Kaiqing Zhang
Post-Training LLMs as Better Decision-Making Agents: A Regret-Minimization Approach
Nov 06, 2025Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) are increasingly deployed as "agents" for decision-making (DM) in interactive and dynamic environments. Yet, since they were not originally designed for DM, recent studies show that LLMs can struggle even in basic online DM problems, failing to achieve low regret or an effective exploration-exploitation tradeoff. To address this, we introduce Iterative Regret-Minimization Fine-Tuning (Iterative RMFT), a post-training procedure that repeatedly distills low-regret decision trajectories back into the base model. At each iteration, the model rolls out multiple decision trajectories, selects the k-lowest regret ones, and fine-tunes itself on them. Unlike prior methods that (a) distill action sequences from known DM algorithms or (b) rely on manually crafted chain-of-thought templates, our approach leverages the regret metric to elicit the model's own DM ability and reasoning rationales. This reliance on model-generated reasoning avoids rigid output engineering and provides more flexible, natural-language training signals. Empirical results show that Iterative RMFT improves LLMs' DM performance across diverse models - from Transformers with numerical input/output, to open-weight LLMs, and advanced closed-weight models like GPT-4o mini. Its flexibility in output and reasoning formats enables generalization across tasks with varying horizons, action spaces, reward processes, and natural-language contexts. Finally, we provide theoretical insight showing that a single-layer Transformer under this paradigm can act as a no-regret learner in a simplified setting. Overall, Iterative RMFT offers a principled and general post-training framework for enhancing LLMs' decision-making capabilities.
MAPoRL: Multi-Agent Post-Co-Training for Collaborative Large Language Models with Reinforcement Learning
Feb 25, 2025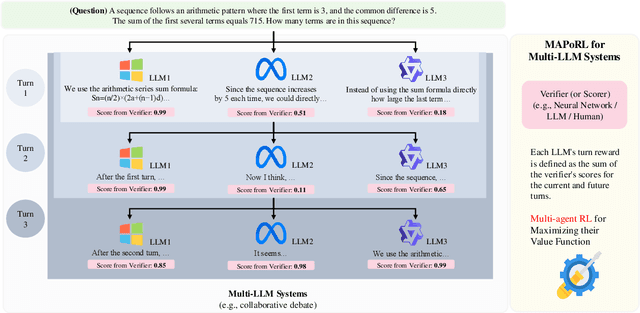
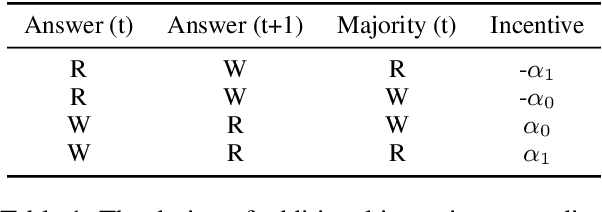
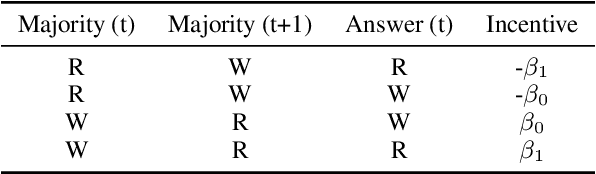
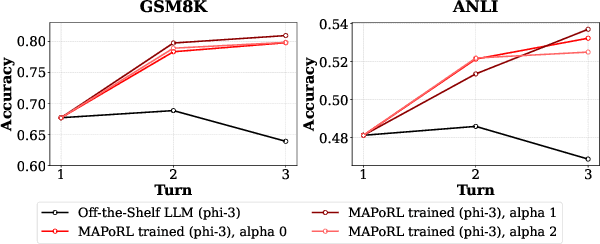
Abstract:Leveraging multiple large language models (LLMs) to build collaborative multi-agentic workflows has demonstrated significant potential. However, most previous studies focus on prompting the out-of-the-box LLMs, relying on their innate capability for collaboration, which may not improve LLMs' performance as shown recently. In this paper, we introduce a new post-training paradigm MAPoRL (Multi-Agent Post-co-training for collaborative LLMs with Reinforcement Learning), to explicitly elicit the collaborative behaviors and further unleash the power of multi-agentic LLM frameworks. In MAPoRL, multiple LLMs first generate their own responses independently and engage in a multi-turn discussion to collaboratively improve the final answer. In the end, a MAPoRL verifier evaluates both the answer and the discussion, by assigning a score that verifies the correctness of the answer, while adding incentives to encourage corrective and persuasive discussions. The score serves as the co-training reward, and is then maximized through multi-agent RL. Unlike existing LLM post-training paradigms, MAPoRL advocates the co-training of multiple LLMs together using RL for better generalization. Accompanied by analytical insights, our experiments demonstrate that training individual LLMs alone is insufficient to induce effective collaboration. In contrast, multi-agent co-training can boost the collaboration performance across benchmarks, with generalization to unseen domains.
Provable Partially Observable Reinforcement Learning with Privileged Information
Dec 01, 2024



Abstract:Partial observability of the underlying states generally presents significant challenges for reinforcement learning (RL). In practice, certain \emph{privileged information}, e.g., the access to states from simulators, has been exploited in training and has achieved prominent empirical successes. To better understand the benefits of privileged information, we revisit and examine several simple and practically used paradigms in this setting. Specifically, we first formalize the empirical paradigm of \emph{expert distillation} (also known as \emph{teacher-student} learning), demonstrating its pitfall in finding near-optimal policies. We then identify a condition of the partially observable environment, the \emph{deterministic filter condition}, under which expert distillation achieves sample and computational complexities that are \emph{both} polynomial. Furthermore, we investigate another useful empirical paradigm of \emph{asymmetric actor-critic}, and focus on the more challenging setting of observable partially observable Markov decision processes. We develop a belief-weighted asymmetric actor-critic algorithm with polynomial sample and quasi-polynomial computational complexities, in which one key component is a new provable oracle for learning belief states that preserve \emph{filter stability} under a misspecified model, which may be of independent interest. Finally, we also investigate the provable efficiency of partially observable multi-agent RL (MARL) with privileged information. We develop algorithms featuring \emph{centralized-training-with-decentralized-execution}, a popular framework in empirical MARL, with polynomial sample and (quasi-)polynomial computational complexities in both paradigms above. Compared with a few recent related theoretical studies, our focus is on understanding practically inspired algorithmic paradigms, without computationally intractable oracles.
Last-Iterate Convergence of Payoff-Based Independent Learning in Zero-Sum Stochastic Games
Sep 02, 2024Abstract:In this paper, we consider two-player zero-sum matrix and stochastic games and develop learning dynamics that are payoff-based, convergent, rational, and symmetric between the two players. Specifically, the learning dynamics for matrix games are based on the smoothed best-response dynamics, while the learning dynamics for stochastic games build upon those for matrix games, with additional incorporation of the minimax value iteration. To our knowledge, our theoretical results present the first finite-sample analysis of such learning dynamics with last-iterate guarantees. In the matrix game setting, the results imply a sample complexity of $O(\epsilon^{-1})$ to find the Nash distribution and a sample complexity of $O(\epsilon^{-8})$ to find a Nash equilibrium. In the stochastic game setting, the results also imply a sample complexity of $O(\epsilon^{-8})$ to find a Nash equilibrium. To establish these results, the main challenge is to handle stochastic approximation algorithms with multiple sets of coupled and stochastic iterates that evolve on (possibly) different time scales. To overcome this challenge, we developed a coupled Lyapunov-based approach, which may be of independent interest to the broader community studying the convergence behavior of stochastic approximation algorithms.
Principled RLHF from Heterogeneous Feedback via Personalization and Preference Aggregation
Apr 30, 2024
Abstract:Reinforcement learning from human feedback (RLHF) has been an effective technique for aligning AI systems with human values, with remarkable successes in fine-tuning large-language models recently. Most existing RLHF paradigms make the underlying assumption that human preferences are relatively homogeneous, and can be encoded by a single reward model. In this paper, we focus on addressing the issues due to the inherent heterogeneity in human preferences, as well as their potential strategic behavior in providing feedback. Specifically, we propose two frameworks to address heterogeneous human feedback in principled ways: personalization-based one and aggregation-based one. For the former, we propose two approaches based on representation learning and clustering, respectively, for learning multiple reward models that trades off the bias (due to preference heterogeneity) and variance (due to the use of fewer data for learning each model by personalization). We then establish sample complexity guarantees for both approaches. For the latter, we aim to adhere to the single-model framework, as already deployed in the current RLHF paradigm, by carefully aggregating diverse and truthful preferences from humans. We propose two approaches based on reward and preference aggregation, respectively: the former utilizes both utilitarianism and Leximin approaches to aggregate individual reward models, with sample complexity guarantees; the latter directly aggregates the human feedback in the form of probabilistic opinions. Under the probabilistic-opinion-feedback model, we also develop an approach to handle strategic human labelers who may bias and manipulate the aggregated preferences with untruthful feedback. Based on the ideas in mechanism design, our approach ensures truthful preference reporting, with the induced aggregation rule maximizing social welfare functions.
Do LLM Agents Have Regret? A Case Study in Online Learning and Games
Mar 25, 2024Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have been increasingly employed for (interactive) decision-making, via the development of LLM-based autonomous agents. Despite their emerging successes, the performance of LLM agents in decision-making has not been fully investigated through quantitative metrics, especially in the multi-agent setting when they interact with each other, a typical scenario in real-world LLM-agent applications. To better understand the limits of LLM agents in these interactive environments, we propose to study their interactions in benchmark decision-making settings in online learning and game theory, through the performance metric of \emph{regret}. We first empirically study the {no-regret} behaviors of LLMs in canonical (non-stationary) online learning problems, as well as the emergence of equilibria when LLM agents interact through playing repeated games. We then provide some theoretical insights into the no-regret behaviors of LLM agents, under certain assumptions on the supervised pre-training and the rationality model of human decision-makers who generate the data. Notably, we also identify (simple) cases where advanced LLMs such as GPT-4 fail to be no-regret. To promote the no-regret behaviors, we propose a novel \emph{unsupervised} training loss of \emph{regret-loss}, which, in contrast to the supervised pre-training loss, does not require the labels of (optimal) actions. We then establish the statistical guarantee of generalization bound for regret-loss minimization, followed by the optimization guarantee that minimizing such a loss may automatically lead to known no-regret learning algorithms. Our further experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of our regret-loss, especially in addressing the above ``regrettable'' cases.
Two-Timescale Q-Learning with Function Approximation in Zero-Sum Stochastic Games
Dec 08, 2023Abstract:We consider two-player zero-sum stochastic games and propose a two-timescale $Q$-learning algorithm with function approximation that is payoff-based, convergent, rational, and symmetric between the two players. In two-timescale $Q$-learning, the fast-timescale iterates are updated in spirit to the stochastic gradient descent and the slow-timescale iterates (which we use to compute the policies) are updated by taking a convex combination between its previous iterate and the latest fast-timescale iterate. Introducing the slow timescale as well as its update equation marks as our main algorithmic novelty. In the special case of linear function approximation, we establish, to the best of our knowledge, the first last-iterate finite-sample bound for payoff-based independent learning dynamics of these types. The result implies a polynomial sample complexity to find a Nash equilibrium in such stochastic games. To establish the results, we model our proposed algorithm as a two-timescale stochastic approximation and derive the finite-sample bound through a Lyapunov-based approach. The key novelty lies in constructing a valid Lyapunov function to capture the evolution of the slow-timescale iterates. Specifically, through a change of variable, we show that the update equation of the slow-timescale iterates resembles the classical smoothed best-response dynamics, where the regularized Nash gap serves as a valid Lyapunov function. This insight enables us to construct a valid Lyapunov function via a generalized variant of the Moreau envelope of the regularized Nash gap. The construction of our Lyapunov function might be of broad independent interest in studying the behavior of stochastic approximation algorithms.
Fleet Policy Learning via Weight Merging and An Application to Robotic Tool-Use
Oct 02, 2023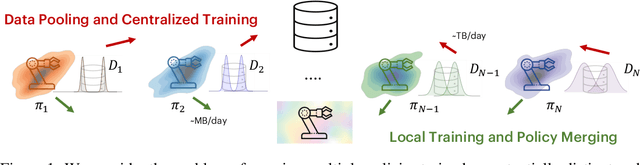

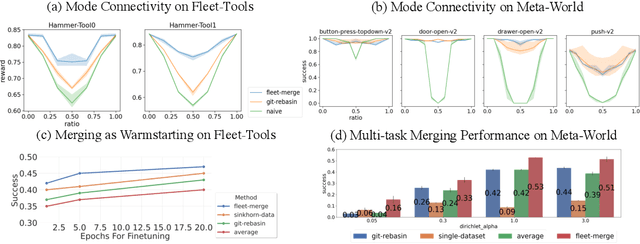
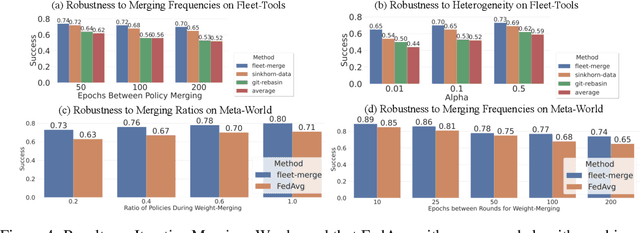
Abstract:Fleets of robots ingest massive amounts of streaming data generated by interacting with their environments, far more than those that can be stored or transmitted with ease. At the same time, we hope that teams of robots can co-acquire diverse skills through their experiences in varied settings. How can we enable such fleet-level learning without having to transmit or centralize fleet-scale data? In this paper, we investigate distributed learning of policies as a potential solution. To efficiently merge policies in the distributed setting, we propose fleet-merge, an instantiation of distributed learning that accounts for the symmetries that can arise in learning policies that are parameterized by recurrent neural networks. We show that fleet-merge consolidates the behavior of policies trained on 50 tasks in the Meta-World environment, with the merged policy achieving good performance on nearly all training tasks at test time. Moreover, we introduce a novel robotic tool-use benchmark, fleet-tools, for fleet policy learning in compositional and contact-rich robot manipulation tasks, which might be of broader interest, and validate the efficacy of fleet-merge on the benchmark.
Partially Observable Multi-agent RL with (Quasi-)Efficiency: The Blessing of Information Sharing
Aug 16, 2023Abstract:We study provable multi-agent reinforcement learning (MARL) in the general framework of partially observable stochastic games (POSGs). To circumvent the known hardness results and the use of computationally intractable oracles, we advocate leveraging the potential \emph{information-sharing} among agents, a common practice in empirical MARL, and a standard model for multi-agent control systems with communications. We first establish several computation complexity results to justify the necessity of information-sharing, as well as the observability assumption that has enabled quasi-efficient single-agent RL with partial observations, for computational efficiency in solving POSGs. We then propose to further \emph{approximate} the shared common information to construct an {approximate model} of the POSG, in which planning an approximate equilibrium (in terms of solving the original POSG) can be quasi-efficient, i.e., of quasi-polynomial-time, under the aforementioned assumptions. Furthermore, we develop a partially observable MARL algorithm that is both statistically and computationally quasi-efficient. We hope our study may open up the possibilities of leveraging and even designing different \emph{information structures}, for developing both sample- and computation-efficient partially observable MARL.
Tackling Combinatorial Distribution Shift: A Matrix Completion Perspective
Jul 28, 2023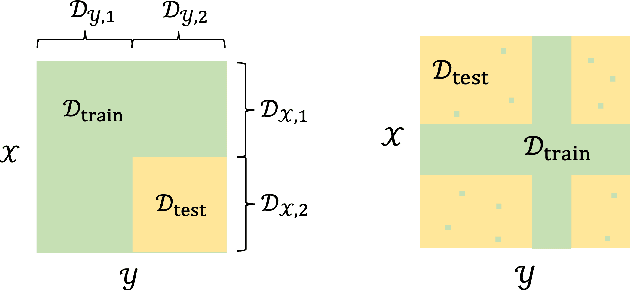
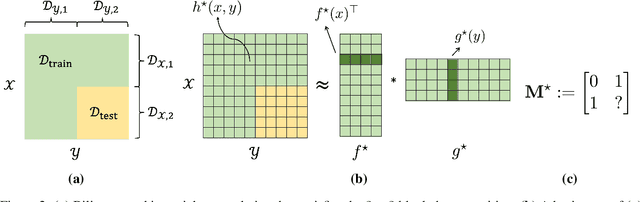
Abstract:Obtaining rigorous statistical guarantees for generalization under distribution shift remains an open and active research area. We study a setting we call combinatorial distribution shift, where (a) under the test- and training-distributions, the labels $z$ are determined by pairs of features $(x,y)$, (b) the training distribution has coverage of certain marginal distributions over $x$ and $y$ separately, but (c) the test distribution involves examples from a product distribution over $(x,y)$ that is {not} covered by the training distribution. Focusing on the special case where the labels are given by bilinear embeddings into a Hilbert space $H$: $\mathbb{E}[z \mid x,y ]=\langle f_{\star}(x),g_{\star}(y)\rangle_{{H}}$, we aim to extrapolate to a test distribution domain that is $not$ covered in training, i.e., achieving bilinear combinatorial extrapolation. Our setting generalizes a special case of matrix completion from missing-not-at-random data, for which all existing results require the ground-truth matrices to be either exactly low-rank, or to exhibit very sharp spectral cutoffs. In this work, we develop a series of theoretical results that enable bilinear combinatorial extrapolation under gradual spectral decay as observed in typical high-dimensional data, including novel algorithms, generalization guarantees, and linear-algebraic results. A key tool is a novel perturbation bound for the rank-$k$ singular value decomposition approximations between two matrices that depends on the relative spectral gap rather than the absolute spectral gap, a result that may be of broader independent interest.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge