Abhishek Saxena
Novosibirsk State University
Application of Liquid Rank Reputation System for Content Recommendation
Sep 15, 2022



Abstract:An effective content recommendation on social media platforms should be able to benefit both creators to earn fair compensation and consumers to enjoy really relevant, interesting, and personalized content. In this paper, we propose a model to implement the liquid democracy principle for the content recommendation system. It uses a personalized recommendation model based on reputation ranking system to encourage personal interests driven recommendation. Moreover, the personalization factors to an end users' higher-order friends on the social network (initial input Twitter channels in our case study) to improve the accuracy and diversity of recommendation results. This paper analyzes the dataset based on cryptocurrency news on Twitter to find the opinion leader using the liquid rank reputation system. This paper deals with the tier-2 implementation of a liquid rank in a content recommendation model. This model can be also used as an additional layer in the other recommendation systems. The paper proposes the implementation, challenges, and future scope of the liquid rank reputation model.
Multi-Touch Attribution Based Budget Allocation in Online Advertising
Feb 24, 2015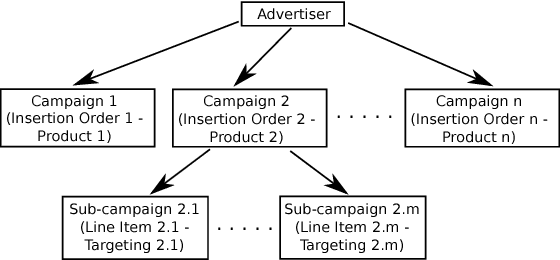
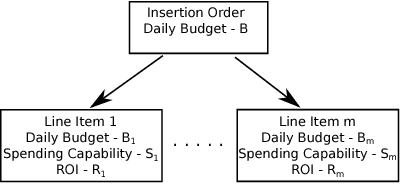
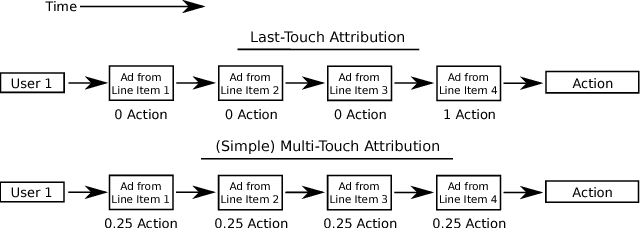
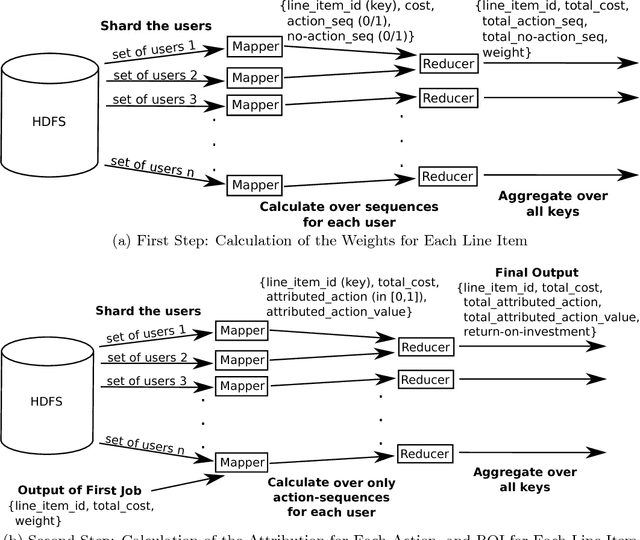
Abstract:Budget allocation in online advertising deals with distributing the campaign (insertion order) level budgets to different sub-campaigns which employ different targeting criteria and may perform differently in terms of return-on-investment (ROI). In this paper, we present the efforts at Turn on how to best allocate campaign budget so that the advertiser or campaign-level ROI is maximized. To do this, it is crucial to be able to correctly determine the performance of sub-campaigns. This determination is highly related to the action-attribution problem, i.e. to be able to find out the set of ads, and hence the sub-campaigns that provided them to a user, that an action should be attributed to. For this purpose, we employ both last-touch (last ad gets all credit) and multi-touch (many ads share the credit) attribution methodologies. We present the algorithms deployed at Turn for the attribution problem, as well as their parallel implementation on the large advertiser performance datasets. We conclude the paper with our empirical comparison of last-touch and multi-touch attribution-based budget allocation in a real online advertising setting.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge