Chunjie Chen
GraspView: Active Perception Scoring and Best-View Optimization for Robotic Grasping in Cluttered Environments
Nov 06, 2025Abstract:Robotic grasping is a fundamental capability for autonomous manipulation, yet remains highly challenging in cluttered environments where occlusion, poor perception quality, and inconsistent 3D reconstructions often lead to unstable or failed grasps. Conventional pipelines have widely relied on RGB-D cameras to provide geometric information, which fail on transparent or glossy objects and degrade at close range. We present GraspView, an RGB-only robotic grasping pipeline that achieves accurate manipulation in cluttered environments without depth sensors. Our framework integrates three key components: (i) global perception scene reconstruction, which provides locally consistent, up-to-scale geometry from a single RGB view and fuses multi-view projections into a coherent global 3D scene; (ii) a render-and-score active perception strategy, which dynamically selects next-best-views to reveal occluded regions; and (iii) an online metric alignment module that calibrates VGGT predictions against robot kinematics to ensure physical scale consistency. Building on these tailor-designed modules, GraspView performs best-view global grasping, fusing multi-view reconstructions and leveraging GraspNet for robust execution. Experiments on diverse tabletop objects demonstrate that GraspView significantly outperforms both RGB-D and single-view RGB baselines, especially under heavy occlusion, near-field sensing, and with transparent objects. These results highlight GraspView as a practical and versatile alternative to RGB-D pipelines, enabling reliable grasping in unstructured real-world environments.
Generative Regression Based Watch Time Prediction for Video Recommendation: Model and Performance
Dec 28, 2024



Abstract:Watch time prediction (WTP) has emerged as a pivotal task in short video recommendation systems, designed to encapsulate user interests. Predicting users' watch times on videos often encounters challenges, including wide value ranges and imbalanced data distributions, which can lead to significant bias when directly regressing watch time. Recent studies have tried to tackle these issues by converting the continuous watch time estimation into an ordinal classification task. While these methods are somewhat effective, they exhibit notable limitations. Inspired by language modeling, we propose a novel Generative Regression (GR) paradigm for WTP based on sequence generation. This approach employs structural discretization to enable the lossless reconstruction of original values while maintaining prediction fidelity. By formulating the prediction problem as a numerical-to-sequence mapping, and with meticulously designed vocabulary and label encodings, each watch time is transformed into a sequence of tokens. To expedite model training, we introduce the curriculum learning with an embedding mixup strategy which can mitigate training-and-inference inconsistency associated with teacher forcing. We evaluate our method against state-of-the-art approaches on four public datasets and one industrial dataset. We also perform online A/B testing on Kuaishou, a leading video app with about 400 million DAUs, to demonstrate the real-world efficacy of our method. The results conclusively show that GR outperforms existing techniques significantly. Furthermore, we successfully apply GR to another regression task in recommendation systems, i.e., Lifetime Value (LTV) prediction, which highlights its potential as a novel and effective solution to general regression challenges.
Hierarchically Constrained Adaptive Ad Exposure in Feeds
May 31, 2022



Abstract:A contemporary feed application usually provides blended results of organic items and sponsored items~(ads) to users. Conventionally, ads are exposed at fixed positions. Such a static exposure strategy is inefficient due to ignoring users' personalized preferences towards ads. To this end, adaptive ad exposure has become an appealing strategy to boost the overall performance of the feed. However, existing approaches to implementing the adaptive ad exposure still suffer from several limitations: 1) they usually fall into sub-optimal solutions because of only focusing on request-level optimization without consideration of the long-term application-level performance and constraints, 2) they neglect the necessity of keeping the game-theoretical properties of ad auctions, which may lead to anarchy in bidding, and 3) they can hardly be deployed in large-scale applications due to high computational complexity. In this paper, we focus on long-term performance optimization under hierarchical constraints in feeds and formulate the adaptive ad exposure as a Dynamic Knapsack Problem. We propose an effective approach: Hierarchically Constrained Adaptive Ad Exposure~(HCA2E). We present that HCA2E possesses desired game-theoretical properties, computational efficiency, and performance robustness. Comprehensive offline and online experiments on a leading e-commerce application demonstrate the significant performance superiority of HCA2E over representative baselines. HCA2E has also been deployed on this application to serve millions of daily users.
Learning to Advertise with Adaptive Exposure via Constrained Two-Level Reinforcement Learning
Sep 10, 2018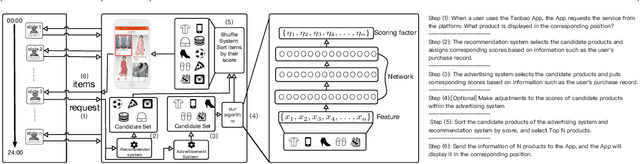
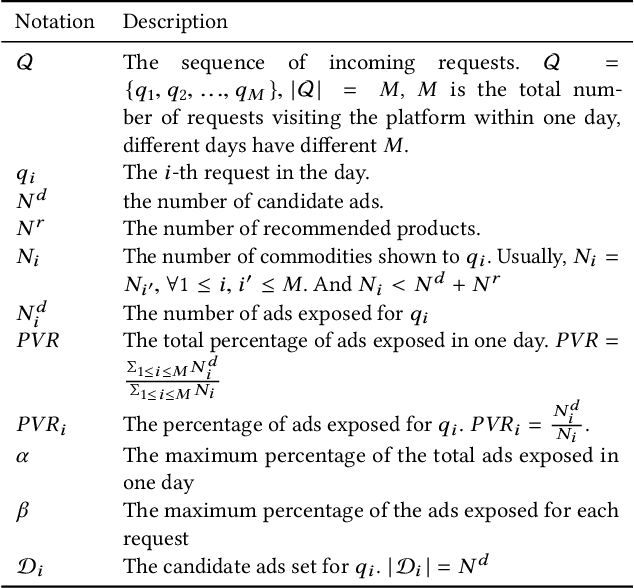
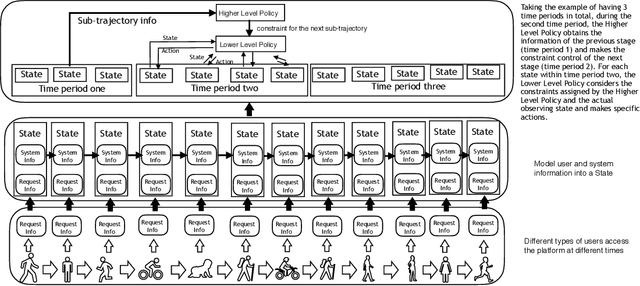
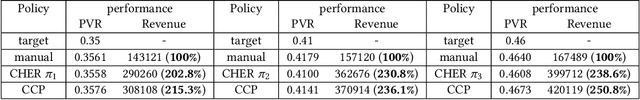
Abstract:For online advertising in e-commerce, the traditional problem is to assign the right ad to the right user on fixed ad slots. In this paper, we investigate the problem of advertising with adaptive exposure, in which the number of ad slots and their locations can dynamically change over time based on their relative scores with recommendation products. In order to maintain user retention and long-term revenue, there are two types of constraints that need to be met in exposure: query-level and day-level constraints. We model this problem as constrained markov decision process with per-state constraint (psCMDP) and propose a constrained two-level reinforcement learning to decouple the original advertising exposure optimization problem into two relatively independent sub-optimization problems. We also propose a constrained hindsight experience replay mechanism to accelerate the policy training process. Experimental results show that our method can improve the advertising revenue while satisfying different levels of constraints under the real-world datasets. Besides, the proposal of constrained hindsight experience replay mechanism can significantly improve the training speed and the stability of policy performance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge