Zhilin Zhang
DARA: Few-shot Budget Allocation in Online Advertising via In-Context Decision Making with RL-Finetuned LLMs
Jan 21, 2026Abstract:Optimizing the advertiser's cumulative value of winning impressions under budget constraints poses a complex challenge in online advertising, under the paradigm of AI-Generated Bidding (AIGB). Advertisers often have personalized objectives but limited historical interaction data, resulting in few-shot scenarios where traditional reinforcement learning (RL) methods struggle to perform effectively. Large Language Models (LLMs) offer a promising alternative for AIGB by leveraging their in-context learning capabilities to generalize from limited data. However, they lack the numerical precision required for fine-grained optimization. To address this limitation, we introduce GRPO-Adaptive, an efficient LLM post-training strategy that enhances both reasoning and numerical precision by dynamically updating the reference policy during training. Built upon this foundation, we further propose DARA, a novel dual-phase framework that decomposes the decision-making process into two stages: a few-shot reasoner that generates initial plans via in-context prompting, and a fine-grained optimizer that refines these plans using feedback-driven reasoning. This separation allows DARA to combine LLMs' in-context learning strengths with precise adaptability required by AIGB tasks. Extensive experiments on both real-world and synthetic data environments demonstrate that our approach consistently outperforms existing baselines in terms of cumulative advertiser value under budget constraints.
DecisionLLM: Large Language Models for Long Sequence Decision Exploration
Jan 15, 2026Abstract:Long-sequence decision-making, which is usually addressed through reinforcement learning (RL), is a critical component for optimizing strategic operations in dynamic environments, such as real-time bidding in computational advertising. The Decision Transformer (DT) introduced a powerful paradigm by framing RL as an autoregressive sequence modeling problem. Concurrently, Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated remarkable success in complex reasoning and planning tasks. This inspires us whether LLMs, which share the same Transformer foundation, but operate at a much larger scale, can unlock new levels of performance in long-horizon sequential decision-making problem. This work investigates the application of LLMs to offline decision making tasks. A fundamental challenge in this domain is the LLMs' inherent inability to interpret continuous values, as they lack a native understanding of numerical magnitude and order when values are represented as text strings. To address this, we propose treating trajectories as a distinct modality. By learning to align trajectory data with natural language task descriptions, our model can autoregressively predict future decisions within a cohesive framework we term DecisionLLM. We establish a set of scaling laws governing this paradigm, demonstrating that performance hinges on three factors: model scale, data volume, and data quality. In offline experimental benchmarks and bidding scenarios, DecisionLLM achieves strong performance. Specifically, DecisionLLM-3B outperforms the traditional Decision Transformer (DT) by 69.4 on Maze2D umaze-v1 and by 0.085 on AuctionNet. It extends the AIGB paradigm and points to promising directions for future exploration in online bidding.
PosterGen: Aesthetic-Aware Paper-to-Poster Generation via Multi-Agent LLMs
Aug 24, 2025Abstract:Multi-agent systems built upon large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated remarkable capabilities in tackling complex compositional tasks. In this work, we apply this paradigm to the paper-to-poster generation problem, a practical yet time-consuming process faced by researchers preparing for conferences. While recent approaches have attempted to automate this task, most neglect core design and aesthetic principles, resulting in posters that require substantial manual refinement. To address these design limitations, we propose PosterGen, a multi-agent framework that mirrors the workflow of professional poster designers. It consists of four collaborative specialized agents: (1) Parser and Curator agents extract content from the paper and organize storyboard; (2) Layout agent maps the content into a coherent spatial layout; (3) Stylist agents apply visual design elements such as color and typography; and (4) Renderer composes the final poster. Together, these agents produce posters that are both semantically grounded and visually appealing. To evaluate design quality, we introduce a vision-language model (VLM)-based rubric that measures layout balance, readability, and aesthetic coherence. Experimental results show that PosterGen consistently matches in content fidelity, and significantly outperforms existing methods in visual designs, generating posters that are presentation-ready with minimal human refinements.
AuctionNet: A Novel Benchmark for Decision-Making in Large-Scale Games
Dec 14, 2024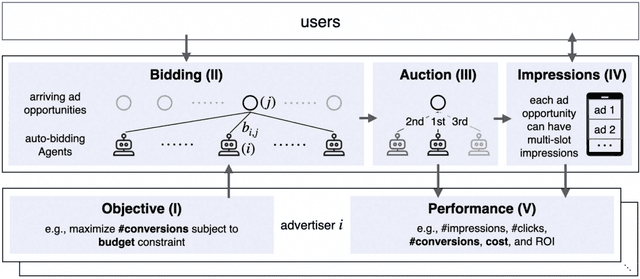
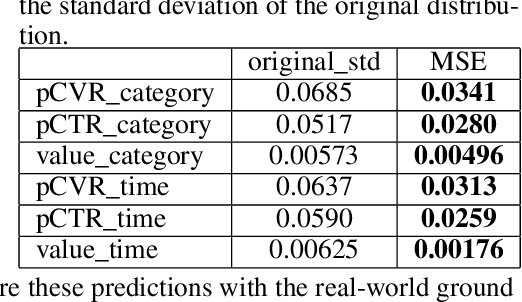
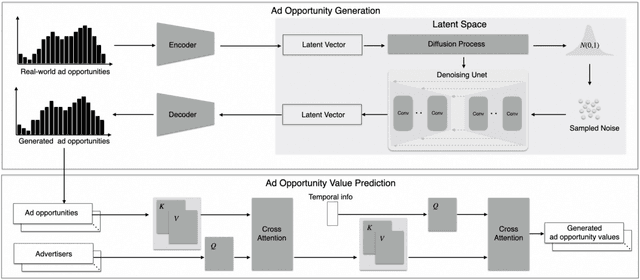
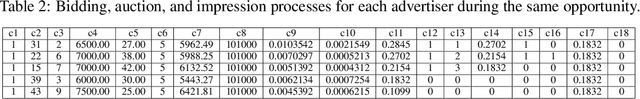
Abstract:Decision-making in large-scale games is an essential research area in artificial intelligence (AI) with significant real-world impact. However, the limited access to realistic large-scale game environments has hindered research progress in this area. In this paper, we present \textbf{AuctionNet}, a benchmark for bid decision-making in large-scale ad auctions derived from a real-world online advertising platform. AuctionNet is composed of three parts: an ad auction environment, a pre-generated dataset based on the environment, and performance evaluations of several baseline bid decision-making algorithms. More specifically, the environment effectively replicates the integrity and complexity of real-world ad auctions through the interaction of several modules: the ad opportunity generation module employs deep generative models to bridge the gap between simulated and real-world data while mitigating the risk of sensitive data exposure; the bidding module implements diverse auto-bidding agents trained with different decision-making algorithms; and the auction module is anchored in the classic Generalized Second Price (GSP) auction but also allows for customization of auction mechanisms as needed. To facilitate research and provide insights into the game environment, we have also pre-generated a substantial dataset based on the environment. The dataset contains trajectories involving 48 diverse agents competing with each other, totaling over 500 million records and occupying 80GB of storage. Performance evaluations of baseline algorithms such as linear programming, reinforcement learning, and generative models for bid decision-making are also presented as part of AuctionNet. We note that AuctionNet is applicable not only to research on bid decision-making algorithms in ad auctions but also to the general area of decision-making in large-scale games.
SentiXRL: An advanced large language Model Framework for Multilingual Fine-Grained Emotion Classification in Complex Text Environment
Nov 27, 2024
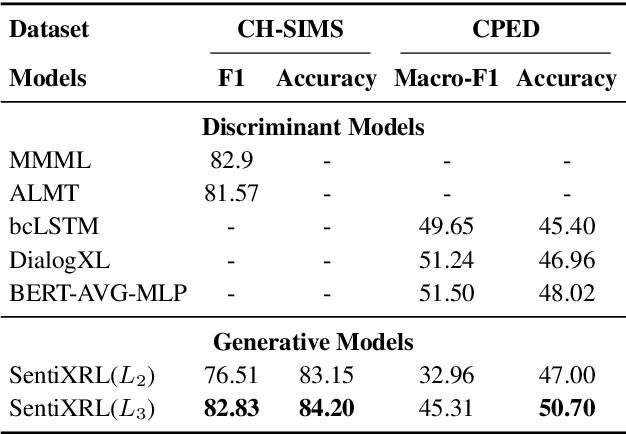


Abstract:With strong expressive capabilities in Large Language Models(LLMs), generative models effectively capture sentiment structures and deep semantics, however, challenges remain in fine-grained sentiment classification across multi-lingual and complex contexts. To address this, we propose the Sentiment Cross-Lingual Recognition and Logic Framework (SentiXRL), which incorporates two modules,an emotion retrieval enhancement module to improve sentiment classification accuracy in complex contexts through historical dialogue and logical reasoning,and a self-circulating analysis negotiation mechanism (SANM)to facilitates autonomous decision-making within a single model for classification tasks.We have validated SentiXRL's superiority on multiple standard datasets, outperforming existing models on CPED and CH-SIMS,and achieving overall better performance on MELD,Emorynlp and IEMOCAP. Notably, we unified labels across several fine-grained sentiment annotation datasets and conducted category confusion experiments, revealing challenges and impacts of class imbalance in standard datasets.
Efficient Bilinear Attention-based Fusion for Medical Visual Question Answering
Oct 28, 2024Abstract:Medical Visual Question Answering (MedVQA) has gained increasing attention at the intersection of computer vision and natural language processing. Its capability to interpret radiological images and deliver precise answers to clinical inquiries positions MedVQA as a valuable tool for supporting diagnostic decision-making for physicians and alleviating the workload on radiologists. While recent approaches focus on using unified pre-trained large models for multi-modal fusion like cross-modal Transformers, research on more efficient fusion methods remains relatively scarce within this discipline. In this paper, we introduce a novel fusion model that integrates Orthogonality loss, Multi-head attention and Bilinear Attention Network (OMniBAN) to achieve high computational efficiency and strong performance without the need for pre-training. We conduct comprehensive experiments and clarify aspects of how to enhance bilinear attention fusion to achieve performance comparable to that of large models. Experimental results show that OMniBAN outperforms traditional models on key MedVQA benchmarks while maintaining a lower computational cost, which indicates its potential for efficient clinical application in radiology and pathology image question answering.
Contrastive Adversarial Training for Unsupervised Domain Adaptation
Jul 17, 2024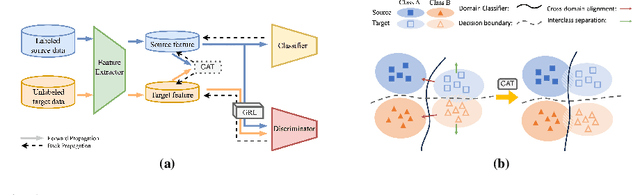
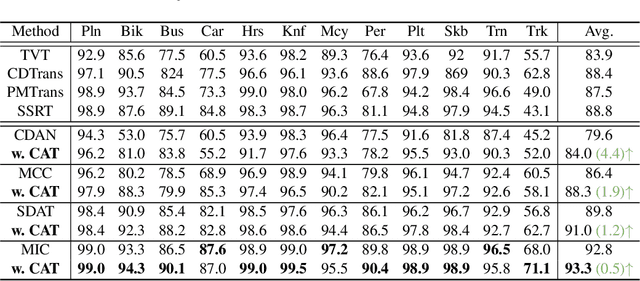
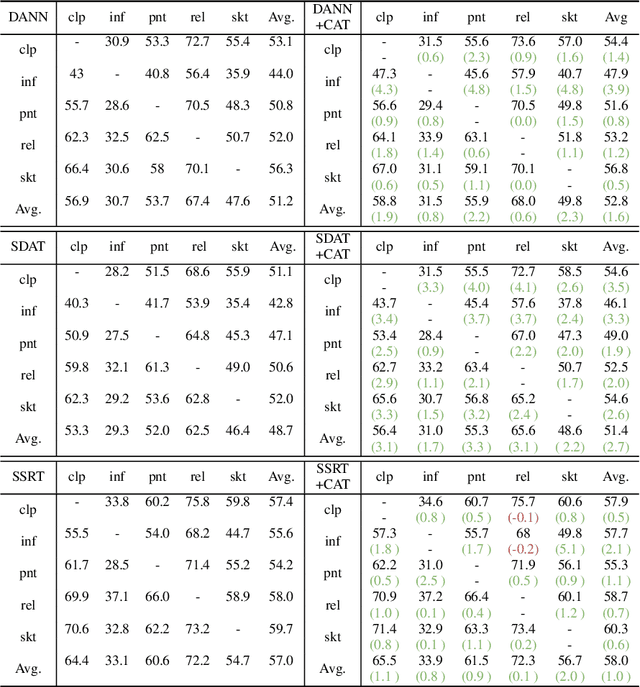
Abstract:Domain adversarial training has shown its effective capability for finding domain invariant feature representations and been successfully adopted for various domain adaptation tasks. However, recent advances of large models (e.g., vision transformers) and emerging of complex adaptation scenarios (e.g., DomainNet) make adversarial training being easily biased towards source domain and hardly adapted to target domain. The reason is twofold: relying on large amount of labelled data from source domain for large model training and lacking of labelled data from target domain for fine-tuning. Existing approaches widely focused on either enhancing discriminator or improving the training stability for the backbone networks. Due to unbalanced competition between the feature extractor and the discriminator during the adversarial training, existing solutions fail to function well on complex datasets. To address this issue, we proposed a novel contrastive adversarial training (CAT) approach that leverages the labeled source domain samples to reinforce and regulate the feature generation for target domain. Typically, the regulation forces the target feature distribution being similar to the source feature distribution. CAT addressed three major challenges in adversarial learning: 1) ensure the feature distributions from two domains as indistinguishable as possible for the discriminator, resulting in a more robust domain-invariant feature generation; 2) encourage target samples moving closer to the source in the feature space, reducing the requirement for generalizing classifier trained on the labeled source domain to unlabeled target domain; 3) avoid directly aligning unpaired source and target samples within mini-batch. CAT can be easily plugged into existing models and exhibits significant performance improvements.
AIGB: Generative Auto-bidding via Diffusion Modeling
May 25, 2024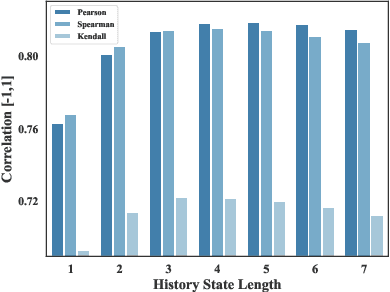
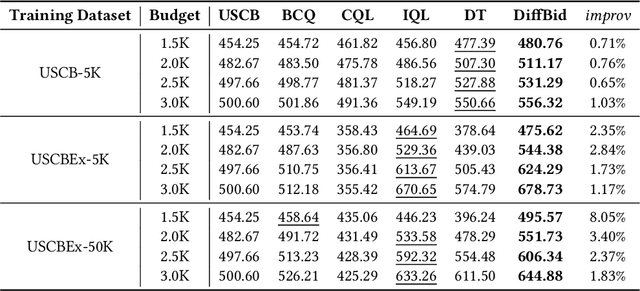
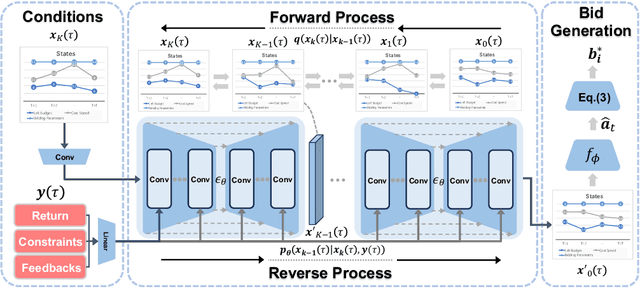
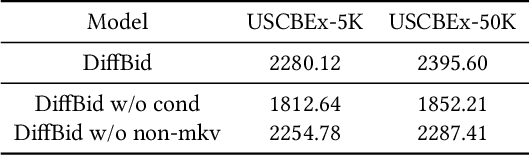
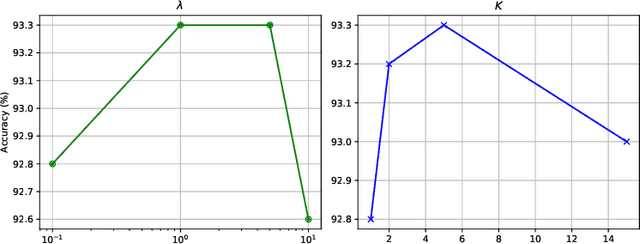
Abstract:Auto-bidding plays a crucial role in facilitating online advertising by automatically providing bids for advertisers. Reinforcement learning (RL) has gained popularity for auto-bidding. However, most current RL auto-bidding methods are modeled through the Markovian Decision Process (MDP), which assumes the Markovian state transition. This assumption restricts the ability to perform in long horizon scenarios and makes the model unstable when dealing with highly random online advertising environments. To tackle this issue, this paper introduces AI-Generated Bidding (AIGB), a novel paradigm for auto-bidding through generative modeling. In this paradigm, we propose DiffBid, a conditional diffusion modeling approach for bid generation. DiffBid directly models the correlation between the return and the entire trajectory, effectively avoiding error propagation across time steps in long horizons. Additionally, DiffBid offers a versatile approach for generating trajectories that maximize given targets while adhering to specific constraints. Extensive experiments conducted on the real-world dataset and online A/B test on Alibaba advertising platform demonstrate the effectiveness of DiffBid, achieving 2.81% increase in GMV and 3.36% increase in ROI.
Enhanced Visual Question Answering: A Comparative Analysis and Textual Feature Extraction Via Convolutions
May 01, 2024Abstract:Visual Question Answering (VQA) has emerged as a highly engaging field in recent years, attracting increasing research efforts aiming to enhance VQA accuracy through the deployment of advanced models such as Transformers. Despite this growing interest, there has been limited exploration into the comparative analysis and impact of textual modalities within VQA, particularly in terms of model complexity and its effect on performance. In this work, we conduct a comprehensive comparison between complex textual models that leverage long dependency mechanisms and simpler models focusing on local textual features within a well-established VQA framework. Our findings reveal that employing complex textual encoders is not invariably the optimal approach for the VQA-v2 dataset. Motivated by this insight, we introduce an improved model, ConvGRU, which incorporates convolutional layers to enhance the representation of question text. Tested on the VQA-v2 dataset, ConvGRU achieves better performance without substantially increasing parameter complexity.
MEBS: Multi-task End-to-end Bid Shading for Multi-slot Display Advertising
Mar 05, 2024



Abstract:Online bidding and auction are crucial aspects of the online advertising industry. Conventionally, there is only one slot for ad display and most current studies focus on it. Nowadays, multi-slot display advertising is gradually becoming popular where many ads could be displayed in a list and shown as a whole to users. However, multi-slot display advertising leads to different cost-effectiveness. Advertisers have the incentive to adjust bid prices so as to win the most economical ad positions. In this study, we introduce bid shading into multi-slot display advertising for bid price adjustment with a Multi-task End-to-end Bid Shading(MEBS) method. We prove the optimality of our method theoretically and examine its performance experimentally. Through extensive offline and online experiments, we demonstrate the effectiveness and efficiency of our method, and we obtain a 7.01% lift in Gross Merchandise Volume, a 7.42% lift in Return on Investment, and a 3.26% lift in ad buy count.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge