Dongfeng Bai
FreeFix: Boosting 3D Gaussian Splatting via Fine-Tuning-Free Diffusion Models
Jan 28, 2026Abstract:Neural Radiance Fields and 3D Gaussian Splatting have advanced novel view synthesis, yet still rely on dense inputs and often degrade at extrapolated views. Recent approaches leverage generative models, such as diffusion models, to provide additional supervision, but face a trade-off between generalization and fidelity: fine-tuning diffusion models for artifact removal improves fidelity but risks overfitting, while fine-tuning-free methods preserve generalization but often yield lower fidelity. We introduce FreeFix, a fine-tuning-free approach that pushes the boundary of this trade-off by enhancing extrapolated rendering with pretrained image diffusion models. We present an interleaved 2D-3D refinement strategy, showing that image diffusion models can be leveraged for consistent refinement without relying on costly video diffusion models. Furthermore, we take a closer look at the guidance signal for 2D refinement and propose a per-pixel confidence mask to identify uncertain regions for targeted improvement. Experiments across multiple datasets show that FreeFix improves multi-frame consistency and achieves performance comparable to or surpassing fine-tuning-based methods, while retaining strong generalization ability.
EVolSplat4D: Efficient Volume-based Gaussian Splatting for 4D Urban Scene Synthesis
Jan 22, 2026Abstract:Novel view synthesis (NVS) of static and dynamic urban scenes is essential for autonomous driving simulation, yet existing methods often struggle to balance reconstruction time with quality. While state-of-the-art neural radiance fields and 3D Gaussian Splatting approaches achieve photorealism, they often rely on time-consuming per-scene optimization. Conversely, emerging feed-forward methods frequently adopt per-pixel Gaussian representations, which lead to 3D inconsistencies when aggregating multi-view predictions in complex, dynamic environments. We propose EvolSplat4D, a feed-forward framework that moves beyond existing per-pixel paradigms by unifying volume-based and pixel-based Gaussian prediction across three specialized branches. For close-range static regions, we predict consistent geometry of 3D Gaussians over multiple frames directly from a 3D feature volume, complemented by a semantically-enhanced image-based rendering module for predicting their appearance. For dynamic actors, we utilize object-centric canonical spaces and a motion-adjusted rendering module to aggregate temporal features, ensuring stable 4D reconstruction despite noisy motion priors. Far-Field scenery is handled by an efficient per-pixel Gaussian branch to ensure full-scene coverage. Experimental results on the KITTI-360, KITTI, Waymo, and PandaSet datasets show that EvolSplat4D reconstructs both static and dynamic environments with superior accuracy and consistency, outperforming both per-scene optimization and state-of-the-art feed-forward baselines.
Spatial4D-Bench: A Versatile 4D Spatial Intelligence Benchmark
Dec 31, 2025Abstract:4D spatial intelligence involves perceiving and processing how objects move or change over time. Humans naturally possess 4D spatial intelligence, supporting a broad spectrum of spatial reasoning abilities. To what extent can Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) achieve human-level 4D spatial intelligence? In this work, we present Spatial4D-Bench, a versatile 4D spatial intelligence benchmark designed to comprehensively assess the 4D spatial reasoning abilities of MLLMs. Unlike existing spatial intelligence benchmarks that are often small-scale or limited in diversity, Spatial4D-Bench provides a large-scale, multi-task evaluation benchmark consisting of ~40,000 question-answer pairs covering 18 well-defined tasks. We systematically organize these tasks into six cognitive categories: object understanding, scene understanding, spatial relationship understanding, spatiotemporal relationship understanding, spatial reasoning and spatiotemporal reasoning. Spatial4D-Bench thereby offers a structured and comprehensive benchmark for evaluating the spatial cognition abilities of MLLMs, covering a broad spectrum of tasks that parallel the versatility of human spatial intelligence. We benchmark various state-of-the-art open-source and proprietary MLLMs on Spatial4D-Bench and reveal their substantial limitations in a wide variety of 4D spatial reasoning aspects, such as route plan, action recognition, and physical plausibility reasoning. We hope that the findings provided in this work offer valuable insights to the community and that our benchmark can facilitate the development of more capable MLLMs toward human-level 4D spatial intelligence. More resources can be found on our project page.
MoVieDrive: Multi-Modal Multi-View Urban Scene Video Generation
Aug 20, 2025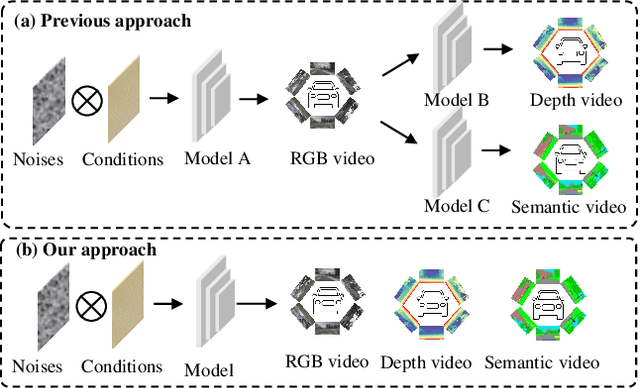
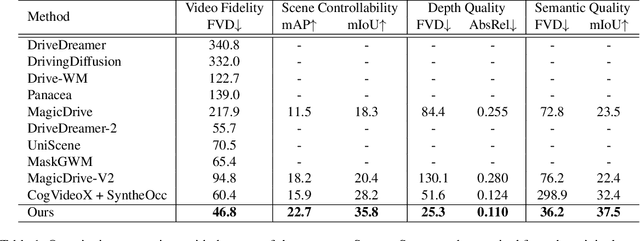
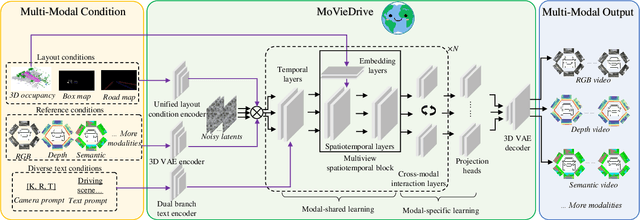
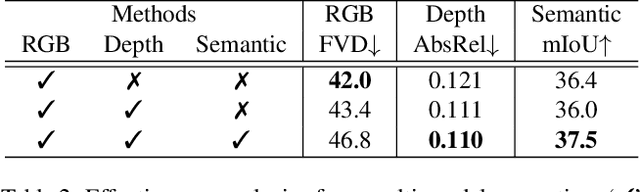
Abstract:Video generation has recently shown superiority in urban scene synthesis for autonomous driving. Existing video generation approaches to autonomous driving primarily focus on RGB video generation and lack the ability to support multi-modal video generation. However, multi-modal data, such as depth maps and semantic maps, are crucial for holistic urban scene understanding in autonomous driving. Although it is feasible to use multiple models to generate different modalities, this increases the difficulty of model deployment and does not leverage complementary cues for multi-modal data generation. To address this problem, in this work, we propose a novel multi-modal multi-view video generation approach to autonomous driving. Specifically, we construct a unified diffusion transformer model composed of modal-shared components and modal-specific components. Then, we leverage diverse conditioning inputs to encode controllable scene structure and content cues into the unified diffusion model for multi-modal multi-view video generation. In this way, our approach is capable of generating multi-modal multi-view driving scene videos in a unified framework. Our experiments on the challenging real-world autonomous driving dataset, nuScenes, show that our approach can generate multi-modal multi-view urban scene videos with high fidelity and controllability, surpassing the state-of-the-art methods.
EVolSplat: Efficient Volume-based Gaussian Splatting for Urban View Synthesis
Mar 26, 2025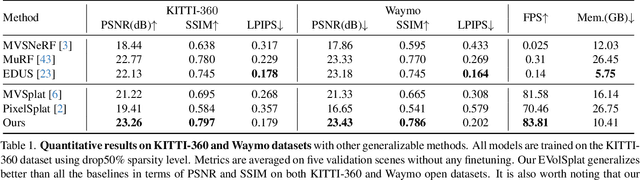
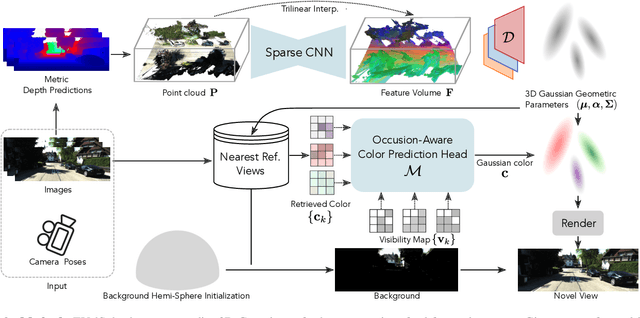
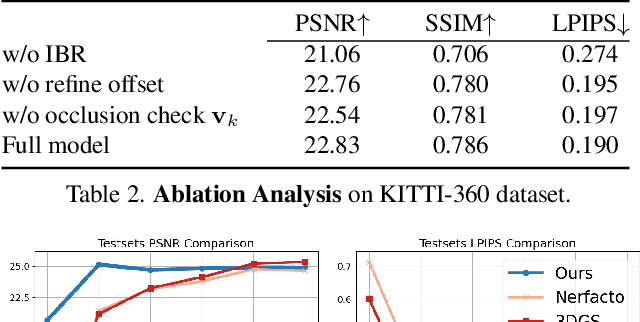
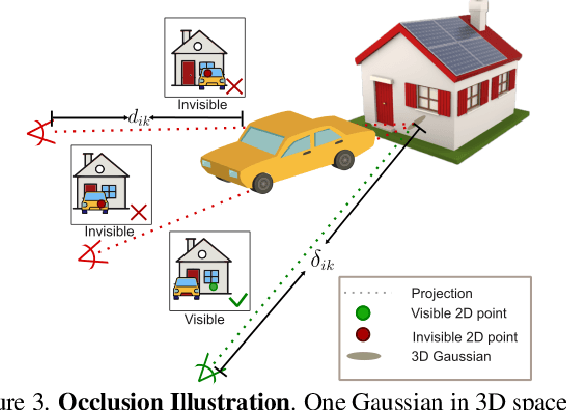
Abstract:Novel view synthesis of urban scenes is essential for autonomous driving-related applications.Existing NeRF and 3DGS-based methods show promising results in achieving photorealistic renderings but require slow, per-scene optimization. We introduce EVolSplat, an efficient 3D Gaussian Splatting model for urban scenes that works in a feed-forward manner. Unlike existing feed-forward, pixel-aligned 3DGS methods, which often suffer from issues like multi-view inconsistencies and duplicated content, our approach predicts 3D Gaussians across multiple frames within a unified volume using a 3D convolutional network. This is achieved by initializing 3D Gaussians with noisy depth predictions, and then refining their geometric properties in 3D space and predicting color based on 2D textures. Our model also handles distant views and the sky with a flexible hemisphere background model. This enables us to perform fast, feed-forward reconstruction while achieving real-time rendering. Experimental evaluations on the KITTI-360 and Waymo datasets show that our method achieves state-of-the-art quality compared to existing feed-forward 3DGS- and NeRF-based methods.
An Efficient Occupancy World Model via Decoupled Dynamic Flow and Image-assisted Training
Dec 18, 2024



Abstract:The field of autonomous driving is experiencing a surge of interest in world models, which aim to predict potential future scenarios based on historical observations. In this paper, we introduce DFIT-OccWorld, an efficient 3D occupancy world model that leverages decoupled dynamic flow and image-assisted training strategy, substantially improving 4D scene forecasting performance. To simplify the training process, we discard the previous two-stage training strategy and innovatively reformulate the occupancy forecasting problem as a decoupled voxels warping process. Our model forecasts future dynamic voxels by warping existing observations using voxel flow, whereas static voxels are easily obtained through pose transformation. Moreover, our method incorporates an image-assisted training paradigm to enhance prediction reliability. Specifically, differentiable volume rendering is adopted to generate rendered depth maps through predicted future volumes, which are adopted in render-based photometric consistency. Experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach, showcasing its state-of-the-art performance on the nuScenes and OpenScene benchmarks for 4D occupancy forecasting, end-to-end motion planning and point cloud forecasting. Concretely, it achieves state-of-the-art performances compared to existing 3D world models while incurring substantially lower computational costs.
HUGSIM: A Real-Time, Photo-Realistic and Closed-Loop Simulator for Autonomous Driving
Dec 02, 2024
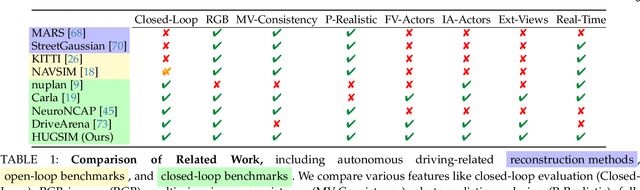
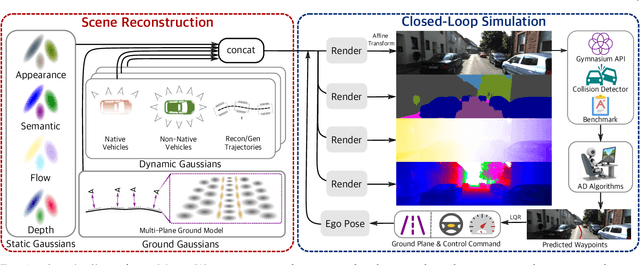
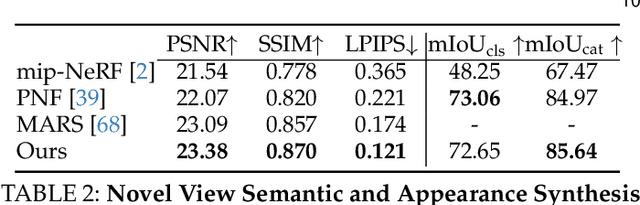
Abstract:In the past few decades, autonomous driving algorithms have made significant progress in perception, planning, and control. However, evaluating individual components does not fully reflect the performance of entire systems, highlighting the need for more holistic assessment methods. This motivates the development of HUGSIM, a closed-loop, photo-realistic, and real-time simulator for evaluating autonomous driving algorithms. We achieve this by lifting captured 2D RGB images into the 3D space via 3D Gaussian Splatting, improving the rendering quality for closed-loop scenarios, and building the closed-loop environment. In terms of rendering, We tackle challenges of novel view synthesis in closed-loop scenarios, including viewpoint extrapolation and 360-degree vehicle rendering. Beyond novel view synthesis, HUGSIM further enables the full closed simulation loop, dynamically updating the ego and actor states and observations based on control commands. Moreover, HUGSIM offers a comprehensive benchmark across more than 70 sequences from KITTI-360, Waymo, nuScenes, and PandaSet, along with over 400 varying scenarios, providing a fair and realistic evaluation platform for existing autonomous driving algorithms. HUGSIM not only serves as an intuitive evaluation benchmark but also unlocks the potential for fine-tuning autonomous driving algorithms in a photorealistic closed-loop setting.
VisionPAD: A Vision-Centric Pre-training Paradigm for Autonomous Driving
Nov 22, 2024



Abstract:This paper introduces VisionPAD, a novel self-supervised pre-training paradigm designed for vision-centric algorithms in autonomous driving. In contrast to previous approaches that employ neural rendering with explicit depth supervision, VisionPAD utilizes more efficient 3D Gaussian Splatting to reconstruct multi-view representations using only images as supervision. Specifically, we introduce a self-supervised method for voxel velocity estimation. By warping voxels to adjacent frames and supervising the rendered outputs, the model effectively learns motion cues in the sequential data. Furthermore, we adopt a multi-frame photometric consistency approach to enhance geometric perception. It projects adjacent frames to the current frame based on rendered depths and relative poses, boosting the 3D geometric representation through pure image supervision. Extensive experiments on autonomous driving datasets demonstrate that VisionPAD significantly improves performance in 3D object detection, occupancy prediction and map segmentation, surpassing state-of-the-art pre-training strategies by a considerable margin.
Efficient Depth-Guided Urban View Synthesis
Jul 17, 2024



Abstract:Recent advances in implicit scene representation enable high-fidelity street view novel view synthesis. However, existing methods optimize a neural radiance field for each scene, relying heavily on dense training images and extensive computation resources. To mitigate this shortcoming, we introduce a new method called Efficient Depth-Guided Urban View Synthesis (EDUS) for fast feed-forward inference and efficient per-scene fine-tuning. Different from prior generalizable methods that infer geometry based on feature matching, EDUS leverages noisy predicted geometric priors as guidance to enable generalizable urban view synthesis from sparse input images. The geometric priors allow us to apply our generalizable model directly in the 3D space, gaining robustness across various sparsity levels. Through comprehensive experiments on the KITTI-360 and Waymo datasets, we demonstrate promising generalization abilities on novel street scenes. Moreover, our results indicate that EDUS achieves state-of-the-art performance in sparse view settings when combined with fast test-time optimization.
AutoSplat: Constrained Gaussian Splatting for Autonomous Driving Scene Reconstruction
Jul 02, 2024



Abstract:Realistic scene reconstruction and view synthesis are essential for advancing autonomous driving systems by simulating safety-critical scenarios. 3D Gaussian Splatting excels in real-time rendering and static scene reconstructions but struggles with modeling driving scenarios due to complex backgrounds, dynamic objects, and sparse views. We propose AutoSplat, a framework employing Gaussian splatting to achieve highly realistic reconstructions of autonomous driving scenes. By imposing geometric constraints on Gaussians representing the road and sky regions, our method enables multi-view consistent simulation of challenging scenarios including lane changes. Leveraging 3D templates, we introduce a reflected Gaussian consistency constraint to supervise both the visible and unseen side of foreground objects. Moreover, to model the dynamic appearance of foreground objects, we estimate residual spherical harmonics for each foreground Gaussian. Extensive experiments on Pandaset and KITTI demonstrate that AutoSplat outperforms state-of-the-art methods in scene reconstruction and novel view synthesis across diverse driving scenarios. Visit our $\href{https://autosplat.github.io/}{\text{project page}}$.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge