Boyu Ning
Integrated Channel Estimation and Sensing for Near-Field ELAA Systems
Jan 26, 2026Abstract:In this paper, we study the problem of uplink channel estimation for near-filed orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) systems, where a base station (BS), equipped with an extremely large-scale antenna array (ELAA), serves multiple users over the same time-frequency resource block. A non-orthogonal pilot transmission scheme is considered to accommodate a larger number of users that can be supported by ELAA systems without incurring an excessive amount of training overhead. To facilitate efficient multi-user channel estimation, we express the received signal as a third-order low-rank tensor, which admits a canonical polyadic decomposition (CPD) model for line-of-sight (LoS) scenarios and a block term decomposition (BTD) model for non-line-of-sight (NLoS) scenarios. An alternating least squares (ALS) algorithm and a non-linear least squares (NLS) algorithm are employed to perform CPD and BTD, respectively. Channel parameters are then efficiently extracted from the recovered factor matrices. By exploiting the geometry of the propagation paths in the estimated channel, users' positions can be precisely determined in LoS scenarios. Moreover, our uniqueness analysis shows that the proposed tensor-based joint multi-user channel estimation framework is effective even when the number of pilot symbols is much smaller than the number of users, revealing its potential in training overhead reduction. Simulation results demonstrate that the proposed method achieves markedly higher channel estimation accuracy than compressed sensing (CS)-based approaches.
Movable Antenna-Enhanced Near-Field Flexible Beamforming: Performance Analysis and Optimization
Jan 25, 2026Abstract:As an emerging wireless communication technology, movable antennas (MAs) offer the ability to adjust the spatial correlation of steering vectors, enabling more flexible beamforming compared to fixed-position antennas (FPAs). In this paper, we investigate the use of MAs for two typical near-field beamforming scenarios: beam nulling and multi-beam forming. In the first scenario, we aim to jointly optimize the positions of multiple MAs and the beamforming vector to maximize the beam gain toward a desired direction while nulling interference toward multiple undesired directions. In the second scenario, the objective is to maximize the minimum beam gain among all the above directions. However, both problems are non-convex and challenging to solve optimally. To gain insights, we first analyze several special cases and show that, with proper positioning of the MAs, directing the beam toward a specific direction can lead to nulls or full gains in other directions in the two scenarios, respectively. For the general cases, we propose a discrete sampling method and an alternating optimization algorithm to obtain high-quality suboptimal solutions to the two formulated problems. Furthermore, considering the practical limitations in antenna positioning accuracy, we analyze the impact of position errors on the performance of the optimized beamforming and MA positions, by introducing a Taylor series approximation for the near-field beam gain at each target. Numerical results validate our theoretical findings and demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed algorithms.
Movable Antenna Enhanced Multi-Region Beam Coverage: A Multi-Notch-Filter-Inspired Design
Dec 30, 2025Abstract:Movable antenna (MA) has emerged as a promising technology to enhance wireless communication performance by exploiting the new degree of freedom (DoF) via antenna position optimization. In this letter, we investigate the MA-enhanced wide beam coverage over multiple subregions in the spatial domain. Specifically, we aim to maximize the minimum beam gain over the desired subregions by jointly optimizing the transmit beamforming and antenna position vector (APV). Although this problem is non-convex, we propose an efficient algorithm to solve it by leveraging the similarity between the considered multi-region coverage and classical multi-notch filter (MNF) design. In particular, we construct a spatial MNF-based transmit beamforming vector by assuming a continuous amplitude and phase-shift profile within the antenna movement region. Based on this continuous profile, we propose a sequential update algorithm to select an optimal subset of MA positions for multi-region coverage, jointly with a Gibbs sampling (GS) procedure to avoid undesired local optimum. Numerical results show that our proposed algorithm can significantly outperform conventional fixed position antennas (FPAs) and achieve a comparable performance to the alternating optimization (AO) algorithm with dramatically lower complexity.
Rotatable Antenna Array-Enhanced Null Steering: Performance Analysis and Optimization
Dec 13, 2025Abstract:Conventional fixed-orientation antenna (FOA) arrays offer limited degrees of freedom (DoF) for flexible beamforming such as null steering. To address this limitation, we propose a new rotatable antenna array (RAA) architecture in this paper, which enables three-dimensional (3D) rotational control of an antenna array to provide enhanced spatial flexibility for null steering. To characterize its performance, we aim to jointly optimize the 3D rotational angles of the RAA, to maximize the beam gain over a given desired direction, while nulling those over multiple interference directions under zero-forcing (ZF) beamforming. However, this problem is non-convex and challenging to tackle due to the highly nonlinear expression of the beam gain in terms of the rotational angles. To gain insights, we first examine several special cases including both isotropic and directional antenna radiation patterns, deriving the conditions under which full beam gain can be achieved over the desired direction while meeting the nulling constraints for interference directions. These conditions clearly indicate that compared with FOA arrays, RAAs can significantly relax the angular separation requirement for achieving effective null steering. For other general cases, we propose a sequential update algorithm, that iteratively refines the 3D rotational angles by discretizing the 3D angular search space. To avoid undesired local optimum, a Gibbs sampling (GS) procedure is also employed between two consecutive rounds of sequential update for solution exploration. Simulation results verify our analytical results and show superior null-steering performance of RAAs to FOA arrays.
Performance Optimization for Movable Antenna Enhanced MISO-OFDM Systems
Oct 02, 2025



Abstract:Movable antenna (MA) technology offers a flexible approach to enhancing wireless channel conditions by adjusting antenna positions within a designated region. While most existing works focus on narrowband MA systems, this paper investigates MA position optimization for an MA-enhanced multiple-input single-output (MISO) orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing (OFDM) system. This problem appears to be particularly challenging due to the frequency-flat nature of MA positioning, which should accommodate the channel conditions across different subcarriers. To overcome this challenge, we discretize the movement region into a multitude of sampling points, thereby converting the continuous position optimization problem into a discrete point selection problem. Although this problem is combinatorial, we develop an efficient partial enumeration algorithm to find the optimal solution using a branch-and-bound framework, where a graph-theoretic method is incorporated to effectively prune suboptimal solutions. In the low signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) regime, a simplified graph-based algorithm is also proposed to obtain the optimal MA positions without the need for enumeration. Simulation results reveal that the proposed algorithm outperforms conventional fixed-position antennas (FPAs), while narrowband-based antenna position optimization can achieve near-optimal performance.
Radiation Pattern Reconfigurable FAS-Empowered Interference-Resilient UAV Communication
Oct 01, 2025Abstract:The widespread use of uncrewed aerial vehicles (UAVs) has propelled the development of advanced techniques on countering unauthorized UAV flights. However, the resistance of legal UAVs to illegal interference remains under-addressed. This paper proposes radiation pattern reconfigurable fluid antenna systems (RPR-FAS)-empowered interference-resilient UAV communication scheme. This scheme integrates the reconfigurable pixel antenna technology, which provides each antenna with an adjustable radiation pattern. Therefore, RPR-FAS can enhance the angular resolution of a UAV with a limited number of antennas, thereby improving spectral efficiency (SE) and interference resilience. Specifically, we first design dedicated radiation pattern adapted from 3GPP-TR-38.901, where the beam direction and half power beamwidth are tailored for UAV communications. Furthermore, we propose a low-storage-overhead orthogonal matching pursuit multiple measurement vectors algorithm, which accurately estimates the angle-of-arrival (AoA) of the communication link, even in the single antenna case. Particularly, by utilizing the Fourier transform to the radiation pattern gain matrix, we design a dimension-reduction technique to achieve 1--2 order-of-magnitude reduction in storage requirements. Meanwhile, we propose a maximum likelihood interference AoA estimation method based on the law of large numbers, so that the SE can be further improved. Finally, alternating optimization is employed to obtain the optimal uplink radiation pattern and combiner, while an exhaustive search is applied to determine the optimal downlink pattern, complemented by the water-filling algorithm for beamforming. Comprehensive simulations demonstrate that the proposed schemes outperform traditional methods in terms of angular sensing precision and spectral efficiency.
Integrating Movable Antennas and Intelligent Reflecting Surfaces (MA-IRS): Fundamentals, Practical Solutions, and Opportunities
Jun 17, 2025



Abstract:Movable antennas (MAs) and intelligent reflecting surfaces (IRSs) enable active antenna repositioning and passive phase-shift tuning for channel reconfiguration, respectively. Integrating MAs and IRSs boosts spatial degrees of freedom, significantly enhancing wireless network capacity, coverage, and reliability. In this article, we first present the fundamentals of MA-IRS integration, involving clarifying the key design issues, revealing performance gain, and identifying the conditions where MA-IRS synergy persists. Then, we examine practical challenges and propose pragmatic design solutions, including optimization schemes, hardware architectures, deployment strategies, and robust designs for hardware impairments and mobility management. In addition, we highlight how MA-IRS architectures uniquely support advanced integrated sensing and communication, enhancing sensing performance and dual-functional flexibility. Overall, MA-IRS integration emerges as a compelling approach toward next-generation reconfigurable wireless systems.
Spectral Efficiency Maximization for DMA-enabled Multiuser MISO with Statistical CSI
Jun 11, 2025Abstract:Dynamic metasurface antennas (DMAs) offer the potential to achieve large-scale antenna arrays with low power consumption and reduced hardware costs, making them a promising technology for future communication systems. This paper investigates the spectral efficiency (SE) of DMA-enabled multiuser multiple-input single-output (MISO) systems in both uplink and downlink transmissions, using only statistical channel state information (CSI) to maximize the ergodic sum rate of multiple users. For the uplink system, we consider two decoding rules: minimum mean square error (MMSE) with and without successive interference cancellation (SIC). For both decoders, we derive closed-form surrogates to substitute the original expressions of ergodic sum rate and formulate tractable optimization problems for designing DMA weights. Then, a weighted MMSE (WMMSE)-based algorithm is proposed to maximize the ergodic sum rate. For the downlink system, we derive an approximate expression for the ergodic sum rate and formulate a hybrid analog/digital beamforming optimization problem that jointly optimizes the digital precoder and DMA weights. A penalty dual decomposition (PDD)-based algorithm is proposed by leveraging the fractional programming framework. Numerical results validate the accuracy of the derived surrogates and highlight the superiority of the proposed algorithms over baseline schemes. It is shown that these algorithms are effective across various DMA settings and are particularly well-suited for system design in fast time-varying channels.
CNN-Based Channel Map Estimation for Movable Antenna Systems
May 27, 2025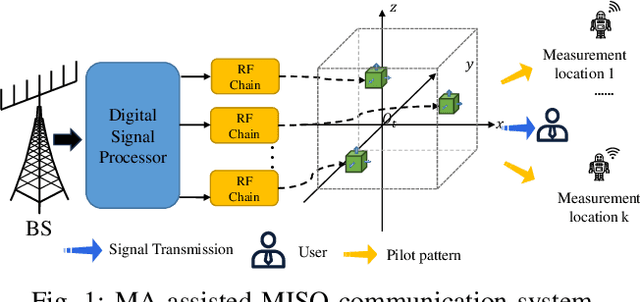
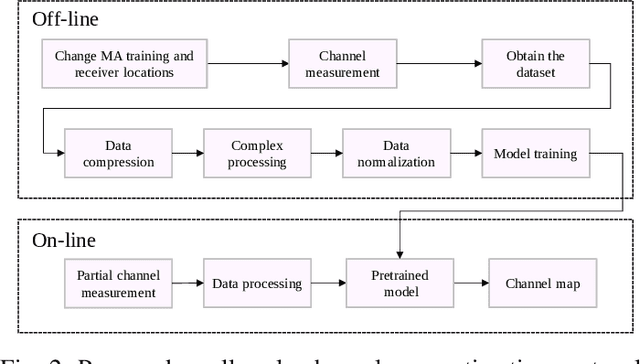
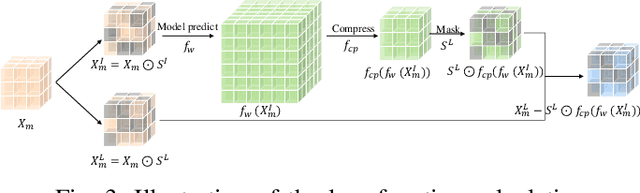
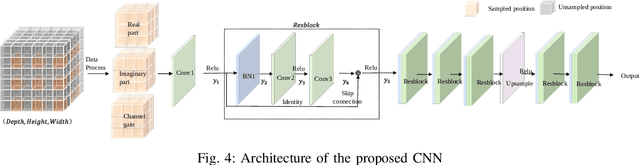
Abstract:Movable antenna (MA) has attracted increasing attention in wireless communications due to its capability of wireless channel reconfiguration through local antenna movement within a confined region at the transmitter/receiver. However, to determine the optimal antenna positions, channel state information (CSI) within the entire region, termed small-scale channel map, is required, which poses a significant challenge due to the unaffordable overhead for exhaustive channel estimation at all positions. To tackle this challenge, in this paper, we propose a new convolutional neural network (CNN)-based estimation scheme to reconstruct the small-scale channel map within a three-dimensional (3D) movement region. Specifically, we first collect a set of CSI measurements corresponding to a subset of MA positions and different receiver locations offline to comprehensively capture the environmental features. Subsequently, we train a CNN using the collected data, which is then used to reconstruct the full channel map during real-time transmission only based on a finite number of channel measurements taken at several selected MA positions within the 3D movement region. Numerical results demonstrate that our proposed scheme can accurately reconstruct the small-scale channel map and outperforms other benchmark schemes.
Robust Movable-Antenna Position Optimization with Imperfect CSI for MISO Systems
May 11, 2025Abstract:Movable antenna (MA) technology has emerged as a promising solution for reconfiguring wireless channel conditions through local antenna movement within confined regions. Unlike previous works assuming perfect channel state information (CSI), this letter addresses the robust MA position optimization problem under imperfect CSI conditions for a multiple-input single-output (MISO) MA system. Specifically, we consider two types of CSI errors: norm-bounded and randomly distributed errors, aiming to maximize the worst-case and non-outage received signal power, respectively. For norm-bounded CSI errors, we derive the worst-case received signal power in closed-form. For randomly distributed CSI errors, due to the intractability of the probabilistic constraints, we apply the Bernstein-type inequality to obtain a closed-form lower bound for the non-outage received signal power. Based on these results, we show the optimality of the maximum-ratio transmission for imperfect CSI in both scenarios and employ a graph-based algorithm to obtain the optimal MA positions. Numerical results show that our proposed scheme can even outperform other benchmark schemes implemented under perfect CSI conditions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge