Abhishek Gupta
BCG Henderson Institute, Montreal AI Ethics Institute, Boston Consulting Group
RFS: Reinforcement learning with Residual flow steering for dexterous manipulation
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:Imitation learning has emerged as an effective approach for bootstrapping sequential decision-making in robotics, achieving strong performance even in high-dimensional dexterous manipulation tasks. Recent behavior cloning methods further leverage expressive generative models, such as diffusion models and flow matching, to represent multimodal action distributions. However, policies pretrained in this manner often exhibit limited generalization and require additional fine-tuning to achieve robust performance at deployment time. Such adaptation must preserve the global exploration benefits of pretraining while enabling rapid correction of local execution errors. We propose Residual Flow Steering(RFS), a data-efficient reinforcement learning framework for adapting pretrained generative policies. RFS steers a pretrained flow-matching policy by jointly optimizing a residual action and a latent noise distribution, enabling complementary forms of exploration: local refinement through residual corrections and global exploration through latent-space modulation. This design allows efficient adaptation while retaining the expressive structure of the pretrained policy. We demonstrate the effectiveness of RFS on dexterous manipulation tasks, showing efficient fine-tuning in both simulation and real-world settings when adapting pretrained base policies. Project website:https://weirdlabuw.github.io/rfs.
Out-of-Distribution Generalization for Neural Physics Solvers
Jan 27, 2026Abstract:Neural physics solvers are increasingly used in scientific discovery, given their potential for rapid in silico insights into physical, materials, or biological systems and their long-time evolution. However, poor generalization beyond their training support limits exploration of novel designs and long-time horizon predictions. We introduce NOVA, a route to generalizable neural physics solvers that can provide rapid, accurate solutions to scenarios even under distributional shifts in partial differential equation parameters, geometries and initial conditions. By learning physics-aligned representations from an initial sparse set of scenarios, NOVA consistently achieves 1-2 orders of magnitude lower out-of-distribution errors than data-driven baselines across complex, nonlinear problems including heat transfer, diffusion-reaction and fluid flow. We further showcase NOVA's dual impact on stabilizing long-time dynamical rollouts and improving generative design through application to the simulation of nonlinear Turing systems and fluidic chip optimization. Unlike neural physics solvers that are constrained to retrieval and/or emulation within an a priori space, NOVA enables reliable extrapolation beyond known regimes, a key capability given the need for exploration of novel hypothesis spaces in scientific discovery
Point Bridge: 3D Representations for Cross Domain Policy Learning
Jan 24, 2026Abstract:Robot foundation models are beginning to deliver on the promise of generalist robotic agents, yet progress remains constrained by the scarcity of large-scale real-world manipulation datasets. Simulation and synthetic data generation offer a scalable alternative, but their usefulness is limited by the visual domain gap between simulation and reality. In this work, we present Point Bridge, a framework that leverages unified, domain-agnostic point-based representations to unlock synthetic datasets for zero-shot sim-to-real policy transfer, without explicit visual or object-level alignment. Point Bridge combines automated point-based representation extraction via Vision-Language Models (VLMs), transformer-based policy learning, and efficient inference-time pipelines to train capable real-world manipulation agents using only synthetic data. With additional co-training on small sets of real demonstrations, Point Bridge further improves performance, substantially outperforming prior vision-based sim-and-real co-training methods. It achieves up to 44% gains in zero-shot sim-to-real transfer and up to 66% with limited real data across both single-task and multitask settings. Videos of the robot are best viewed at: https://pointbridge3d.github.io/
PolaRiS: Scalable Real-to-Sim Evaluations for Generalist Robot Policies
Dec 18, 2025Abstract:A significant challenge for robot learning research is our ability to accurately measure and compare the performance of robot policies. Benchmarking in robotics is historically challenging due to the stochasticity, reproducibility, and time-consuming nature of real-world rollouts. This challenge is exacerbated for recent generalist policies, which has to be evaluated across a wide variety of scenes and tasks. Evaluation in simulation offers a scalable complement to real world evaluations, but the visual and physical domain gap between existing simulation benchmarks and the real world has made them an unreliable signal for policy improvement. Furthermore, building realistic and diverse simulated environments has traditionally required significant human effort and expertise. To bridge the gap, we introduce Policy Evaluation and Environment Reconstruction in Simulation (PolaRiS), a scalable real-to-sim framework for high-fidelity simulated robot evaluation. PolaRiS utilizes neural reconstruction methods to turn short video scans of real-world scenes into interactive simulation environments. Additionally, we develop a simple simulation data co-training recipe that bridges remaining real-to-sim gaps and enables zero-shot evaluation in unseen simulation environments. Through extensive paired evaluations between simulation and the real world, we demonstrate that PolaRiS evaluations provide a much stronger correlation to real world generalist policy performance than existing simulated benchmarks. Its simplicity also enables rapid creation of diverse simulated environments. As such, this work takes a step towards distributed and democratized evaluation for the next generation of robotic foundation models.
Parametric Expensive Multi-Objective Optimization via Generative Solution Modeling
Nov 17, 2025Abstract:Many real-world applications require solving families of expensive multi-objective optimization problems~(EMOPs) under varying operational conditions. This gives rise to parametric expensive multi-objective optimization problems (P-EMOPs) where each task parameter defines a distinct optimization instance. Current multi-objective Bayesian optimization methods have been widely used for finding finite sets of Pareto optimal solutions for individual tasks. However, P-EMOPs present a fundamental challenge: the continuous task parameter space can contain infinite distinct problems, each requiring separate expensive evaluations. This demands learning an inverse model that can directly predict optimized solutions for any task-preference query without expensive re-evaluation. This paper introduces the first parametric multi-objective Bayesian optimizer that learns this inverse model by alternating between (1) acquisition-driven search leveraging inter-task synergies and (2) generative solution sampling via conditional generative models. This approach enables efficient optimization across related tasks and finally achieves direct solution prediction for unseen parameterized EMOPs without additional expensive evaluations. We theoretically justify the faster convergence by leveraging inter-task synergies through task-aware Gaussian processes. Meanwhile, empirical studies in synthetic and real-world benchmarks further verify the effectiveness of our alternating framework.
The Reality Gap in Robotics: Challenges, Solutions, and Best Practices
Oct 23, 2025Abstract:Machine learning has facilitated significant advancements across various robotics domains, including navigation, locomotion, and manipulation. Many such achievements have been driven by the extensive use of simulation as a critical tool for training and testing robotic systems prior to their deployment in real-world environments. However, simulations consist of abstractions and approximations that inevitably introduce discrepancies between simulated and real environments, known as the reality gap. These discrepancies significantly hinder the successful transfer of systems from simulation to the real world. Closing this gap remains one of the most pressing challenges in robotics. Recent advances in sim-to-real transfer have demonstrated promising results across various platforms, including locomotion, navigation, and manipulation. By leveraging techniques such as domain randomization, real-to-sim transfer, state and action abstractions, and sim-real co-training, many works have overcome the reality gap. However, challenges persist, and a deeper understanding of the reality gap's root causes and solutions is necessary. In this survey, we present a comprehensive overview of the sim-to-real landscape, highlighting the causes, solutions, and evaluation metrics for the reality gap and sim-to-real transfer.
VAMOS: A Hierarchical Vision-Language-Action Model for Capability-Modulated and Steerable Navigation
Oct 23, 2025Abstract:A fundamental challenge in robot navigation lies in learning policies that generalize across diverse environments while conforming to the unique physical constraints and capabilities of a specific embodiment (e.g., quadrupeds can walk up stairs, but rovers cannot). We propose VAMOS, a hierarchical VLA that decouples semantic planning from embodiment grounding: a generalist planner learns from diverse, open-world data, while a specialist affordance model learns the robot's physical constraints and capabilities in safe, low-cost simulation. We enabled this separation by carefully designing an interface that lets a high-level planner propose candidate paths directly in image space that the affordance model then evaluates and re-ranks. Our real-world experiments show that VAMOS achieves higher success rates in both indoor and complex outdoor navigation than state-of-the-art model-based and end-to-end learning methods. We also show that our hierarchical design enables cross-embodied navigation across legged and wheeled robots and is easily steerable using natural language. Real-world ablations confirm that the specialist model is key to embodiment grounding, enabling a single high-level planner to be deployed across physically distinct wheeled and legged robots. Finally, this model significantly enhances single-robot reliability, achieving 3X higher success rates by rejecting physically infeasible plans. Website: https://vamos-vla.github.io/
Semantic World Models
Oct 22, 2025Abstract:Planning with world models offers a powerful paradigm for robotic control. Conventional approaches train a model to predict future frames conditioned on current frames and actions, which can then be used for planning. However, the objective of predicting future pixels is often at odds with the actual planning objective; strong pixel reconstruction does not always correlate with good planning decisions. This paper posits that instead of reconstructing future frames as pixels, world models only need to predict task-relevant semantic information about the future. For such prediction the paper poses world modeling as a visual question answering problem about semantic information in future frames. This perspective allows world modeling to be approached with the same tools underlying vision language models. Thus vision language models can be trained as "semantic" world models through a supervised finetuning process on image-action-text data, enabling planning for decision-making while inheriting many of the generalization and robustness properties from the pretrained vision-language models. The paper demonstrates how such a semantic world model can be used for policy improvement on open-ended robotics tasks, leading to significant generalization improvements over typical paradigms of reconstruction-based action-conditional world modeling. Website available at https://weirdlabuw.github.io/swm.
DRAWER: Digital Reconstruction and Articulation With Environment Realism
Apr 22, 2025Abstract:Creating virtual digital replicas from real-world data unlocks significant potential across domains like gaming and robotics. In this paper, we present DRAWER, a novel framework that converts a video of a static indoor scene into a photorealistic and interactive digital environment. Our approach centers on two main contributions: (i) a reconstruction module based on a dual scene representation that reconstructs the scene with fine-grained geometric details, and (ii) an articulation module that identifies articulation types and hinge positions, reconstructs simulatable shapes and appearances and integrates them into the scene. The resulting virtual environment is photorealistic, interactive, and runs in real time, with compatibility for game engines and robotic simulation platforms. We demonstrate the potential of DRAWER by using it to automatically create an interactive game in Unreal Engine and to enable real-to-sim-to-real transfer for robotics applications.
Unified World Models: Coupling Video and Action Diffusion for Pretraining on Large Robotic Datasets
Apr 03, 2025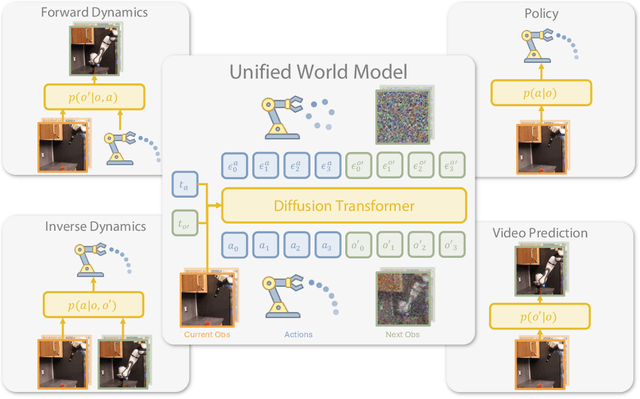
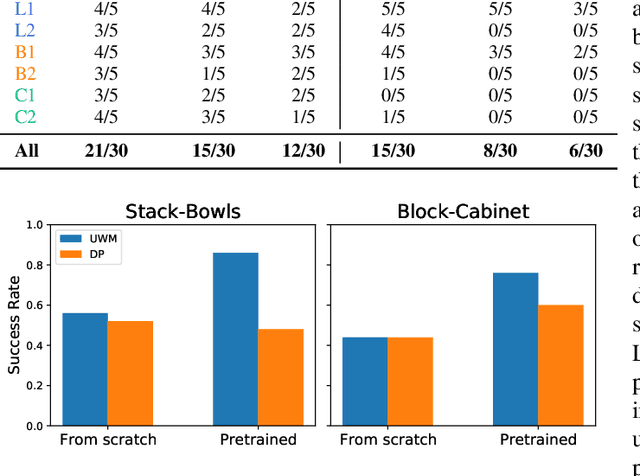
Abstract:Imitation learning has emerged as a promising approach towards building generalist robots. However, scaling imitation learning for large robot foundation models remains challenging due to its reliance on high-quality expert demonstrations. Meanwhile, large amounts of video data depicting a wide range of environments and diverse behaviors are readily available. This data provides a rich source of information about real-world dynamics and agent-environment interactions. Leveraging this data directly for imitation learning, however, has proven difficult due to the lack of action annotation required for most contemporary methods. In this work, we present Unified World Models (UWM), a framework that allows for leveraging both video and action data for policy learning. Specifically, a UWM integrates an action diffusion process and a video diffusion process within a unified transformer architecture, where independent diffusion timesteps govern each modality. We show that by simply controlling each diffusion timestep, UWM can flexibly represent a policy, a forward dynamics, an inverse dynamics, and a video generator. Through simulated and real-world experiments, we show that: (1) UWM enables effective pretraining on large-scale multitask robot datasets with both dynamics and action predictions, resulting in more generalizable and robust policies than imitation learning, (2) UWM naturally facilitates learning from action-free video data through independent control of modality-specific diffusion timesteps, further improving the performance of finetuned policies. Our results suggest that UWM offers a promising step toward harnessing large, heterogeneous datasets for scalable robot learning, and provides a simple unification between the often disparate paradigms of imitation learning and world modeling. Videos and code are available at https://weirdlabuw.github.io/uwm/.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge