Zongqing Lu
Being-H0.5: Scaling Human-Centric Robot Learning for Cross-Embodiment Generalization
Jan 19, 2026Abstract:We introduce Being-H0.5, a foundational Vision-Language-Action (VLA) model designed for robust cross-embodiment generalization across diverse robotic platforms. While existing VLAs often struggle with morphological heterogeneity and data scarcity, we propose a human-centric learning paradigm that treats human interaction traces as a universal "mother tongue" for physical interaction. To support this, we present UniHand-2.0, the largest embodied pre-training recipe to date, comprising over 35,000 hours of multimodal data across 30 distinct robotic embodiments. Our approach introduces a Unified Action Space that maps heterogeneous robot controls into semantically aligned slots, enabling low-resource robots to bootstrap skills from human data and high-resource platforms. Built upon this human-centric foundation, we design a unified sequential modeling and multi-task pre-training paradigm to bridge human demonstrations and robotic execution. Architecturally, Being-H0.5 utilizes a Mixture-of-Transformers design featuring a novel Mixture-of-Flow (MoF) framework to decouple shared motor primitives from specialized embodiment-specific experts. Finally, to make cross-embodiment policies stable in the real world, we introduce Manifold-Preserving Gating for robustness under sensory shift and Universal Async Chunking to universalize chunked control across embodiments with different latency and control profiles. We empirically demonstrate that Being-H0.5 achieves state-of-the-art results on simulated benchmarks, such as LIBERO (98.9%) and RoboCasa (53.9%), while also exhibiting strong cross-embodiment capabilities on five robotic platforms.
SmoothSync: Dual-Stream Diffusion Transformers for Jitter-Robust Beat-Synchronized Gesture Generation from Quantized Audio
Jan 04, 2026Abstract:Co-speech gesture generation is a critical area of research aimed at synthesizing speech-synchronized human-like gestures. Existing methods often suffer from issues such as rhythmic inconsistency, motion jitter, foot sliding and limited multi-sampling diversity. In this paper, we present SmoothSync, a novel framework that leverages quantized audio tokens in a novel dual-stream Diffusion Transformer (DiT) architecture to synthesis holistic gestures and enhance sampling variation. Specifically, we (1) fuse audio-motion features via complementary transformer streams to achieve superior synchronization, (2) introduce a jitter-suppression loss to improve temporal smoothness, (3) implement probabilistic audio quantization to generate distinct gesture sequences from identical inputs. To reliably evaluate beat synchronization under jitter, we introduce Smooth-BC, a robust variant of the beat consistency metric less sensitive to motion noise. Comprehensive experiments on the BEAT2 and SHOW datasets demonstrate SmoothSync's superiority, outperforming state-of-the-art methods by -30.6% FGD, 10.3% Smooth-BC, and 8.4% Diversity on BEAT2, while reducing jitter and foot sliding by -62.9% and -17.1% respectively. The code will be released to facilitate future research.
UniTacHand: Unified Spatio-Tactile Representation for Human to Robotic Hand Skill Transfer
Dec 24, 2025Abstract:Tactile sensing is crucial for robotic hands to achieve human-level dexterous manipulation, especially in scenarios with visual occlusion. However, its application is often hindered by the difficulty of collecting large-scale real-world robotic tactile data. In this study, we propose to collect low-cost human manipulation data using haptic gloves for tactile-based robotic policy learning. The misalignment between human and robotic tactile data makes it challenging to transfer policies learned from human data to robots. To bridge this gap, we propose UniTacHand, a unified representation to align robotic tactile information captured by dexterous hands with human hand touch obtained from gloves. First, we project tactile signals from both human hands and robotic hands onto a morphologically consistent 2D surface space of the MANO hand model. This unification standardizes the heterogeneous data structures and inherently embeds the tactile signals with spatial context. Then, we introduce a contrastive learning method to align them into a unified latent space, trained on only 10 minutes of paired data from our data collection system. Our approach enables zero-shot tactile-based policy transfer from humans to a real robot, generalizing to objects unseen in the pre-training data. We also demonstrate that co-training on mixed data, including both human and robotic demonstrations via UniTacHand, yields better performance and data efficiency compared with using only robotic data. UniTacHand paves a path toward general, scalable, and data-efficient learning for tactile-based dexterous hands.
Universal Dexterous Functional Grasping via Demonstration-Editing Reinforcement Learning
Dec 15, 2025Abstract:Reinforcement learning (RL) has achieved great success in dexterous grasping, significantly improving grasp performance and generalization from simulation to the real world. However, fine-grained functional grasping, which is essential for downstream manipulation tasks, remains underexplored and faces several challenges: the complexity of specifying goals and reward functions for functional grasps across diverse objects, the difficulty of multi-task RL exploration, and the challenge of sim-to-real transfer. In this work, we propose DemoFunGrasp for universal dexterous functional grasping. We factorize functional grasping conditions into two complementary components - grasping style and affordance - and integrate them into an RL framework that can learn to grasp any object with any functional grasping condition. To address the multi-task optimization challenge, we leverage a single grasping demonstration and reformulate the RL problem as one-step demonstration editing, substantially enhancing sample efficiency and performance. Experimental results in both simulation and the real world show that DemoFunGrasp generalizes to unseen combinations of objects, affordances, and grasping styles, outperforming baselines in both success rate and functional grasping accuracy. In addition to strong sim-to-real capability, by incorporating a vision-language model (VLM) for planning, our system achieves autonomous instruction-following grasp execution.
GTR-Turbo: Merged Checkpoint is Secretly a Free Teacher for Agentic VLM Training
Dec 15, 2025Abstract:Multi-turn reinforcement learning (RL) for multi-modal agents built upon vision-language models (VLMs) is hampered by sparse rewards and long-horizon credit assignment. Recent methods densify the reward by querying a teacher that provides step-level feedback, e.g., Guided Thought Reinforcement (GTR) and On-Policy Distillation, but rely on costly, often privileged models as the teacher, limiting practicality and reproducibility. We introduce GTR-Turbo, a highly efficient upgrade to GTR, which matches the performance without training or querying an expensive teacher model. Specifically, GTR-Turbo merges the weights of checkpoints produced during the ongoing RL training, and then uses this merged model as a "free" teacher to guide the subsequent RL via supervised fine-tuning or soft logit distillation. This design removes dependence on privileged VLMs (e.g., GPT or Gemini), mitigates the "entropy collapse" observed in prior work, and keeps training stable. Across diverse visual agentic tasks, GTR-Turbo improves the accuracy of the baseline model by 10-30% while reducing wall-clock training time by 50% and compute cost by 60% relative to GTR.
Spatial-Aware VLA Pretraining through Visual-Physical Alignment from Human Videos
Dec 15, 2025Abstract:Vision-Language-Action (VLA) models provide a promising paradigm for robot learning by integrating visual perception with language-guided policy learning. However, most existing approaches rely on 2D visual inputs to perform actions in 3D physical environments, creating a significant gap between perception and action grounding. To bridge this gap, we propose a Spatial-Aware VLA Pretraining paradigm that performs explicit alignment between visual space and physical space during pretraining, enabling models to acquire 3D spatial understanding before robot policy learning. Starting from pretrained vision-language models, we leverage large-scale human demonstration videos to extract 3D visual and 3D action annotations, forming a new source of supervision that aligns 2D visual observations with 3D spatial reasoning. We instantiate this paradigm with VIPA-VLA, a dual-encoder architecture that incorporates a 3D visual encoder to augment semantic visual representations with 3D-aware features. When adapted to downstream robot tasks, VIPA-VLA achieves significantly improved grounding between 2D vision and 3D action, resulting in more robust and generalizable robotic policies.
Robust Motion Generation using Part-level Reliable Data from Videos
Dec 14, 2025Abstract:Extracting human motion from large-scale web videos offers a scalable solution to the data scarcity issue in character animation. However, some human parts in many video frames cannot be seen due to off-screen captures or occlusions. It brings a dilemma: discarding the data missing any part limits scale and diversity, while retaining it compromises data quality and model performance. To address this problem, we propose leveraging credible part-level data extracted from videos to enhance motion generation via a robust part-aware masked autoregression model. First, we decompose a human body into five parts and detect the parts clearly seen in a video frame as "credible". Second, the credible parts are encoded into latent tokens by our proposed part-aware variational autoencoder. Third, we propose a robust part-level masked generation model to predict masked credible parts, while ignoring those noisy parts. In addition, we contribute K700-M, a challenging new benchmark comprising approximately 200k real-world motion sequences, for evaluation. Experimental results indicate that our method successfully outperforms baselines on both clean and noisy datasets in terms of motion quality, semantic consistency and diversity. Project page: https://boyuaner.github.io/ropar-main/
Towards Proprioception-Aware Embodied Planning for Dual-Arm Humanoid Robots
Oct 09, 2025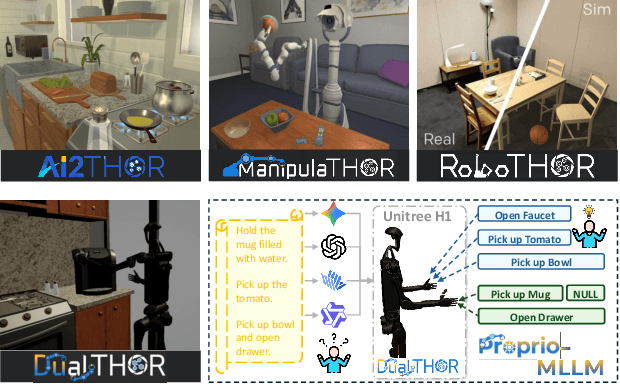


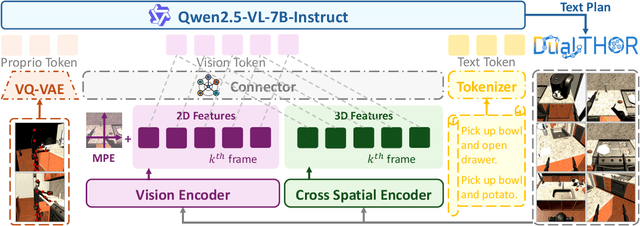
Abstract:In recent years, Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) have demonstrated the ability to serve as high-level planners, enabling robots to follow complex human instructions. However, their effectiveness, especially in long-horizon tasks involving dual-arm humanoid robots, remains limited. This limitation arises from two main challenges: (i) the absence of simulation platforms that systematically support task evaluation and data collection for humanoid robots, and (ii) the insufficient embodiment awareness of current MLLMs, which hinders reasoning about dual-arm selection logic and body positions during planning. To address these issues, we present DualTHOR, a new dual-arm humanoid simulator, with continuous transition and a contingency mechanism. Building on this platform, we propose Proprio-MLLM, a model that enhances embodiment awareness by incorporating proprioceptive information with motion-based position embedding and a cross-spatial encoder. Experiments show that, while existing MLLMs struggle in this environment, Proprio-MLLM achieves an average improvement of 19.75% in planning performance. Our work provides both an essential simulation platform and an effective model to advance embodied intelligence in humanoid robotics. The code is available at https://anonymous.4open.science/r/DualTHOR-5F3B.
DemoGrasp: Universal Dexterous Grasping from a Single Demonstration
Sep 26, 2025Abstract:Universal grasping with multi-fingered dexterous hands is a fundamental challenge in robotic manipulation. While recent approaches successfully learn closed-loop grasping policies using reinforcement learning (RL), the inherent difficulty of high-dimensional, long-horizon exploration necessitates complex reward and curriculum design, often resulting in suboptimal solutions across diverse objects. We propose DemoGrasp, a simple yet effective method for learning universal dexterous grasping. We start from a single successful demonstration trajectory of grasping a specific object and adapt to novel objects and poses by editing the robot actions in this trajectory: changing the wrist pose determines where to grasp, and changing the hand joint angles determines how to grasp. We formulate this trajectory editing as a single-step Markov Decision Process (MDP) and use RL to optimize a universal policy across hundreds of objects in parallel in simulation, with a simple reward consisting of a binary success term and a robot-table collision penalty. In simulation, DemoGrasp achieves a 95% success rate on DexGraspNet objects using the Shadow Hand, outperforming previous state-of-the-art methods. It also shows strong transferability, achieving an average success rate of 84.6% across diverse dexterous hand embodiments on six unseen object datasets, while being trained on only 175 objects. Through vision-based imitation learning, our policy successfully grasps 110 unseen real-world objects, including small, thin items. It generalizes to spatial, background, and lighting changes, supports both RGB and depth inputs, and extends to language-guided grasping in cluttered scenes.
Being-M0.5: A Real-Time Controllable Vision-Language-Motion Model
Aug 11, 2025Abstract:Human motion generation has emerged as a critical technology with transformative potential for real-world applications. However, existing vision-language-motion models (VLMMs) face significant limitations that hinder their practical deployment. We identify controllability as a main bottleneck, manifesting in five key aspects: inadequate response to diverse human commands, limited pose initialization capabilities, poor performance on long-term sequences, insufficient handling of unseen scenarios, and lack of fine-grained control over individual body parts. To overcome these limitations, we present Being-M0.5, the first real-time, controllable VLMM that achieves state-of-the-art performance across multiple motion generation tasks. Our approach is built upon HuMo100M, the largest and most comprehensive human motion dataset to date, comprising over 5 million self-collected motion sequences, 100 million multi-task instructional instances, and detailed part-level annotations that address a critical gap in existing datasets. We introduce a novel part-aware residual quantization technique for motion tokenization that enables precise, granular control over individual body parts during generation. Extensive experimental validation demonstrates Being-M0.5's superior performance across diverse motion benchmarks, while comprehensive efficiency analysis confirms its real-time capabilities. Our contributions include design insights and detailed computational analysis to guide future development of practical motion generators. We believe that HuMo100M and Being-M0.5 represent significant advances that will accelerate the adoption of motion generation technologies in real-world applications. The project page is available at https://beingbeyond.github.io/Being-M0.5.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge