Yueheng Li
Analysis of Sensing in OFDM-based ISAC under the Influence of Sampling Jitter
Jan 21, 2026Abstract:To enable integrated sensing and communication (ISAC) in cellular networks, a wide range of additional requirements and challenges are either imposed or become more critical. One such impairment is sampling jitter (SJ), which arises due to imperfections in the sampling instants of the clocks of digital-to-analog converters (DACs) and analog-to-digital converters (ADCs). While SJ is already well studied for communication systems based on orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing (OFDM), which is expected to be the waveform of choice for most sixth-generation (6G) scenarios where ISAC could be possible, the implications of SJ on the OFDM-based radar sensing must still be thoroughly analyzed. Considering that phase-locked loop (PLL)-based oscillators are used to derive sampling clocks, which leads to colored SJ, i.e., SJ with non-flat power spectral density, this article analyzes the resulting distortion of the adopted digital constellation modulation and sensing performance in OFDM-based ISAC for both baseband (BB) and bandpass (BP) sampling strategies and different oversampling factors. For BB sampling, it is seen that SJ induces intercarrier interference (ICI), while for BP sampling, it causes carrier phase error and more severe ICI due to a phase noise-like effect at the digital intermediate frequency. Obtained results for a single-input single-output OFDM-based ISAC system with various OFDM signal parameterizations demonstrate that SJ-induced degradation becomes non-negligible for both BB and BP sampling only for root mean square (RMS) SJ values above 10^-11 s at both DAC and ADC, which corresponds to 0.5*10^-2 times the considered critical sampling period without oversampling. Based on the achieved results, it can be concluded that state-of-the-art hardware enables sufficient communication and sensing robustness against SJ, as RMS SJ values in the femtosecond range can be achieved.
Multi-RIS Deployment Optimization for mmWave ISAC Systems in Real-World Environments
Aug 10, 2025Abstract:Reconfigurable intelligent surface-assisted integrated sensing and communication (RIS-ISAC) presents a promising system architecture to leverage the wide bandwidth available at millimeter-wave (mmWave) frequencies, while mitigating severe signal propagation losses and reducing infrastructure costs. To enhance ISAC functionalities in the future air-ground integrated network applications, RIS deployment must be carefully designed and evaluated, which forms the core motivation of this paper. To ensure practical relevance, a multi-RIS-ISAC system is established, with its signal model at mmWave frequencies demonstrated using ray-launching calibrated to real-world environments. On this basis, an energy-efficiency-driven optimization problem is formulated to minimize the multi-RIS size-to-coverage sum ratio, comprehensively considering real-world RIS deployment constraints, positions, orientations, as well as ISAC beamforming strategies at both the base station and the RISs. To solve the resulting non-convex mixed-integer problem, a simplified reformulation based on equivalent gain scaling method is introduced. A two-step iterative algorithm is then proposed, in which the deployment parameters are determined under fixed RIS positions in the first step, and the RIS position set is updated in the second step to progressively approach the optimum solution. Simulation results based on realistic parameter benchmarks present that the optimized RISs deployment significantly enhances communication coverage and sensing accuracy with the minimum RIS sizes, outperforming existing approaches.
Multi-Agent Guided Policy Optimization
Jul 24, 2025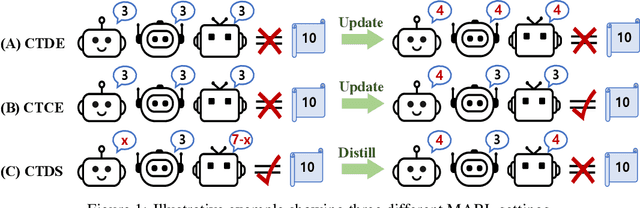
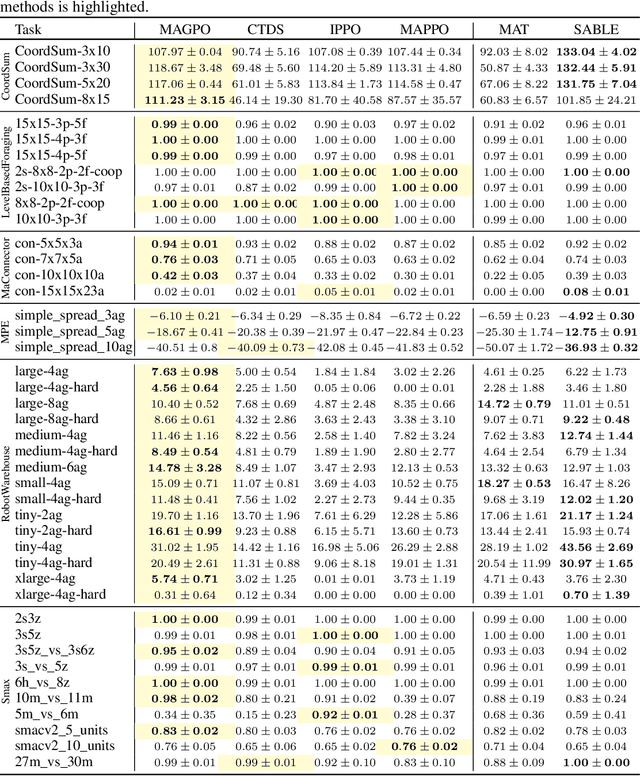
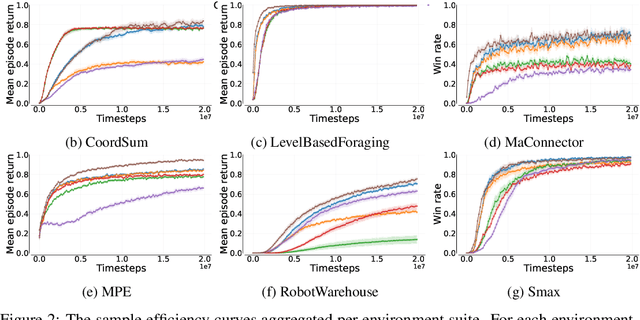
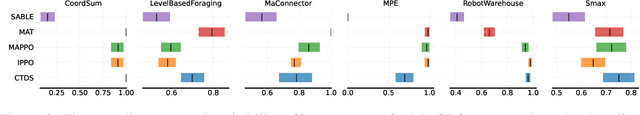
Abstract:Due to practical constraints such as partial observability and limited communication, Centralized Training with Decentralized Execution (CTDE) has become the dominant paradigm in cooperative Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning (MARL). However, existing CTDE methods often underutilize centralized training or lack theoretical guarantees. We propose Multi-Agent Guided Policy Optimization (MAGPO), a novel framework that better leverages centralized training by integrating centralized guidance with decentralized execution. MAGPO uses an auto-regressive joint policy for scalable, coordinated exploration and explicitly aligns it with decentralized policies to ensure deployability under partial observability. We provide theoretical guarantees of monotonic policy improvement and empirically evaluate MAGPO on 43 tasks across 6 diverse environments. Results show that MAGPO consistently outperforms strong CTDE baselines and matches or surpasses fully centralized approaches, offering a principled and practical solution for decentralized multi-agent learning. Our code and experimental data can be found in https://github.com/liyheng/MAGPO.
Guided Policy Optimization under Partial Observability
May 21, 2025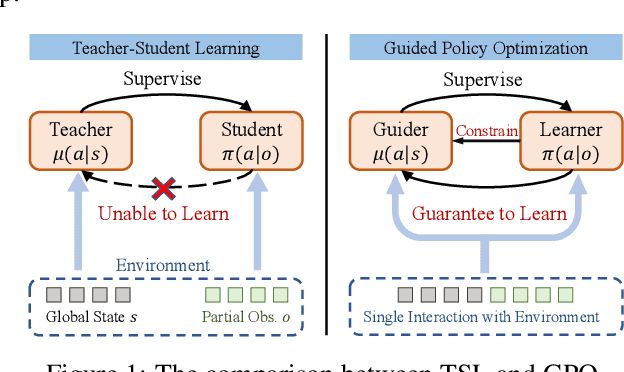
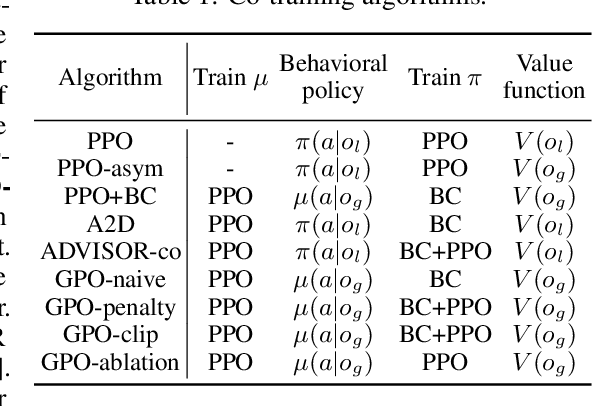
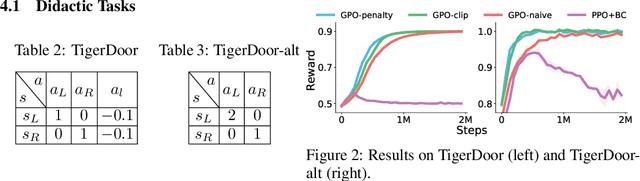
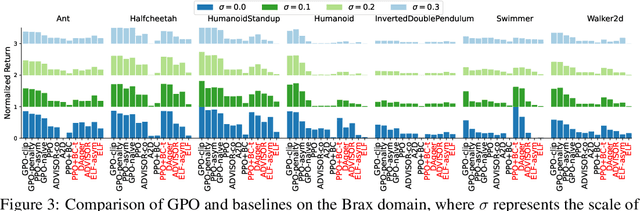
Abstract:Reinforcement Learning (RL) in partially observable environments poses significant challenges due to the complexity of learning under uncertainty. While additional information, such as that available in simulations, can enhance training, effectively leveraging it remains an open problem. To address this, we introduce Guided Policy Optimization (GPO), a framework that co-trains a guider and a learner. The guider takes advantage of privileged information while ensuring alignment with the learner's policy that is primarily trained via imitation learning. We theoretically demonstrate that this learning scheme achieves optimality comparable to direct RL, thereby overcoming key limitations inherent in existing approaches. Empirical evaluations show strong performance of GPO across various tasks, including continuous control with partial observability and noise, and memory-based challenges, significantly outperforming existing methods.
Emergent Specialization: Rare Token Neurons in Language Models
May 19, 2025Abstract:Large language models struggle with representing and generating rare tokens despite their importance in specialized domains. In this study, we identify neuron structures with exceptionally strong influence on language model's prediction of rare tokens, termed as rare token neurons, and investigate the mechanism for their emergence and behavior. These neurons exhibit a characteristic three-phase organization (plateau, power-law, and rapid decay) that emerges dynamically during training, evolving from a homogeneous initial state to a functionally differentiated architecture. In the activation space, rare token neurons form a coordinated subnetwork that selectively co-activates while avoiding co-activation with other neurons. This functional specialization potentially correlates with the development of heavy-tailed weight distributions, suggesting a statistical mechanical basis for emergent specialization.
System Concept and Demonstration of Bistatic MIMO-OFDM-based ISAC
Apr 10, 2025Abstract:In future sixth-generation (6G) mobile networks, radar sensing is expected to be offered as an additional service to its original purpose of communication. Merging these two functions results in integrated sensing and communication (ISAC) systems. In this context, bistatic ISAC appears as a possibility to exploit the distributed nature of cellular networks while avoiding highly demanding hardware requirements such as full-duplex operation. Recent studies have introduced strategies to perform required synchronization and data exchange between nodes for bistatic ISAC operation, based on orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing (OFDM), however, only for single-input single-output architectures. In this article, a system concept for a bistatic multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO)-OFDM-based ISAC system with beamforming at both transmitter and receiver is proposed, and a distribution synchronization concept to ensure coherence among the different receive channels for direction-of-arrival estimation is presented. After a discussion on the ISAC processing chain, including relevant aspects for practical deployments such as transmitter digital pre-distortion and receiver calibration, a 4x8 MIMO measurement setup at 27.5 GHz and results are presented to validate the proposed system and distribution synchronization concepts.
Joint BS Deployment and Power Optimization for Minimum EMF Exposure with RL in Real-World Based Urban Scenario
Apr 07, 2025Abstract:Conventional base station (BS) deployments typically prioritize coverage, quality of service (QoS), or cost reduction, often overlooking electromagnetic field (EMF) exposure. Whereas EMF exposure triggers significant public concern due to its potential health implications, making it crucial to address when deploying BS in densely populated areas. To this end, this paper addresses minimizing average EMF exposure while maintaining coverage in a 3D urban scenario by jointly optimizing BS deployment and power. To address this, firstly, accurate EMF prediction is essential, as traditional empirical models lack the required accuracy, necessitating a deterministic channel model. A novel least-time shoot-and-bounce ray (SBR) ray-launching (RL) algorithm is therefore developed to overcome several limitations of current simulators and is validated with real-world measurements. Secondly, to further reduce computational complexity, unlike using a fixed grid size to discretize the target area, the adaptive grid refinement (AGR) algorithm is designed with a flexible grid to predict the overall EMF exposure. Finally, based on the EMF exposure predictions, the Nelder-Mead (NM) method is used in the joint optimization, and urban user equipment (UE) distributions are incorporated to better reflect real-world conditions. When evaluating the benefits of the whole process, the results are compared against using empirical channel models, revealing notable differences and underestimation of EMF exposure that highlight the importance of considering real-world scenario.
On the Sensing Performance of OFDM-based ISAC under the Influence of Oscillator Phase Noise
Oct 17, 2024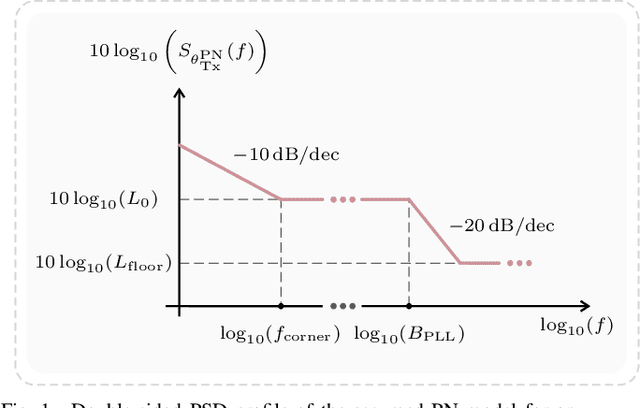
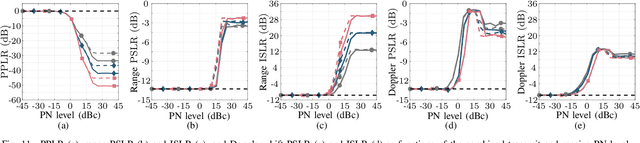
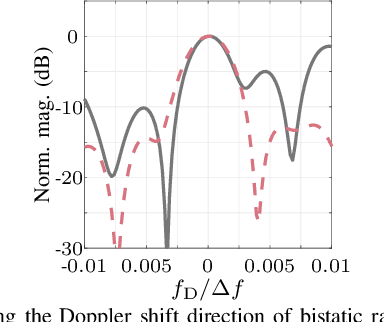
Abstract:Integrated sensing and communication (ISAC) is a novel capability expected for sixth generation (6G) cellular networks. To that end, several challenges must be addressed to enable both mono- and bistatic sensing in existing deployments. A common impairment in both architectures is oscillator phase noise (PN), which not only degrades communication performance, but also severely impairs radar sensing. To enable a broader understanding of orthogonal-frequency division multiplexing (OFDM)-based sensing impaired by PN, this article presents an analysis of sensing peformance in OFDM-based ISAC for different waveform parameter choices and settings in both mono- and bistatic architectures. In this context, the distortion of the adopted digital constellation modulation is analyzed and the resulting PN-induced effects in range-Doppler radar images are investigated both without and with PN compensation. These effects include peak power loss of target reflections and higher sidelobe levels, especially in the Doppler shift direction. In the conducted analysis, these effects are measured by the peak power loss ratio, peak-to-sidelobe level ratio, and integrated sidelobe level ratio parameters, the two latter being evaluated in both range and Doppler shift directions. In addition, the signal-to-interference ratio is analyzed to allow not only quantifying the distortion of a target reflection, but also measuring the interference floor level in a radar image. The achieved results allow to quantify not only the PN-induced impairments to a single target, but also how the induced degradation may impair the sensing performance of OFDM-based ISAC systems in multi-target scenarios.
Pilot-Based SFO Estimation for Bistatic Integrated Sensing and Communication
Jul 10, 2024Abstract:Enabling bistatic radar sensing within the context of integrated sensing and communication (ISAC) for future sixth generation mobile networks demands strict synchronization accuracy, which is particularly challenging to be achieved with over-the-air synchronization. Existing algorithms handle time and frequency offsets adequately, but provide insufficiently accurate sampling frequency offset (SFO) estimates that result in degradation of obtained radar images in the form of signal-to-noise ratio loss and migration of range and Doppler shift. This article introduces an SFO estimation algorithm named tilt inference of time offset (TITO) for orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing (OFDM)-based ISAC. Using available pilot subcarriers, TITO obtains channel impulse response estimates and extracts information on the SFO-induced delay migration to a dominant reference path with constant range, Doppler shift, and angle between transmit and receive ISAC nodes. TITO then adaptively selects the delay estimates that are only negligibly impaired by SFO-induced intersymbol interference, ultimately employing them to estimate the SFO. Assuming a scenario without a direct line-of-sight (LoS) between the aforementioned transmitting and receiving ISAC nodes, a system concept with a relay reflective intelligent surface (RIS) is used to create the aforementioned reference path is proposed. Besides a mathematical derivation of accuracy bounds, simulation and measurements at 26.2 GHz are presented to demonstrate TITO's superiority over existing methods in terms of SFO estimation accuracy and robustness.
Bistatic OFDM-based ISAC with Over-the-Air Synchronization: System Concept and Performance Analysis
May 08, 2024



Abstract:Integrated sensing and communication (ISAC) has been defined as one goal for 6G mobile communication systems. In this context, this article introduces a bistatic ISAC system based on orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing (OFDM). While the bistatic architecture brings advantages such as not demanding full duplex operation with respect to the monostatic one, the need for synchronizing transmitter and receiver is imposed. In this context, this article introuces a bistatic ISAC signal processing framework where an incoming OFDM-based ISAC signal undergoes over-the-air synchronization based on preamble symbols and pilots. Afterwards, bistatic radar processing is performed using either only pilot subcarriers or the full OFDM frame. The latter approach requires estimation of the originally transmitted frame based on communication processing and therefore error-free communication, which can be achieved via appropriate channel coding. The performance and limitations of the introduced system based on both aforementioned approaches are assessed via an analysis of the impact of residual synchronization mismatches and data decoding failures on both communication and radar performances. Finally, the performed analyses are validated by proof-of-concept measurement results.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge