Marius Memmel
DRAWER: Digital Reconstruction and Articulation With Environment Realism
Apr 22, 2025Abstract:Creating virtual digital replicas from real-world data unlocks significant potential across domains like gaming and robotics. In this paper, we present DRAWER, a novel framework that converts a video of a static indoor scene into a photorealistic and interactive digital environment. Our approach centers on two main contributions: (i) a reconstruction module based on a dual scene representation that reconstructs the scene with fine-grained geometric details, and (ii) an articulation module that identifies articulation types and hinge positions, reconstructs simulatable shapes and appearances and integrates them into the scene. The resulting virtual environment is photorealistic, interactive, and runs in real time, with compatibility for game engines and robotic simulation platforms. We demonstrate the potential of DRAWER by using it to automatically create an interactive game in Unreal Engine and to enable real-to-sim-to-real transfer for robotics applications.
STRAP: Robot Sub-Trajectory Retrieval for Augmented Policy Learning
Dec 19, 2024Abstract:Robot learning is witnessing a significant increase in the size, diversity, and complexity of pre-collected datasets, mirroring trends in domains such as natural language processing and computer vision. Many robot learning methods treat such datasets as multi-task expert data and learn a multi-task, generalist policy by training broadly across them. Notably, while these generalist policies can improve the average performance across many tasks, the performance of generalist policies on any one task is often suboptimal due to negative transfer between partitions of the data, compared to task-specific specialist policies. In this work, we argue for the paradigm of training policies during deployment given the scenarios they encounter: rather than deploying pre-trained policies to unseen problems in a zero-shot manner, we non-parametrically retrieve and train models directly on relevant data at test time. Furthermore, we show that many robotics tasks share considerable amounts of low-level behaviors and that retrieval at the "sub"-trajectory granularity enables significantly improved data utilization, generalization, and robustness in adapting policies to novel problems. In contrast, existing full-trajectory retrieval methods tend to underutilize the data and miss out on shared cross-task content. This work proposes STRAP, a technique for leveraging pre-trained vision foundation models and dynamic time warping to retrieve sub-sequences of trajectories from large training corpora in a robust fashion. STRAP outperforms both prior retrieval algorithms and multi-task learning methods in simulated and real experiments, showing the ability to scale to much larger offline datasets in the real world as well as the ability to learn robust control policies with just a handful of real-world demonstrations.
URDFormer: A Pipeline for Constructing Articulated Simulation Environments from Real-World Images
May 19, 2024



Abstract:Constructing simulation scenes that are both visually and physically realistic is a problem of practical interest in domains ranging from robotics to computer vision. This problem has become even more relevant as researchers wielding large data-hungry learning methods seek new sources of training data for physical decision-making systems. However, building simulation models is often still done by hand. A graphic designer and a simulation engineer work with predefined assets to construct rich scenes with realistic dynamic and kinematic properties. While this may scale to small numbers of scenes, to achieve the generalization properties that are required for data-driven robotic control, we require a pipeline that is able to synthesize large numbers of realistic scenes, complete with 'natural' kinematic and dynamic structures. To attack this problem, we develop models for inferring structure and generating simulation scenes from natural images, allowing for scalable scene generation from web-scale datasets. To train these image-to-simulation models, we show how controllable text-to-image generative models can be used in generating paired training data that allows for modeling of the inverse problem, mapping from realistic images back to complete scene models. We show how this paradigm allows us to build large datasets of scenes in simulation with semantic and physical realism. We present an integrated end-to-end pipeline that generates simulation scenes complete with articulated kinematic and dynamic structures from real-world images and use these for training robotic control policies. We then robustly deploy in the real world for tasks like articulated object manipulation. In doing so, our work provides both a pipeline for large-scale generation of simulation environments and an integrated system for training robust robotic control policies in the resulting environments.
ASID: Active Exploration for System Identification in Robotic Manipulation
Apr 18, 2024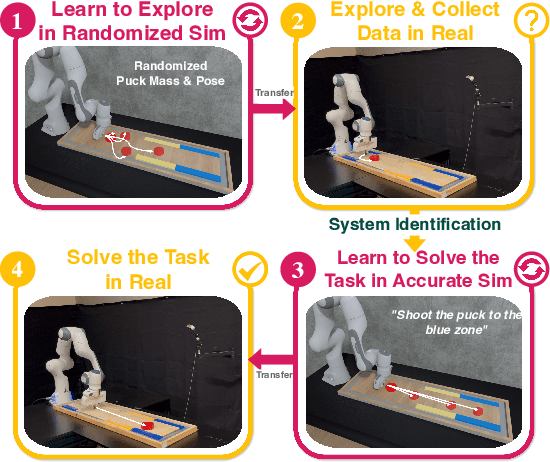

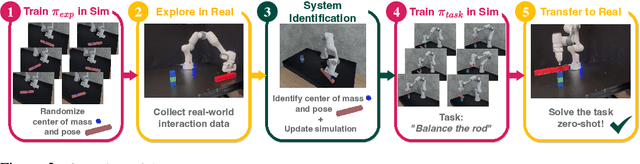
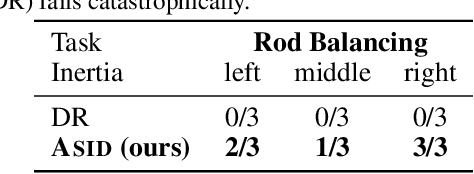
Abstract:Model-free control strategies such as reinforcement learning have shown the ability to learn control strategies without requiring an accurate model or simulator of the world. While this is appealing due to the lack of modeling requirements, such methods can be sample inefficient, making them impractical in many real-world domains. On the other hand, model-based control techniques leveraging accurate simulators can circumvent these challenges and use a large amount of cheap simulation data to learn controllers that can effectively transfer to the real world. The challenge with such model-based techniques is the requirement for an extremely accurate simulation, requiring both the specification of appropriate simulation assets and physical parameters. This requires considerable human effort to design for every environment being considered. In this work, we propose a learning system that can leverage a small amount of real-world data to autonomously refine a simulation model and then plan an accurate control strategy that can be deployed in the real world. Our approach critically relies on utilizing an initial (possibly inaccurate) simulator to design effective exploration policies that, when deployed in the real world, collect high-quality data. We demonstrate the efficacy of this paradigm in identifying articulation, mass, and other physical parameters in several challenging robotic manipulation tasks, and illustrate that only a small amount of real-world data can allow for effective sim-to-real transfer. Project website at https://weirdlabuw.github.io/asid
DROID: A Large-Scale In-The-Wild Robot Manipulation Dataset
Mar 19, 2024
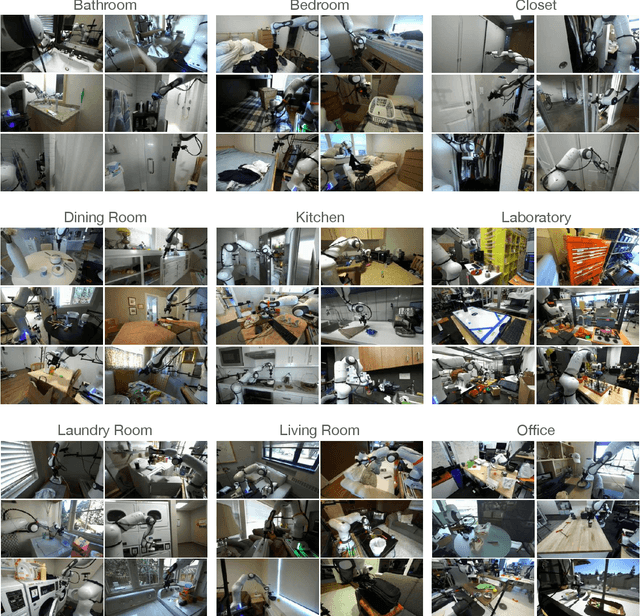


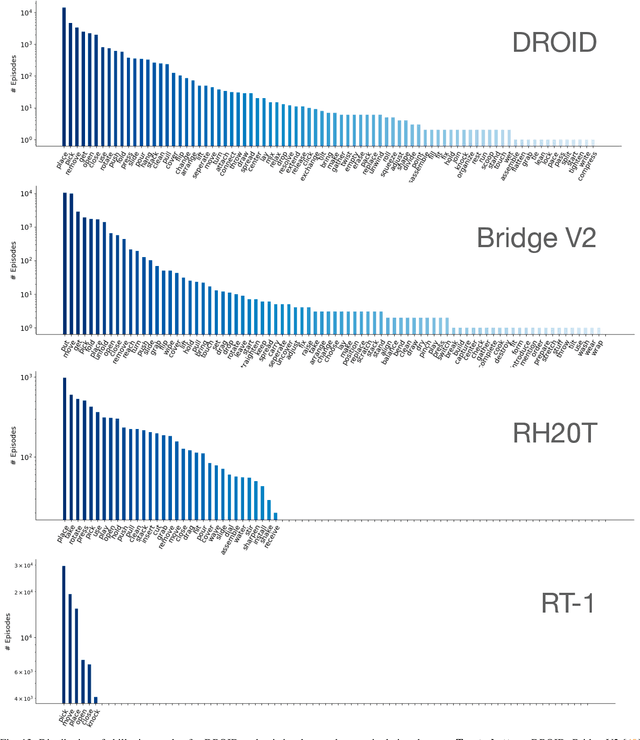
Abstract:The creation of large, diverse, high-quality robot manipulation datasets is an important stepping stone on the path toward more capable and robust robotic manipulation policies. However, creating such datasets is challenging: collecting robot manipulation data in diverse environments poses logistical and safety challenges and requires substantial investments in hardware and human labour. As a result, even the most general robot manipulation policies today are mostly trained on data collected in a small number of environments with limited scene and task diversity. In this work, we introduce DROID (Distributed Robot Interaction Dataset), a diverse robot manipulation dataset with 76k demonstration trajectories or 350 hours of interaction data, collected across 564 scenes and 84 tasks by 50 data collectors in North America, Asia, and Europe over the course of 12 months. We demonstrate that training with DROID leads to policies with higher performance and improved generalization ability. We open source the full dataset, policy learning code, and a detailed guide for reproducing our robot hardware setup.
Modality-invariant Visual Odometry for Embodied Vision
Apr 29, 2023



Abstract:Effectively localizing an agent in a realistic, noisy setting is crucial for many embodied vision tasks. Visual Odometry (VO) is a practical substitute for unreliable GPS and compass sensors, especially in indoor environments. While SLAM-based methods show a solid performance without large data requirements, they are less flexible and robust w.r.t. to noise and changes in the sensor suite compared to learning-based approaches. Recent deep VO models, however, limit themselves to a fixed set of input modalities, e.g., RGB and depth, while training on millions of samples. When sensors fail, sensor suites change, or modalities are intentionally looped out due to available resources, e.g., power consumption, the models fail catastrophically. Furthermore, training these models from scratch is even more expensive without simulator access or suitable existing models that can be fine-tuned. While such scenarios get mostly ignored in simulation, they commonly hinder a model's reusability in real-world applications. We propose a Transformer-based modality-invariant VO approach that can deal with diverse or changing sensor suites of navigation agents. Our model outperforms previous methods while training on only a fraction of the data. We hope this method opens the door to a broader range of real-world applications that can benefit from flexible and learned VO models.
Dimensionality Reduction and Prioritized Exploration for Policy Search
Mar 19, 2022



Abstract:Black-box policy optimization is a class of reinforcement learning algorithms that explores and updates the policies at the parameter level. This class of algorithms is widely applied in robotics with movement primitives or non-differentiable policies. Furthermore, these approaches are particularly relevant where exploration at the action level could cause actuator damage or other safety issues. However, Black-box optimization does not scale well with the increasing dimensionality of the policy, leading to high demand for samples, which are expensive to obtain in real-world systems. In many practical applications, policy parameters do not contribute equally to the return. Identifying the most relevant parameters allows to narrow down the exploration and speed up the learning. Furthermore, updating only the effective parameters requires fewer samples, improving the scalability of the method. We present a novel method to prioritize the exploration of effective parameters and cope with full covariance matrix updates. Our algorithm learns faster than recent approaches and requires fewer samples to achieve state-of-the-art results. To select the effective parameters, we consider both the Pearson correlation coefficient and the Mutual Information. We showcase the capabilities of our approach on the Relative Entropy Policy Search algorithm in several simulated environments, including robotics simulations. Code is available at https://git.ias.informatik.tu-darmstadt.de/ias\_code/aistats2022/dr-creps}{git.ias.informatik.tu-darmstadt.de/ias\_code/aistats2022/dr-creps.
Scalable 3D Semantic Segmentation for Gun Detection in CT Scans
Dec 07, 2021
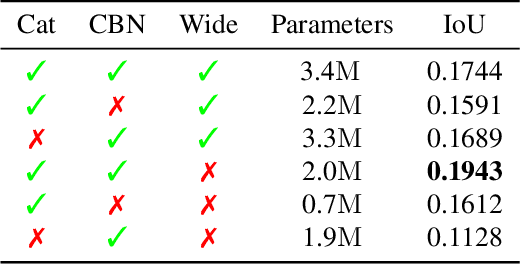
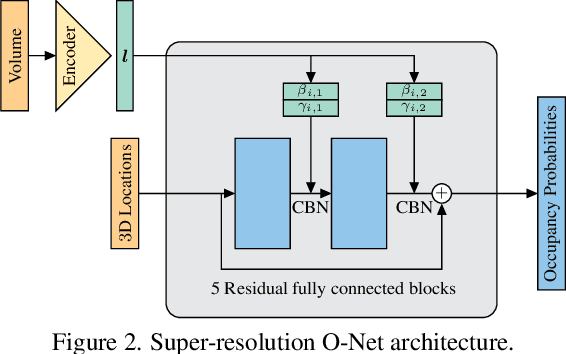
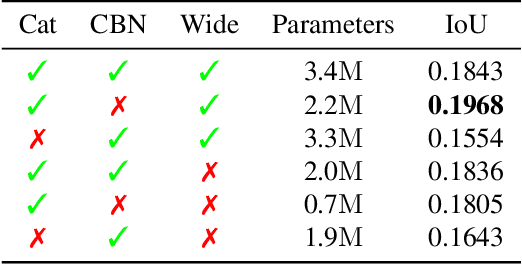
Abstract:With the increased availability of 3D data, the need for solutions processing those also increased rapidly. However, adding dimension to already reliably accurate 2D approaches leads to immense memory consumption and higher computational complexity. These issues cause current hardware to reach its limitations, with most methods forced to reduce the input resolution drastically. Our main contribution is a novel deep 3D semantic segmentation method for gun detection in baggage CT scans that enables fast training and low video memory consumption for high-resolution voxelized volumes. We introduce a moving pyramid approach that utilizes multiple forward passes at inference time for segmenting an instance.
Interactive Disentanglement: Learning Concepts by Interacting with their Prototype Representations
Dec 04, 2021



Abstract:Learning visual concepts from raw images without strong supervision is a challenging task. In this work, we show the advantages of prototype representations for understanding and revising the latent space of neural concept learners. For this purpose, we introduce interactive Concept Swapping Networks (iCSNs), a novel framework for learning concept-grounded representations via weak supervision and implicit prototype representations. iCSNs learn to bind conceptual information to specific prototype slots by swapping the latent representations of paired images. This semantically grounded and discrete latent space facilitates human understanding and human-machine interaction. We support this claim by conducting experiments on our novel data set "Elementary Concept Reasoning" (ECR), focusing on visual concepts shared by geometric objects.
Adversarial Continual Learning for Multi-Domain Hippocampal Segmentation
Jul 25, 2021



Abstract:Deep learning for medical imaging suffers from temporal and privacy-related restrictions on data availability. To still obtain viable models, continual learning aims to train in sequential order, as and when data is available. The main challenge that continual learning methods face is to prevent catastrophic forgetting, i.e., a decrease in performance on the data encountered earlier. This issue makes continuous training of segmentation models for medical applications extremely difficult. Yet, often, data from at least two different domains is available which we can exploit to train the model in a way that it disregards domain-specific information. We propose an architecture that leverages the simultaneous availability of two or more datasets to learn a disentanglement between the content and domain in an adversarial fashion. The domain-invariant content representation then lays the base for continual semantic segmentation. Our approach takes inspiration from domain adaptation and combines it with continual learning for hippocampal segmentation in brain MRI. We showcase that our method reduces catastrophic forgetting and outperforms state-of-the-art continual learning methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge