Tareq Y. Al-Naffouri
LEO Constellations as a Decentralized GNSS Network: Optimizing PNT Corrections in Space
Dec 24, 2025
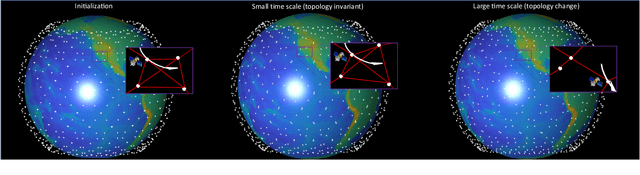
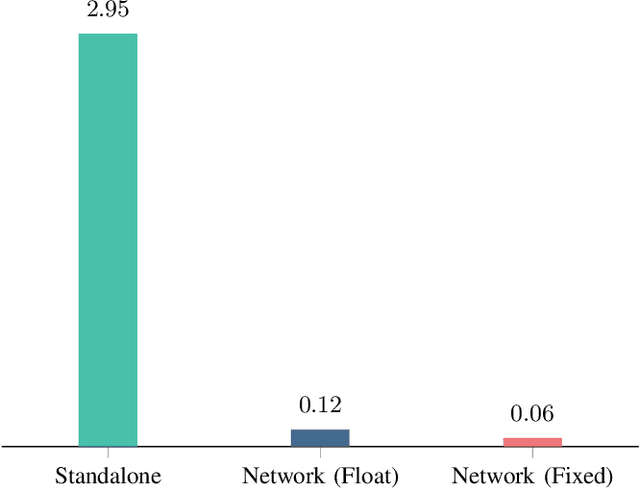
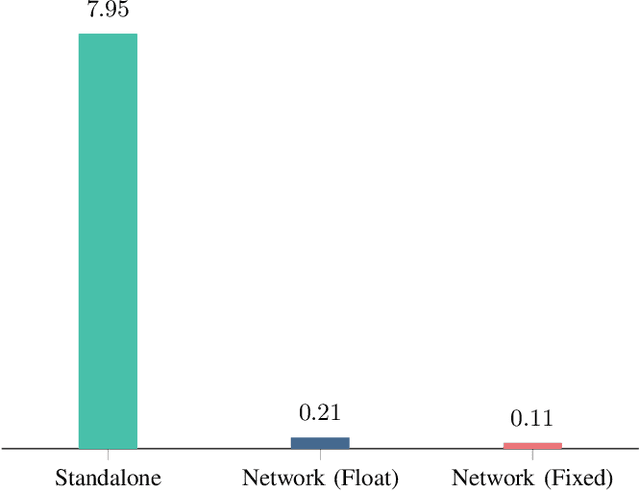
Abstract:With the rapid expansion of low Earth orbit (LEO) constellations, thousands of satellites are now in operation, many equipped with onboard GNSS receivers capable of continuous orbit determination and time synchronization. This development is creating an unprecedented spaceborne GNSS network, offering new opportunities for network-driven precise LEO orbit and clock estimation. Yet, current onboard GNSS processing is largely standalone and often insufficient for high-precision applications, while centralized fusion is challenging due to computational bottlenecks and the lack of in-orbit infrastructure. In this work, we report a decentralized GNSS network over large-scale LEO constellations, where each satellite processes its own measurements while exchanging compact information with neighboring nodes to enable precise orbit and time determination. We model the moving constellation as a dynamic graph and tailor a momentum-accelerated gradient tracking (GT) method to ensure steady convergence despite topology changes. Numerical simulations with constellations containing hundreds of satellites show that the proposed method matches the accuracy of an ideal centralized benchmark, while substantially reducing communication burdens. Ultimately, this framework supports the development of autonomous and self-organizing space systems, enabling high-precision navigation with reduced dependence on continuous ground contact.
Decentralized GNSS at Global Scale via Graph-Aware Diffusion Adaptation
Dec 23, 2025



Abstract:Network-based Global Navigation Satellite Systems (GNSS) underpin critical infrastructure and autonomous systems, yet typically rely on centralized processing hubs that limit scalability, resilience, and latency. Here we report a global-scale, decentralized GNSS architecture spanning hundreds of ground stations. By modeling the receiver network as a time-varying graph, we employ a deep linear neural network approach to learn topology-aware mixing schedules that optimize information exchange. This enables a gradient tracking diffusion strategy wherein stations execute local inference and exchange succinct messages to achieve two concurrent objectives: centimeter-level self-localization and network-wide consensus on satellite correction products. The consensus products are broadcast to user receivers as corrections, supporting precise point positioning (PPP) and precise point positioning-real-time kinematic (PPP-RTK). Numerical results demonstrate that our method matches the accuracy of centralized baselines while significantly outperforming existing decentralized methods in convergence speed and communication overhead. By reframing decentralized GNSS as a networked signal processing problem, our results pave the way for integrating decentralized optimization, consensus-based inference, and graph-aware learning as effective tools in operational satellite navigation.
Decentralized Cooperative Beamforming for Networked LEO Satellites with Statistical CSI
Dec 21, 2025Abstract:Inter-satellite-link-enabled low-Earth-orbit (LEO) satellite constellations are evolving toward networked architectures that support constellation-level cooperation, enabling multiple satellites to jointly serve user terminals through cooperative beamforming. While such cooperation can substantially enhance link budgets and achievable rates, its practical realization is challenged by the scalability limitations of centralized beamforming designs and the stringent computational and signaling constraints of large LEO constellations. This paper develops a fully decentralized cooperative beamforming framework for networked LEO satellite downlinks. Using an ergodic-rate-based formulation, we first derive a centralized weighted minimum mean squared error (WMMSE) solution as a performance benchmark. Building on this formulation, we propose a topology-agnostic decentralized beamforming algorithm by localizing the benchmark and exchanging a set of globally coupled variables whose dimensions are independent of the antenna number and enforcing consensus over arbitrary connected inter-satellite networks. The resulting algorithm admits fully parallel execution across satellites. To further enhance scalability, we eliminate the consensus-related auxiliary variables in closed form and derive a low-complexity per-satellite update rule that is optimal to local iteration and admits a quasi-closed-form solution via scalar line search. Simulation results show that the proposed decentralized schemes closely approach centralized performance under practical inter-satellite topologies, while significantly reducing computational complexity and signaling overhead, enabling scalable cooperative beamforming for large LEO constellations.
Integrated Positioning and Communication for Cooperative Multi-LEO Uplink Communications: A Dual-Timescale Kalman Filter-Aided Approach
Nov 18, 2025Abstract:Low Earth orbit (LEO) satellites are a crucial component of the future non-terrestrial networks (NTN) due to lower latency, robust signal strengths, shorter revisit times, and dense constellations. However, acquiring reliable channel state information (CSI) in LEO satellite communication remains challenging owing to severe signal attenuation over long propagation distances and short coherence times. Despite these challenges, LEO channels benefit from pronounced line-of-sight dominance and geometric properties inherently tied to positioning information. In this work, we propose an integrated positioning and communication (IPAC) framework for multi-LEO satellite networks to address the unique challenges posed by LEO channels. Specifically, we leverage in-the-loop LEO positioning to exploit users' position information for improving uplink CSI acquisition. To overcome the link-budget limitations of single-satellite systems, cooperative multi-LEO uplink data detection is adopted. By exploiting the different coherent timescales of position-related parameters and random channel gains, we develop a dual-timescale Kalman filter-based IPAC framework: an unscented Kalman filter (UKF) for tracking users' position and velocity in the large-timescale, and a Kalman filter that leverages the position information obtained in the large-timescale for improved data-aided uplink channel estimation in the small-timescale. Finally, the two tasks of channel estimation and cooperative data detection are jointly addressed through the expectation maximization (EM) algorithm. Numerical results demonstrate that the proposed IPAC approach outperforms the conventional baseline in terms of channel estimation accuracy and communication performance.
Towards Human-AI-Robot Collaboration and AI-Agent based Digital Twins for Parkinson's Disease Management: Review and Outlook
Nov 08, 2025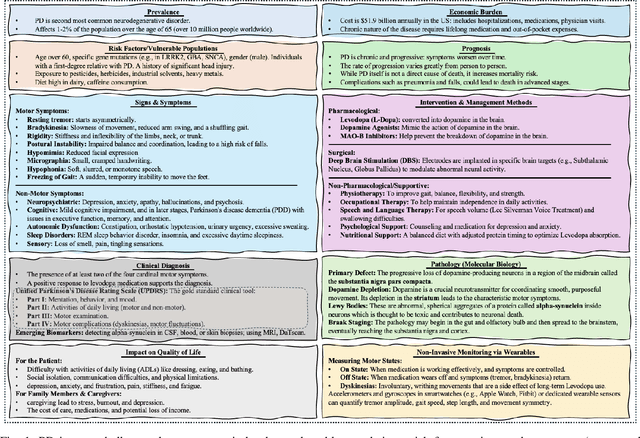
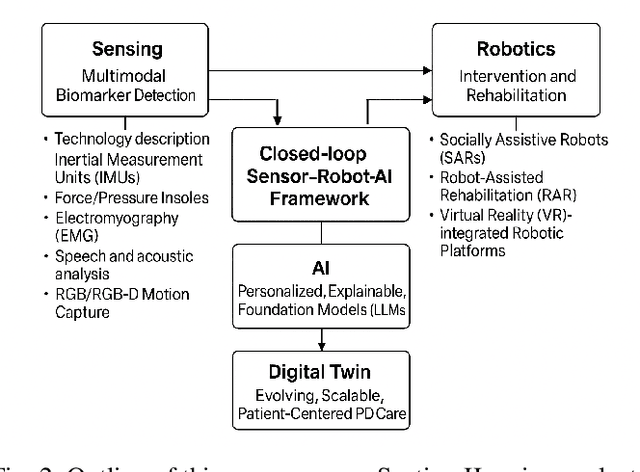
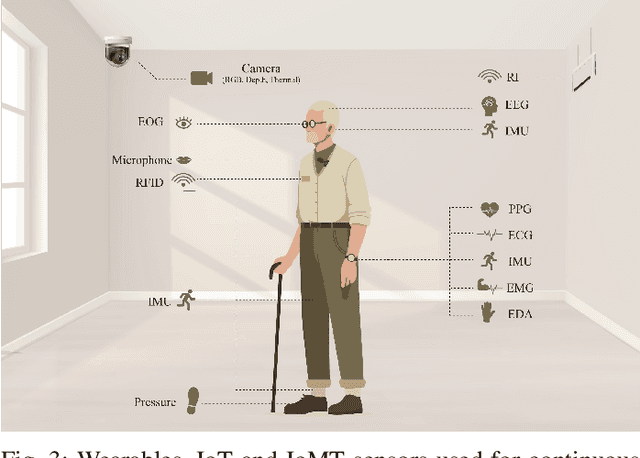
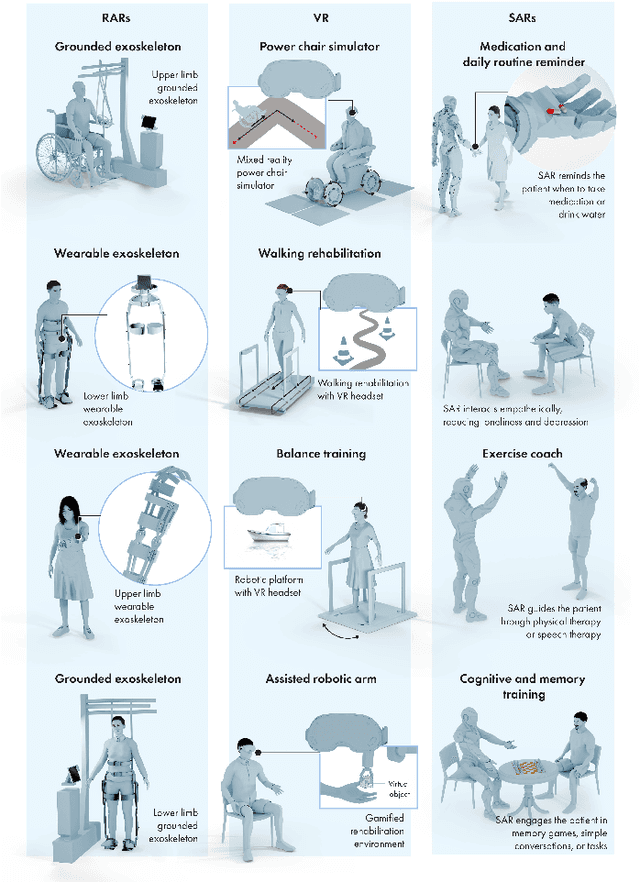
Abstract:The current body of research on Parkinson's disease (PD) screening, monitoring, and management has evolved along two largely independent trajectories. The first research community focuses on multimodal sensing of PD-related biomarkers using noninvasive technologies such as inertial measurement units (IMUs), force/pressure insoles, electromyography (EMG), electroencephalography (EEG), speech and acoustic analysis, and RGB/RGB-D motion capture systems. These studies emphasize data acquisition, feature extraction, and machine learning-based classification for PD screening, diagnosis, and disease progression modeling. In parallel, a second research community has concentrated on robotic intervention and rehabilitation, employing socially assistive robots (SARs), robot-assisted rehabilitation (RAR) systems, and virtual reality (VR)-integrated robotic platforms for improving motor and cognitive function, enhancing social engagement, and supporting caregivers. Despite the complementary goals of these two domains, their methodological and technological integration remains limited, with minimal data-level or decision-level coupling between the two. With the advent of advanced artificial intelligence (AI), including large language models (LLMs), agentic AI systems, a unique opportunity now exists to unify these research streams. We envision a closed-loop sensor-AI-robot framework in which multimodal sensing continuously guides the interaction between the patient, caregiver, humanoid robot (and physician) through AI agents that are powered by a multitude of AI models such as robotic and wearables foundation models, LLM-based reasoning, reinforcement learning, and continual learning. Such closed-loop system enables personalized, explainable, and context-aware intervention, forming the basis for digital twin of the PD patient that can adapt over time to deliver intelligent, patient-centered PD care.
Positioning Using LEO Satellite Communication Signals Under Orbital Errors
Nov 08, 2025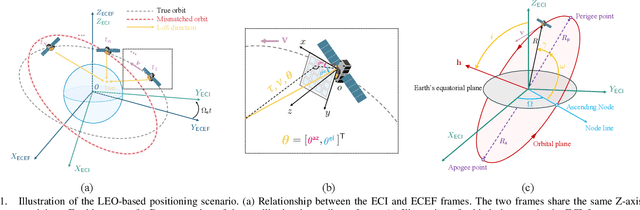
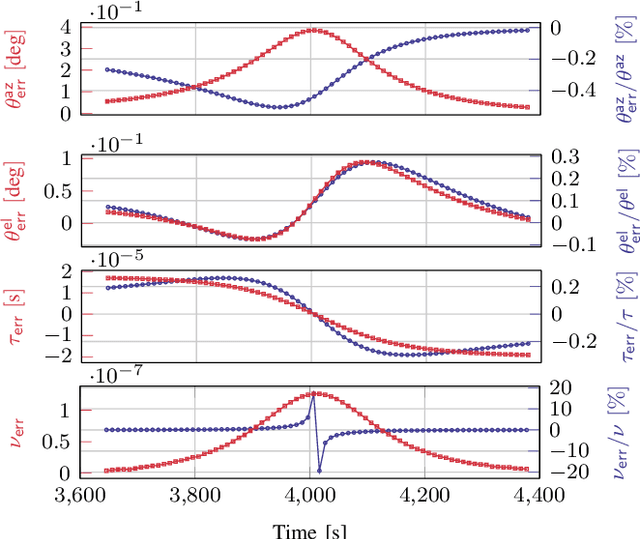
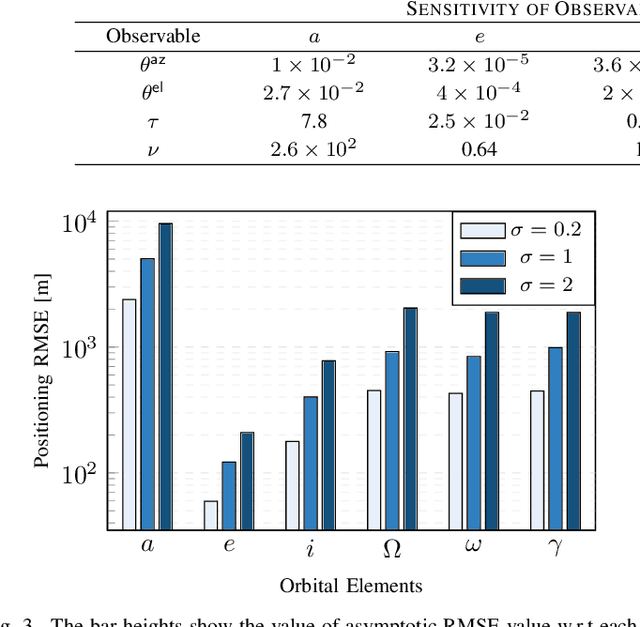
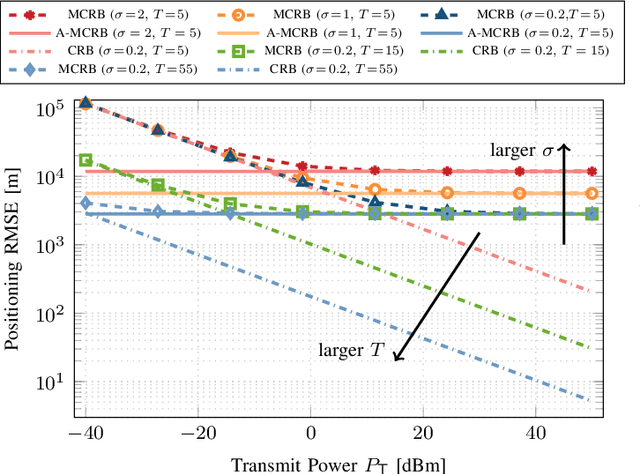
Abstract:Low Earth orbit (LEO) satellites offer a promising alternative to global navigation satellite systems for precise positioning; however, their relatively low altitudes make them more susceptible to orbital perturbations, which in turn degrade positioning accuracy. In this work, we study LEO-based positioning under orbital errors within a signal-of-opportunity framework. First, we introduce a LEO orbit model that accounts for Earth's non-sphericity and derive a wideband communication model that captures fast- and slow-time Doppler effects and multipath propagation. Subsequently, we perform a misspecified Cramér-Rao bound (MCRB) analysis to evaluate the impact of orbital errors on positioning performance. Then, we propose a two-stage positioning method starting with a (i) MCRB-based weighted orbit calibration, followed by (ii) least-squares user positioning using the corrected orbit. The MCRB analysis indicates that orbital errors can induce kilometer-level position biases. Extensive simulations show that the proposed estimator can considerably enhance the positioning accuracy relative to the orbit-mismatched baseline, yielding errors on the order of a few meters.
THz-Band Near-Field RIS Channel Modeling for Linear Channel Estimation
May 14, 2025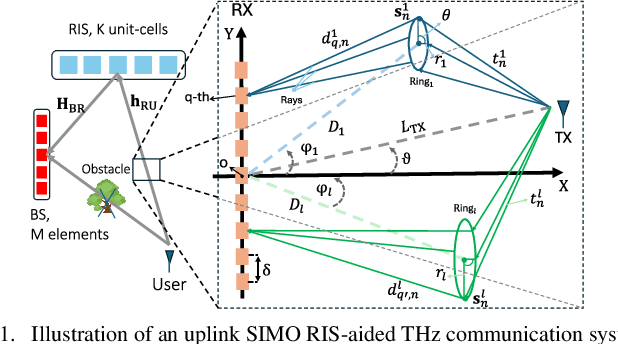
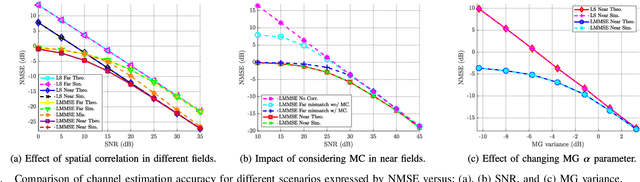
Abstract:Reconfigurable intelligent surface (RIS)-aided terahertz (THz)-band communications are promising enablers for future wireless networks. However, array densification at high frequencies introduces significant challenges in accurate channel modeling and estimation, particularly with THz-specific fading, mutual coupling (MC), spatial correlation, and near-field effects. In this work, we model THz outdoor small-scale fading channels using the mixture gamma (MG) distribution, considering absorption losses, spherical wave propagation, MC, and spatial correlation across large base stations and RISs. We derive the distribution of the cascaded RIS-aided channel and investigate linear channel estimation techniques, analyzing the impact of various channel parameters. Numerical results based on precise THz parameters reveal that accounting for spatial correlation, MC, and near-field modeling substantially enhances estimation accuracy, especially in ultra-massive arrays and short-range scenarios. These results underscore the importance of incorporating these effects for precise, physically consistent channel modeling.
Tri-Hybrid Multi-User Precoding Using Pattern-Reconfigurable Antennas: Fundamental Models and Practical Algorithms
May 13, 2025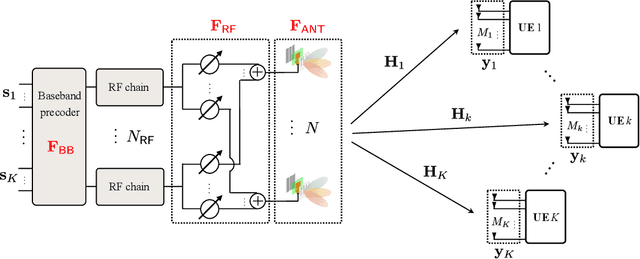


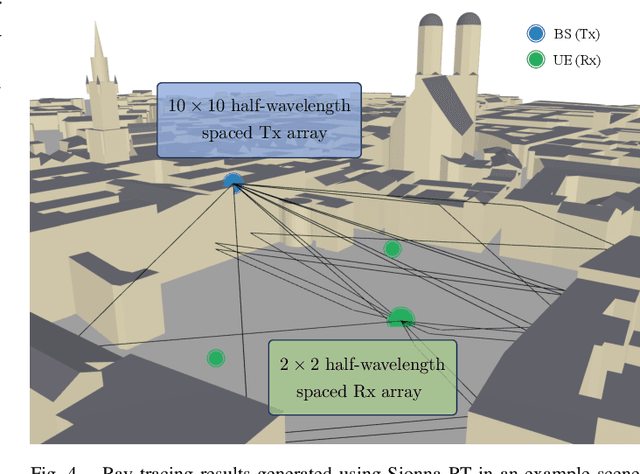
Abstract:The integration of pattern-reconfigurable antennas into hybrid multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) architectures presents a promising path toward high-efficiency and low-cost transceiver solutions. Pattern-reconfigurable antennas can dynamically steer per-antenna radiation patterns, enabling more efficient power utilization and interference suppression. In this work, we study a tri-hybrid MIMO architecture for multi-user communication that integrates digital, analog, and antenna-domain precoding using pattern-reconfigurable antennas. For characterizing the reconfigurability of antenna radiation patterns, we develop two models -- Model~I and Model~II. Model~I captures realistic hardware constraints through limited pattern selection, while Model~II explores the performance upper bound by assuming arbitrary pattern generation. Based on these models, we develop two corresponding tri-hybrid precoding algorithms grounded in the weighted minimum mean square error (WMMSE) framework, which alternately optimize the digital, analog, and antenna precoders under practical per-antenna power constraints. Realistic simulations conducted in ray-tracing generated environments are utilized to evaluate the proposed system and algorithms. The results demonstrate the significant potential of the considered tri-hybrid architecture in enhancing communication performance and hardware efficiency. However, they also reveal that the existing hardware is not yet capable of fully realizing these performance gains, underscoring the need for joint progress in antenna design and communication theory development.
Tri-Hybrid Multi-User Precoding Based on Electromagnetically Reconfigurable Antennas
May 04, 2025Abstract:The tri-hybrid precoding architecture based on electromagnetically reconfigurable antennas (ERAs) is a promising solution for overcoming key limitations in multiple-input multiple-output communication systems. Aiming to further understand its potential, this paper investigates the tri-hybrid multi-user precoding problem using pattern reconfigurable ERAs. To reduce model complexity and improve practicality, we characterize each antenna's radiation pattern using a spherical harmonics decomposition. While mathematically tractable, this approach may lead to over-optimized patterns that are physically unrealizable. To address this, we introduce a projection step that maps the optimized patterns onto a realizable set. Simulation results demonstrate that spherical harmonics-based radiation pattern optimization significantly enhances sum rate performance. However, after projection onto a realizable set obtained from real ERA hardware, the performance gain is notably reduced or even negligible, underscoring the need for more effective projection techniques and improved reconfigurable antenna hardware.
Diversity Analysis for Indoor Terahertz Communication Systems under Small-Scale Fading
Apr 15, 2025Abstract:Harnessing diversity is fundamental to wireless communication systems, particularly in the terahertz (THz) band, where severe path loss and small-scale fading pose significant challenges to system reliability and performance. In this paper, we present a comprehensive diversity analysis for indoor THz communication systems, accounting for the combined effects of path loss and small-scale fading, with the latter modeled as an $\alpha-\mu$ distribution to reflect THz indoor channel conditions. We derive closed-form expressions for the bit error rate (BER) as a function of the reciprocal of the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) and propose an asymptotic expression. Furthermore, we validate these expressions through extensive simulations, which show strong agreement with the theoretical analysis, confirming the accuracy and robustness of the proposed methods. Our results show that the diversity order in THz systems is primarily determined by the combined effects of the number of independent paths, the severity of fading, and the degree of channel frequency selectivity, providing clear insights into how diversity gains can be optimized in high-frequency wireless networks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge