Jianqiang Shen
Learning to Retrieve for Job Matching
Feb 21, 2024



Abstract:Web-scale search systems typically tackle the scalability challenge with a two-step paradigm: retrieval and ranking. The retrieval step, also known as candidate selection, often involves extracting standardized entities, creating an inverted index, and performing term matching for retrieval. Such traditional methods require manual and time-consuming development of query models. In this paper, we discuss applying learning-to-retrieve technology to enhance LinkedIns job search and recommendation systems. In the realm of promoted jobs, the key objective is to improve the quality of applicants, thereby delivering value to recruiter customers. To achieve this, we leverage confirmed hire data to construct a graph that evaluates a seeker's qualification for a job, and utilize learned links for retrieval. Our learned model is easy to explain, debug, and adjust. On the other hand, the focus for organic jobs is to optimize seeker engagement. We accomplished this by training embeddings for personalized retrieval, fortified by a set of rules derived from the categorization of member feedback. In addition to a solution based on a conventional inverted index, we developed an on-GPU solution capable of supporting both KNN and term matching efficiently.
LinkSAGE: Optimizing Job Matching Using Graph Neural Networks
Feb 20, 2024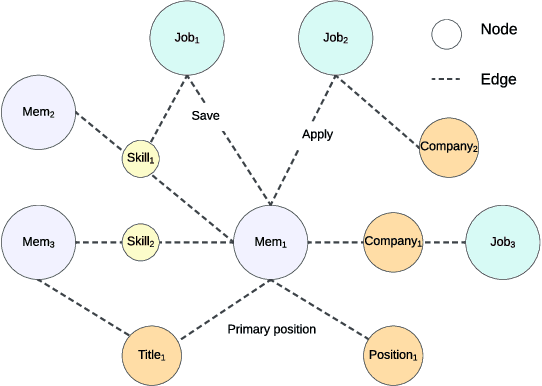

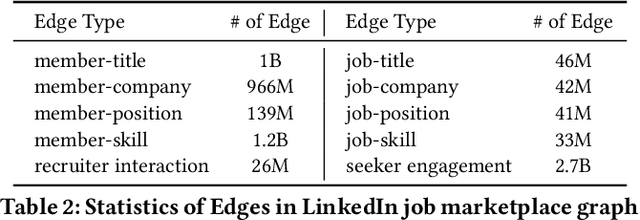

Abstract:We present LinkSAGE, an innovative framework that integrates Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) into large-scale personalized job matching systems, designed to address the complex dynamics of LinkedIns extensive professional network. Our approach capitalizes on a novel job marketplace graph, the largest and most intricate of its kind in industry, with billions of nodes and edges. This graph is not merely extensive but also richly detailed, encompassing member and job nodes along with key attributes, thus creating an expansive and interwoven network. A key innovation in LinkSAGE is its training and serving methodology, which effectively combines inductive graph learning on a heterogeneous, evolving graph with an encoder-decoder GNN model. This methodology decouples the training of the GNN model from that of existing Deep Neural Nets (DNN) models, eliminating the need for frequent GNN retraining while maintaining up-to-date graph signals in near realtime, allowing for the effective integration of GNN insights through transfer learning. The subsequent nearline inference system serves the GNN encoder within a real-world setting, significantly reducing online latency and obviating the need for costly real-time GNN infrastructure. Validated across multiple online A/B tests in diverse product scenarios, LinkSAGE demonstrates marked improvements in member engagement, relevance matching, and member retention, confirming its generalizability and practical impact.
Towards Data Quality Assessment in Online Advertising
Nov 30, 2017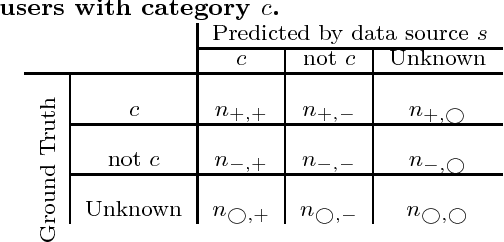
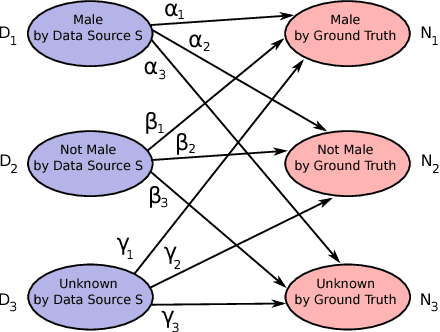
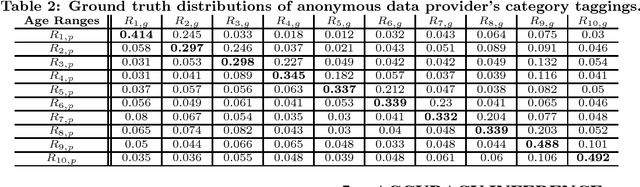
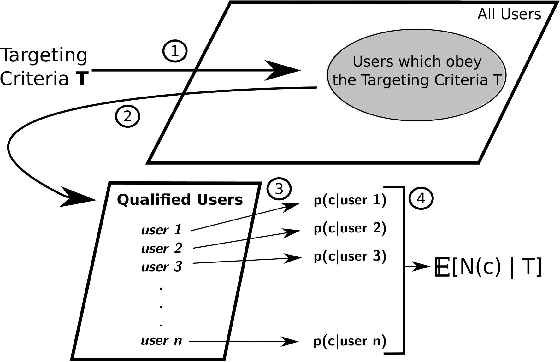
Abstract:In online advertising, our aim is to match the advertisers with the most relevant users to optimize the campaign performance. In the pursuit of achieving this goal, multiple data sources provided by the advertisers or third-party data providers are utilized to choose the set of users according to the advertisers' targeting criteria. In this paper, we present a framework that can be applied to assess the quality of such data sources in large scale. This framework efficiently evaluates the similarity of a specific data source categorization to that of the ground truth, especially for those cases when the ground truth is accessible only in aggregate, and the user-level information is anonymized or unavailable due to privacy reasons. We propose multiple methodologies within this framework, present some preliminary assessment results, and evaluate how the methodologies compare to each other. We also present two use cases where we can utilize the data quality assessment results: the first use case is targeting specific user categories, and the second one is forecasting the desirable audiences we can reach for an online advertising campaign with pre-set targeting criteria.
* 10 pages, 7 Figures. This work has been presented in the KDD 2016 Workshop on Enterprise Intelligence
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge