Siqiang Wang
Deep Learning-Enabled ISAC-OTFS Pre-equalization Design for Aerial-Terrestrial Networks
Dec 06, 2024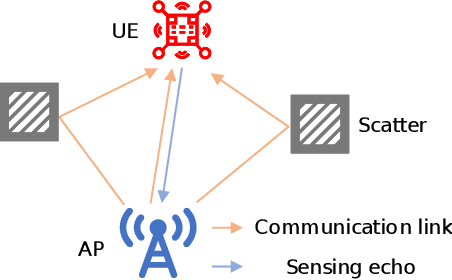
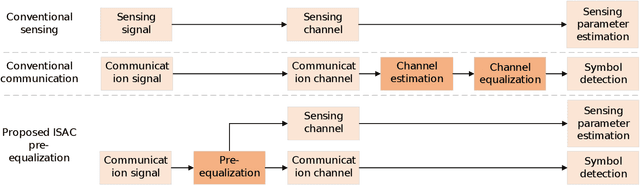
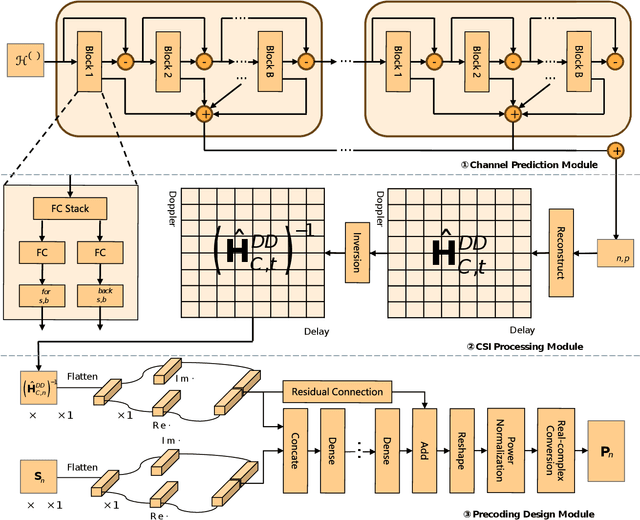
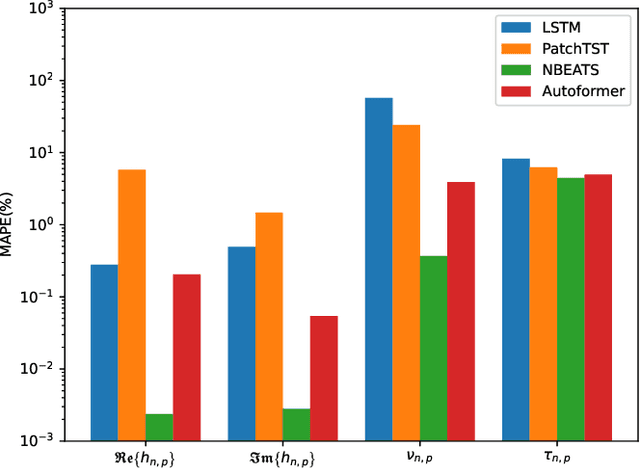
Abstract:Orthogonal time frequency space (OTFS) modulation has been viewed as a promising technique for integrated sensing and communication (ISAC) systems and aerial-terrestrial networks, due to its delay-Doppler domain transmission property and strong Doppler-resistance capability. However, it also suffers from high processing complexity at the receiver. In this work, we propose a novel pre-equalization based ISAC-OTFS transmission framework, where the terrestrial base station (BS) executes pre-equalization based on its estimated channel state information (CSI). In particular, the mean square error of OTFS symbol demodulation and Cramer-Rao lower bound of sensing parameter estimation are derived, and their weighted sum is utilized as the metric for optimizing the pre-equalization matrix. To address the formulated problem while taking the time-varying CSI into consideration, a deep learning enabled channel prediction-based pre-equalization framework is proposed, where a parameter-level channel prediction module is utilized to decouple OTFS channel parameters, and a low-dimensional prediction network is leveraged to correct outdated CSI. A CSI processing module is then used to initialize the input of the pre-equalization module. Finally, a residual-structured deep neural network is cascaded to execute pre-equalization. Simulation results show that under the proposed framework, the demodulation complexity at the receiver as well as the pilot overhead for channel estimation, are significantly reduced, while the symbol detection performance approaches those of conventional minimum mean square error equalization and perfect CSI.
Mutual Information-oriented ISAC Beamforming Design under Statistical CSI
Nov 20, 2024Abstract:Existing integrated sensing and communication (ISAC) beamforming design were mostly designed under perfect instantaneous channel state information (CSI), limiting their use in practical dynamic environments. In this paper, we study the beamforming design for multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) ISAC systems based on statistical CSI, with the weighted mutual information (MI) comprising sensing and communication perspectives adopted as the performance metric. In particular, the operator-valued free probability theory is utilized to derive the closed-form expression for the weighted MI under statistical CSI. Subsequently, an efficient projected gradient ascent (PGA) algorithm is proposed to optimize the transmit beamforming matrix with the aim of maximizing the weighted MI.Numerical results validate that the derived closed-form expression matches well with the Monte Carlo simulation results and the proposed optimization algorithm is able to improve the weighted MI significantly. We also illustrate the trade-off between sensing and communication MI.
Analysis and Optimization of Multiple-STAR-RIS Assisted MIMO-NOMA with GSVD Precoding: An Operator-Valued Free Probability Approach
Nov 14, 2024



Abstract:Among the key enabling 6G techniques, multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) and non-orthogonal multiple-access (NOMA) play an important role in enhancing the spectral efficiency of the wireless communication systems. To further extend the coverage and the capacity, the simultaneously transmitting and reflecting reconfigurable intelligent surface (STAR-RIS) has recently emerged out as a cost-effective technology. To exploit the benefit of STAR-RIS in the MIMO-NOMA systems, in this paper, we investigate the analysis and optimization of the downlink dual-user MIMO-NOMA systems assisted by multiple STAR-RISs under the generalized singular value decomposition (GSVD) precoding scheme, in which the channel is assumed to be Rician faded with the Weichselberger's correlation structure. To analyze the asymptotic information rate of the users, we apply the operator-valued free probability theory to obtain the Cauchy transform of the generalized singular values (GSVs) of the MIMO-NOMA channel matrices, which can be used to obtain the information rate by Riemann integral. Then, considering the special case when the channels between the BS and the STAR-RISs are deterministic, we obtain the closed-form expression for the asymptotic information rates of the users. Furthermore, a projected gradient ascent method (PGAM) is proposed with the derived closed-form expression to design the STAR-RISs thereby maximizing the sum rate based on the statistical channel state information. The numerical results show the accuracy of the asymptotic expression compared to the Monte Carlo simulations and the superiority of the proposed PGAM algorithm.
Scalable Virtual Valuations Combinatorial Auction Design by Combining Zeroth-Order and First-Order Optimization Method
Feb 19, 2024Abstract:Automated auction design seeks to discover empirically high-revenue and incentive-compatible mechanisms using machine learning. Ensuring dominant strategy incentive compatibility (DSIC) is crucial, and the most effective approach is to confine the mechanism to Affine Maximizer Auctions (AMAs). Nevertheless, existing AMA-based approaches encounter challenges such as scalability issues (arising from combinatorial candidate allocations) and the non-differentiability of revenue. In this paper, to achieve a scalable AMA-based method, we further restrict the auction mechanism to Virtual Valuations Combinatorial Auctions (VVCAs), a subset of AMAs with significantly fewer parameters. Initially, we employ a parallelizable dynamic programming algorithm to compute the winning allocation of a VVCA. Subsequently, we propose a novel optimization method that combines both zeroth-order and first-order techniques to optimize the VVCA parameters. Extensive experiments demonstrate the efficacy and scalability of our proposed approach, termed Zeroth-order and First-order Optimization of VVCAs (ZFO-VVCA), particularly when applied to large-scale auctions.
OTFS-based Robust MMSE Precoding Design in Over-the-air Computation
Jul 04, 2023



Abstract:Over-the-air computation (AirComp), as a data aggregation method that can improve network efficiency by exploiting the superposition characteristics of wireless channels, has received much attention recently. Meanwhile, the orthogonal time frequency space (OTFS) modulation can provide a strong Doppler resilience and facilitates reliable transmission for high-mobility communications. Hence, in this work, we investigate an OTFS-based AirComp system in the presence of time-frequency dual-selective channels. In particular, we commence from the development of a novel transmission framework for the considered system, where the pilot signal is sent together with data and the channel estimation is implemented according to the echo from the access point to the sensor, thereby reducing the overhead of channel state information (CSI) feedback. Hereafter, based on the CSI estimated from the previous frame, a robust precoding matrix aiming at minimizing mean square error in the current frame is designed, which takes into account the estimation error from the receiver noise and the outdated CSI. The simulation results demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed robust precoding scheme by comparing it with the non-robust precoding. The performance gain is more obvious in high signal-to-noise ratio in case of large channel estimation errors.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge