Hongchi Xia
SAGE: Scalable Agentic 3D Scene Generation for Embodied AI
Feb 10, 2026Abstract:Real-world data collection for embodied agents remains costly and unsafe, calling for scalable, realistic, and simulator-ready 3D environments. However, existing scene-generation systems often rely on rule-based or task-specific pipelines, yielding artifacts and physically invalid scenes. We present SAGE, an agentic framework that, given a user-specified embodied task (e.g., "pick up a bowl and place it on the table"), understands the intent and automatically generates simulation-ready environments at scale. The agent couples multiple generators for layout and object composition with critics that evaluate semantic plausibility, visual realism, and physical stability. Through iterative reasoning and adaptive tool selection, it self-refines the scenes until meeting user intent and physical validity. The resulting environments are realistic, diverse, and directly deployable in modern simulators for policy training. Policies trained purely on this data exhibit clear scaling trends and generalize to unseen objects and layouts, demonstrating the promise of simulation-driven scaling for embodied AI. Code, demos, and the SAGE-10k dataset can be found on the project page here: https://nvlabs.github.io/sage.
Openpi Comet: Competition Solution For 2025 BEHAVIOR Challenge
Dec 12, 2025Abstract:The 2025 BEHAVIOR Challenge is designed to rigorously track progress toward solving long-horizon tasks by physical agents in simulated environments. BEHAVIOR-1K focuses on everyday household tasks that people most want robots to assist with and these tasks introduce long-horizon mobile manipulation challenges in realistic settings, bridging the gap between current research and real-world, human-centric applications. This report presents our solution to the 2025 BEHAVIOR Challenge in a very close 2nd place and substantially outperforms the rest of the submissions. Building on $π_{0.5}$, we focus on systematically building our solution by studying the effects of training techniques and data. Through careful ablations, we show the scaling power in pre-training and post-training phases for competitive performance. We summarize our practical lessons and design recommendations that we hope will provide actionable insights for the broader embodied AI community when adapting powerful foundation models to complex embodied scenarios.
DRAWER: Digital Reconstruction and Articulation With Environment Realism
Apr 22, 2025Abstract:Creating virtual digital replicas from real-world data unlocks significant potential across domains like gaming and robotics. In this paper, we present DRAWER, a novel framework that converts a video of a static indoor scene into a photorealistic and interactive digital environment. Our approach centers on two main contributions: (i) a reconstruction module based on a dual scene representation that reconstructs the scene with fine-grained geometric details, and (ii) an articulation module that identifies articulation types and hinge positions, reconstructs simulatable shapes and appearances and integrates them into the scene. The resulting virtual environment is photorealistic, interactive, and runs in real time, with compatibility for game engines and robotic simulation platforms. We demonstrate the potential of DRAWER by using it to automatically create an interactive game in Unreal Engine and to enable real-to-sim-to-real transfer for robotics applications.
AutoVFX: Physically Realistic Video Editing from Natural Language Instructions
Nov 04, 2024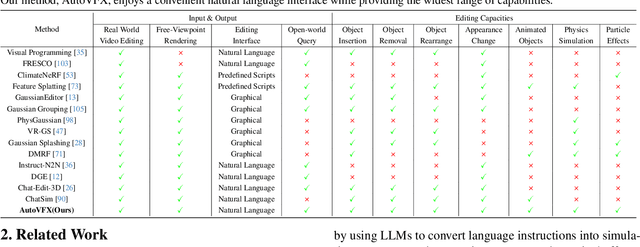
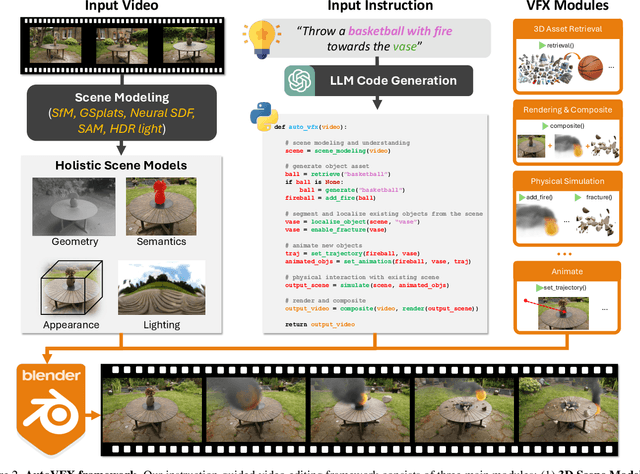
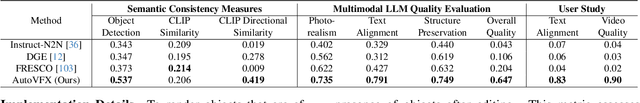
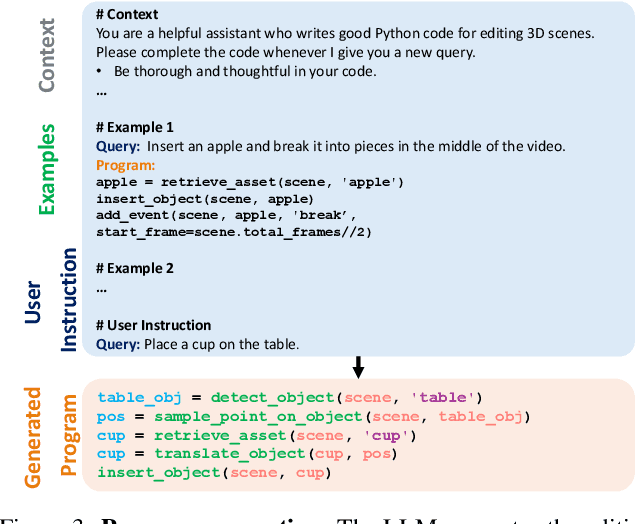
Abstract:Modern visual effects (VFX) software has made it possible for skilled artists to create imagery of virtually anything. However, the creation process remains laborious, complex, and largely inaccessible to everyday users. In this work, we present AutoVFX, a framework that automatically creates realistic and dynamic VFX videos from a single video and natural language instructions. By carefully integrating neural scene modeling, LLM-based code generation, and physical simulation, AutoVFX is able to provide physically-grounded, photorealistic editing effects that can be controlled directly using natural language instructions. We conduct extensive experiments to validate AutoVFX's efficacy across a diverse spectrum of videos and instructions. Quantitative and qualitative results suggest that AutoVFX outperforms all competing methods by a large margin in generative quality, instruction alignment, editing versatility, and physical plausibility.
Video2Game: Real-time, Interactive, Realistic and Browser-Compatible Environment from a Single Video
Apr 15, 2024Abstract:Creating high-quality and interactive virtual environments, such as games and simulators, often involves complex and costly manual modeling processes. In this paper, we present Video2Game, a novel approach that automatically converts videos of real-world scenes into realistic and interactive game environments. At the heart of our system are three core components:(i) a neural radiance fields (NeRF) module that effectively captures the geometry and visual appearance of the scene; (ii) a mesh module that distills the knowledge from NeRF for faster rendering; and (iii) a physics module that models the interactions and physical dynamics among the objects. By following the carefully designed pipeline, one can construct an interactable and actionable digital replica of the real world. We benchmark our system on both indoor and large-scale outdoor scenes. We show that we can not only produce highly-realistic renderings in real-time, but also build interactive games on top.
RGBD Objects in the Wild: Scaling Real-World 3D Object Learning from RGB-D Videos
Jan 24, 2024



Abstract:We introduce a new RGB-D object dataset captured in the wild called WildRGB-D. Unlike most existing real-world object-centric datasets which only come with RGB capturing, the direct capture of the depth channel allows better 3D annotations and broader downstream applications. WildRGB-D comprises large-scale category-level RGB-D object videos, which are taken using an iPhone to go around the objects in 360 degrees. It contains around 8500 recorded objects and nearly 20000 RGB-D videos across 46 common object categories. These videos are taken with diverse cluttered backgrounds with three setups to cover as many real-world scenarios as possible: (i) a single object in one video; (ii) multiple objects in one video; and (iii) an object with a static hand in one video. The dataset is annotated with object masks, real-world scale camera poses, and reconstructed aggregated point clouds from RGBD videos. We benchmark four tasks with WildRGB-D including novel view synthesis, camera pose estimation, object 6d pose estimation, and object surface reconstruction. Our experiments show that the large-scale capture of RGB-D objects provides a large potential to advance 3D object learning. Our project page is https://wildrgbd.github.io/.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge