Tuo Wu
From Optimization to Learning: Dual-Approach Resource Allocation for Over-the-Air Edge Computing Under Execution Uncertainty
Dec 23, 2025Abstract:The exponential proliferation of mobile devices and data-intensive applications in future wireless networks imposes substantial computational burdens on resource-constrained devices, thereby fostering the emergence of over-the-air computation (AirComp) as a transformative paradigm for edge intelligence.} To enhance the efficiency and scalability of AirComp systems, this paper proposes a comprehensive dual-approach framework that systematically transitions from traditional mathematical optimization to deep reinforcement learning (DRL) for resource allocation under execution uncertainty. Specifically, we establish a rigorous system model capturing execution uncertainty via Gamma-distributed computational workloads, resulting in challenging nonlinear optimization problems involving complex Gamma functions. For single-user scenarios, we design advanced block coordinate descent (BCD) and majorization-maximization (MM) algorithms, which yield semi-closed-form solutions with provable performance guarantees. However, conventional optimization approaches become computationally intractable in dynamic multi-user environments due to inter-user interference and resource contention. To this end, we introduce a Deep Q-Network (DQN)-based DRL framework capable of adaptively learning optimal policies through environment interaction. Our dual methodology effectively bridges analytical tractability with adaptive intelligence, leveraging optimization for foundational insight and learning for real-time adaptability. Extensive numerical results corroborate the performance gains achieved via increased edge server density and validate the superiority of our optimization-to-learning paradigm in next-generation AirComp systems.
FAS-RIS for V2X: Unlocking Realistic Performance Analysis with Finite Elements
Dec 22, 2025Abstract:The synergy of fluid antenna systems (FAS) and reconfigurable intelligent surfaces (RIS) is poised to unlock robust Vehicle-to-Everything (V2X) communications. However, a critical gap persists between theoretical predictions and real-world performance. Existing analyses predominantly rely on the Central Limit Theorem (CLT), an assumption valid only for a large number of RIS elements, which fails to represent practical, finite-sized deployments constrained by cost and urban infrastructure. This paper bridges this gap by presenting a novel framework that unlocks a realistic performance analysis for FAS-RIS systems with finite elements. Leveraging a Gamma distribution approximation, we derive a new, tractable closed-form expression for the outage probability. Numerical results validate our approach, demonstrating that it offers a significantly more accurate performance characterization than conventional CLT-based methods, particularly in the practical regime of small-scale RIS. This work provides a crucial foundation for the design and deployment of reliable FAS-RIS-aided vehicular networks.
Intelligent Sky Mirrors: SAC-Driven MF-RIS Optimization for Secure NOMA in Low-Altitude Economy
Dec 22, 2025Abstract:Low-altitude economy (LAE) has become a key driving force for smart cities and economic growth. To address spectral efficiency and communication security challenges in LAE, this paper investigates secure energy efficiency (SEE) maximization using intelligent sky mirrors, UAV-mounted multifunctional reconfigurable intelligent surfaces (MF-RIS) assisting nonorthogonal multiple access (NOMA) systems. These aerial mirrors intelligently amplify legitimate signals while simultaneously generating jamming against eavesdroppers. We formulate a joint optimization problem encompassing UAV trajectory, base station power allocation, RIS phase shifts, amplification factors, and scheduling matrices. Given the fractional SEE objective and dynamic UAV scenarios, we propose a two-layer optimization scheme: SAC-driven first layer for trajectory and power management, and channel alignment-based second layer for phase optimization. Simulations demonstrate that our proposed scheme significantly outperforms benchmark approaches.
An Fluid Antenna Array-Enabled DOA Estimation Method: End-Fire Effect Suppression
Dec 22, 2025



Abstract:Direction of Arrival (DOA) estimation serves as a critical sensing technology poised to play a vital role in future intelligent and ubiquitous communication systems. Despite the development of numerous mature super-resolution algorithms, the inherent end-fire effect problem in fixed antenna arrays remains inadequately addressed. This work proposed a novel array architecture composed of fluid antennas. By exploiting the spatial reconfigurability of their positions to equivalently modulate the array steering vector and integrating it with the classical MUSIC algorithm, this approach achieved high-precision DOA estimation. Simulation results demonstrated that the proposed method delivers outstanding estimation performance even in highly challenging end-fire regions.
Reimagining Wireless Connectivity: The FAS-RIS Synergy for 6G Smart Cities
Dec 22, 2025Abstract:Fluid antenna system (FAS) represents the concept of treating antenna as a reconfigurable physical-layer resource to broaden system design and network optimization and inspire next-generation reconfigurable antennas. FAS can unleash new degree of freedom (DoF) via antenna reconfigurations for novel spatial diversity. Reconfigurable intelligent surfaces (RISs) on the other hand can reshape wireless propagation environments but often face limitations from double path-loss and minimal signal processing capability when operating independently. This article envisions a transformative FAS-RIS integrated architecture for future smart city networks, uniting the adaptability of FAS with the environmental control of RIS. The proposed framework has five key applications: FAS-enabled base stations (BSs) for large-scale beamforming, FAS-equipped user devices with finest spatial diversity, and three novel RIS paradigms -- fluid RIS (FRIS) with reconfigurable elements, FAS-embedded RIS as active relays, and enormous FAS (E-FAS) exploiting surface waves on facades to re-establish line-of-sight (LoS) communication. A two-timescale control mechanism coordinates network-level beamforming with rapid, device-level adaptation. Applications spanning from simultaneous wireless information and power transfer (SWIPT) to integrated sensing and communications (ISAC), with challenges in co-design, channel modeling, and optimization, are discussed. This article concludes with simulation results demonstrating the robustness and effectiveness of the FAS-RIS system.
FAS-ARIS: Turning Multipath Challenges Into Localization Opportunities
Sep 15, 2025



Abstract:Traditional single-input single-output (SISO) systems face fundamental limitations in achieving accurate three-dimensional (3D) localization due to limited spatial degrees of freedom (DoF) and the adverse impact of multipath propagation. This paper proposes a novel fluid antenna system (FAS)-active reconfigurable intelligent surface (ARIS) framework that transforms multipath effects from a hindrance into a resource for enhanced localization. By synergistically combining the signal amplification capabilities of ARIS with the spatial diversity enabled by FAS, the proposed system achieves robust 3D user equipment (UE) positioning -- without relying on auxiliary information such as time-of-arrival (ToA) or frequency diversity. The system exploits both line-of-sight (LoS) and non-line-of-sight (NLoS) components through a tailored signal decoupling strategy. We design novel UE pilot sequences and ARIS phase configurations to effectively separate LoS and NLoS channels, enabling independent parameter estimation. A multi-stage estimation algorithm is then applied: the multiple signal classification (MUSIC) algorithm estimates angle-of-arrival (AoA) from the direct path, while maximum likelihood estimation with interior-point refinement recovers cascaded channel parameters from the reflected path. Finally, geometric triangulation using least-squares estimation determines the UE's 3D position based on the extracted AoA information. Comprehensive performance analysis, including the derivation of Cram\'{e}r-Rao bounds for both channel and position estimation, establishes theoretical benchmarks. Simulation results confirm that the proposed FAS-ARIS framework achieves near-optimal localization accuracy while maintaining robustness in rich multipath environments -- effectively turning conventional localization challenges into advantages.
Meta-Learning Driven Lightweight Phase Shift Compression for IRS-Assisted Wireless Systems
May 07, 2025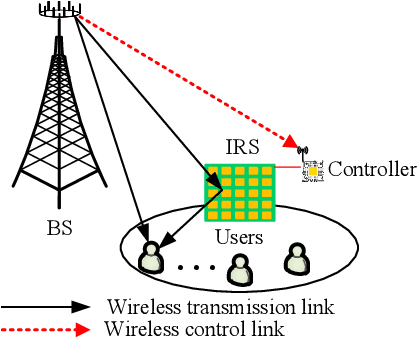
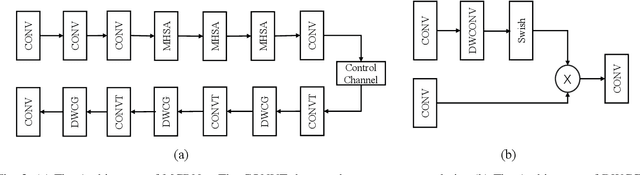
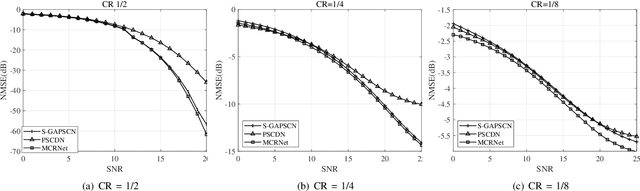
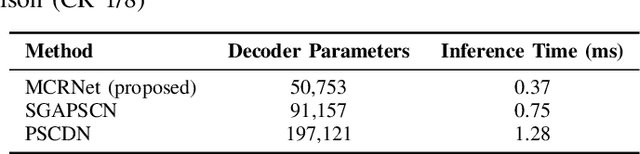
Abstract:The phase shift information (PSI) overhead poses a critical challenge to enabling real-time intelligent reflecting surface (IRS)-assisted wireless systems, particularly under dynamic and resource-constrained conditions. In this paper, we propose a lightweight PSI compression framework, termed meta-learning-driven compression and reconstruction network (MCRNet). By leveraging a few-shot adaptation strategy via model-agnostic meta-learning (MAML), MCRNet enables rapid generalization across diverse IRS configurations with minimal retraining overhead. Furthermore, a novel depthwise convolutional gating (DWCG) module is incorporated into the decoder to achieve adaptive local feature modulation with low computational cost, significantly improving decoding efficiency. Extensive simulations demonstrate that MCRNet achieves competitive normalized mean square error performance compared to state-of-the-art baselines across various compression ratios, while substantially reducing model size and inference latency. These results validate the effectiveness of the proposed asymmetric architecture and highlight the practical scalability and real-time applicability of MCRNet for dynamic IRS-assisted wireless deployments.
Modular XL-Array-Enabled 3-D Localization based on Hybrid Spherical-Planar Wave Model in Terahertz Systems
Apr 18, 2025Abstract:This work considers the three-dimensional (3-D) positioning problem in a Terahertz (THz) system enabled by a modular extra-large (XL) array with sub-connected architecture. Our purpose is to estimate the Cartesian Coordinates of multiple user equipments (UEs) with the received signal of the RF chains while considering the spatial non-stationarity (SNS). We apply the hybrid spherical-planar wave model (HSPWM) as the channel model owing to the structual feature of the modular array, and propose a 3-D localization algorithm with relatively high accuracy and low complexity. Specifically, we first distinguish the visible sub-arrays (SAs) located in the VR and estimate the angles-of-arrival (AoAs) from each UE to typical visible SAs with the largest receive power via compressed sensing (CS) method. In addition, we apply the weighted least square (WLS) method to obtain a coarse 3-D position estimation of each UE according to the AoA estimations. Then, we estimate the AoAs of the other SAs with a reduced dictionary (RD)-CS-based method for lower computational complexity, and utilize all the efficient AoA estimations to derive a fine position estimation. Simulation results indicate that the proposed positioning framework based on modular XL-array can achieve satisfactory accuracy with evident reduction in complexity. Furthermore, the deployment of SAs and the allocation of antenna elements need to be specially designed for better positioning performance.
Holographic MIMO Multi-Cell Communications
Feb 23, 2025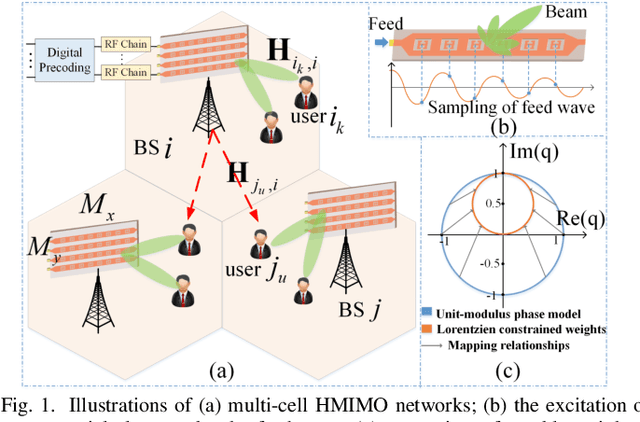
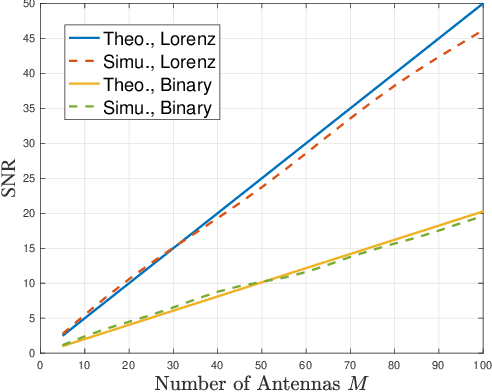
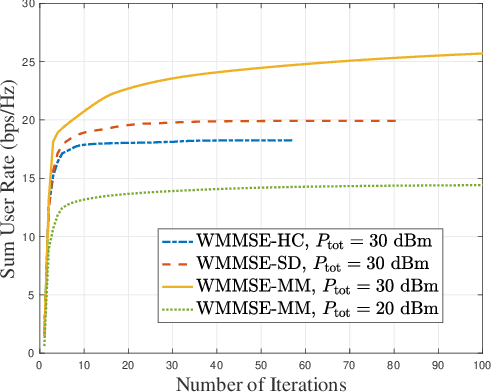
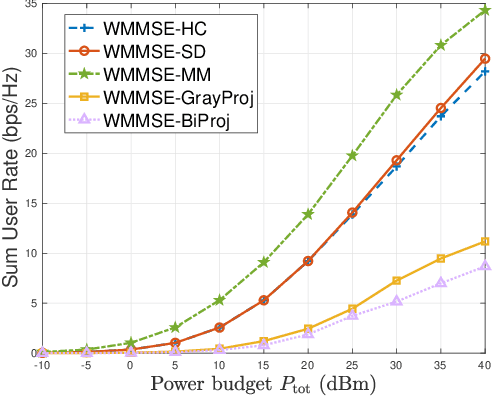
Abstract:Metamaterial antennas are appealing for next-generation wireless networks due to their simplified hardware and much-reduced size, power, and cost. This paper investigates the holographic multiple-input multiple-output (HMIMO)-aided multi-cell systems with practical per-radio frequency (RF) chain power constraints. With multiple antennas at both base stations (BSs) and users, we design the baseband digital precoder and the tuning response of HMIMO metamaterial elements to maximize the weighted sum user rate. Specifically, under the framework of block coordinate descent (BCD) and weighted minimum mean square error (WMMSE) techniques, we derive the low-complexity closed-form solution for baseband precoder without requiring bisection search and matrix inversion. Then, for the design of HMIMO metamaterial elements under binary tuning constraints, we first propose a low-complexity suboptimal algorithm with closed-form solutions by exploiting the hidden convexity (HC) in the quadratic problem and then further propose an accelerated sphere decoding (SD)-based algorithm which yields global optimal solution in the iteration. For HMIMO metamaterial element design under the Lorentzian-constrained phase model, we propose a maximization-minorization (MM) algorithm with closed-form solutions at each iteration step. Furthermore, in a simplified multiple-input single-output (MISO) scenario, we derive the scaling law of downlink single-to-noise (SNR) for HMIMO with binary and Lorentzian tuning constraints and theoretically compare it with conventional fully digital/hybrid arrays. Simulation results demonstrate the effectiveness of our algorithms compared to benchmarks and the benefits of HMIMO compared to conventional arrays.
A Hybrid Dynamic Subarray Architecture for Efficient DOA Estimation in THz Ultra-Massive Hybrid MIMO Systems
Jan 30, 2025Abstract:Terahertz (THz) communication combined with ultra-massive multiple-input multiple-output (UM-MIMO) technology is promising for 6G wireless systems, where fast and precise direction-of-arrival (DOA) estimation is crucial for effective beamforming. However, finding DOAs in THz UM-MIMO systems faces significant challenges: while reducing hardware complexity, the hybrid analog-digital (HAD) architecture introduces inherent difficulties in spatial information acquisition the large-scale antenna array causes significant deviations in eigenvalue decomposition results; and conventional two-dimensional DOA estimation methods incur prohibitively high computational overhead, hindering fast and accurate realization. To address these challenges, we propose a hybrid dynamic subarray (HDS) architecture that strategically divides antenna elements into subarrays, ensuring phase differences between subarrays correlate exclusively with single-dimensional DOAs. Leveraging this architectural innovation, we develop two efficient algorithms for DOA estimation: a reduced-dimension MUSIC (RD-MUSIC) algorithm that enables fast processing by correcting large-scale array estimation bias, and an improved version that further accelerates estimation by exploiting THz channel sparsity to obtain initial closed-form solutions through specialized two-RF-chain configuration. Furthermore, we develop a theoretical framework through Cram\'{e}r-Rao lower bound analysis, providing fundamental insights for different HDS configurations. Extensive simulations demonstrate that our solution achieves both superior estimation accuracy and computational efficiency, making it particularly suitable for practical THz UM-MIMO systems.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge