Tie Jun Cui
Metasurfaces Enable Active-Like Passive Radar
Dec 09, 2025Abstract:Passive radars (PRs) provide a low-cost and energy-efficient approach to object detection by reusing existing wireless transmissions instead of emitting dedicated probing signals. Yet, conventional passive systems require prior knowledge of non-cooperative source waveforms, are vulnerable to strong interference, and rely on Doppler signatures, limiting their ability to detect subtle or slow-moving targets. Here, we introduce a metasurface-enabled PR (MEPR) concept that integrates a space-time-coding programmable metasurface to imprint distinct spatiotemporal tags onto ambient wireless wavefields. This mechanism transforms a PR into an active-like sensing platform without the need for source control, enabling interference suppression, signal enhancement, and accurate target localization and tracking in cluttered environments. A proof-of-concept implementation operating at 5.48 GHz confirms real-time imaging and tracking of unmanned aerial vehicles under interference-rich conditions, with performance comparable to active radar systems. These results establish MEPR as a solid foundation for scalable, adaptive, and energy-efficient next-generation integrated sensing and communication systems.
Stacked Intelligent Metasurfaces for Multi-Modal Semantic Communications
Jun 14, 2025Abstract:Semantic communication (SemCom) powered by generative artificial intelligence enables highly efficient and reliable information transmission. However, it still necessitates the transmission of substantial amounts of data when dealing with complex scene information. In contrast, the stacked intelligent metasurface (SIM), leveraging wave-domain computing, provides a cost-effective solution for directly imaging complex scenes. Building on this concept, we propose an innovative SIM-aided multi-modal SemCom system. Specifically, an SIM is positioned in front of the transmit antenna for transmitting visual semantic information of complex scenes via imaging on the uniform planar array at the receiver. Furthermore, the simple scene description that contains textual semantic information is transmitted via amplitude-phase modulation over electromagnetic waves. To simultaneously transmit multi-modal information, we optimize the amplitude and phase of meta-atoms in the SIM using a customized gradient descent algorithm. The optimization aims to gradually minimize the mean squared error between the normalized energy distribution on the receiver array and the desired pattern corresponding to the visual semantic information. By combining the textual and visual semantic information, a conditional generative adversarial network is used to recover the complex scene accurately. Extensive numerical results verify the effectiveness of the proposed multi-modal SemCom system in reducing bandwidth overhead as well as the capability of the SIM for imaging the complex scene.
Rapid diagnostics of reconfigurable intelligent surfaces using space-time-coding modulation
May 06, 2025Abstract:Reconfigurable intelligent surfaces (RISs) have emerged as a key technology for shaping smart wireless environments in next-generation wireless communication systems. To support the large-scale deployment of RISs, a reliable and efficient diagnostic method is essential to ensure optimal performance. In this work, a robust and efficient approach for RIS diagnostics is proposed using a space-time coding strategy with orthogonal codes. The method encodes the reflected signals from individual RIS elements into distinct code channels, enabling the recovery of channel power at the receiving terminals for fault identification. Theoretical analysis shows that the normally functioning elements generate high power in their respective code channels, whereas the faulty elements exhibit significantly lower power. This distinction enables rapid and accurate diagnostics of elements' operational states through simple signal processing techniques. Simulation results validate the effectiveness of the proposed method, even under high fault ratios and varying reception angles. Proof-of-principle experiments on two RIS prototypes are conducted, implementing two coding strategies: direct and segmented. Experimental results in a realistic scenario confirm the reliability of the diagnostic method, demonstrating its potential for large-scale RIS deployment in future wireless communication systems and radar applications.
Fluid Antennas: Reshaping Intrinsic Properties for Flexible Radiation Characteristics in Intelligent Wireless Networks
Jan 06, 2025



Abstract:Fluid antennas present a relatively new idea for harnessing the fading and interference issues in multiple user wireless systems, such as 6G. Here, we systematically compare their unique radiation beam forming mechanism to the existing multiple-antenna systems in a wireless system. Subsequently, a unified mathematical model for fluid antennas is deduced based on the eigenmode theory. As mathematically derived from the multimode resonant theory, the spectral expansion model of any antennas which occupy variable spaces and have changeable feeding schemes can be generalized as fluid antennas. Non-liquid and liquid fluid antenna examples are presented, simulated and discussed. The symmetry or modal parity of eigenmodes is explored as an additional degree of freedom to design the fluid antennas for future wireless systems. As conceptually deduced and illustrated, the multi-dimensional and continuously adaptive ability of eigenmodes can be considered as the most fundamental intrinsic characteristic of the fluid antenna systems. It opens an uncharted area in the developments of intelligent antennas (IAs), which brings more flexibility to on-demand antenna beam null manipulating techniques for future wireless applications.
Emerging Technologies in Intelligent Metasurfaces: Shaping the Future of Wireless Communications
Nov 21, 2024Abstract:Intelligent metasurfaces have demonstrated great promise in revolutionizing wireless communications. One notable example is the two-dimensional (2D) programmable metasurface, which is also known as reconfigurable intelligent surfaces (RIS) to manipulate the wireless propagation environment to enhance network coverage. More recently, three-dimensional (3D) stacked intelligent metasurfaces (SIM) have been developed to substantially improve signal processing efficiency by directly processing analog electromagnetic signals in the wave domain. Another exciting breakthrough is the flexible intelligent metasurface (FIM), which possesses the ability to morph its 3D surface shape in response to dynamic wireless channels and thus achieve diversity gain. In this paper, we provide a comprehensive overview of these emerging intelligent metasurface technologies. We commence by examining recent experiments of RIS and exploring its applications from four perspectives. Furthermore, we delve into the fundamental principles underlying SIM, discussing relevant prototypes as well as their applications. Numerical results are also provided to illustrate the potential of SIM for analog signal processing. Finally, we review the state-of-the-art of FIM technology, discussing its impact on wireless communications and identifying the key challenges of integrating FIMs into wireless networks.
A physics-based perspective for understanding and utilizing spatial resources of wireless channels
Oct 08, 2024



Abstract:To satisfy the increasing demands for transmission rates of wireless communications, it is necessary to use spatial resources of electromagnetic (EM) waves. In this context, EM information theory (EIT) has become a hot topic by integrating the theoretical framework of deterministic mathematics and stochastic statistics to explore the transmission mechanisms of continuous EM waves. However, the previous studies were primarily focused on frame analysis, with limited exploration of practical applications and a comprehensive understanding of its essential physical characteristics. In this paper, we present a three-dimensional (3-D) line-of-sight channel capacity formula that captures the vector EM physics and accommodates both near- and far-field scenes. Based on the rigorous mathematical equation and the physical mechanism of fast multipole expansion, a channel model is established, and the finite angular spectral bandwidth feature of scattered waves is revealed. To adapt to the feature of the channel, an optimization problem is formulated for determining the mode currents on the transmitter, aiming to obtain the optimal design of the precoder and combiner. We make comprehensive analyses to investigate the relationship among the spatial degree of freedom, noise, and transmitted power, thereby establishing a rigorous upper bound of channel capacity. A series of simulations are conducted to validate the theoretical model and numerical method. This work offers a novel perspective and methodology for understanding and leveraging EIT, and provides a theoretical foundation for the design and optimization of future wireless communications.
Pilot-Based SFO Estimation for Bistatic Integrated Sensing and Communication
Jul 10, 2024Abstract:Enabling bistatic radar sensing within the context of integrated sensing and communication (ISAC) for future sixth generation mobile networks demands strict synchronization accuracy, which is particularly challenging to be achieved with over-the-air synchronization. Existing algorithms handle time and frequency offsets adequately, but provide insufficiently accurate sampling frequency offset (SFO) estimates that result in degradation of obtained radar images in the form of signal-to-noise ratio loss and migration of range and Doppler shift. This article introduces an SFO estimation algorithm named tilt inference of time offset (TITO) for orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing (OFDM)-based ISAC. Using available pilot subcarriers, TITO obtains channel impulse response estimates and extracts information on the SFO-induced delay migration to a dominant reference path with constant range, Doppler shift, and angle between transmit and receive ISAC nodes. TITO then adaptively selects the delay estimates that are only negligibly impaired by SFO-induced intersymbol interference, ultimately employing them to estimate the SFO. Assuming a scenario without a direct line-of-sight (LoS) between the aforementioned transmitting and receiving ISAC nodes, a system concept with a relay reflective intelligent surface (RIS) is used to create the aforementioned reference path is proposed. Besides a mathematical derivation of accuracy bounds, simulation and measurements at 26.2 GHz are presented to demonstrate TITO's superiority over existing methods in terms of SFO estimation accuracy and robustness.
Electromagnetic Property Sensing Based on Diffusion Model in ISAC System
Jul 03, 2024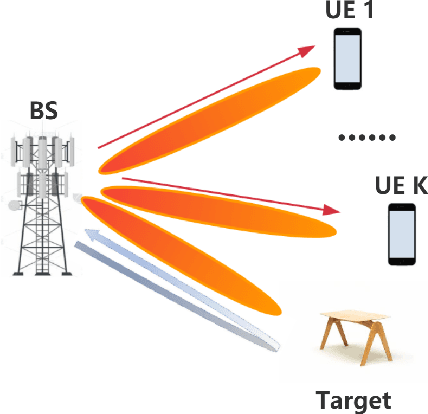
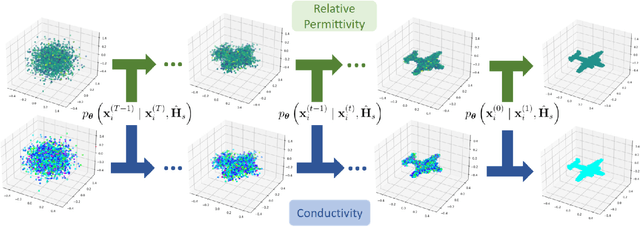
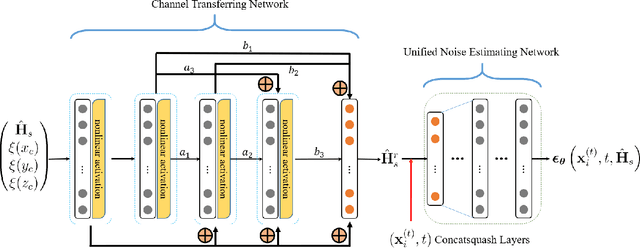
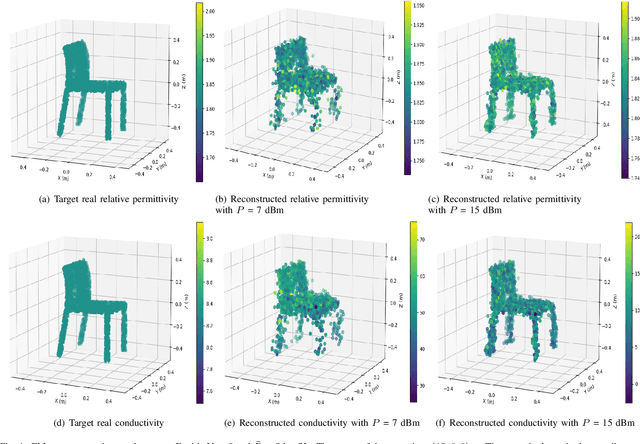
Abstract:Integrated sensing and communications (ISAC) has opened up numerous game-changing opportunities for future wireless systems. In this paper, we develop a novel ISAC scheme that utilizes the diffusion model to sense the electromagnetic (EM) property of the target in a predetermined sensing area. Specifically, we first estimate the sensing channel by using both the communications and the sensing signals echoed back from the target. Then we employ the diffusion model to generate the point cloud that represents the target and thus enables 3D visualization of the target's EM property distribution. In order to minimize the mean Chamfer distance (MCD) between the ground truth and the estimated point clouds, we further design the communications and sensing beamforming matrices under the constraint of a maximum transmit power and a minimum communications achievable rate for each user equipment (UE). Simulation results demonstrate the efficacy of the proposed method in achieving high-quality reconstruction of the target's shape, relative permittivity, and conductivity. Besides, the proposed method can sense the EM property of the target effectively in any position of the sensing area.
Integrating sensing and communications: Simultaneously transmitting and reflecting digital coding metasurfaces
Jun 16, 2024



Abstract:Wireless networks are undergoing a transformative shift, driven by the crucial factors of cost effectiveness and sustainability. Digital coding metasurfaces (DCMs) might play a key role in realizing cost-effective digital modulators by harnessing energy embedded in electromagnetic waves traversing through the air. Integrated sensing and communication (ISAC) optimize power and spectral resources by combining sensing and communication functionalities on a shared hardware platform. This article presents a tutorial-style overview of the applications and advantages of DCMs in ISAC-based networks. Emphasis is placed on the dual-functionality of ISAC, necessitating the design of DCMs with simultaneously transmitting and reflecting (STAR) capabilities for comprehensive space control. Additionally, the article explores key signal processing challenges and outlines future research directions stemming from the convergence of ISAC and emerging STAR-DCM technologies.
Holography inspired self-controlled reconfigurable intelligent surface
Mar 24, 2024



Abstract:Among various promising candidate technologies for the sixth-generation (6G) wireless communications, recent advances in microwave metasurfaces have sparked a new research area of reconfigurable intelligent surfaces (RISs). By controllably reprogramming the wireless propagation channel, RISs are envisioned to achieve low-cost wireless capacity boosting, coverage extension, and enhanced energy efficiency. To reprogram the channel, each meta-atom on RIS needs an external control signal, which is usually generated by base station (BS). However, BS-controlled RISs require complicated control cables, which hamper their massive deployments. Here, we eliminate the need for BS control by proposing a self-controlled RIS (SC-RIS), which is inspired by the optical holography principle. Different from the existing BS-controlled RISs, each meta-atom of SC-RIS is integrated with an additional power detector for holographic recording. By applying the classical Fourier-transform processing to the measured hologram, SC-RIS is capable of retrieving the user's channel state information required for beamforming, thus enabling autonomous RIS beamforming without control cables. Owing to this WiFi-like plug-and-play capability without the BS control, SC-RISs are expected to enable easy and massive deployments in the future 6G systems.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge