Ali Dasdan
The Convergent Ethics of AI? Analyzing Moral Foundation Priorities in Large Language Models with a Multi-Framework Approach
Apr 27, 2025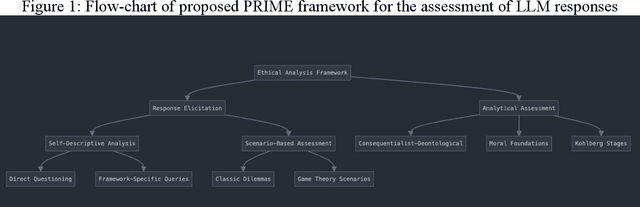
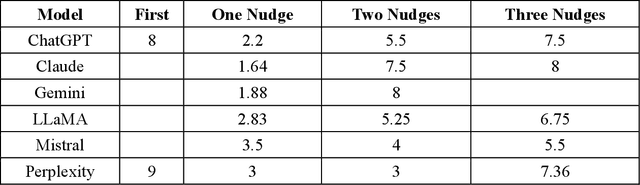
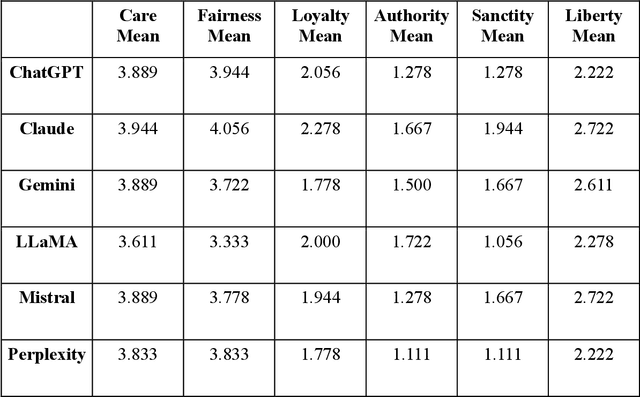
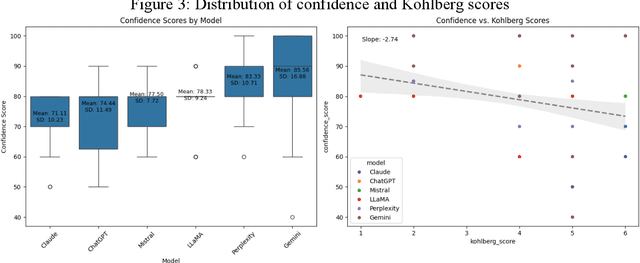
Abstract:As large language models (LLMs) are increasingly deployed in consequential decision-making contexts, systematically assessing their ethical reasoning capabilities becomes a critical imperative. This paper introduces the Priorities in Reasoning and Intrinsic Moral Evaluation (PRIME) framework--a comprehensive methodology for analyzing moral priorities across foundational ethical dimensions including consequentialist-deontological reasoning, moral foundations theory, and Kohlberg's developmental stages. We apply this framework to six leading LLMs through a dual-protocol approach combining direct questioning and response analysis to established ethical dilemmas. Our analysis reveals striking patterns of convergence: all evaluated models demonstrate strong prioritization of care/harm and fairness/cheating foundations while consistently underweighting authority, loyalty, and sanctity dimensions. Through detailed examination of confidence metrics, response reluctance patterns, and reasoning consistency, we establish that contemporary LLMs (1) produce decisive ethical judgments, (2) demonstrate notable cross-model alignment in moral decision-making, and (3) generally correspond with empirically established human moral preferences. This research contributes a scalable, extensible methodology for ethical benchmarking while highlighting both the promising capabilities and systematic limitations in current AI moral reasoning architectures--insights critical for responsible development as these systems assume increasingly significant societal roles.
Auditing the Ethical Logic of Generative AI Models
Apr 24, 2025Abstract:As generative AI models become increasingly integrated into high-stakes domains, the need for robust methods to evaluate their ethical reasoning becomes increasingly important. This paper introduces a five-dimensional audit model -- assessing Analytic Quality, Breadth of Ethical Considerations, Depth of Explanation, Consistency, and Decisiveness -- to evaluate the ethical logic of leading large language models (LLMs). Drawing on traditions from applied ethics and higher-order thinking, we present a multi-battery prompt approach, including novel ethical dilemmas, to probe the models' reasoning across diverse contexts. We benchmark seven major LLMs finding that while models generally converge on ethical decisions, they vary in explanatory rigor and moral prioritization. Chain-of-Thought prompting and reasoning-optimized models significantly enhance performance on our audit metrics. This study introduces a scalable methodology for ethical benchmarking of AI systems and highlights the potential for AI to complement human moral reasoning in complex decision-making contexts.
Leveraging LLMs to Enable Natural Language Search on Go-to-market Platforms
Nov 07, 2024



Abstract:Enterprise searches require users to have complex knowledge of queries, configurations, and metadata, rendering it difficult for them to access information as needed. Most go-to-market (GTM) platforms utilize advanced search, an interface that enables users to filter queries by various fields using categories or keywords, which, historically, however, has proven to be exceedingly cumbersome, as users are faced with seemingly hundreds of options, fields, and buttons. Consequently, querying with natural language has long been ideal, a notion further empowered by Large Language Models (LLMs). In this paper, we implement and evaluate a solution for the Zoominfo product for sellers, which prompts the LLM with natural language, producing search fields through entity extraction that are then converted into a search query. The intermediary search fields offer numerous advantages for each query, including the elimination of syntax errors, simpler ground truths, and an intuitive format for the LLM to interpret. We paired this pipeline with many advanced prompt engineering strategies, featuring an intricate system message, few-shot prompting, chain-of-thought (CoT) reasoning, and execution refinement. Furthermore, we manually created the ground truth for 500+ natural language queries, enabling the supervised fine-tuning of Llama-3-8B-Instruct and the introduction of sophisticated numerical metrics. Comprehensive experiments with closed, open source, and fine-tuned LLM models were conducted through exact, Jaccard, cosine, and semantic similarity on individual search entities to demonstrate the efficacy of our approach. Overall, the most accurate closed model had an average accuracy of 97% per query, with only one field performing under 90%, with comparable results observed from the fine-tuned models.
Towards Data Quality Assessment in Online Advertising
Nov 30, 2017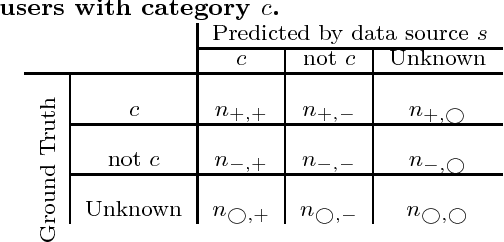
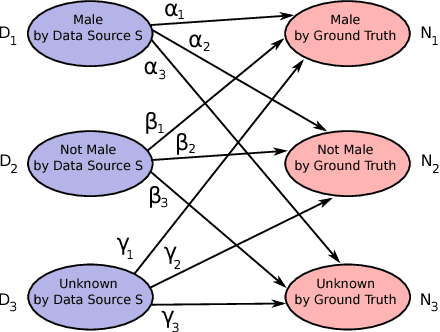
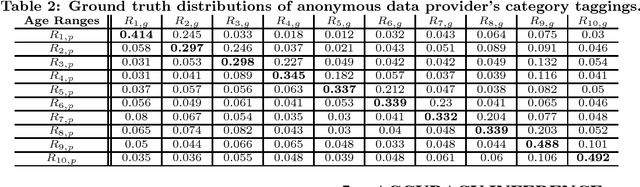
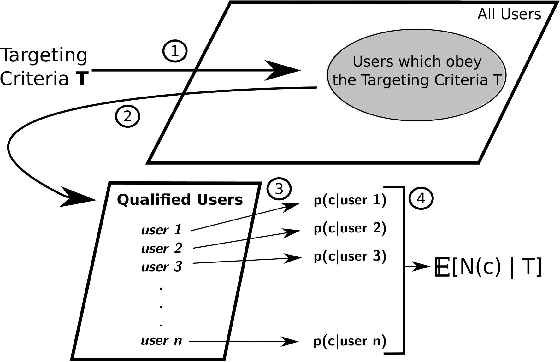
Abstract:In online advertising, our aim is to match the advertisers with the most relevant users to optimize the campaign performance. In the pursuit of achieving this goal, multiple data sources provided by the advertisers or third-party data providers are utilized to choose the set of users according to the advertisers' targeting criteria. In this paper, we present a framework that can be applied to assess the quality of such data sources in large scale. This framework efficiently evaluates the similarity of a specific data source categorization to that of the ground truth, especially for those cases when the ground truth is accessible only in aggregate, and the user-level information is anonymized or unavailable due to privacy reasons. We propose multiple methodologies within this framework, present some preliminary assessment results, and evaluate how the methodologies compare to each other. We also present two use cases where we can utilize the data quality assessment results: the first use case is targeting specific user categories, and the second one is forecasting the desirable audiences we can reach for an online advertising campaign with pre-set targeting criteria.
* 10 pages, 7 Figures. This work has been presented in the KDD 2016 Workshop on Enterprise Intelligence
Online Model Evaluation in a Large-Scale Computational Advertising Platform
Aug 31, 2015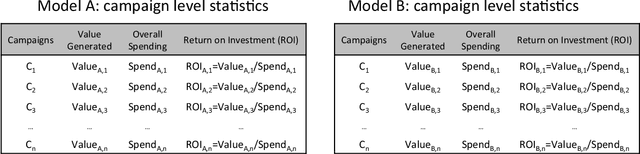
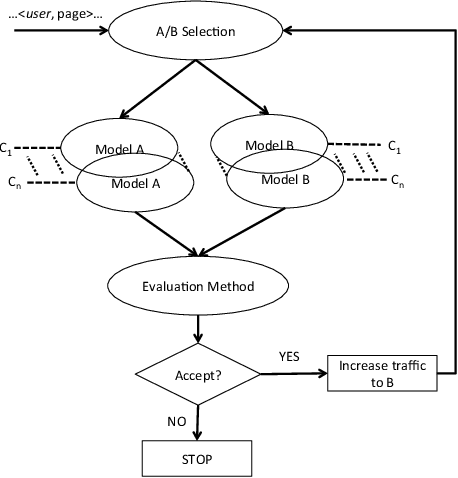
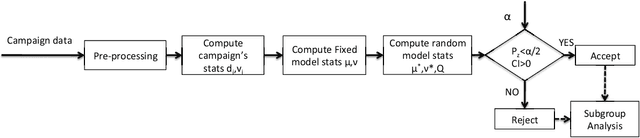

Abstract:Online media provides opportunities for marketers through which they can deliver effective brand messages to a wide range of audiences. Advertising technology platforms enable advertisers to reach their target audience by delivering ad impressions to online users in real time. In order to identify the best marketing message for a user and to purchase impressions at the right price, we rely heavily on bid prediction and optimization models. Even though the bid prediction models are well studied in the literature, the equally important subject of model evaluation is usually overlooked. Effective and reliable evaluation of an online bidding model is crucial for making faster model improvements as well as for utilizing the marketing budgets more efficiently. In this paper, we present an experimentation framework for bid prediction models where our focus is on the practical aspects of model evaluation. Specifically, we outline the unique challenges we encounter in our platform due to a variety of factors such as heterogeneous goal definitions, varying budget requirements across different campaigns, high seasonality and the auction-based environment for inventory purchasing. Then, we introduce return on investment (ROI) as a unified model performance (i.e., success) metric and explain its merits over more traditional metrics such as click-through rate (CTR) or conversion rate (CVR). Most importantly, we discuss commonly used evaluation and metric summarization approaches in detail and propose a more accurate method for online evaluation of new experimental models against the baseline. Our meta-analysis-based approach addresses various shortcomings of other methods and yields statistically robust conclusions that allow us to conclude experiments more quickly in a reliable manner. We demonstrate the effectiveness of our evaluation strategy on real campaign data through some experiments.
* Accepted to ICDM2015
User Clustering in Online Advertising via Topic Models
Feb 24, 2015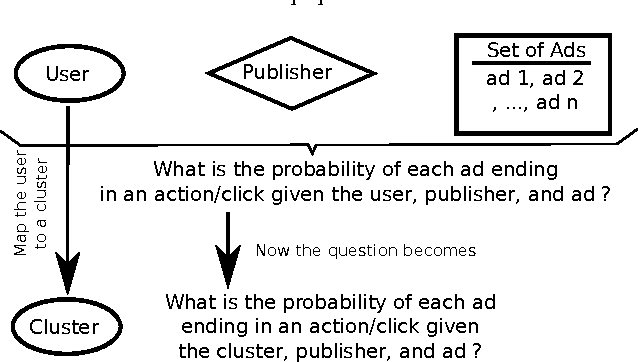
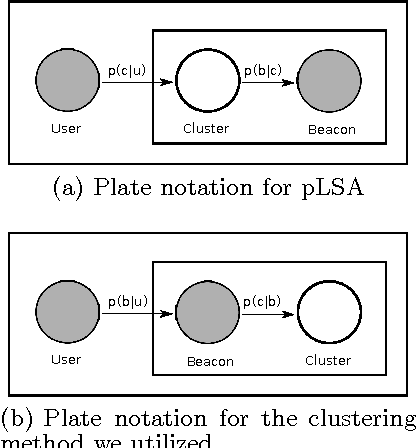

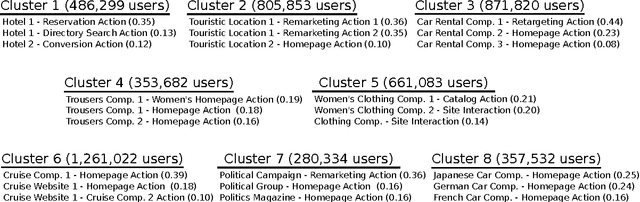
Abstract:In the domain of online advertising, our aim is to serve the best ad to a user who visits a certain webpage, to maximize the chance of a desired action to be performed by this user after seeing the ad. While it is possible to generate a different prediction model for each user to tell if he/she will act on a given ad, the prediction result typically will be quite unreliable with huge variance, since the desired actions are extremely sparse, and the set of users is huge (hundreds of millions) and extremely volatile, i.e., a lot of new users are introduced everyday, or are no longer valid. In this paper we aim to improve the accuracy in finding users who will perform the desired action, by assigning each user to a cluster, where the number of clusters is much smaller than the number of users (in the order of hundreds). Each user will fall into the same cluster with another user if their event history are similar. For this purpose, we modify the probabilistic latent semantic analysis (pLSA) model by assuming the independence of the user and the cluster id, given the history of events. This assumption helps us to identify a cluster of a new user without re-clustering all the users. We present the details of the algorithm we employed as well as the distributed implementation on Hadoop, and some initial results on the clusters that were generated by the algorithm.
Multi-Touch Attribution Based Budget Allocation in Online Advertising
Feb 24, 2015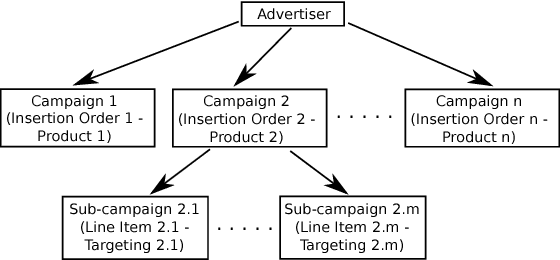
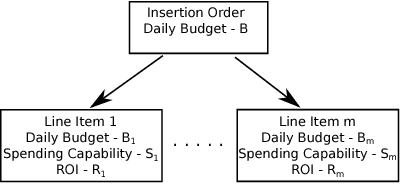
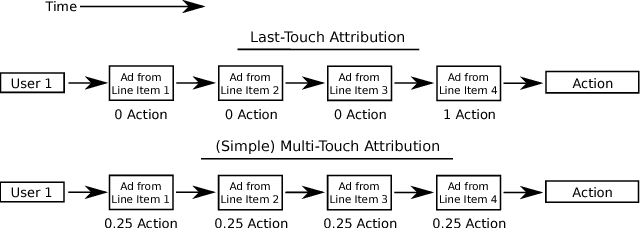
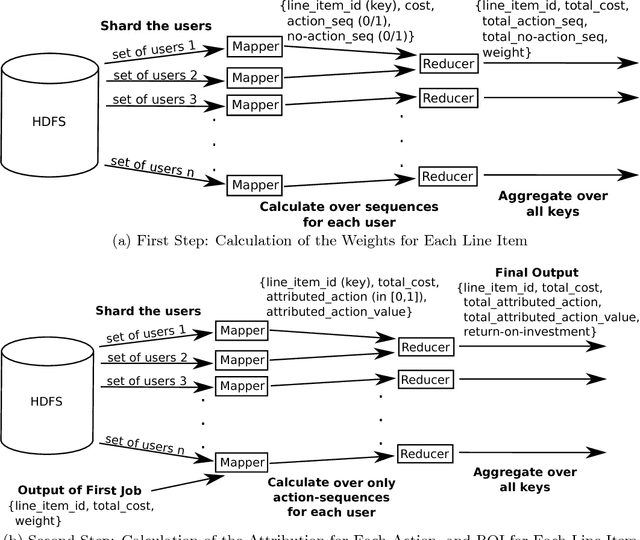
Abstract:Budget allocation in online advertising deals with distributing the campaign (insertion order) level budgets to different sub-campaigns which employ different targeting criteria and may perform differently in terms of return-on-investment (ROI). In this paper, we present the efforts at Turn on how to best allocate campaign budget so that the advertiser or campaign-level ROI is maximized. To do this, it is crucial to be able to correctly determine the performance of sub-campaigns. This determination is highly related to the action-attribution problem, i.e. to be able to find out the set of ads, and hence the sub-campaigns that provided them to a user, that an action should be attributed to. For this purpose, we employ both last-touch (last ad gets all credit) and multi-touch (many ads share the credit) attribution methodologies. We present the algorithms deployed at Turn for the attribution problem, as well as their parallel implementation on the large advertiser performance datasets. We conclude the paper with our empirical comparison of last-touch and multi-touch attribution-based budget allocation in a real online advertising setting.
Scalable Audience Reach Estimation in Real-time Online Advertising
May 14, 2013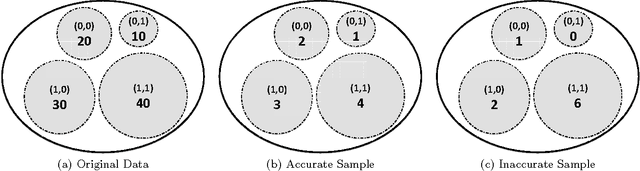

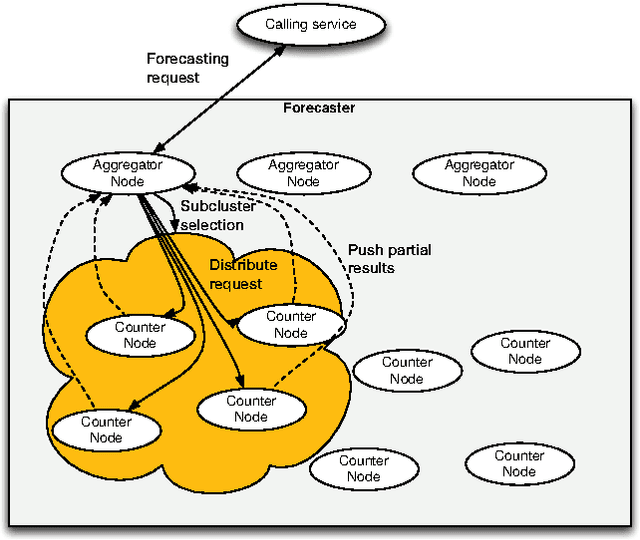
Abstract:Online advertising has been introduced as one of the most efficient methods of advertising throughout the recent years. Yet, advertisers are concerned about the efficiency of their online advertising campaigns and consequently, would like to restrict their ad impressions to certain websites and/or certain groups of audience. These restrictions, known as targeting criteria, limit the reachability for better performance. This trade-off between reachability and performance illustrates a need for a forecasting system that can quickly predict/estimate (with good accuracy) this trade-off. Designing such a system is challenging due to (a) the huge amount of data to process, and, (b) the need for fast and accurate estimates. In this paper, we propose a distributed fault tolerant system that can generate such estimates fast with good accuracy. The main idea is to keep a small representative sample in memory across multiple machines and formulate the forecasting problem as queries against the sample. The key challenge is to find the best strata across the past data, perform multivariate stratified sampling while ensuring fuzzy fall-back to cover the small minorities. Our results show a significant improvement over the uniform and simple stratified sampling strategies which are currently widely used in the industry.
Real Time Bid Optimization with Smooth Budget Delivery in Online Advertising
May 14, 2013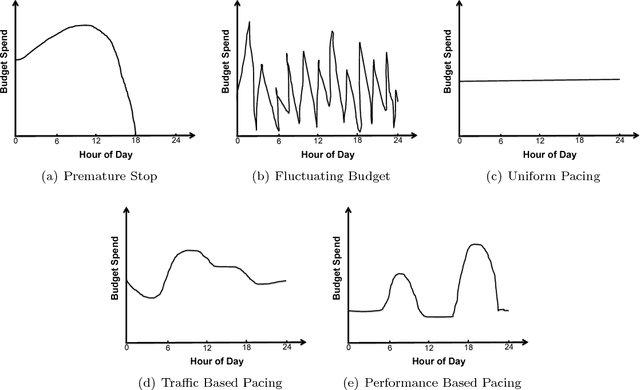
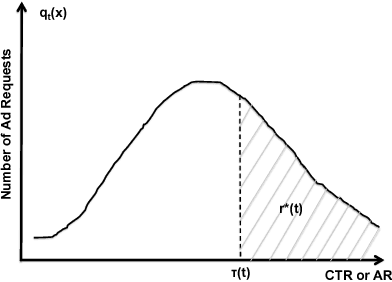
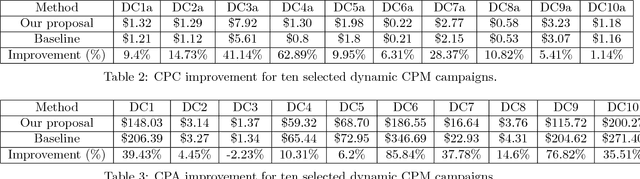
Abstract:Today, billions of display ad impressions are purchased on a daily basis through a public auction hosted by real time bidding (RTB) exchanges. A decision has to be made for advertisers to submit a bid for each selected RTB ad request in milliseconds. Restricted by the budget, the goal is to buy a set of ad impressions to reach as many targeted users as possible. A desired action (conversion), advertiser specific, includes purchasing a product, filling out a form, signing up for emails, etc. In addition, advertisers typically prefer to spend their budget smoothly over the time in order to reach a wider range of audience accessible throughout a day and have a sustainable impact. However, since the conversions occur rarely and the occurrence feedback is normally delayed, it is very challenging to achieve both budget and performance goals at the same time. In this paper, we present an online approach to the smooth budget delivery while optimizing for the conversion performance. Our algorithm tries to select high quality impressions and adjust the bid price based on the prior performance distribution in an adaptive manner by distributing the budget optimally across time. Our experimental results from real advertising campaigns demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed approach.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge