Xiaohu You
Sherman
Experimental Performance of Bidirectional Phase Coherent Transmission and Sensing for mmWave Cell-free Massive MIMO Systems with Reciprocity Calibration
Jan 21, 2026Abstract:Phase synchronization among distributed transmission reception points (TRPs) is a prerequisite for enabling coherent joint transmission and high-precision sensing in millimeter wave (mmWave) cell-free massive multiple-input and multiple-output (MIMO) systems. This paper proposes a bidirectional calibration scheme and a calibration coefficient estimation method for phase synchronization, and presents a calibration coefficient phase tracking method using unilateral uplink/downlink channel state information (CSI). Furthermore, this paper introduces the use of reciprocity calibration to eliminate non-ideal factors in sensing and leverages sensing results to achieve calibration coefficient phase tracking in dynamic scenarios, thus enabling bidirectional empowerment of both communication and sensing. Simulation results demonstrate that the proposed method can effectively implement reciprocal calibration with lower overhead, enabling coherent collaborative transmission, and resolving non-ideal factors to acquire lower sensing error in sensing applications. Experimental results show that, in the mmWave band, over-the-air (OTA) bidirectional calibration enables coherent collaborative transmission for both collaborative TRPs and collaborative user equipments (UEs), achieving beamforming gain and long-time coherent sensing capabilities.
Two-Stage Signal Reconstruction for Amplitude-Phase-Time Block Modulation-based Communications
Dec 20, 2025Abstract:Operating power amplifiers (PAs) at lower input back-off (IBO) levels is an effective way to improve PA efficiency, but often introduces severe nonlinear distortion that degrades transmission performance. Amplitude-phase-time block modulation (APTBM) has recently emerged as an effective solution to this problem. By leveraging the intrinsic amplitude and phase constraints of each APTBM block, PA-induced nonlinear distortion can be mitigated through constraint-guided signal reconstruction. However, existing reconstruction methods apply these constraints only heuristically and statistically, limiting the achievable IBO reduction and PA efficiency improvement. This paper addresses this limitation by decomposing the nonlinear distortion into dominant and residual components, and accordingly develops a novel two-stage signal reconstruction algorithm consisting of coarse and fine reconstruction stages. The coarse reconstruction stage eliminates the dominant distortion by jointly exploiting the APTBM block structure and PA nonlinear characteristics. The fine reconstruction stage minimizes the residual distortion by formulating a nonconvex optimization problem that explicitly enforces the APTBM constraints. To handle this problem efficiently, a low-complexity iterative variable substitution method is introduced, which relaxes the problem into a sequence of trust-region subproblems, each solvable in closed form. The proposed algorithm is validated through comprehensive numerical simulations and testbed experiments. Results show that it achieves up to 4 dB IBO reduction in simulations and up to 2 dB IBO reduction in experiments while maintaining transmission performance, corresponding to PA efficiency improvements of 59.1\% and 33.9\%, respectively, over existing methods.
A Theoretical Analysis of State Similarity Between Markov Decision Processes
Dec 19, 2025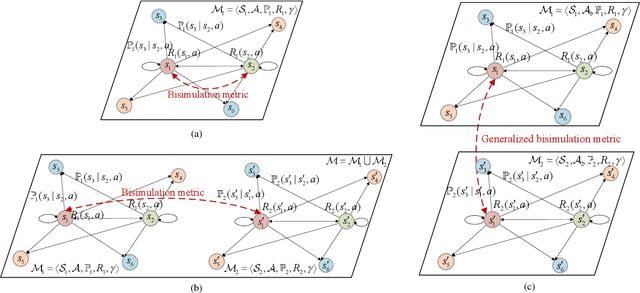
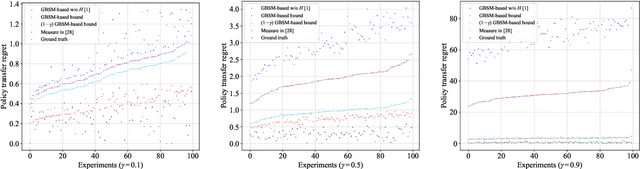
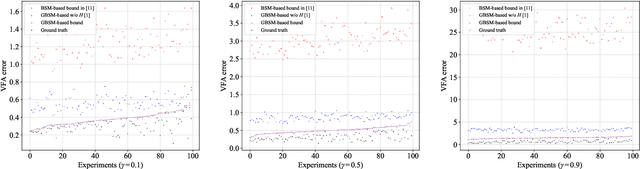
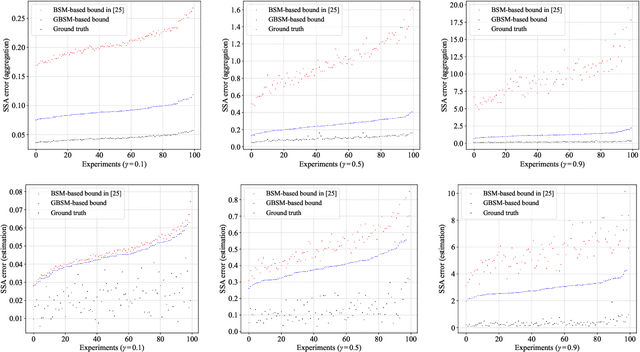
Abstract:The bisimulation metric (BSM) is a powerful tool for analyzing state similarities within a Markov decision process (MDP), revealing that states closer in BSM have more similar optimal value functions. While BSM has been successfully utilized in reinforcement learning (RL) for tasks like state representation learning and policy exploration, its application to state similarity between multiple MDPs remains challenging. Prior work has attempted to extend BSM to pairs of MDPs, but a lack of well-established mathematical properties has limited further theoretical analysis between MDPs. In this work, we formally establish a generalized bisimulation metric (GBSM) for measuring state similarity between arbitrary pairs of MDPs, which is rigorously proven with three fundamental metric properties, i.e., GBSM symmetry, inter-MDP triangle inequality, and a distance bound on identical spaces. Leveraging these properties, we theoretically analyze policy transfer, state aggregation, and sampling-based estimation across MDPs, obtaining explicit bounds that are strictly tighter than existing ones derived from the standard BSM. Additionally, GBSM provides a closed-form sample complexity for estimation, improving upon existing asymptotic results based on BSM. Numerical results validate our theoretical findings and demonstrate the effectiveness of GBSM in multi-MDP scenarios.
Generalized Pinching-Antenna Systems: A Tutorial on Principles, Design Strategies, and Future Directions
Oct 15, 2025Abstract:Pinching-antenna systems have emerged as a novel and transformative flexible-antenna architecture for next-generation wireless networks. They offer unprecedented flexibility and spatial reconfigurability by enabling dynamic positioning and activation of radiating elements along a signal-guiding medium (e.g., dielectric waveguides), which is not possible with conventional fixed antenna systems. In this paper, we introduce the concept of generalized pinching antenna systems, which retain the core principle of creating localized radiation points on demand, but can be physically realized in a variety of settings. These include implementations based on dielectric waveguides, leaky coaxial cables, surface-wave guiding structures, and other types of media, employing different feeding methods and activation mechanisms (e.g., mechanical, electronic, or hybrid). Despite differences in their physical realizations, they all share the same inherent ability to form, reposition, or deactivate radiation sites as needed, enabling user-centric and dynamic coverage. We first describe the underlying physical mechanisms of representative generalized pinching-antenna realizations and their associated wireless channel models, highlighting their unique propagation and reconfigurability characteristics compared with conventional antennas. Then, we review several representative pinching-antenna system architectures, ranging from single- to multiple-waveguide configurations, and discuss advanced design strategies tailored to these flexible deployments. Furthermore, we examine their integration with emerging wireless technologies to enable synergistic, user-centric solutions. Finally, we identify key open research challenges and outline future directions, charting a pathway toward the practical deployment of generalized pinching antennas in next-generation wireless networks.
A Tutorial on MIMO-OFDM ISAC: From Far-Field to Near-Field
Apr 27, 2025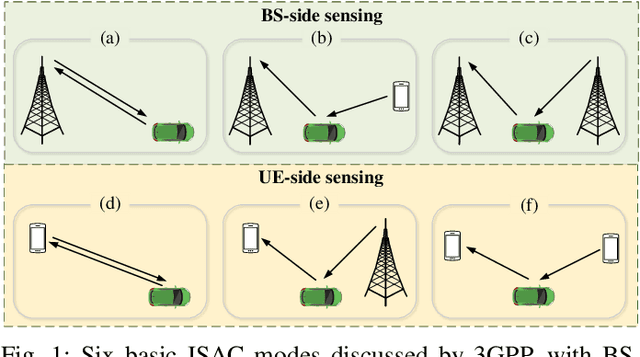
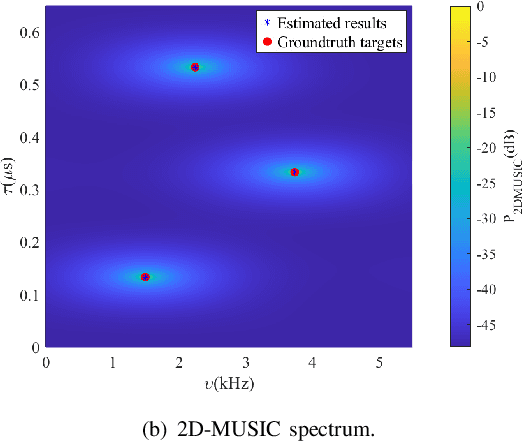
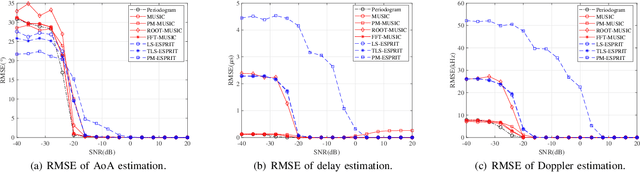
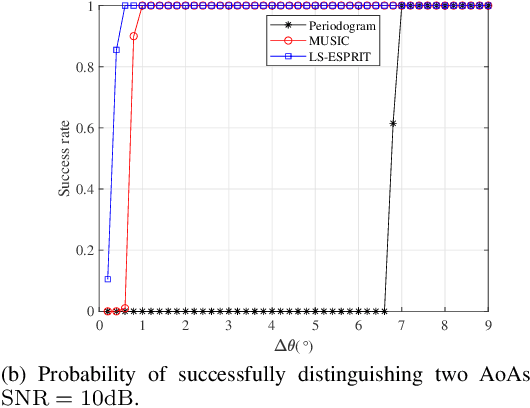
Abstract:Integrated sensing and communication (ISAC) is one of the key usage scenarios for future sixth-generation (6G) mobile communication networks, where communication and sensing (C&S) services are simultaneously provided through shared wireless spectrum, signal processing modules, hardware, and network infrastructure. Such an integration is strengthened by the technology trends in 6G, such as denser network nodes, larger antenna arrays, wider bandwidths, higher frequency bands, and more efficient utilization of spectrum and hardware resources, which incentivize and empower enhanced sensing capabilities. As the dominant waveform used in contemporary communication systems, orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) is still expected to be a very competitive technology for 6G, rendering it necessary to thoroughly investigate the potential and challenges of OFDM ISAC. Thus, this paper aims to provide a comprehensive tutorial overview of ISAC systems enabled by large-scale multi-input multi-output (MIMO) and OFDM technologies and to discuss their fundamental principles, advantages, and enabling signal processing methods. To this end, a unified MIMO-OFDM ISAC system model is first introduced, followed by four frameworks for estimating parameters across the spatial, delay, and Doppler domains, including parallel one-domain, sequential one-domain, joint two-domain, and joint three-domain parameter estimation. Next, sensing algorithms and performance analyses are presented in detail for far-field scenarios where uniform plane wave (UPW) propagation is valid, followed by their extensions to near-field scenarios where uniform spherical wave (USW) characteristics need to be considered. Finally, this paper points out open challenges and outlines promising avenues for future research on MIMO-OFDM ISAC.
Provable Performance Bounds for Digital Twin-driven Deep Reinforcement Learning in Wireless Networks: A Novel Digital-Twin Bisimulation Metric
Feb 25, 2025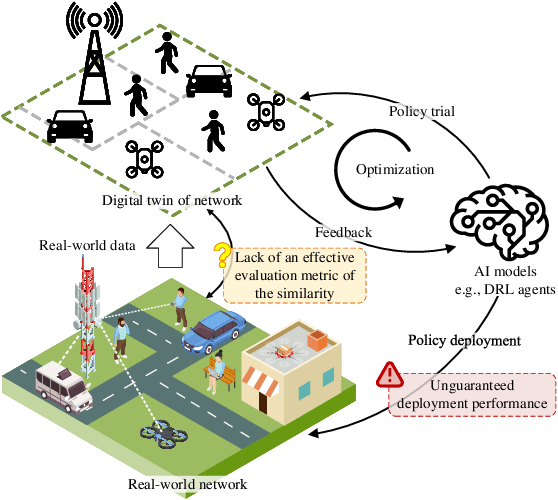
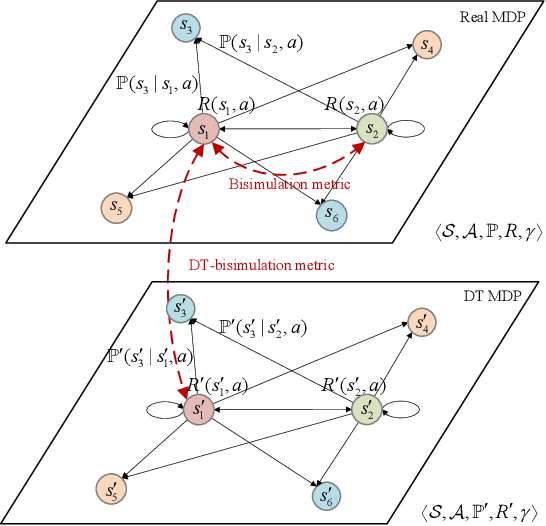
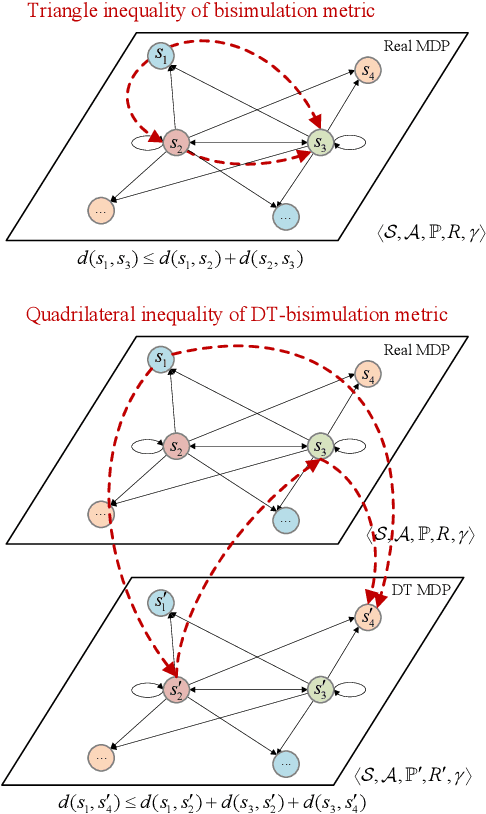
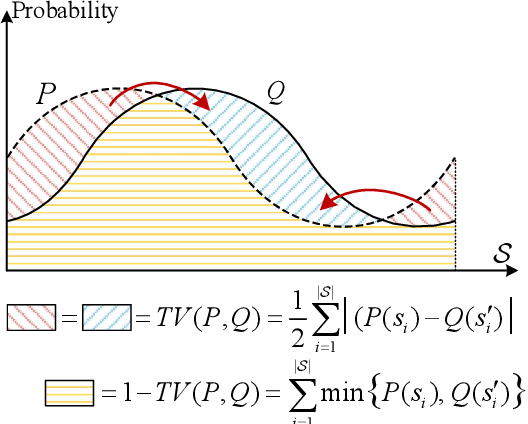
Abstract:Digital twin (DT)-driven deep reinforcement learning (DRL) has emerged as a promising paradigm for wireless network optimization, offering safe and efficient training environment for policy exploration. However, in theory existing methods cannot always guarantee real-world performance of DT-trained policies before actual deployment, due to the absence of a universal metric for assessing DT's ability to support reliable DRL training transferrable to physical networks. In this paper, we propose the DT bisimulation metric (DT-BSM), a novel metric based on the Wasserstein distance, to quantify the discrepancy between Markov decision processes (MDPs) in both the DT and the corresponding real-world wireless network environment. We prove that for any DT-trained policy, the sub-optimality of its performance (regret) in the real-world deployment is bounded by a weighted sum of the DT-BSM and its sub-optimality within the MDP in the DT. Then, a modified DT-BSM based on the total variation distance is also introduced to avoid the prohibitive calculation complexity of Wasserstein distance for large-scale wireless network scenarios. Further, to tackle the challenge of obtaining accurate transition probabilities of the MDP in real world for the DT-BSM calculation, we propose an empirical DT-BSM method based on statistical sampling. We prove that the empirical DT-BSM always converges to the desired theoretical one, and quantitatively establish the relationship between the required sample size and the target level of approximation accuracy. Numerical experiments validate this first theoretical finding on the provable and calculable performance bounds for DT-driven DRL.
Combating Interference for Over-the-Air Federated Learning: A Statistical Approach via RIS
Jan 27, 2025Abstract:Over-the-air computation (AirComp) integrates analog communication with task-oriented computation, serving as a key enabling technique for communication-efficient federated learning (FL) over wireless networks. However, owing to its analog characteristics, AirComp-enabled FL (AirFL) is vulnerable to both unintentional and intentional interference. In this paper, we aim to attain robustness in AirComp aggregation against interference via reconfigurable intelligent surface (RIS) technology to artificially reconstruct wireless environments. Concretely, we establish performance objectives tailored for interference suppression in wireless FL systems, aiming to achieve unbiased gradient estimation and reduce its mean square error (MSE). Oriented at these objectives, we introduce the concept of phase-manipulated favorable propagation and channel hardening for AirFL, which relies on the adjustment of RIS phase shifts to realize statistical interference elimination and reduce the error variance of gradient estimation. Building upon this concept, we propose two robust aggregation schemes of power control and RIS phase shifts design, both ensuring unbiased gradient estimation in the presence of interference. Theoretical analysis of the MSE and FL convergence affirms the anti-interference capability of the proposed schemes. It is observed that computation and interference errors diminish by an order of $\mathcal{O}\left(\frac{1}{N}\right)$ where $N$ is the number of RIS elements, and the ideal convergence rate without interference can be asymptotically achieved by increasing $N$. Numerical results confirm the analytical results and validate the superior performance of the proposed schemes over existing baselines.
Cooperative ISAC-empowered Low-Altitude Economy
Dec 29, 2024Abstract:This paper proposes a cooperative integrated sensing and communication (ISAC) scheme for the low-altitude sensing scenario, aiming at estimating the parameters of the unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) and enhancing the sensing performance via cooperation. The proposed scheme consists of two stages. In Stage I, we formulate the monostatic parameter estimation problem via using a tensor decomposition model. By leveraging the Vandermonde structure of the factor matrix, a spatial smoothing tensor decomposition scheme is introduced to estimate the UAVs' parameters. To further reduce the computational complexity, we design a reduced-dimensional (RD) angle of arrival (AoA) estimation algorithm based on generalized Rayleigh quotient (GRQ). In Stage II, the positions and true velocities of the UAVs are determined through the data fusion across multiple base stations (BSs). Specifically, we first develop a false removing minimum spanning tree (MST)-based data association method to accurately match the BSs' parameter estimations to the same UAV. Then, a Pareto optimality method and a residual weighting scheme are developed to facilitate the position and velocity estimation, respectively. We further extend our approach to the dual-polarized system. Simulation results validate the effectiveness of the proposed schemes in comparison to the conventional techniques.
Overview of AI and Communication for 6G Network: Fundamentals, Challenges, and Future Research Opportunities
Dec 19, 2024



Abstract:With the increasing demand for seamless connectivity and intelligent communication, the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and communication for sixth-generation (6G) network is emerging as a revolutionary architecture. This paper presents a comprehensive overview of AI and communication for 6G networks, emphasizing their foundational principles, inherent challenges, and future research opportunities. We commence with a retrospective analysis of AI and the evolution of large-scale AI models, underscoring their pivotal roles in shaping contemporary communication technologies. The discourse then transitions to a detailed exposition of the envisioned integration of AI within 6G networks, delineated across three progressive developmental stages. The initial stage, AI for Network, focuses on employing AI to augment network performance, optimize efficiency, and enhance user service experiences. The subsequent stage, Network for AI, highlights the role of the network in facilitating and buttressing AI operations and presents key enabling technologies, including digital twins for AI and semantic communication. In the final stage, AI as a Service, it is anticipated that future 6G networks will innately provide AI functions as services and support application scenarios like immersive communication and intelligent industrial robots. Specifically, we have defined the quality of AI service, which refers to the measurement framework system of AI services within the network. In addition to these developmental stages, we thoroughly examine the standardization processes pertinent to AI in network contexts, highlighting key milestones and ongoing efforts. Finally, we outline promising future research opportunities that could drive the evolution and refinement of AI and communication for 6G, positioning them as a cornerstone of next-generation communication infrastructure.
Distributed satellite information networks: Architecture, enabling technologies, and trends
Dec 17, 2024



Abstract:Driven by the vision of ubiquitous connectivity and wireless intelligence, the evolution of ultra-dense constellation-based satellite-integrated Internet is underway, now taking preliminary shape. Nevertheless, the entrenched institutional silos and limited, nonrenewable heterogeneous network resources leave current satellite systems struggling to accommodate the escalating demands of next-generation intelligent applications. In this context, the distributed satellite information networks (DSIN), exemplified by the cohesive clustered satellites system, have emerged as an innovative architecture, bridging information gaps across diverse satellite systems, such as communication, navigation, and remote sensing, and establishing a unified, open information network paradigm to support resilient space information services. This survey first provides a profound discussion about innovative network architectures of DSIN, encompassing distributed regenerative satellite network architecture, distributed satellite computing network architecture, and reconfigurable satellite formation flying, to enable flexible and scalable communication, computing and control. The DSIN faces challenges from network heterogeneity, unpredictable channel dynamics, sparse resources, and decentralized collaboration frameworks. To address these issues, a series of enabling technologies is identified, including channel modeling and estimation, cloud-native distributed MIMO cooperation, grant-free massive access, network routing, and the proper combination of all these diversity techniques. Furthermore, to heighten the overall resource efficiency, the cross-layer optimization techniques are further developed to meet upper-layer deterministic, adaptive and secure information services requirements. In addition, emerging research directions and new opportunities are highlighted on the way to achieving the DSIN vision.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge