented large language models (LLMs) has shown promise, their ability to achieve comprehensive medical understanding is still largely unexplored. In this paper, we present Med-U1, a unified framework for robust reasoning across medical QA tasks with diverse output formats, ranging from MCQs to complex generation and computation tasks. Med-U1 employs pure large-scale reinforcement learning with mixed rule-based binary reward functions, incorporating a length penalty to manage output verbosity. With multi-objective reward optimization, Med-U1 directs LLMs to produce concise and verifiable reasoning chains. Empirical results reveal that Med-U1 significantly improves performance across multiple challenging Med-QA benchmarks, surpassing even larger specialized and proprietary models. Furthermore, Med-U1 demonstrates robust generalization to out-of-distribution (OOD) tasks. Extensive analysis presents insights into training strategies, reasoning chain length control, and reward design for medical LLMs. The code will be released.
BiasFilter: An Inference-Time Debiasing Framework for Large Language Models
May 28, 2025Abstract:Mitigating social bias in large language models (LLMs) has become an increasingly important research objective. However, existing debiasing methods often incur high human and computational costs, exhibit limited effectiveness, and struggle to scale to larger models and open-ended generation tasks. To address these limitations, this paper proposes BiasFilter, a model-agnostic, inference-time debiasing framework that integrates seamlessly with both open-source and API-based LLMs. Instead of relying on retraining with balanced data or modifying model parameters, BiasFilter enforces fairness by filtering generation outputs in real time. Specifically, it periodically evaluates intermediate outputs every few tokens, maintains an active set of candidate continuations, and incrementally completes generation by discarding low-reward segments based on a fairness reward signal. To support this process, we construct a fairness preference dataset and train an implicit reward model to assess token-level fairness in generated responses. Extensive experiments demonstrate that BiasFilter effectively mitigates social bias across a range of LLMs while preserving overall generation quality.
FRN: Fractal-Based Recursive Spectral Reconstruction Network
May 21, 2025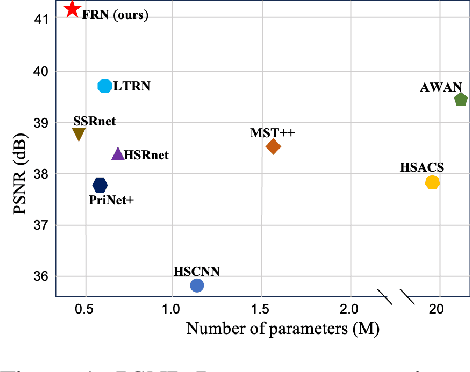
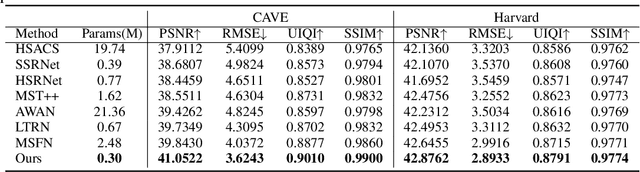
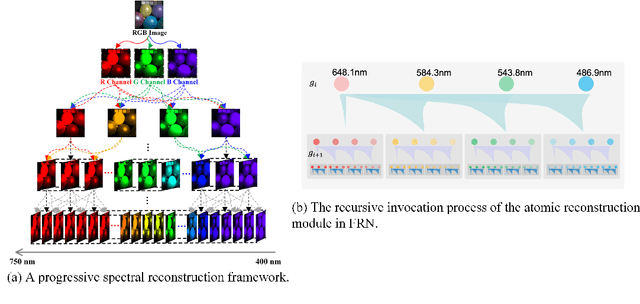

Abstract:Generating hyperspectral images (HSIs) from RGB images through spectral reconstruction can significantly reduce the cost of HSI acquisition. In this paper, we propose a Fractal-Based Recursive Spectral Reconstruction Network (FRN), which differs from existing paradigms that attempt to directly integrate the full-spectrum information from the R, G, and B channels in a one-shot manner. Instead, it treats spectral reconstruction as a progressive process, predicting from broad to narrow bands or employing a coarse-to-fine approach for predicting the next wavelength. Inspired by fractals in mathematics, FRN establishes a novel spectral reconstruction paradigm by recursively invoking an atomic reconstruction module. In each invocation, only the spectral information from neighboring bands is used to provide clues for the generation of the image at the next wavelength, which follows the low-rank property of spectral data. Moreover, we design a band-aware state space model that employs a pixel-differentiated scanning strategy at different stages of the generation process, further suppressing interference from low-correlation regions caused by reflectance differences. Through extensive experimentation across different datasets, FRN achieves superior reconstruction performance compared to state-of-the-art methods in both quantitative and qualitative evaluations.
BiasGuard: A Reasoning-enhanced Bias Detection Tool For Large Language Models
Apr 30, 2025Abstract:Identifying bias in LLM-generated content is a crucial prerequisite for ensuring fairness in LLMs. Existing methods, such as fairness classifiers and LLM-based judges, face limitations related to difficulties in understanding underlying intentions and the lack of criteria for fairness judgment. In this paper, we introduce BiasGuard, a novel bias detection tool that explicitly analyzes inputs and reasons through fairness specifications to provide accurate judgments. BiasGuard is implemented through a two-stage approach: the first stage initializes the model to explicitly reason based on fairness specifications, while the second stage leverages reinforcement learning to enhance its reasoning and judgment capabilities. Our experiments, conducted across five datasets, demonstrate that BiasGuard outperforms existing tools, improving accuracy and reducing over-fairness misjudgments. We also highlight the importance of reasoning-enhanced decision-making and provide evidence for the effectiveness of our two-stage optimization pipeline.
FairSteer: Inference Time Debiasing for LLMs with Dynamic Activation Steering
Apr 20, 2025Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) are prone to capturing biases from training corpus, leading to potential negative social impacts. Existing prompt-based debiasing methods exhibit instability due to their sensitivity to prompt changes, while fine-tuning-based techniques incur substantial computational overhead and catastrophic forgetting. In this paper, we propose FairSteer, a novel inference-time debiasing framework without requiring customized prompt design or model retraining. Motivated by the linear representation hypothesis, our preliminary investigation demonstrates that fairness-related features can be encoded into separable directions in the hidden activation space. FairSteer operates in three steps: biased activation detection, debiasing steering vector (DSV) computation, and dynamic activation steering. Specifically, it first trains a lightweight linear classifier to detect bias signatures in activations, and then computes DSVs as intervention directions derived from small contrastive prompt pairs. Subsequently, it performs debiasing by adjusting activations with DSVs in the inference stage. Comprehensive evaluation with six LLMs demonstrates the superiority of FairSteer across question-answering, counterfactual input evaluation and open-ended text generation tasks. Code will be released.
An All-Atom Generative Model for Designing Protein Complexes
Apr 17, 2025Abstract:Proteins typically exist in complexes, interacting with other proteins or biomolecules to perform their specific biological roles. Research on single-chain protein modeling has been extensively and deeply explored, with advancements seen in models like the series of ESM and AlphaFold. Despite these developments, the study and modeling of multi-chain proteins remain largely uncharted, though they are vital for understanding biological functions. Recognizing the importance of these interactions, we introduce APM (All-Atom Protein Generative Model), a model specifically designed for modeling multi-chain proteins. By integrating atom-level information and leveraging data on multi-chain proteins, APM is capable of precisely modeling inter-chain interactions and designing protein complexes with binding capabilities from scratch. It also performs folding and inverse-folding tasks for multi-chain proteins. Moreover, APM demonstrates versatility in downstream applications: it achieves enhanced performance through supervised fine-tuning (SFT) while also supporting zero-shot sampling in certain tasks, achieving state-of-the-art results. Code will be released at https://github.com/bytedance/apm.
Persona-judge: Personalized Alignment of Large Language Models via Token-level Self-judgment
Apr 17, 2025Abstract:Aligning language models with human preferences presents significant challenges, particularly in achieving personalization without incurring excessive computational costs. Existing methods rely on reward signals and additional annotated data, limiting their scalability and adaptability to diverse human values. To address these challenges, we introduce Persona-judge, a novel discriminative paradigm that enables training-free personalized alignment with unseen preferences. Instead of optimizing policy parameters through external reward feedback, Persona-judge leverages the intrinsic preference judgment capabilities of the model. Specifically, a draft model generates candidate tokens conditioned on a given preference, while a judge model, embodying another preference, cross-validates the predicted tokens whether to be accepted. Experimental results demonstrate that Persona-judge, using the inherent preference evaluation mechanisms of the model, offers a scalable and computationally efficient solution to personalized alignment, paving the way for more adaptive customized alignment.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge