Chuan Yu
DARA: Few-shot Budget Allocation in Online Advertising via In-Context Decision Making with RL-Finetuned LLMs
Jan 21, 2026Abstract:Optimizing the advertiser's cumulative value of winning impressions under budget constraints poses a complex challenge in online advertising, under the paradigm of AI-Generated Bidding (AIGB). Advertisers often have personalized objectives but limited historical interaction data, resulting in few-shot scenarios where traditional reinforcement learning (RL) methods struggle to perform effectively. Large Language Models (LLMs) offer a promising alternative for AIGB by leveraging their in-context learning capabilities to generalize from limited data. However, they lack the numerical precision required for fine-grained optimization. To address this limitation, we introduce GRPO-Adaptive, an efficient LLM post-training strategy that enhances both reasoning and numerical precision by dynamically updating the reference policy during training. Built upon this foundation, we further propose DARA, a novel dual-phase framework that decomposes the decision-making process into two stages: a few-shot reasoner that generates initial plans via in-context prompting, and a fine-grained optimizer that refines these plans using feedback-driven reasoning. This separation allows DARA to combine LLMs' in-context learning strengths with precise adaptability required by AIGB tasks. Extensive experiments on both real-world and synthetic data environments demonstrate that our approach consistently outperforms existing baselines in terms of cumulative advertiser value under budget constraints.
DecisionLLM: Large Language Models for Long Sequence Decision Exploration
Jan 15, 2026Abstract:Long-sequence decision-making, which is usually addressed through reinforcement learning (RL), is a critical component for optimizing strategic operations in dynamic environments, such as real-time bidding in computational advertising. The Decision Transformer (DT) introduced a powerful paradigm by framing RL as an autoregressive sequence modeling problem. Concurrently, Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated remarkable success in complex reasoning and planning tasks. This inspires us whether LLMs, which share the same Transformer foundation, but operate at a much larger scale, can unlock new levels of performance in long-horizon sequential decision-making problem. This work investigates the application of LLMs to offline decision making tasks. A fundamental challenge in this domain is the LLMs' inherent inability to interpret continuous values, as they lack a native understanding of numerical magnitude and order when values are represented as text strings. To address this, we propose treating trajectories as a distinct modality. By learning to align trajectory data with natural language task descriptions, our model can autoregressively predict future decisions within a cohesive framework we term DecisionLLM. We establish a set of scaling laws governing this paradigm, demonstrating that performance hinges on three factors: model scale, data volume, and data quality. In offline experimental benchmarks and bidding scenarios, DecisionLLM achieves strong performance. Specifically, DecisionLLM-3B outperforms the traditional Decision Transformer (DT) by 69.4 on Maze2D umaze-v1 and by 0.085 on AuctionNet. It extends the AIGB paradigm and points to promising directions for future exploration in online bidding.
Mem-PAL: Towards Memory-based Personalized Dialogue Assistants for Long-term User-Agent Interaction
Nov 17, 2025Abstract:With the rise of smart personal devices, service-oriented human-agent interactions have become increasingly prevalent. This trend highlights the need for personalized dialogue assistants that can understand user-specific traits to accurately interpret requirements and tailor responses to individual preferences. However, existing approaches often overlook the complexities of long-term interactions and fail to capture users' subjective characteristics. To address these gaps, we present PAL-Bench, a new benchmark designed to evaluate the personalization capabilities of service-oriented assistants in long-term user-agent interactions. In the absence of available real-world data, we develop a multi-step LLM-based synthesis pipeline, which is further verified and refined by human annotators. This process yields PAL-Set, the first Chinese dataset comprising multi-session user logs and dialogue histories, which serves as the foundation for PAL-Bench. Furthermore, to improve personalized service-oriented interactions, we propose H$^2$Memory, a hierarchical and heterogeneous memory framework that incorporates retrieval-augmented generation to improve personalized response generation. Comprehensive experiments on both our PAL-Bench and an external dataset demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed memory framework.
Enhancing Generative Auto-bidding with Offline Reward Evaluation and Policy Search
Sep 19, 2025Abstract:Auto-bidding is an essential tool for advertisers to enhance their advertising performance. Recent progress has shown that AI-Generated Bidding (AIGB), which formulates the auto-bidding as a trajectory generation task and trains a conditional diffusion-based planner on offline data, achieves superior and stable performance compared to typical offline reinforcement learning (RL)-based auto-bidding methods. However, existing AIGB methods still encounter a performance bottleneck due to their neglect of fine-grained generation quality evaluation and inability to explore beyond static datasets. To address this, we propose AIGB-Pearl (\emph{Planning with EvAluator via RL}), a novel method that integrates generative planning and policy optimization. The key to AIGB-Pearl is to construct a non-bootstrapped \emph{trajectory evaluator} to assign rewards and guide policy search, enabling the planner to optimize its generation quality iteratively through interaction. Furthermore, to enhance trajectory evaluator accuracy in offline settings, we incorporate three key techniques: (i) a Large Language Model (LLM)-based architecture for better representational capacity, (ii) hybrid point-wise and pair-wise losses for better score learning, and (iii) adaptive integration of expert feedback for better generalization ability. Extensive experiments on both simulated and real-world advertising systems demonstrate the state-of-the-art performance of our approach.
Nash Equilibrium Constrained Auto-bidding With Bi-level Reinforcement Learning
Mar 13, 2025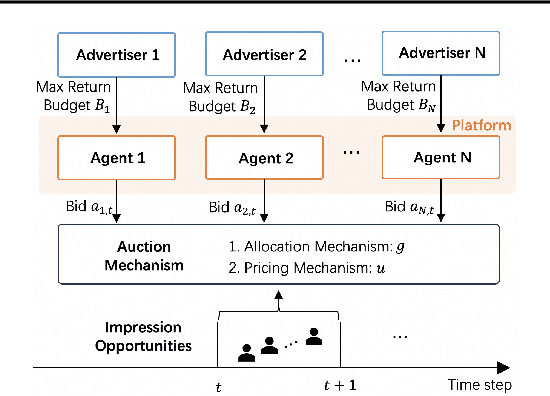
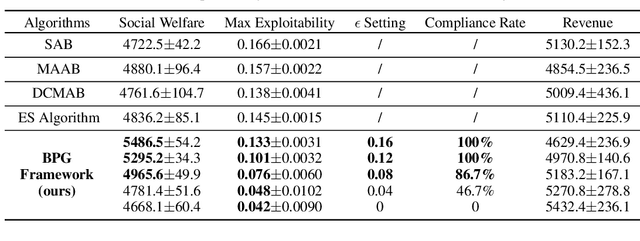
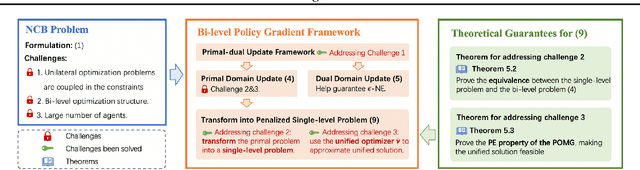
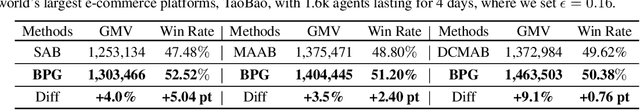
Abstract:Many online advertising platforms provide advertisers with auto-bidding services to enhance their advertising performance. However, most existing auto-bidding algorithms fail to accurately capture the auto-bidding problem formulation that the platform truly faces, let alone solve it. Actually, we argue that the platform should try to help optimize each advertiser's performance to the greatest extent -- which makes $\epsilon$-Nash Equilibrium ($\epsilon$-NE) a necessary solution concept -- while maximizing the social welfare of all the advertisers for the platform's long-term value. Based on this, we introduce the \emph{Nash-Equilibrium Constrained Bidding} (NCB), a new formulation of the auto-bidding problem from the platform's perspective. Specifically, it aims to maximize the social welfare of all advertisers under the $\epsilon$-NE constraint. However, the NCB problem presents significant challenges due to its constrained bi-level structure and the typically large number of advertisers involved. To address these challenges, we propose a \emph{Bi-level Policy Gradient} (BPG) framework with theoretical guarantees. Notably, its computational complexity is independent of the number of advertisers, and the associated gradients are straightforward to compute. Extensive simulated and real-world experiments validate the effectiveness of the BPG framework.
AuctionNet: A Novel Benchmark for Decision-Making in Large-Scale Games
Dec 14, 2024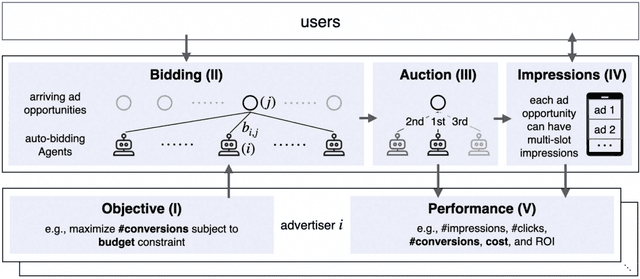
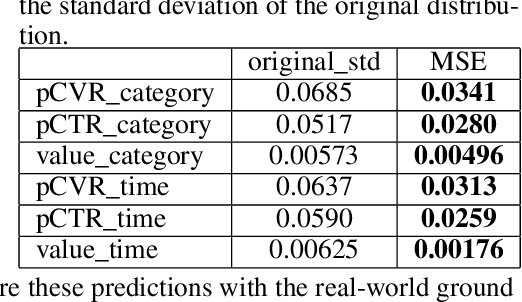
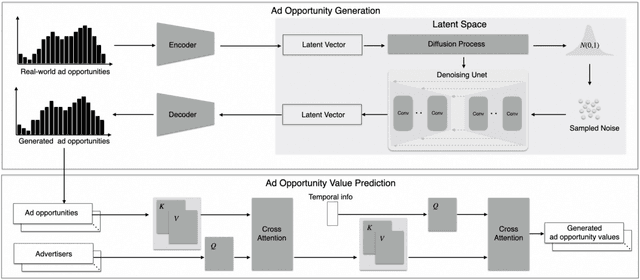
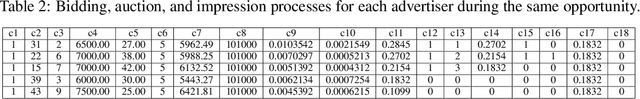
Abstract:Decision-making in large-scale games is an essential research area in artificial intelligence (AI) with significant real-world impact. However, the limited access to realistic large-scale game environments has hindered research progress in this area. In this paper, we present \textbf{AuctionNet}, a benchmark for bid decision-making in large-scale ad auctions derived from a real-world online advertising platform. AuctionNet is composed of three parts: an ad auction environment, a pre-generated dataset based on the environment, and performance evaluations of several baseline bid decision-making algorithms. More specifically, the environment effectively replicates the integrity and complexity of real-world ad auctions through the interaction of several modules: the ad opportunity generation module employs deep generative models to bridge the gap between simulated and real-world data while mitigating the risk of sensitive data exposure; the bidding module implements diverse auto-bidding agents trained with different decision-making algorithms; and the auction module is anchored in the classic Generalized Second Price (GSP) auction but also allows for customization of auction mechanisms as needed. To facilitate research and provide insights into the game environment, we have also pre-generated a substantial dataset based on the environment. The dataset contains trajectories involving 48 diverse agents competing with each other, totaling over 500 million records and occupying 80GB of storage. Performance evaluations of baseline algorithms such as linear programming, reinforcement learning, and generative models for bid decision-making are also presented as part of AuctionNet. We note that AuctionNet is applicable not only to research on bid decision-making algorithms in ad auctions but also to the general area of decision-making in large-scale games.
CUSIDE-T: Chunking, Simulating Future and Decoding for Transducer based Streaming ASR
Jul 14, 2024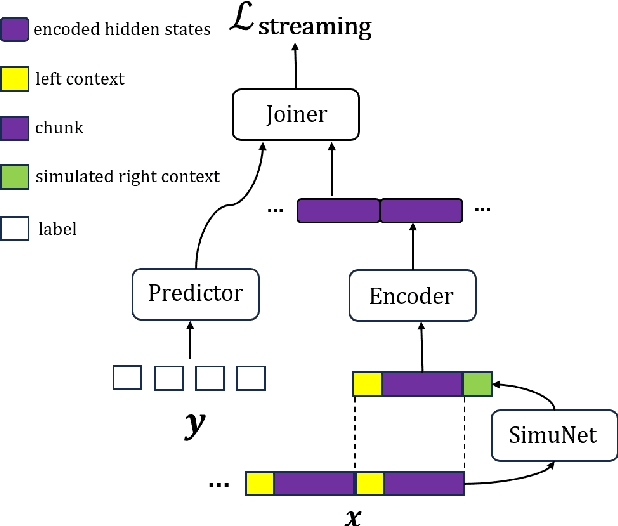
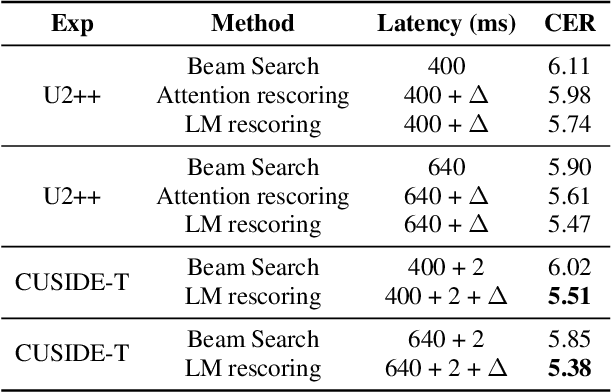
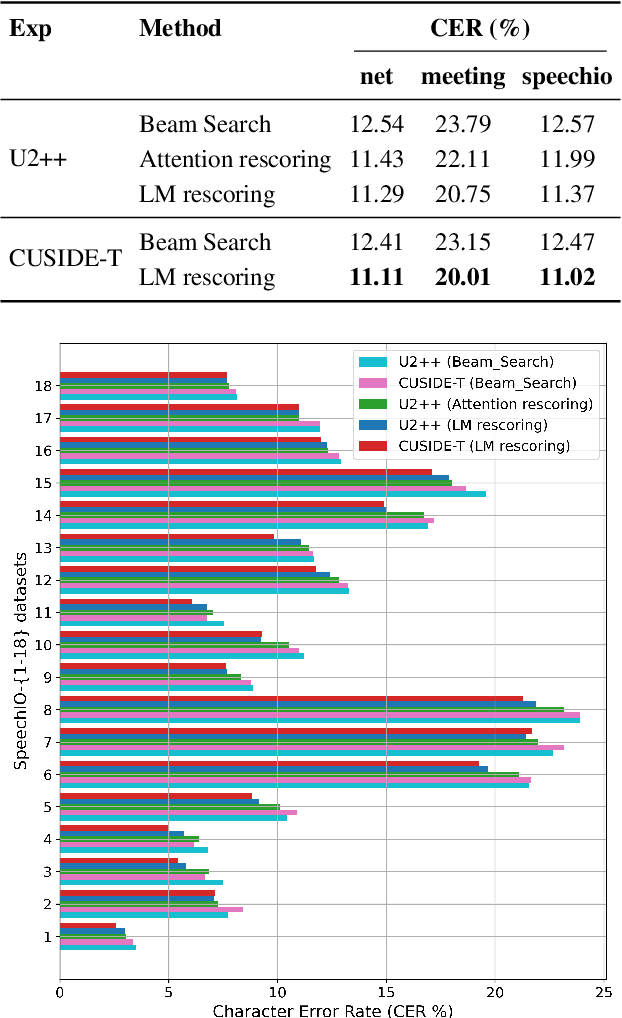
Abstract:Streaming automatic speech recognition (ASR) is very important for many real-world ASR applications. However, a notable challenge for streaming ASR systems lies in balancing operational performance against latency constraint. Recently, a method of chunking, simulating future context and decoding, called CUSIDE, has been proposed for connectionist temporal classification (CTC) based streaming ASR, which obtains a good balance between reduced latency and high recognition accuracy. In this paper, we present CUSIDE-T, which successfully adapts the CUSIDE method over the recurrent neural network transducer (RNN-T) ASR architecture, instead of being based on the CTC architecture. We also incorporate language model rescoring in CUSIDE-T to further enhance accuracy, while only bringing a small additional latency. Extensive experiments are conducted over the AISHELL-1, WenetSpeech and SpeechIO datasets, comparing CUSIDE-T and U2++ (both based on RNN-T). U2++ is an existing counterpart of chunk based streaming ASR method. It is shown that CUSIDE-T achieves superior accuracy performance for streaming ASR, with equal settings of latency.
AIGB: Generative Auto-bidding via Diffusion Modeling
May 25, 2024
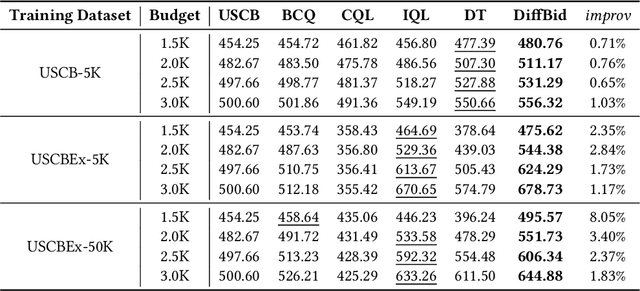
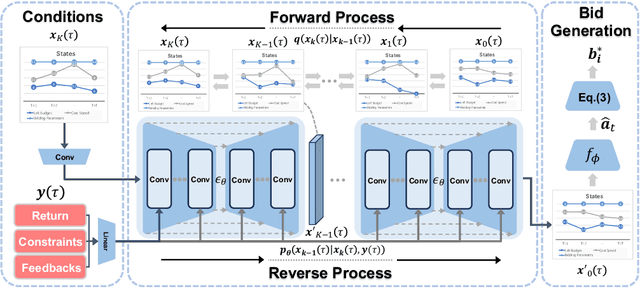
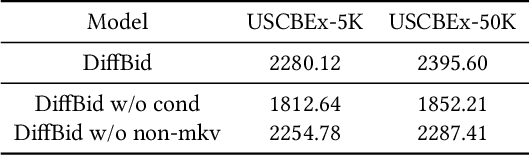
Abstract:Auto-bidding plays a crucial role in facilitating online advertising by automatically providing bids for advertisers. Reinforcement learning (RL) has gained popularity for auto-bidding. However, most current RL auto-bidding methods are modeled through the Markovian Decision Process (MDP), which assumes the Markovian state transition. This assumption restricts the ability to perform in long horizon scenarios and makes the model unstable when dealing with highly random online advertising environments. To tackle this issue, this paper introduces AI-Generated Bidding (AIGB), a novel paradigm for auto-bidding through generative modeling. In this paradigm, we propose DiffBid, a conditional diffusion modeling approach for bid generation. DiffBid directly models the correlation between the return and the entire trajectory, effectively avoiding error propagation across time steps in long horizons. Additionally, DiffBid offers a versatile approach for generating trajectories that maximize given targets while adhering to specific constraints. Extensive experiments conducted on the real-world dataset and online A/B test on Alibaba advertising platform demonstrate the effectiveness of DiffBid, achieving 2.81% increase in GMV and 3.36% increase in ROI.
MEBS: Multi-task End-to-end Bid Shading for Multi-slot Display Advertising
Mar 05, 2024



Abstract:Online bidding and auction are crucial aspects of the online advertising industry. Conventionally, there is only one slot for ad display and most current studies focus on it. Nowadays, multi-slot display advertising is gradually becoming popular where many ads could be displayed in a list and shown as a whole to users. However, multi-slot display advertising leads to different cost-effectiveness. Advertisers have the incentive to adjust bid prices so as to win the most economical ad positions. In this study, we introduce bid shading into multi-slot display advertising for bid price adjustment with a Multi-task End-to-end Bid Shading(MEBS) method. We prove the optimality of our method theoretically and examine its performance experimentally. Through extensive offline and online experiments, we demonstrate the effectiveness and efficiency of our method, and we obtain a 7.01% lift in Gross Merchandise Volume, a 7.42% lift in Return on Investment, and a 3.26% lift in ad buy count.
Trajectory-wise Iterative Reinforcement Learning Framework for Auto-bidding
Feb 23, 2024



Abstract:In online advertising, advertisers participate in ad auctions to acquire ad opportunities, often by utilizing auto-bidding tools provided by demand-side platforms (DSPs). The current auto-bidding algorithms typically employ reinforcement learning (RL). However, due to safety concerns, most RL-based auto-bidding policies are trained in simulation, leading to a performance degradation when deployed in online environments. To narrow this gap, we can deploy multiple auto-bidding agents in parallel to collect a large interaction dataset. Offline RL algorithms can then be utilized to train a new policy. The trained policy can subsequently be deployed for further data collection, resulting in an iterative training framework, which we refer to as iterative offline RL. In this work, we identify the performance bottleneck of this iterative offline RL framework, which originates from the ineffective exploration and exploitation caused by the inherent conservatism of offline RL algorithms. To overcome this bottleneck, we propose Trajectory-wise Exploration and Exploitation (TEE), which introduces a novel data collecting and data utilization method for iterative offline RL from a trajectory perspective. Furthermore, to ensure the safety of online exploration while preserving the dataset quality for TEE, we propose Safe Exploration by Adaptive Action Selection (SEAS). Both offline experiments and real-world experiments on Alibaba display advertising platform demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed method.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge