Guojie Hu
Movable Antenna Array Aided Ultra Reliable Covert Communications
Dec 29, 2024



Abstract:In this paper, we construct a framework of the movable antenna (MA) aided covert communication shielded by the general noise uncertainty for the first time. According to the analysis performance on the derived closed-form expressions of the sum of the probabilities of the detection errors and the communication outage probability, the perfect covertness and the ultra reliability can be achieved by adjusting the antenna position in the MA array. Then, we formulate the communication covertness maximization problem with the constraints of the ultra reliability and the independent discrete movable position to optimize the transmitter's parameter. With the maximal ratio transmitting (MRT) design for the beamforming, we solve the closed-form optimal information transmit power and design a lightweight discrete projected gradient descent (DPGD) algorithm to determine the optimal antenna position. The numerical results show that the optimal achievable covertness and the feasible region of the steering angle with the MA array is significant larger than the one with the fixed-position antenna (FPA) array.
Throughput Maximization for Movable Antenna Systems with Movement Delay Consideration
Nov 21, 2024



Abstract:In this paper, we model the minimum achievable throughput within a transmission block of restricted duration and aim to maximize it in movable antenna (MA)-enabled multiuser downlink communications. Particularly, we account for the antenna moving delay caused by mechanical movement, which has not been fully considered in previous studies, and reveal the trade-off between the delay and signal-to-interference-plus-noise ratio at users. To this end, we first consider a single-user setup to analyze the necessity of antenna movement. By quantizing the virtual angles of arrival, we derive the requisite region size for antenna moving, design the initial MA position, and elucidate the relationship between quantization resolution and moving region size. Furthermore, an efficient algorithm is developed to optimize MA position via successive convex approximation, which is subsequently extended to the general multiuser setup. Numerical results demonstrate that the proposed algorithms outperform fixed-position antenna schemes and existing ones without consideration of movement delay. Additionally, our algorithms exhibit excellent adaptability and stability across various transmission block durations and moving region sizes, and are robust to different antenna moving speeds. This allows the hardware cost of MA-aided systems to be reduced by employing low rotational speed motors.
Two-Timescale Design for Movable Antennas Enabled-Multiuser MIMO Systems
Oct 08, 2024Abstract:Movable antennas (MAs), which can be swiftly repositioned within a defined region, offer a promising solution to the limitations of fixed-position antennas (FPAs) in adapting to spatial variations in wireless channels, thereby improving channel conditions and communication between transceivers. However, frequent MA position adjustments based on instantaneous channel state information (CSI) incur high operational complexity, making real-time CSI acquisition impractical, especially in fast-fading channels. To address these challenges, we propose a two-timescale transmission framework for MA-enabled multiuser multiple-input-multiple-output (MU-MIMO) systems. In the large timescale, statistical CSI is exploited to optimize MA positions for long-term ergodic performance, whereas, in the small timescale, beamforming vectors are designed using instantaneous CSI to handle short-term channel fluctuations. Within this new framework, we analyze the ergodic sum rate and develop efficient MA position optimization algorithms for both maximum-ratio-transmission (MRT) and zero-forcing (ZF) beamforming schemes. These algorithms employ alternating optimization (AO), successive convex approximation (SCA), and majorization-minimization (MM) techniques, iteratively optimizing antenna positions and refining surrogate functions that approximate the ergodic sum rate. Numerical results show significant ergodic sum rate gains with the proposed two-timescale MA design over conventional FPA systems, particularly under moderate to strong line-of-sight (LoS) conditions. Notably, MA with ZF beamforming consistently outperforms MA with MRT, highlighting the synergy between beamforming and MAs for superior interference management in environments with moderate Rician factors and high user density, while MA with MRT can offer a simplified alternative to complex beamforming designs in strong LoS conditions.
Two-Timescale Design for Movable Antenna Array-Enabled Multiuser Uplink Communications
Jul 25, 2024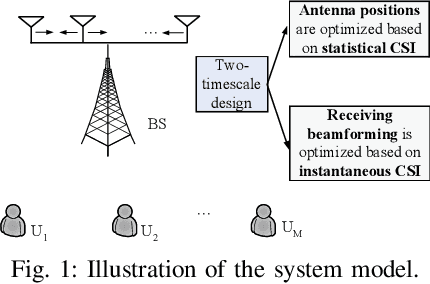
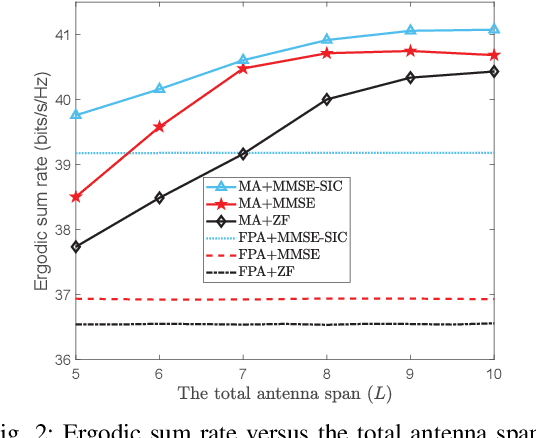
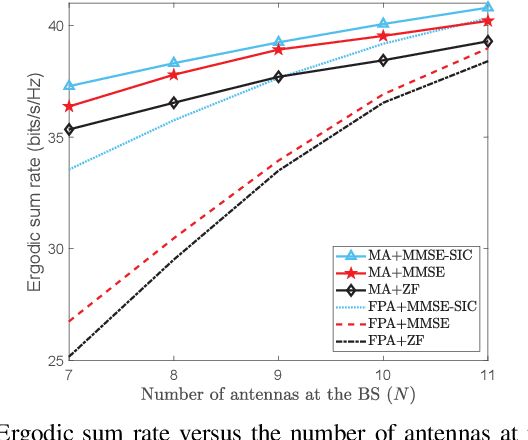
Abstract:Movable antenna (MA) technology can flexibly reconfigure wireless channels by adjusting antenna positions in a local region, thus owing great potential for enhancing communication performance. This letter investigates MA technology enabled multiuser uplink communications over general Rician fading channels, which consist of a base station (BS) equipped with the MA array and multiple single-antenna users. Since it is practically challenging to collect all instantaneous channel state information (CSI) by traversing all possible antenna positions at the BS, we instead propose a two-timescale scheme for maximizing the ergodic sum rate. Specifically, antenna positions at the BS are first optimized using only the statistical CSI. Subsequently, the receiving beamforming at the BS (for which we consider the three typical zero-forcing (ZF), minimum mean-square error (MMSE) and MMSE with successive interference cancellation (MMSE-SIC) receivers) is designed based on the instantaneous CSI with optimized antenna positions, thus significantly reducing practical implementation complexities. The formulated problems are highly non-convex and we develop projected gradient ascent (PGA) algorithms to effectively handle them. Simulation results illustrate that compared to conventional fixed-position antenna (FPA) array, the MA array can achieve significant performance gains by reaping an additional spatial degree of freedom.
Movable-Antenna Array Enabled Multiuser Uplink: A Low-Complexity Gradient Descent for Total Transmit Power Minimization
Dec 10, 2023



Abstract:We investigate multiuser uplink communication from multiple single-antenna users to a base station (BS), which is equipped with a movable-antenna (MA) array and adopts zero-forcing receivers to decode multiple signals. We aim to optimize the MAs' positions at the BS, to minimize the total transmit power of all users subject to the minimum rate requirement. After applying transformations, we show that the problem is equivalent to minimizing the sum of each eigenvalue's reciprocal of a matrix, which is a function of all MAs' positions. Subsequently, the projected gradient descent (PGD) method is utilized to find a locally optimal solution. In particular, different from the latest related work, we exploit the eigenvalue decomposition to successfully derive a closed-form gradient for the PGD, which facilitates the practical implementation greatly. We demonstrate by simulations that via careful optimization for all MAs' positions in our proposed design, the total transmit power of all users can be decreased significantly as compared to competitive benchmarks.
Movable-Antenna Array-Enabled Wireless Communication with CoMP Reception
Nov 20, 2023

Abstract:We consider the movable antenna (MA) array-enabled wireless communication with coordinate multi-point (CoMP) reception, where multiple destinations adopt the maximal ratio combination technique to jointly decode the common message sent from the transmitter equipped with the MA array. Our goal is to maximize the effective received signal-to-noise ratio, by jointly optimizing the transmit beamforming and the positions of the MA array. Although the formulated problem is highly non-convex, we reveal that it is fundamental to maximize the principal eigenvalue of a hermite channel matrix which is a function of the positions of the MA array. The corresponding sub-problem is still non-convex, for which we develop a computationally efficient algorithm. Afterwards, the optimal transmit beamforming is determined with a closed-form solution. In addition, the theoretical performance upper bound is analyzed. Since the MA array brings an additional spatial degree of freedom by flexibly adjusting all antennas' positions, it achieves significant performance gain compared to competitive benchmarks.
Secure Wireless Communication via Movable-Antenna Array
Nov 13, 2023



Abstract:Movable antenna (MA) array is a novel technology recently developed where positions of transmit/receive antennas can be flexibly adjusted in the specified region to reconfigure the wireless channel and achieve a higher capacity. In this letter, we, for the first time, investigate the MA array-assisted physical-layer security where the confidential information is transmitted from a MA array-enabled Alice to a single-antenna Bob, in the presence of multiple single-antenna and colluding eavesdroppers. We aim to maximize the achievable secrecy rate by jointly designing the transmit beamforming and positions of all antennas at Alice subject to the transmit power budget and specified regions for positions of all transmit antennas. The resulting problem is highly non-convex, for which the projected gradient ascent (PGA) and the alternating optimization methods are utilized to obtain a high-quality suboptimal solution. Simulation results demonstrate that since the additional spatial degree of freedom (DoF) can be fully exploited, the MA array significantly enhances the secrecy rate compared to the conventional fixed-position antenna (FPA) array.
Intelligent Reflecting Surface-Aided Wireless Communication with Movable Elements
Nov 04, 2023



Abstract:Intelligent reflecting surface (IRS) has been recognized as a powerful technology for boosting communication performance. To reduce manufacturing and control costs, it is preferable to consider discrete phase shifts (DPSs) for IRS, which are set by default as uniformly distributed in the range of $[ - \pi,\pi )$ in the literature. Such setting, however, cannot achieve a desirable performance over the general Rician fading where the channel phase concentrates in a narrow range with a higher probability. Motivated by this drawback, we in this paper design optimal non-uniform DPSs for IRS to achieve a desirable performance level. The fundamental challenge is the \textit{possible offset in phase distribution across different cascaded source-element-destination channels}, if adopting conventional IRS where the position of each element is fixed. Such phenomenon leads to different patterns of optimal non-uniform DPSs for each IRS element and thus causes huge manufacturing costs especially when the number of IRS elements is large. Driven by the recently emerging fluid antenna system (or movable antenna technology), we demonstrate that if the position of each IRS element can be flexibly adjusted, the above phase distribution offset can be surprisingly eliminated, leading to the same pattern of DPSs for each IRS element. Armed with this, we then determine the form of unified non-uniform DPSs based on a low-complexity iterative algorithm. Simulations show that our proposed design significantly improves the system performance compared to competitive benchmarks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge