Hong Ren
Theoretical and Empirical Study of Spatial Power Focusing Effect for Sparse Arrays at Terahertz Band
Nov 19, 2025Abstract:This work investigates the spatial power focusing effect for large-scale sparse arrays at terahertz (THz) band, combining theoretical analysis with experimental validation. Specifically, based on a Green's function channel model, we analyze the power distribution along the $z$-axis, deriving a closed-form expression to characterize the focusing effect. Furthermore, the factors influencing the focusing effect, including phase noise and positional deviations, are theoretically analyzed and numerically simulated. Finally, a 300 GHz measurement platform based on a vector network analyzer (VNA) is constructed for experimental validation. The measurement results demonstrate close consistence with theoretical simulation results, confirming the spatial power focusing effect for sparse arrays.
A Two-Stage ISAC Framework for Low-Altitude Economy Based on 5G NR Signals
Nov 18, 2025Abstract:The evolution of next-generation wireless networks has spurred the vigorous development of the low-altitude economy (LAE). To support this emerging field while remaining compatible with existing network architectures, integrated sensing and communication (ISAC) based on 5G New Radio (NR) signals is regarded as a promising solution. However, merely leveraging standard 5G NR signals, such as the Synchronization Signal Block (SSB), presents fundamental limitations in sensing resolution. To address the issue, this paper proposes a two-stage coarse-to-fine sensing framework that utilizes standard 5G NR initial access signals augmented by a custom-designed sparse pilot structure (SPS) for high-precision unmanned aerial vehicles (UAV) sensing. In Stage I, we first fuse information from the SSB, Type\#0-PDCCH, and system information block 1 (SIB1) to ensure the initial target detection. In Stage II, a refined estimation algorithm is introduced to overcome the resolution limitations of these signals. Inspired by the sparse array theory, this stage employs a novel SPS, which is inserted into resource blocks (RBs) within the CORSET\#0 bandwidth. To accurately extract the off-grid range and velocity parameters from these sparse pilots, we develop a corresponding high-resolution algorithm based on the weighted unwrapped phase (WUP) technique and the RELAX-based iterative method. Finally, the density-based spatial clustering of applications with noise (DBSCAN) algorithm is adopted to prune the redundant detections arising from beam overlap. Comprehensive simulation results demonstrate the superior estimation accuracy and computational efficiency of the proposed framework in comparison to other techniques.
Mutual Coupling Aware Channel Estimation for RIS-Aided Multi-User mmWave Systems
Nov 11, 2025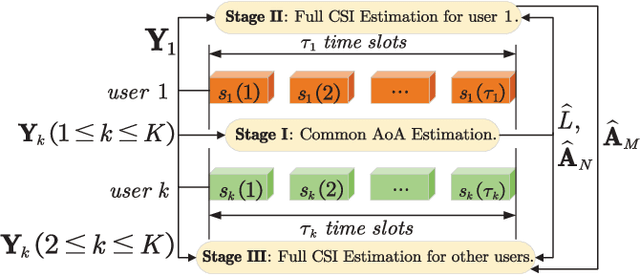
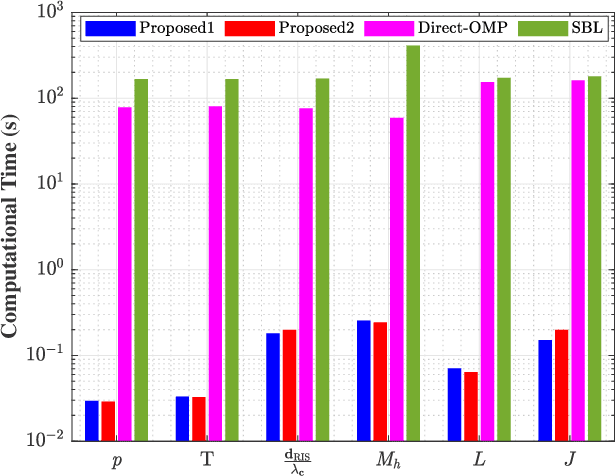
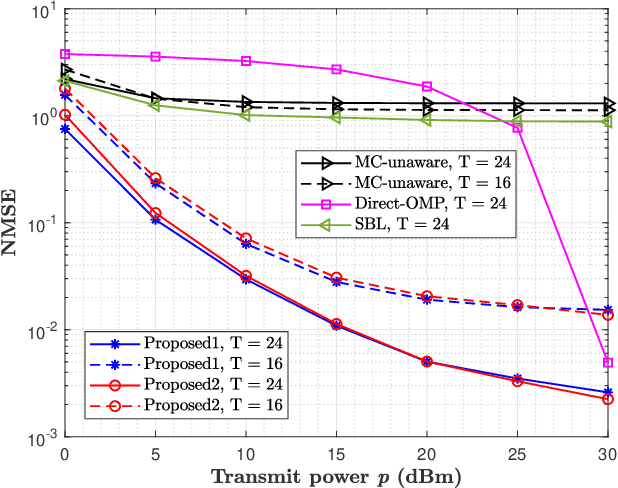
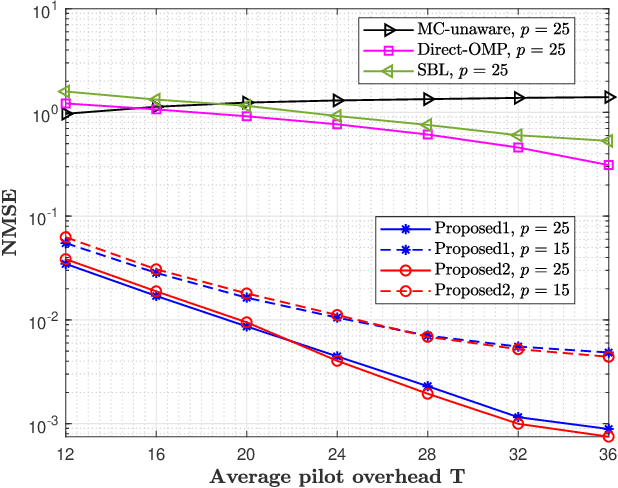
Abstract:This paper proposes a three-stage uplink channel estimation protocol for reconfigurable intelligent surface (RIS)-aided multi-user (MU) millimeter-wave (mmWave) multiple-input single-output (MISO) systems, where both the base station (BS) and the RIS are equipped with uniform planar arrays (UPAs). The proposed approach explicitly accounts for the mutual coupling (MC) effect, modeled via scattering parameter multiport network theory. In Stage~I, a dimension-reduced subspace-based method is proposed to estimate the common angle of arrival (AoA) at the BS using the received signals across all users. In Stage~II, MC-aware cascaded channel estimation is performed for a typical user. The equivalent measurement vectors for each cascaded path are extracted and the reference column is reconstructed using a compressed sensing (CS)-based approach. By leveraging the structure of the cascaded channel, the reference column is rearranged to estimate the AoA at the RIS, thereby reducing the computational complexity associated with estimating other columns. Additionally, the common angle of departure (AoD) at the RIS is also obtained in this stage, which significantly reduces the pilot overhead for estimating the cascaded channels of other users in Stage~III. The RIS phase shift training matrix is designed to optimize performance in the presence of MC and outperforms random phase scheme. Simulation results validate that the proposed method yields better performance than the MC-unaware and existing approaches in terms of estimation accuracy and pilot efficiency.
4D Imaging in ISAC Systems: A Framework Based on 5G NR Downlink Signals
Nov 07, 2025Abstract:Integrated sensing and communication (ISAC) has emerged as a key enabler for sixth-generation (6G) wireless networks, supporting spectrum sharing and hardware integration. Beyond communication enhancement, ISAC also enables high-accuracy environment reconstruction and imaging, which are crucial for applications such as autonomous driving and digital twins. This paper proposes a 4D imaging framework fully compliant with the 5G New Radio (NR) protocol, ensuring compatibility with cellular systems. Specifically, we develop an end-to-end processing chain that covers waveform generation, echo processing, and multi-BS point cloud fusion. Furthermore, we introduce Zoom-OMP, a coarse-to-fine sparse recovery algorithm for high-resolution angle estimation that achieves high accuracy with reduced computational cost. The simulation results demonstrate that the proposed framework achieves robust 4D imaging performance with superior spatial accuracy and reconstruction quality compared to conventional benchmarks, paving the way for practical ISAC-enabled environment reconstruction in 6G networks.
Large-Model AI for Near Field Beam Prediction: A CNN-GPT2 Framework for 6G XL-MIMO
Oct 26, 2025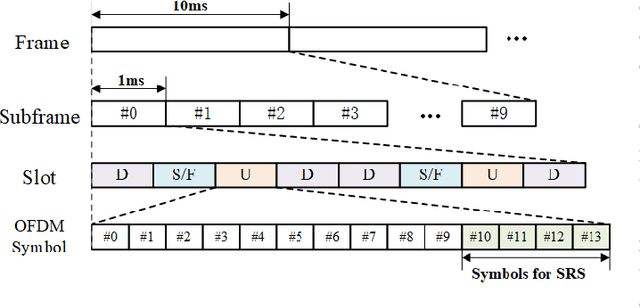
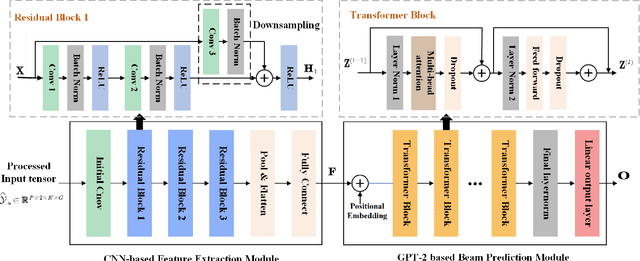
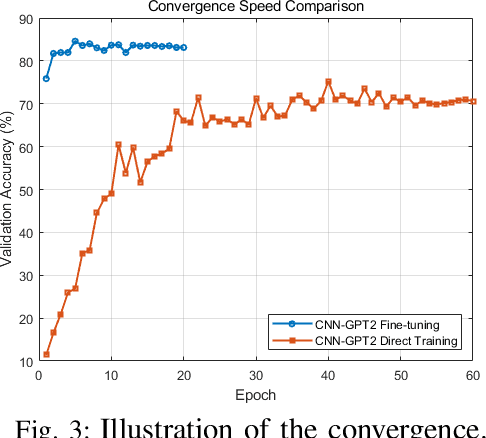
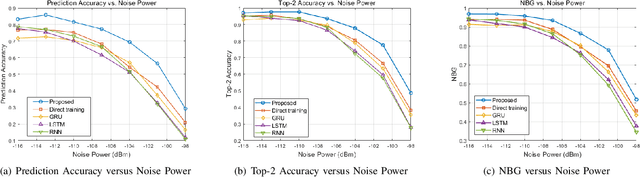
Abstract:The emergence of extremely large-scale antenna arrays (ELAA) in millimeter-wave (mmWave) communications, particularly in high-mobility scenarios, highlights the importance of near-field beam prediction. Unlike the conventional far-field assumption, near-field beam prediction requires codebooks that jointly sample the angular and distance domains, which leads to a dramatic increase in pilot overhead. Moreover, unlike the far- field case where the optimal beam evolution is temporally smooth, the optimal near-field beam index exhibits abrupt and nonlinear dynamics due to its joint dependence on user angle and distance, posing significant challenges for temporal modeling. To address these challenges, we propose a novel Convolutional Neural Network-Generative Pre-trained Transformer 2 (CNN-GPT2) based near-field beam prediction framework. Specifically, an uplink pilot transmission strategy is designed to enable efficient channel probing through widebeam analog precoding and frequency-varying digital precoding. The received pilot signals are preprocessed and passed through a CNN-based feature extractor, followed by a GPT-2 model that captures temporal dependencies across multiple frames and directly predicts the near-field beam index in an end-to-end manner.
Performance Analysis of Cooperative Integrated Sensing and Communications for 6G Networks
May 14, 2025Abstract:In this work, we aim to effectively characterize the performance of cooperative integrated sensing and communication (ISAC) networks and to reveal how performance metrics relate to network parameters. To this end, we introduce a generalized stochastic geometry framework to model the cooperative ISAC networks, which approximates the spatial randomness of the network deployment. Based on this framework, we derive analytical expressions for key performance metrics in both communication and sensing domains, with a particular focus on communication coverage probability and radar information rate. The analytical expressions derived explicitly highlight how performance metrics depend on network parameters, thereby offering valuable insights into the deployment and design of cooperative ISAC networks. In the end, we validate the theoretical performance analysis through Monte Carlo simulation results. Our results demonstrate that increasing the number of cooperative base stations (BSs) significantly improves both metrics, while increasing the BS deployment density has a limited impact on communication coverage probability but substantially enhances the radar information rate. Additionally, increasing the number of transmit antennas is effective when the total number of transmit antennas is relatively small. The incremental performance gain reduces with the increase of the number of transmit antennas, suggesting that indiscriminately increasing antennas is not an efficient strategy to improve the performance of the system in cooperative ISAC networks.
Modular XL-Array-Enabled 3-D Localization based on Hybrid Spherical-Planar Wave Model in Terahertz Systems
Apr 18, 2025Abstract:This work considers the three-dimensional (3-D) positioning problem in a Terahertz (THz) system enabled by a modular extra-large (XL) array with sub-connected architecture. Our purpose is to estimate the Cartesian Coordinates of multiple user equipments (UEs) with the received signal of the RF chains while considering the spatial non-stationarity (SNS). We apply the hybrid spherical-planar wave model (HSPWM) as the channel model owing to the structual feature of the modular array, and propose a 3-D localization algorithm with relatively high accuracy and low complexity. Specifically, we first distinguish the visible sub-arrays (SAs) located in the VR and estimate the angles-of-arrival (AoAs) from each UE to typical visible SAs with the largest receive power via compressed sensing (CS) method. In addition, we apply the weighted least square (WLS) method to obtain a coarse 3-D position estimation of each UE according to the AoA estimations. Then, we estimate the AoAs of the other SAs with a reduced dictionary (RD)-CS-based method for lower computational complexity, and utilize all the efficient AoA estimations to derive a fine position estimation. Simulation results indicate that the proposed positioning framework based on modular XL-array can achieve satisfactory accuracy with evident reduction in complexity. Furthermore, the deployment of SAs and the allocation of antenna elements need to be specially designed for better positioning performance.
A Framework for Uplink ISAC Receiver Designs: Performance Analysis and Algorithm Development
Mar 04, 2025



Abstract:Uplink integrated sensing and communication (ISAC) systems have recently emerged as a promising research direction, enabling simultaneous uplink signal detection and target sensing. In this paper, we propose flexible projection (FP)-type receivers that unify the projection-type receivers and the successive interference cancellation (SIC)-type receivers by using a flexible tradeoff factor to adapt to dynamically changing uplink ISAC scenarios. The FP-type receivers address the joint signal detection and target response estimation problem through two coordinated phases: 1) Communication signal detection using a reconstructed signal whose composition is controlled by the tradeoff factor, followed by 2) Target response estimation performed through subtraction of the detected communication signal from the received signal. With adjustable tradeoff factors, the FP-type receivers can balance the enhancement of the signal-to-interference-plus-noise ratio (SINR) with the reduction of correlation in the reconstructed signal for communication signal detection. The pairwise error probabilities (PEPs) are analyzed for both maximum likelihood (ML) and zero-forcing (ZF) detectors, revealing that the optimal tradeoff factor should be determined based on the adopted detection algorithm and the relative power of the sensing and communication (S&C) signal. A homotopy optimization framework is first applied for the FP-type receivers with a fixed trade-off factor. This framework is then extended to develop dynamic FP (DFP)-type receivers, which iteratively adjust the trade-off factor for improved algorithm performance and environmental adaptability. Subsequently, two extensions are explored to further enhance the receivers' performance: parallel DFP (PDFP)-type receivers and a block-structured receiver design. Finally, the effectiveness of the proposed receiver designs is verified via simulations.
Uplink Transmission Design for Fluid Antenna-Enabled Multiuser MIMO Systems with Imperfect CSI
Mar 03, 2025



Abstract:This paper investigates a two-timescale uplink transmission framework for a fluid antenna-enabled multiuser multi-input multi-output system (MIMO-FAS). Antenna positions are optimized based on statistical channel state information (CSI), while beamforming vectors at the base station (BS) adapt to instantaneous CSI. Under a Rician fading channel with imperfect CSI, we establish a linear minimum mean square error (LMMSE)-based channel estimation approach and derive a closed-form expression for the achievable uplink rate using a low-complexity maximal-ratio-combining (MRC) detector. The optimization problem is formulated as a minimum user rate maximization problem by optimizing the fluid antenna positions, subject to the feasible region and the minimum spacing distance constraints. To address this non-convex problem, a genetic algorithm (GA) method is proposed, encoding antenna configurations as population individuals. Additionally, an accelerated gradient ascent algorithm is proposed to enhance computational efficiency. Numerical results validate the mathematical derivations and demonstrate that the proposed two-timescale transmission strategy significantly outperforms traditional FPA systems, with both algorithms achieving enhanced gains.
Channel Estimation for RIS-Aided MU-MIMO mmWave Systems with Practical Hybrid Architecture
Feb 08, 2025



Abstract:This paper proposes a correlation-based three-stage channel estimation strategy with low pilot overhead for reconfigurable intelligent surface (RIS)-aided millimeter wave (mmWave) multi-user (MU) MIMO systems, in which both users and base station (BS) are equipped with a hybrid RF architecture. In Stage I, all users jointly transmit pilots and recover the uncompressed received signals to estimate the angle of arrival (AoA) at the BS using the discrete Fourier transform (DFT). Based on the observation that the overall cascaded MIMO channel can be decomposed into multiple sub-channels, the cascaded channel for a typical user is estimated in Stage II. Specifically, using the invariance of angles and the linear correlation of gains related to different cascaded subchannels, we use compressive sensing (CS), least squares (LS), and a one-dimensional search to estimate the Angles of Departure (AoDs), based on which the overall cascaded channel is obtained. In Stage III, the remaining users independently transmit pilots to estimate their individual cascaded channel with the same approach as in Stage II, which exploits the equivalent common RIS-BS channel obtained in Stage II to reduce the pilot overhead. In addition, the hybrid combining matrix and the RIS phase shift matrix are designed to reduce the noise power, thereby further improving the estimation performance. Simulation results demonstrate that the proposed algorithm can achieve high estimation accuracy especially when the number of antennas at the users is small, and reduce pilot overhead by more than five times compared with the existing benchmark approach.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge