Ying Gao
Cell-Free MIMO with Rotatable Antennas: When Macro-Diversity Meets Antenna Directivity
Jan 23, 2026Abstract:Cell-free networks leverage distributed access points (APs) to achieve macro-diversity, yet their performance is often constrained by large disparities in channel quality arising from user geometry and blockages. To address this, rotatable antennas (RAs) add a lightweight hardware degree of freedom by steering the antenna boresight toward dominant propagation directions to strengthen unfavorable links, thereby enabling the network to better exploit macro-diversity for higher and more uniform performance. This paper investigates an RA-enabled cell-free downlink network and formulates a max-min rate problem that jointly optimizes transmit beamforming and antenna orientations. To tackle this challenging problem, we develop an alternating-optimization-based algorithm that iteratively updates the beamformers via a second-order cone program (SOCP) and optimizes the antenna orientations using successive convex approximation. To reduce complexity, we further propose an efficient two-stage scheme that first designs orientations by maximizing a proportional-fair log-utility using manifold-aware Frank-Wolfe updates, and then computes the beamformers using an SOCP-based design. Simulation results demonstrate that the proposed orientation-aware designs achieve a substantially higher worst-user rate than conventional beamforming-only benchmarks. Furthermore, larger antenna directivity enhances fairness with proper orientation but can degrade the worst-user performance otherwise.
Two-Scale Spatial Deployment for Cost-Effective Wireless Networks via Cooperative IRSs and Movable Antennas
Jan 14, 2026Abstract:This paper proposes a two-scale spatial deployment strategy to ensure reliable coverage for multiple target areas, integrating macroscopic intelligent reflecting surfaces (IRSs) and fine-grained movable antennas (MAs). Specifically, IRSs are selectively deployed from candidate sites to shape the propagation geometry, while MAs are locally repositioned among discretized locations to exploit small-scale channel variations. The objective is to minimize the total deployment cost of MAs and IRSs by jointly optimizing the IRS site selection, MA positions, transmit precoding, and IRS phase shifts, subject to the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) requirements for all target areas. This leads to a challenging mixed-integer non-convex optimization problem that is intractable to solve directly. To address this, we first formulate an auxiliary problem to verify the feasibility. A penalty-based double-loop algorithm integrating alternating optimization and successive convex approximation (SCA) is developed to solve this feasibility issue, which is subsequently adapted to obtain a suboptimal solution for the original cost minimization problem. Finally, based on the obtained solution, we formulate an element refinement problem to further reduce the deployment cost, which is solved by a penalty-based SCA algorithm. Simulation results demonstrate that the proposed designs consistently outperform benchmarks relying on independent area planning or full IRS deployment in terms of cost-efficiency. Moreover, for cost minimization, MA architectures are preferable in large placement apertures, whereas fully populated FPA architectures excel in compact ones; for worst-case SNR maximization, MA architectures exhibit a lower cost threshold for feasibility, while FPA architectures can attain peak SNR at a lower total cost.
Low-Altitude ISAC with Rotatable Active and Passive Arrays
Dec 24, 2025Abstract:This paper investigates a low-altitude integrated sensing and communication (ISAC) system that leverages cooperative rotatable active and passive arrays. We consider a downlink scenario where a base station (BS) with an active rotatable array serves multiple communication users and senses low-altitude targets, assisted by a rotatable reconfigurable intelligent surface (RIS). A rotation-aware geometry-based multipath model is developed to capture the impact of three-dimensional (3D) array orientations on both steering vectors and direction-dependent element gains. On this basis, we formulate a new optimization problem that maximizes the downlink sum rate subject to a transmit power budget, RIS unit-modulus constraints, mechanical rotation limits, and a sensing beampattern mean-squared-error (MSE) constraint. To address the resulting highly non-convex problem, we propose a penalty-based alternating-optimization (AO) framework that alternately updates the BS precoder, RIS phase shifts, and BS/RIS array rotation angles. The three blocks are efficiently handled via a convex optimization method based on quadratic-transform (QT) and majorization-minorization (MM), Riemannian conjugate gradient (RCG) on the unit-modulus manifold, and projected gradient descent (PGD) with Barzilai-Borwein step sizes, respectively. Numerical results in low-altitude geometries demonstrate that the proposed jointly rotatable BS-RIS architecture achieves significant sum-rate gains over fixed or partially rotatable baselines while guaranteeing sensing requirements, especially with directional antennas and in interference-limited regimes.
Reconfigurable Airspace: Synergizing Movable Antenna and Intelligent Surface for Low-Altitude ISAC Networks
Nov 13, 2025Abstract:Low-altitude unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) networks are integral to future 6G integrated sensing and communication (ISAC) systems. However, their deployment is hindered by challenges stemming from high mobility of UAVs, complex propagation environments, and the inherent trade-offs between coexisting sensing and communication functions. This article proposes a novel framework that leverages movable antennas (MAs) and intelligent reflecting surfaces (IRSs) as dual enablers to overcome these limitations. MAs, through active transceiver reconfiguration, and IRSs, via passive channel reconstruction, can work in synergy to significantly enhance system performance. Our analysis first elaborates on the fundamental gains offered by MAs and IRSs, and provides simulation results that validate the immense potential of the MA-IRS-enabled ISAC architecture. Two core UAV deployment scenarios are then investigated: (i) UAVs as ISAC users, where we focus on achieving high-precision tracking and aerial safety, and (ii) UAVs as aerial network nodes, where we address robust design and complex coupled resource optimization. Finally, key technical challenges and research opportunities are identified and analyzed for each scenario, charting a clear course for the future design of advanced low-altitude ISAC networks.
Wireless Sensing with Movable Intelligent Surface
Sep 19, 2025Abstract:Future wireless networks are envisioned to deliver not only gigabit communications but also ubiquitous sensing. Reconfigurable intelligent surfaces (RISs) have emerged to reshape radio propagation, recently showing considerable promise for wireless sensing. Still, their per-element electronic tuning incurs prohibitive hardware cost and power consumption. Motivated by the concept of fluid antenna system (FAS), this paper introduces a low-cost movable intelligent surface (MIS) for wireless sensing, which replaces element-wise electronic phase tuning with panel-wise mechanical reconfiguration. The MIS stacks a large fixed and a smaller movable pre-phased metasurface layers, whose differential position shifts synthesize distinct composite phase patterns, enabling multiple beam patterns for multi-target detection. We characterize a MIS-enabled multi-hop echo signal model with multi-target interference and then formulate a worst-case sensing signal-to-interference-plus-noise ratio (SINR) maximization problem that jointly designs MIS phase shifts and schedules MS2's position. A Riemannian Augmented Lagrangian Method (RALM)-based algorithm is developed to solve the formulated mixed-integer non-convex problem. We also derive a heuristic MIS beam steering design with closed-form phase distribution and position scheduling. Simulations validate MIS's beam pattern reconfiguration capability, show that the RALM-based scheme significantly outperforms the closed-form scheme in improving sensing SINR, and uncover a gain-diversity trade-off in beam patterns that informs the optimal choice of MIS configuration.
Integrating Movable Antennas and Intelligent Reflecting Surfaces (MA-IRS): Fundamentals, Practical Solutions, and Opportunities
Jun 17, 2025



Abstract:Movable antennas (MAs) and intelligent reflecting surfaces (IRSs) enable active antenna repositioning and passive phase-shift tuning for channel reconfiguration, respectively. Integrating MAs and IRSs boosts spatial degrees of freedom, significantly enhancing wireless network capacity, coverage, and reliability. In this article, we first present the fundamentals of MA-IRS integration, involving clarifying the key design issues, revealing performance gain, and identifying the conditions where MA-IRS synergy persists. Then, we examine practical challenges and propose pragmatic design solutions, including optimization schemes, hardware architectures, deployment strategies, and robust designs for hardware impairments and mobility management. In addition, we highlight how MA-IRS architectures uniquely support advanced integrated sensing and communication, enhancing sensing performance and dual-functional flexibility. Overall, MA-IRS integration emerges as a compelling approach toward next-generation reconfigurable wireless systems.
Teochew-Wild: The First In-the-wild Teochew Dataset with Orthographic Annotations
May 08, 2025



Abstract:This paper reports the construction of the Teochew-Wild, a speech corpus of the Teochew dialect. The corpus includes 18.9 hours of in-the-wild Teochew speech data from multiple speakers, covering both formal and colloquial expressions, with precise orthographic and pinyin annotations. Additionally, we provide supplementary text processing tools and resources to propel research and applications in speech tasks for this low-resource language, such as automatic speech recognition (ASR) and text-to-speech (TTS). To the best of our knowledge, this is the first publicly available Teochew dataset with accurate orthographic annotations. We conduct experiments on the corpus, and the results validate its effectiveness in ASR and TTS tasks.
Throughput Maximization for Movable Antenna Systems with Movement Delay Consideration
Nov 21, 2024



Abstract:In this paper, we model the minimum achievable throughput within a transmission block of restricted duration and aim to maximize it in movable antenna (MA)-enabled multiuser downlink communications. Particularly, we account for the antenna moving delay caused by mechanical movement, which has not been fully considered in previous studies, and reveal the trade-off between the delay and signal-to-interference-plus-noise ratio at users. To this end, we first consider a single-user setup to analyze the necessity of antenna movement. By quantizing the virtual angles of arrival, we derive the requisite region size for antenna moving, design the initial MA position, and elucidate the relationship between quantization resolution and moving region size. Furthermore, an efficient algorithm is developed to optimize MA position via successive convex approximation, which is subsequently extended to the general multiuser setup. Numerical results demonstrate that the proposed algorithms outperform fixed-position antenna schemes and existing ones without consideration of movement delay. Additionally, our algorithms exhibit excellent adaptability and stability across various transmission block durations and moving region sizes, and are robust to different antenna moving speeds. This allows the hardware cost of MA-aided systems to be reduced by employing low rotational speed motors.
Movable Antennas Enabled Wireless-Powered NOMA: Continuous and Discrete Positioning Designs
Sep 30, 2024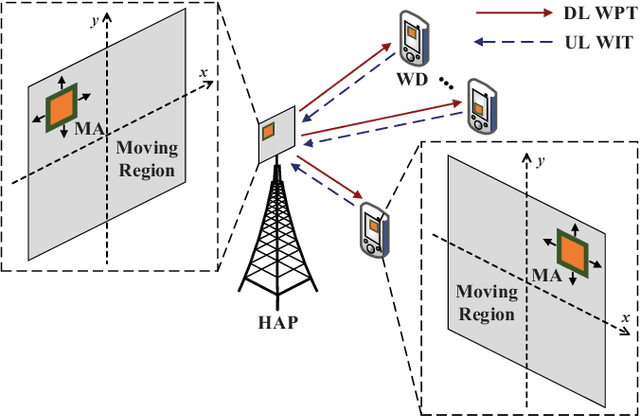
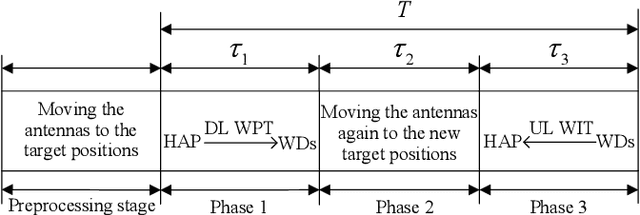
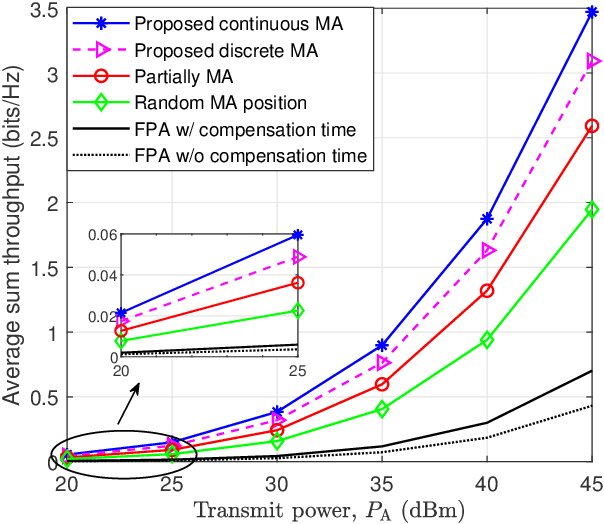
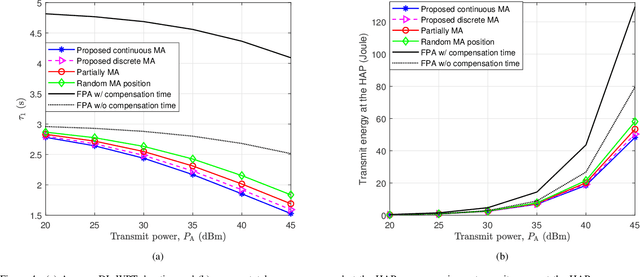
Abstract:This paper investigates a movable antenna (MA)-enabled wireless-powered communication network (WPCN), where multiple wireless devices (WDs) first harvest energy from the downlink (DL) signal broadcast by a hybrid access point (HAP) and then transmit information in the uplink (UL) using non-orthogonal multiple access. Unlike conventional WPCNs with fixed-position antennas (FPAs), this MA-enabled WPCN allows the MAs at the HAP and the WDs to adjust their positions twice: once before DL wireless power transfer and once before DL wireless information transmission. Our goal is to maximize the system sum throughput by jointly optimizing the MA positions, the time allocation, and the UL power allocation. Considering the characteristics of antenna movement, we explore both continuous and discrete positioning designs, which, after formulation, are found to be non-convex optimization problems. Before tackling these problems, we rigorously prove that using identical MA positions for both DL and UL is the optimal strategy in both scenarios, thereby greatly simplifying the problems and enabling easier practical implementation of the system. We then propose alternating optimization-based algorithms for the resulting simplified problems. Simulation results show that: 1) the proposed continuous MA scheme can enhance the sum throughput by up to 395.71% compared to the benchmark with FPAs, even when additional compensation transmission time is provided to the latter; 2) a step size of one-quarter wavelength for the MA motion driver is generally sufficient for the proposed discrete MA scheme to achieve over 80% of the sum throughput performance of the continuous MA scheme; 3) when each moving region is large enough to include multiple optimal positions for the continuous MA scheme, the discrete MA scheme can achieve comparable sum throughput without requiring an excessively small step size.
Human-like object concept representations emerge naturally in multimodal large language models
Jul 01, 2024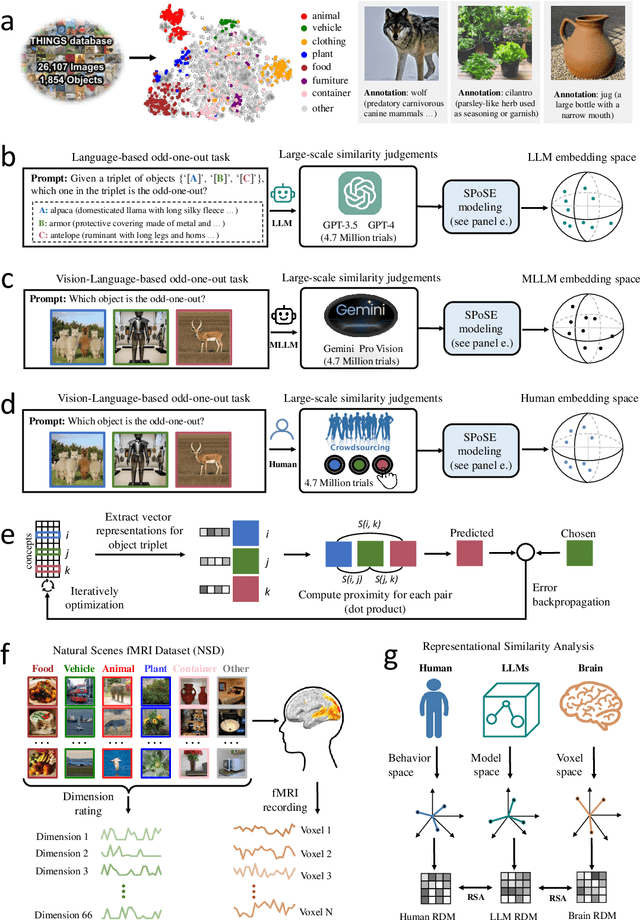
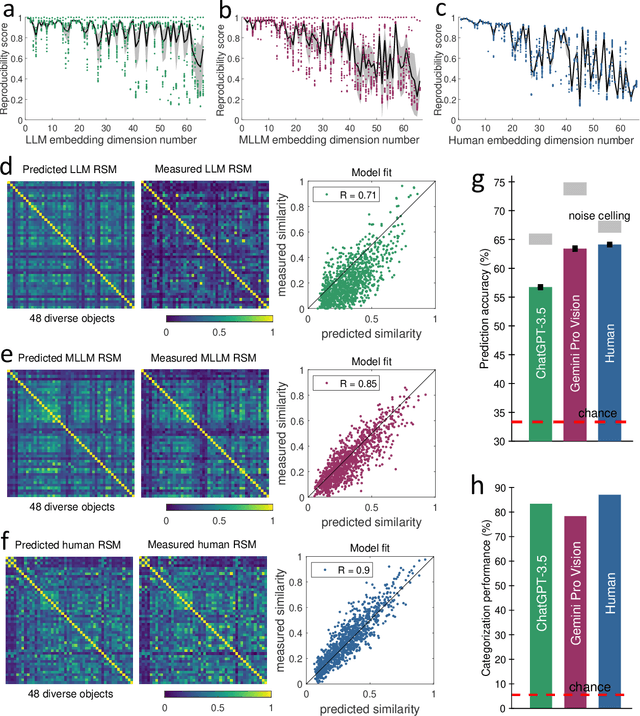

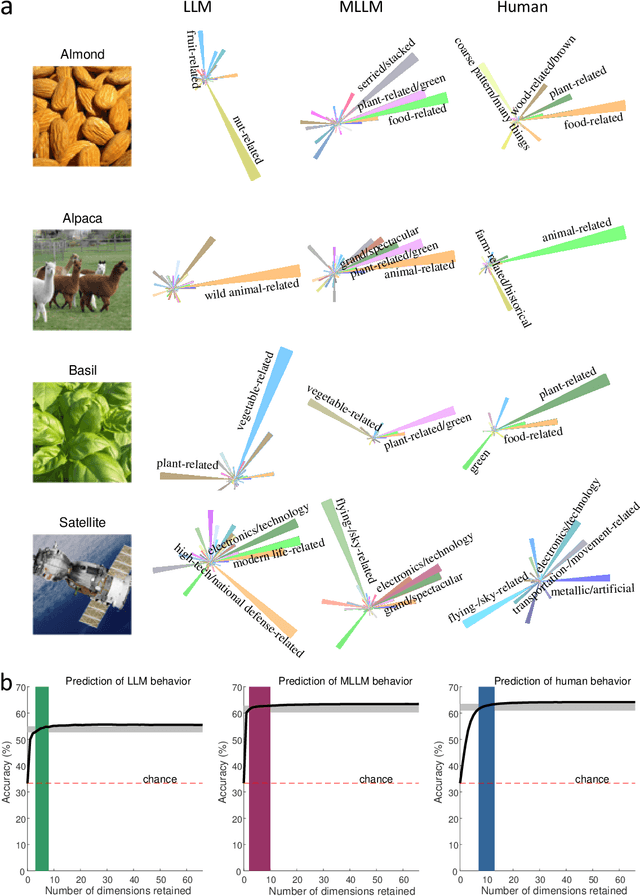
Abstract:The conceptualization and categorization of natural objects in the human mind have long intrigued cognitive scientists and neuroscientists, offering crucial insights into human perception and cognition. Recently, the rapid development of Large Language Models (LLMs) has raised the attractive question of whether these models can also develop human-like object representations through exposure to vast amounts of linguistic and multimodal data. In this study, we combined behavioral and neuroimaging analysis methods to uncover how the object concept representations in LLMs correlate with those of humans. By collecting large-scale datasets of 4.7 million triplet judgments from LLM and Multimodal LLM (MLLM), we were able to derive low-dimensional embeddings that capture the underlying similarity structure of 1,854 natural objects. The resulting 66-dimensional embeddings were found to be highly stable and predictive, and exhibited semantic clustering akin to human mental representations. Interestingly, the interpretability of the dimensions underlying these embeddings suggests that LLM and MLLM have developed human-like conceptual representations of natural objects. Further analysis demonstrated strong alignment between the identified model embeddings and neural activity patterns in many functionally defined brain ROIs (e.g., EBA, PPA, RSC and FFA). This provides compelling evidence that the object representations in LLMs, while not identical to those in the human, share fundamental commonalities that reflect key schemas of human conceptual knowledge. This study advances our understanding of machine intelligence and informs the development of more human-like artificial cognitive systems.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge