Hyundong Shin
Beyond $λ/2$: Can Arbitrary EMVS Arrays Achieve Unambiguous NLOS Localization?
Feb 07, 2026Abstract:Conventional radar array design mandates interelement spacing not exceeding half a wavelength ($λ/2$) to avoid spatial ambiguity, fundamentally limiting array aperture and angular resolution. This paper addresses the fundamental question: Can arbitrary electromagnetic vector sensor (EMVS) arrays achieve unambiguous reconfigurable intelligent surface (RIS)-aided localization when element spacing exceeds $λ/2$? We provide an affirmative answer by exploiting the multi-component structure of EMVS measurements and developing a synergistic estimation and optimization framework for non-line-of-sight (NLOS) bistatic multiple input multiple output (MIMO) radar. A third-order parallel factor (PARAFAC) model is constructed from EMVS observations, enabling natural separation of spatial, polarimetric, and propagation effects via the trilinear alternating least squares (TALS) algorithm. A novel phase-disambiguation procedure leverages rotational invariance across the six electromagnetic components of EMVSs to resolve $2π$ phase wrapping in arbitrary array geometries, allowing unambiguous joint estimation of two-dimensional (2-D) direction of departure (DOD), two-dimensional direction of arrival (DOA), and polarization parameters with automatic pairing. To support localization in NLOS environments and enhance estimation robustness, a reconfigurable intelligent surface (RIS) is incorporated and its phase shifts are optimized via semidefinite programming (SDP) relaxation to maximize received signal power, improving signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) and further suppressing spatial ambiguities through iterative refinement.
Sampling-Free Diffusion Transformers for Low-Complexity MIMO Channel Estimation
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:Diffusion model-based channel estimators have shown impressive performance but suffer from high computational complexity because they rely on iterative reverse sampling. This paper proposes a sampling-free diffusion transformer (DiT) for low-complexity MIMO channel estimation, termed SF-DiT-CE. Exploiting angular-domain sparsity of MIMO channels, we train a lightweight DiT to directly predict the clean channels from their perturbed observations and noise levels. At inference, the least square (LS) estimate and estimation noise condition the DiT to recover the channel in a single forward pass, eliminating iterative sampling. Numerical results demonstrate that our method achieves superior estimation accuracy and robustness with significantly lower complexity than state-of-the-art baselines.
RL based Beamforming Optimization for 3D Pinching Antenna assisted ISAC Systems
Jan 28, 2026Abstract:In this paper, a three-dimensional (3D) deployment scheme of pinching antenna array is proposed, aiming to enhances the performance of integrated sensing and communication (ISAC) systems. To fully realize the potential of 3D deployment, a joint antenna positioning, time allocation and transmit power optimization problem is formulated to maximize the sum communication rate with the constraints of target sensing rates and system energy. To solve the sum rate maximization problem, we propose a heterogeneous graph neural network based reinforcement learning (HGRL) algorithm. Simulation results prove that 3D deployment of pinching antenna array outperforms 1D and 2D counterparts in ISAC systems. Moreover, the proposed HGRL algorithm surpasses other baselines in both performance and convergence speed due to the advanced observation construction of the environment.
Adaptive Hybrid Optimizer based Framework for Lumpy Skin Disease Identification
Jan 05, 2026Abstract:Lumpy Skin Disease (LSD) is a contagious viral infection that significantly deteriorates livestock health, thereby posing a serious threat to the global economy and food security. Owing to its rapid spread characteristics, early and precise identification is crucial to prevent outbreaks and ensure timely intervention. In this paper, we propose a hybrid deep learning-based approach called LUMPNet for the early detection of LSD. LUMPNet utilizes image data to detect and classify skin nodules -- the primary indicator of LSD. To this end, LUMPNet uses YOLOv11, EfficientNet-based CNN classifier with compound scaling, and a novel adaptive hybrid optimizer. More precisely, LUMPNet detects and localizes LSD skin nodules and lesions on cattle images. It exploits EfficientNet to classify the localized cattle images into LSD-affected or healthy categories. To stabilize and accelerate the training of YOLOv11 and EfficientNet hybrid model, a novel adaptive hybrid optimizer is proposed and utilized. We evaluate LUMPNet at various stages of LSD using a publicly available dataset. Results indicate that the proposed scheme achieves 99% LSD detection training accuracy, and outperforms existing schemes. The model also achieves validation accuracy of 98%. Moreover, for further evaluation, we conduct a case study using an optimized EfficientNet-B0 model trained with the AdamW optimizer, and compare its performance with LUMPNet. The results show that LUMPNet achieves superior performance.
Quantum Intelligence Meets BD-RIS-Enabled AmBC: Challenges, Opportunities, and Practical Insights
Dec 31, 2025Abstract:A beyond-diagonal reconfigurable intelligent surface (BD-RIS) is an innovative type of reconfigurable intelligent surface (RIS) that has recently been proposed and is considered a revolutionary advancement in wave manipulation. Unlike the mutually disconnected arrangement of elements in traditional RISs, BD-RIS creates cost-effective and simple inter-element connections, allowing for greater freedom in configuring the amplitude and phase of impinging waves. However, there are numerous underlying challenges in realizing the advantages associated with BD-RIS, prompting the research community to actively investigate cutting-edge schemes and algorithms in this direction. Particularly, the passive beamforming design for BD-RIS under specific environmental conditions has become a major focus in this research area. In this article, we provide a systematic introduction to BD-RIS, elaborating on its functional principles concerning architectural design, promising advantages, and classification. Subsequently, we present recent advances and identify a series of challenges and opportunities. Additionally, we consider a specific case study where beamforming is designed using four different algorithms, and we analyze their performance with respect to sum rate and computation cost. To augment the beamforming capabilities in 6G BD-RIS with quantum enhancement, we analyze various hybrid quantum-classical machine learning (ML) models to improve beam prediction performance, employing real-world communication Scenario 8 from the DeepSense 6G dataset. Consequently, we derive useful insights about the practical implications of BD-RIS.
Multiconnectivity for SAGIN: Current Trends, Challenges, AI-driven Solutions, and Opportunities
Dec 25, 2025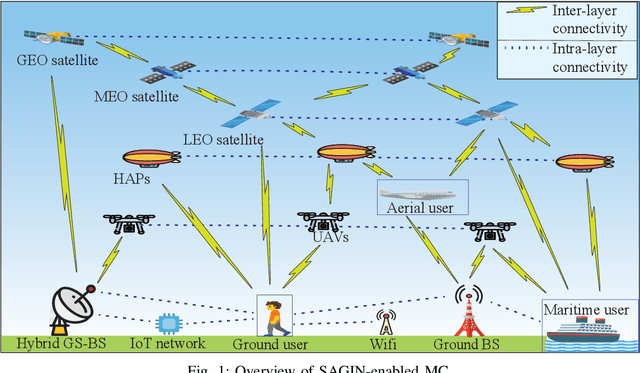
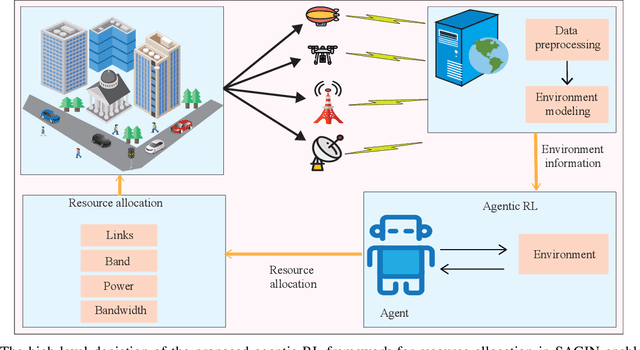
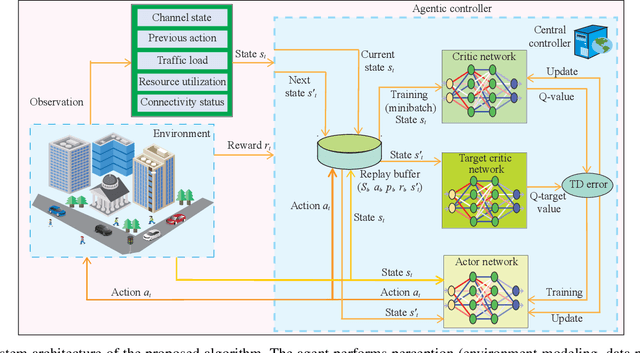
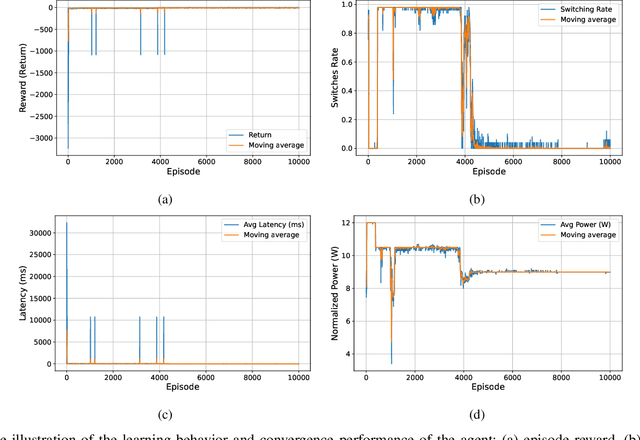
Abstract:Space-air-ground-integrated network (SAGIN)-enabled multiconnectivity (MC) is emerging as a key enabler for next-generation networks, enabling users to simultaneously utilize multiple links across multi-layer non-terrestrial networks (NTN) and multi-radio access technology (multi-RAT) terrestrial networks (TN). However, the heterogeneity of TN and NTN introduces complex architectural challenges that complicate MC implementation. Specifically, the diversity of link types, spanning air-to-air, air-to-space, space-to-space, space-to-ground, and ground-to-ground communications, renders optimal resource allocation highly complex. Recent advancements in reinforcement learning (RL) and agentic artificial intelligence (AI) have shown remarkable effectiveness in optimal decision-making in complex and dynamic environments. In this paper, we review the current developments in SAGIN-enabled MC and outline the key challenges associated with its implementation. We further highlight the transformative potential of AI-driven approaches for resource optimization in a heterogeneous SAGIN environment. To this end, we present a case study on resource allocation optimization enabled by agentic RL for SAGIN-enabled MC involving diverse radio access technologies (RATs). Results show that learning-based methods can effectively handle complex scenarios and substantially enhance network performance in terms of latency and capacity while incurring a moderate increase in power consumption as an acceptable tradeoff. Finally, open research problems and future directions are presented to realize efficient SAGIN-enabled MC.
Anti-Malicious ISAC: How to Jointly Monitor and Disrupt Your Foes?
Dec 22, 2025Abstract:Integrated sensing and communication (ISAC) systems are key enablers of future networks but raise significant security concerns. In this realm, the emergence of malicious ISAC systems has amplified the need for authorized parties to legitimately monitor suspicious communication links and protect legitimate targets from potential detection or exploitation by malicious foes. In this paper, we propose a new wireless proactive monitoring paradigm, where a legitimate monitor intercepts a suspicious communication link while performing cognitive jamming to enhance the monitoring success probability (MSP) and simultaneously safeguard the target. To this end, we derive closed-form expressions of the signal-to-interference-plus-noise-ratio (SINR) at the user (UE), sensing access points (S-APs), and an approximating expression of the SINR at the proactive monitor. Moreover, we propose an optimization technique under which the legitimate monitor minimizes the success detection probability (SDP) of the legitimate target, by optimizing the jamming power allocation over both communication and sensing channels subject to total power constraints and monitoring performance requirement. To enhance the monitor's longevity and reduce the risk of detection by malicious ISAC systems, we further propose an adaptive power allocation scheme aimed at minimizing the total transmit power at the monitor while meeting a pre-selected sensing SINR threshold and ensuring successful monitoring. Our numerical results show that the proposed algorithm significantly compromises the sensing and communication performance of malicious ISAC.
Fundamental Limits of Localization with Fluid Antenna Systems: A Fisher Information Analysis
Dec 15, 2025Abstract:In this letter, we investigate the fundamental limits of localization in fluid antenna systems (FAS) utilizing a Fisher-information-theoretic framework. We develop a unified model to quantify the localization information extractable from time-of-arrival (ToA) and angle-of-arrival (AoA) measurements, explicitly capturing the synthetic aperture effects induced by FAS. Closed-form expressions are derived for the equivalent Fisher information matrix (EFIM) and the corresponding positioning error bound (PEB) in both user-side and base-station (BS)-side FAS configurations. Also, we propose optimal port-selection strategies based on greedy algorithms and convex relaxation to maximize the information gain under a constrained number of activated ports. Numerical results demonstrate that the proposed port-selection schemes can substantially tighten the PEB compared with random activation, thereby confirming the strong potential of FAS to enable high-precision localization. These results offer analytical insights and practical design guidelines for FAS-aided positioning in future-generation wireless networks
Tri-Hybrid Beamforming Design for Fully-Connected Pinching Antenna Systems
Nov 18, 2025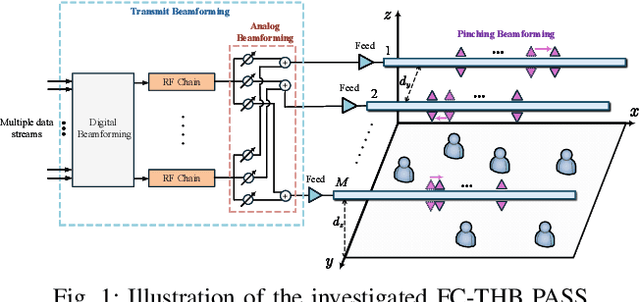
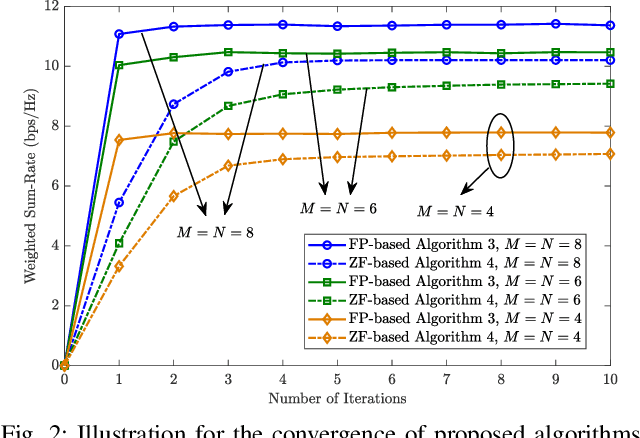
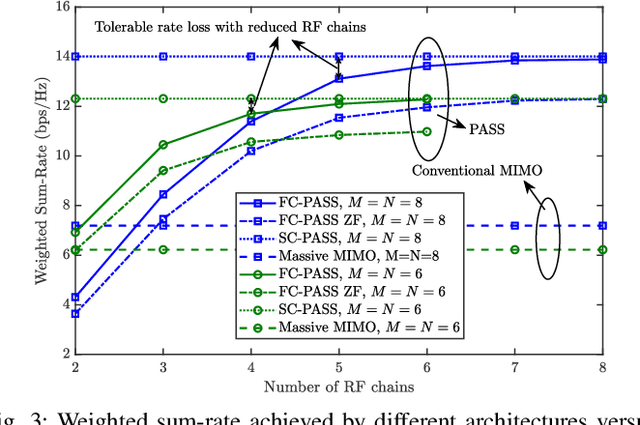
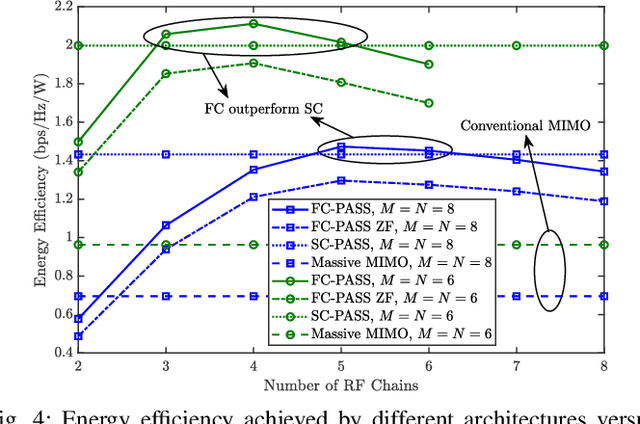
Abstract:A novel fully-connected (FC) tri-hybrid beamforming (THB) architecture is proposed for pinching antenna systems (PASS). In contrast to conventional sub-connected (SC) PASS, the proposed FC architecture employs a tunable phase-shifter network to interconnect all radio frequency (RF) chains with all waveguides. This facilitates a THB framework that integrates conventional hybrid analog-digital beamforming with pinching beamforming. A weighted sum-rate (WSR) optimization problem is then formulated to jointly optimize the transmit beamformers and pinching antenna (PA) positions. Two algorithms are developed to address this challenging non-convex problem. 1) Fractional programming (FP)-based algorithm: This algorithm directly maximizes the WSR using an FP-based alternating optimization framework. Particularly, a success-history based adaptive differential evolution (SHADE) method is proposed to optimize PA positions, effectively addressing the intractable multimodal objective function. 2) Zero-forcing (ZF)-based algorithm: To reduce design complexity, zero-forcing is employed for transmit beamforming. The PA positions are subsequently optimized to maximize the WSR via a modified SHADE method. Simulation results validate the effectiveness of the proposed algorithms, revealing that the FC-THB PASS achieves WSR comparable to the SC architecture while delivering superior energy efficiency with fewer RF chains.
Spectral Efficiency Analysis of Near-Field Holographic MIMO over Ricean Fading Channels
May 02, 2025



Abstract:With the denser distribution of antenna elements, stronger mutual coupling effects would kick in among antenna elements, which would eventually affect the communication performance. Meanwhile, as the holographic array usually has large physical size, the possibility of near-field communication increases. This paper investigates a near-field multi-user downlink HMIMO system and characterizes the spectral efficiency (SE) under the mutual coupling effect over Ricean fading channels. Both perfect and imperfect channel state information (CSI) scenarios are considered. (i) For the perfect CSI case, the mutual coupling and radiation efficiency model are first established. Then, the closed-form SE is derived under maximum ratio transmission (MRT). By comparing the SE between the cases with and without mutual coupling, it is unveiled that the system SE with mutual coupling might outperform that without mutual coupling in the low transmit power regime for a given aperture size. Moreover, it is also unveiled that the inter-user interference cannot be eliminated unless the physical size of the array increases to infinity. Fortunately, the additional distance term in the near-field channel can be exploited for the inter-user interference mitigation, especially for the worst case, where the users' angular positions overlap to a great extent. (ii) For the imperfect CSI case, the channel estimation error is considered for the derivation of the closed-form SE under MRT. It shows that in the low transmit power regime, the system SE can be enhanced by increasing the pilot power and the antenna element density, the latter of which will lead to severe mutual coupling. In the high transmit power regime, increasing the pilot power has a limited effect on improving the system SE. However, increasing the antenna element density remains highly beneficial for enhancing the system SE.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge