Zihuan Mao
Model-driven deep neural network for enhanced direction finding with commodity 5G gNodeB
Dec 14, 2024



Abstract:Pervasive and high-accuracy positioning has become increasingly important as a fundamental enabler for intelligent connected devices in mobile networks. Nevertheless, current wireless networks heavily rely on pure model-driven techniques to achieve positioning functionality, often succumbing to performance deterioration due to hardware impairments in practical scenarios. Here we reformulate the direction finding or angle-of-arrival (AoA) estimation problem as an image recovery task of the spatial spectrum and propose a new model-driven deep neural network (MoD-DNN) framework. The proposed MoD-DNN scheme comprises three modules: a multi-task autoencoder-based beamformer, a coarray spectrum generation module, and a model-driven deep learning-based spatial spectrum reconstruction module. Our technique enables automatic calibration of angular-dependent phase error thereby enhancing the resilience of direction-finding precision against realistic system non-idealities. We validate the proposed scheme both using numerical simulations and field tests. The results show that the proposed MoD-DNN framework enables effective spectrum calibration and accurate AoA estimation. To the best of our knowledge, this study marks the first successful demonstration of hybrid data-and-model-driven direction finding utilizing readily available commodity 5G gNodeB.
Access Point Deployment for Localizing Accuracy and User Rate in Cell-Free Systems
Dec 10, 2024



Abstract:Evolving next-generation mobile networks is designed to provide ubiquitous coverage and networked sensing. With utility of multi-view sensing and multi-node joint transmission, cell-free is a promising technique to realize this prospect. This paper aims to tackle the problem of access point (AP) deployment in cell-free systems to balance the sensing accuracy and user rate. By merging the D-optimality with Euclidean criterion, a novel integrated metric is proposed to be the objective function for both max-sum and max-min problems, which respectively guarantee the overall and lowest performance in multi-user communication and target tracking scenario. To solve the corresponding high dimensional non-convex multi-objective problem, the Soft actor-critic (SAC) is utilized to avoid risk of local optimal result. Numerical results demonstrate that proposed SAC-based APs deployment method achieves $20\%$ of overall performance and $120\%$ of lowest performance.
Joint DoA-Range Estimation Using Space-Frequency Virtual Difference Coarray
Apr 15, 2022
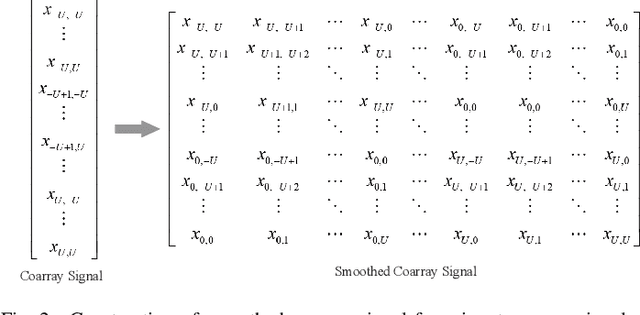
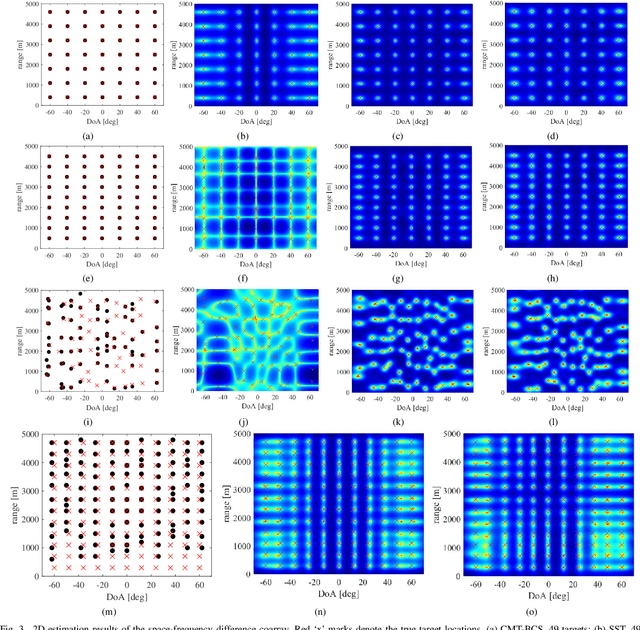
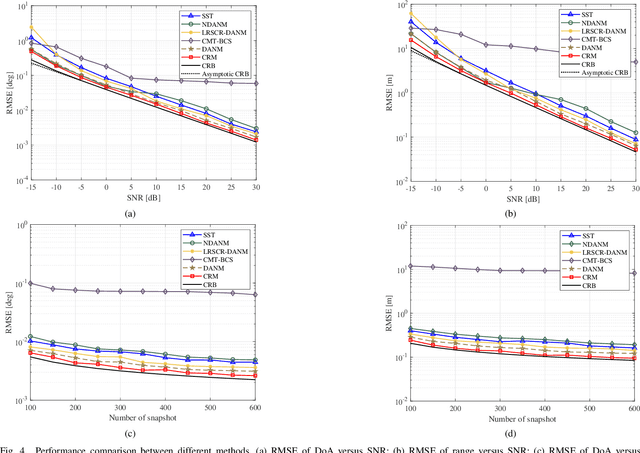
Abstract:In this paper, we address the problem of joint direction-of-arrival (DoA) and range estimation using frequency diverse coprime array (FDCA). By incorporating the coprime array structure and coprime frequency offsets, a two-dimensional space-frequency virtual difference coarray corresponding to uniform array and uniform frequency offset is considered to increase the number of degrees-of-freedom (DoFs). However, the reconstruction of the doubly-Toeplitz covariance matrix is computationally prohibitive. To solve this problem, we propose an interpolation algorithm based on decoupled atomic norm minimization (DANM), which converts the coarray signal to a simple matrix form. On this basis, a relaxation-based optimization problem is formulated to achieve joint DoA-range estimation with enhanced DoFs. The reconstructed coarray signal enables application of existing subspace-based spectral estimation methods. The proposed DANM problem is further reformulated as an equivalent rank-minimization problem which is solved by cyclic rank minimization. This approach avoids the approximation errors introduced in nuclear norm-based approach, thereby achieving superior root-mean-square error which is closer to the Cramer-Rao bound. The effectiveness of proposed method is confirmed by theoretical analyses and numerical simulations.
Rank Minimization-based Toeplitz Reconstruction for DoA Estimation Using Coprime Array
Mar 29, 2021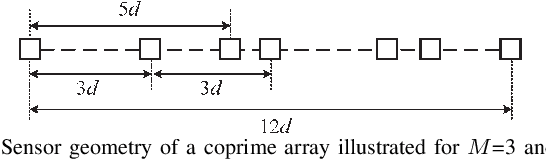
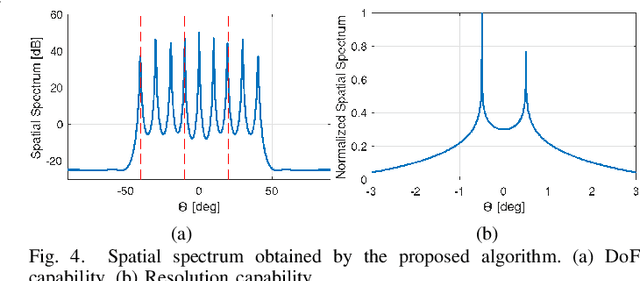

Abstract:In this paper, we address the problem of direction finding using coprime array, which is one of the most preferred sparse array configurations. Motivated by the fact that non-uniform element spacing hinders full utilization of the underlying information in the receive signals, we propose a direction-of-arrival (DoA) estimation algorithm based on low-rank reconstruction of the Toeplitz covariance matrix. The atomic-norm representation of the measurements from the interpolated virtual array is considered, and the equivalent dual-variable rank minimization problem is formulated and solved using a cyclic optimization approach. The recovered covariance matrix enables the application of conventional subspace-based spectral estimation algorithms, such as MUSIC, to achieve enhanced DoA estimation performance. The estimation performance of the proposed approach, in terms of the degrees-of-freedom and spatial resolution, is examined. We also show the superiority of the proposed method over the competitive approaches in the root-mean-square error sense.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge