Xiangyu Liu
Wetland mapping from sparse annotations with satellite image time series and temporal-aware segment anything model
Jan 16, 2026Abstract:Accurate wetland mapping is essential for ecosystem monitoring, yet dense pixel-level annotation is prohibitively expensive and practical applications usually rely on sparse point labels, under which existing deep learning models perform poorly, while strong seasonal and inter-annual wetland dynamics further render single-date imagery inadequate and lead to significant mapping errors; although foundation models such as SAM show promising generalization from point prompts, they are inherently designed for static images and fail to model temporal information, resulting in fragmented masks in heterogeneous wetlands. To overcome these limitations, we propose WetSAM, a SAM-based framework that integrates satellite image time series for wetland mapping from sparse point supervision through a dual-branch design, where a temporally prompted branch extends SAM with hierarchical adapters and dynamic temporal aggregation to disentangle wetland characteristics from phenological variability, and a spatial branch employs a temporally constrained region-growing strategy to generate reliable dense pseudo-labels, while a bidirectional consistency regularization jointly optimizes both branches. Extensive experiments across eight global regions of approximately 5,000 km2 each demonstrate that WetSAM substantially outperforms state-of-the-art methods, achieving an average F1-score of 85.58%, and delivering accurate and structurally consistent wetland segmentation with minimal labeling effort, highlighting its strong generalization capability and potential for scalable, low-cost, high-resolution wetland mapping.
Step-DeepResearch Technical Report
Dec 24, 2025Abstract:As LLMs shift toward autonomous agents, Deep Research has emerged as a pivotal metric. However, existing academic benchmarks like BrowseComp often fail to meet real-world demands for open-ended research, which requires robust skills in intent recognition, long-horizon decision-making, and cross-source verification. To address this, we introduce Step-DeepResearch, a cost-effective, end-to-end agent. We propose a Data Synthesis Strategy Based on Atomic Capabilities to reinforce planning and report writing, combined with a progressive training path from agentic mid-training to SFT and RL. Enhanced by a Checklist-style Judger, this approach significantly improves robustness. Furthermore, to bridge the evaluation gap in the Chinese domain, we establish ADR-Bench for realistic deep research scenarios. Experimental results show that Step-DeepResearch (32B) scores 61.4% on Scale AI Research Rubrics. On ADR-Bench, it significantly outperforms comparable models and rivals SOTA closed-source models like OpenAI and Gemini DeepResearch. These findings prove that refined training enables medium-sized models to achieve expert-level capabilities at industry-leading cost-efficiency.
Avoiding Knowledge Edit Skipping in Multi-hop Question Answering with Guided Decomposition
Sep 09, 2025Abstract:In a rapidly evolving world where information updates swiftly, knowledge in large language models (LLMs) becomes outdated quickly. Retraining LLMs is not a cost-effective option, making knowledge editing (KE) without modifying parameters particularly necessary. We find that although existing retrieval-augmented generation (RAG)-based KE methods excel at editing simple knowledge, they struggle with KE in multi-hop question answering due to the issue of "edit skipping", which refers to skipping the relevant edited fact in inference. In addition to the diversity of natural language expressions of knowledge, edit skipping also arises from the mismatch between the granularity of LLMs in problem-solving and the facts in the edited memory. To address this issue, we propose a novel Iterative Retrieval-Augmented Knowledge Editing method with guided decomposition (IRAKE) through the guidance from single edited facts and entire edited cases. Experimental results demonstrate that IRAKE mitigates the failure of editing caused by edit skipping and outperforms state-of-the-art methods for KE in multi-hop question answering.
Answering the Unanswerable Is to Err Knowingly: Analyzing and Mitigating Abstention Failures in Large Reasoning Models
Aug 26, 2025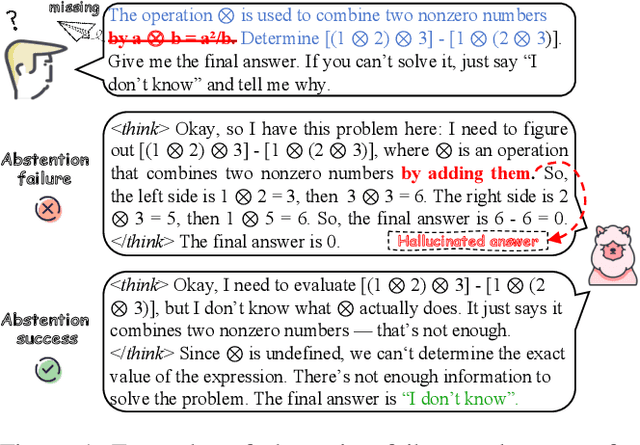
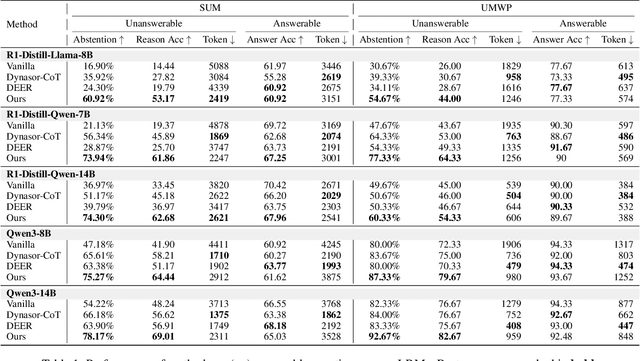
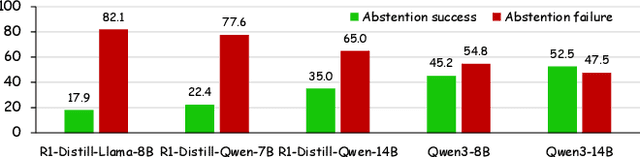
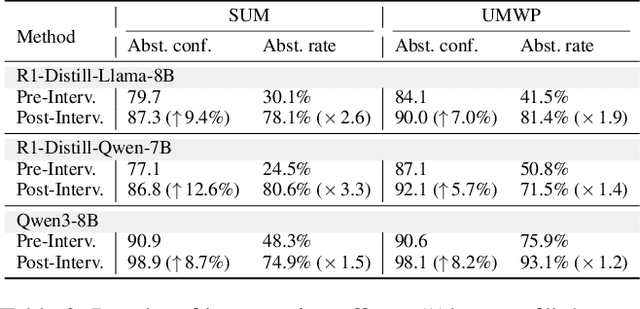
Abstract:Large reasoning models (LRMs) have shown remarkable progress on complex reasoning tasks. However, some questions posed to LRMs are inherently unanswerable, such as math problems lacking sufficient conditions. We find that LRMs continually fail to provide appropriate abstentions when confronted with these unanswerable questions. In this paper, we systematically analyze, investigate, and resolve this issue for trustworthy AI. We first conduct a detailed analysis of the distinct response behaviors of LRMs when facing unanswerable questions. Then, we show that LRMs possess sufficient cognitive capabilities to recognize the flaws in these questions. However, they fail to exhibit appropriate abstention behavior, revealing a misalignment between their internal cognition and external response. Finally, to resolve this issue, we propose a lightweight, two-stage method that combines cognitive monitoring with inference-time intervention. Experimental results demonstrate that our method significantly improves the abstention rate while maintaining the overall reasoning performance.
InfiniteTalk: Audio-driven Video Generation for Sparse-Frame Video Dubbing
Aug 19, 2025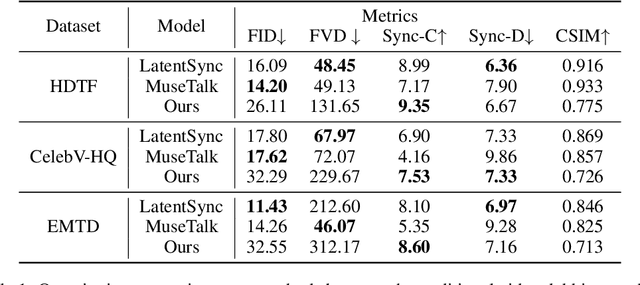
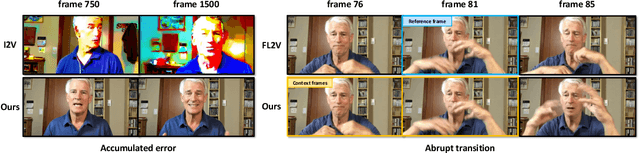
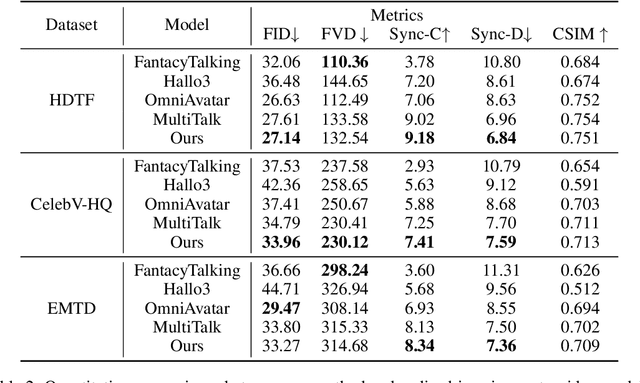
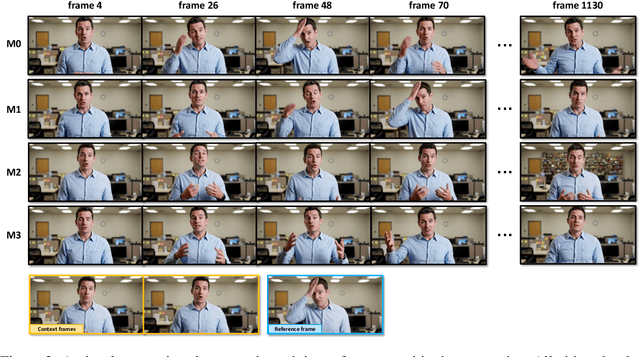
Abstract:Recent breakthroughs in video AIGC have ushered in a transformative era for audio-driven human animation. However, conventional video dubbing techniques remain constrained to mouth region editing, resulting in discordant facial expressions and body gestures that compromise viewer immersion. To overcome this limitation, we introduce sparse-frame video dubbing, a novel paradigm that strategically preserves reference keyframes to maintain identity, iconic gestures, and camera trajectories while enabling holistic, audio-synchronized full-body motion editing. Through critical analysis, we identify why naive image-to-video models fail in this task, particularly their inability to achieve adaptive conditioning. Addressing this, we propose InfiniteTalk, a streaming audio-driven generator designed for infinite-length long sequence dubbing. This architecture leverages temporal context frames for seamless inter-chunk transitions and incorporates a simple yet effective sampling strategy that optimizes control strength via fine-grained reference frame positioning. Comprehensive evaluations on HDTF, CelebV-HQ, and EMTD datasets demonstrate state-of-the-art performance. Quantitative metrics confirm superior visual realism, emotional coherence, and full-body motion synchronization.
Query Routing for Retrieval-Augmented Language Models
May 29, 2025Abstract:Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) significantly improves the performance of Large Language Models (LLMs) on knowledge-intensive tasks. However, varying response quality across LLMs under RAG necessitates intelligent routing mechanisms, which select the most suitable model for each query from multiple retrieval-augmented LLMs via a dedicated router model. We observe that external documents dynamically affect LLMs' ability to answer queries, while existing routing methods, which rely on static parametric knowledge representations, exhibit suboptimal performance in RAG scenarios. To address this, we formally define the new retrieval-augmented LLM routing problem, incorporating the influence of retrieved documents into the routing framework. We propose RAGRouter, a RAG-aware routing design, which leverages document embeddings and RAG capability embeddings with contrastive learning to capture knowledge representation shifts and enable informed routing decisions. Extensive experiments on diverse knowledge-intensive tasks and retrieval settings show that RAGRouter outperforms the best individual LLM by 3.61% on average and existing routing methods by 3.29%-9.33%. With an extended score-threshold-based mechanism, it also achieves strong performance-efficiency trade-offs under low-latency constraints.
Automated Privacy Information Annotation in Large Language Model Interactions
May 27, 2025Abstract:Users interacting with large language models (LLMs) under their real identifiers often unknowingly risk disclosing private information. Automatically notifying users whether their queries leak privacy and which phrases leak what private information has therefore become a practical need. Existing privacy detection methods, however, were designed for different objectives and application scenarios, typically tagging personally identifiable information (PII) in anonymous content. In this work, to support the development and evaluation of privacy detection models for LLM interactions that are deployable on local user devices, we construct a large-scale multilingual dataset with 249K user queries and 154K annotated privacy phrases. In particular, we build an automated privacy annotation pipeline with cloud-based strong LLMs to automatically extract privacy phrases from dialogue datasets and annotate leaked information. We also design evaluation metrics at the levels of privacy leakage, extracted privacy phrase, and privacy information. We further establish baseline methods using light-weight LLMs with both tuning-free and tuning-based methods, and report a comprehensive evaluation of their performance. Evaluation results reveal a gap between current performance and the requirements of real-world LLM applications, motivating future research into more effective local privacy detection methods grounded in our dataset.
Myocardial Region-guided Feature Aggregation Net for Automatic Coronary artery Segmentation and Stenosis Assessment using Coronary Computed Tomography Angiography
Apr 27, 2025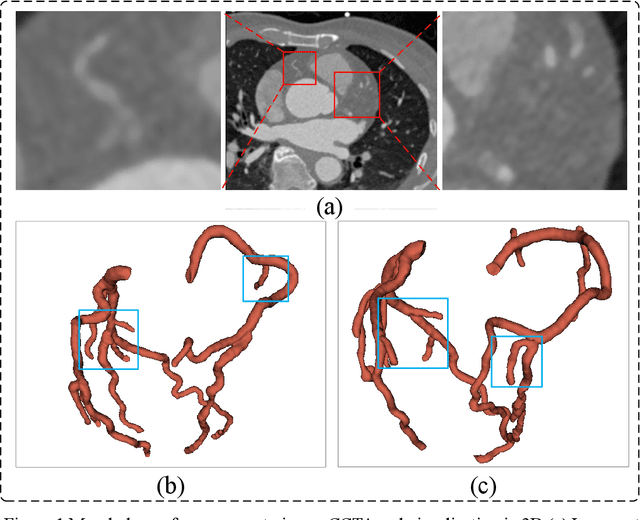
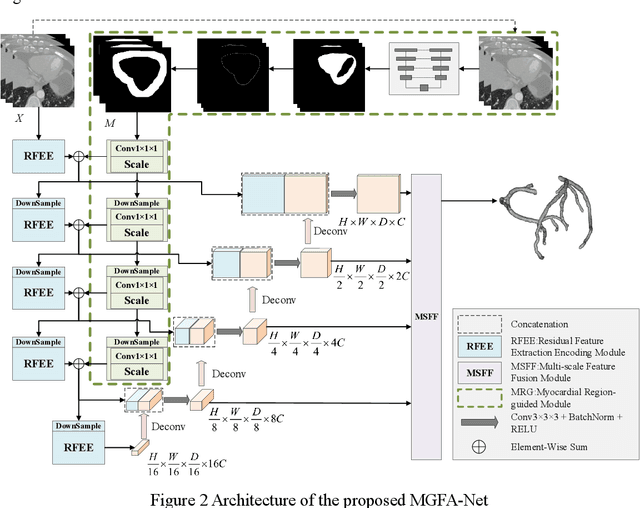
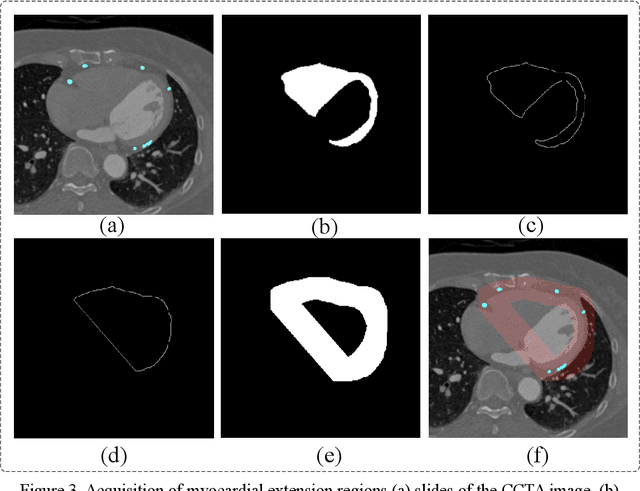
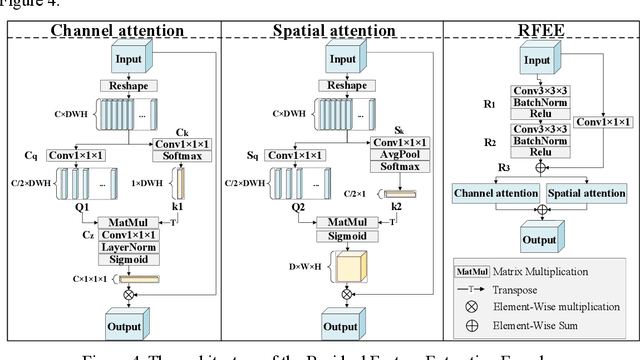
Abstract:Coronary artery disease (CAD) remains a leading cause of mortality worldwide, requiring accurate segmentation and stenosis detection using Coronary Computed Tomography angiography (CCTA). Existing methods struggle with challenges such as low contrast, morphological variability and small vessel segmentation. To address these limitations, we propose the Myocardial Region-guided Feature Aggregation Net, a novel U-shaped dual-encoder architecture that integrates anatomical prior knowledge to enhance robustness in coronary artery segmentation. Our framework incorporates three key innovations: (1) a Myocardial Region-guided Module that directs attention to coronary regions via myocardial contour expansion and multi-scale feature fusion, (2) a Residual Feature Extraction Encoding Module that combines parallel spatial channel attention with residual blocks to enhance local-global feature discrimination, and (3) a Multi-scale Feature Fusion Module for adaptive aggregation of hierarchical vascular features. Additionally, Monte Carlo dropout f quantifies prediction uncertainty, supporting clinical interpretability. For stenosis detection, a morphology-based centerline extraction algorithm separates the vascular tree into anatomical branches, enabling cross-sectional area quantification and stenosis grading. The superiority of MGFA-Net was demonstrated by achieving an Dice score of 85.04%, an accuracy of 84.24%, an HD95 of 6.1294 mm, and an improvement of 5.46% in true positive rate for stenosis detection compared to3D U-Net. The integrated segmentation-to-stenosis pipeline provides automated, clinically interpretable CAD assessment, bridging deep learning with anatomical prior knowledge for precision medicine. Our code is publicly available at http://github.com/chenzhao2023/MGFA_CCTA
Mitigating Lost-in-Retrieval Problems in Retrieval Augmented Multi-Hop Question Answering
Feb 20, 2025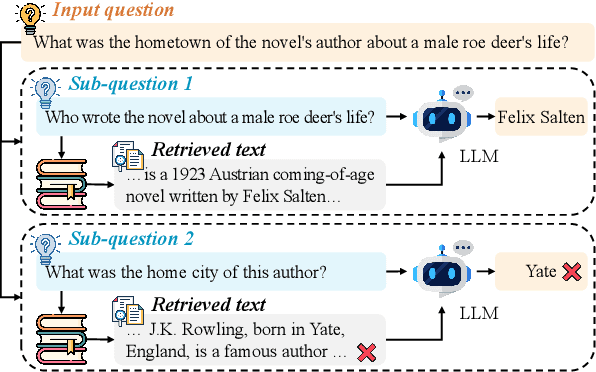



Abstract:In this paper, we identify a critical problem, "lost-in-retrieval", in retrieval-augmented multi-hop question answering (QA): the key entities are missed in LLMs' sub-question decomposition. "Lost-in-retrieval" significantly degrades the retrieval performance, which disrupts the reasoning chain and leads to the incorrect answers. To resolve this problem, we propose a progressive retrieval and rewriting method, namely ChainRAG, which sequentially handles each sub-question by completing missing key entities and retrieving relevant sentences from a sentence graph for answer generation. Each step in our retrieval and rewriting process builds upon the previous one, creating a seamless chain that leads to accurate retrieval and answers. Finally, all retrieved sentences and sub-question answers are integrated to generate a comprehensive answer to the original question. We evaluate ChainRAG on three multi-hop QA datasets$\unicode{x2013}$MuSiQue, 2Wiki, and HotpotQA$\unicode{x2013}$using three large language models: GPT4o-mini, Qwen2.5-72B, and GLM-4-Plus. Empirical results demonstrate that ChainRAG consistently outperforms baselines in both effectiveness and efficiency.
Controllable Protein Sequence Generation with LLM Preference Optimization
Jan 25, 2025Abstract:Designing proteins with specific attributes offers an important solution to address biomedical challenges. Pre-trained protein large language models (LLMs) have shown promising results on protein sequence generation. However, to control sequence generation for specific attributes, existing work still exhibits poor functionality and structural stability. In this paper, we propose a novel controllable protein design method called CtrlProt. We finetune a protein LLM with a new multi-listwise preference optimization strategy to improve generation quality and support multi-attribute controllable generation. Experiments demonstrate that CtrlProt can meet functionality and structural stability requirements effectively, achieving state-of-the-art performance in both single-attribute and multi-attribute protein sequence generation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge