Yang Fu
TalkCuts: A Large-Scale Dataset for Multi-Shot Human Speech Video Generation
Oct 08, 2025Abstract:In this work, we present TalkCuts, a large-scale dataset designed to facilitate the study of multi-shot human speech video generation. Unlike existing datasets that focus on single-shot, static viewpoints, TalkCuts offers 164k clips totaling over 500 hours of high-quality human speech videos with diverse camera shots, including close-up, half-body, and full-body views. The dataset includes detailed textual descriptions, 2D keypoints and 3D SMPL-X motion annotations, covering over 10k identities, enabling multimodal learning and evaluation. As a first attempt to showcase the value of the dataset, we present Orator, an LLM-guided multi-modal generation framework as a simple baseline, where the language model functions as a multi-faceted director, orchestrating detailed specifications for camera transitions, speaker gesticulations, and vocal modulation. This architecture enables the synthesis of coherent long-form videos through our integrated multi-modal video generation module. Extensive experiments in both pose-guided and audio-driven settings show that training on TalkCuts significantly enhances the cinematographic coherence and visual appeal of generated multi-shot speech videos. We believe TalkCuts provides a strong foundation for future work in controllable, multi-shot speech video generation and broader multimodal learning.
3D Aware Region Prompted Vision Language Model
Sep 16, 2025



Abstract:We present Spatial Region 3D (SR-3D) aware vision-language model that connects single-view 2D images and multi-view 3D data through a shared visual token space. SR-3D supports flexible region prompting, allowing users to annotate regions with bounding boxes, segmentation masks on any frame, or directly in 3D, without the need for exhaustive multi-frame labeling. We achieve this by enriching 2D visual features with 3D positional embeddings, which allows the 3D model to draw upon strong 2D priors for more accurate spatial reasoning across frames, even when objects of interest do not co-occur within the same view. Extensive experiments on both general 2D vision language and specialized 3D spatial benchmarks demonstrate that SR-3D achieves state-of-the-art performance, underscoring its effectiveness for unifying 2D and 3D representation space on scene understanding. Moreover, we observe applicability to in-the-wild videos without sensory 3D inputs or ground-truth 3D annotations, where SR-3D accurately infers spatial relationships and metric measurements.
SpatialRGPT: Grounded Spatial Reasoning in Vision Language Model
Jun 03, 2024



Abstract:Vision Language Models (VLMs) have demonstrated remarkable performance in 2D vision and language tasks. However, their ability to reason about spatial arrangements remains limited. In this work, we introduce Spatial Region GPT (SpatialRGPT) to enhance VLMs' spatial perception and reasoning capabilities. SpatialRGPT advances VLMs' spatial understanding through two key innovations: (1) a data curation pipeline that enables effective learning of regional representation from 3D scene graphs, and (2) a flexible plugin module for integrating depth information into the visual encoder of existing VLMs. During inference, when provided with user-specified region proposals, SpatialRGPT can accurately perceive their relative directions and distances. Additionally, we propose SpatialRGBT-Bench, a benchmark with ground-truth 3D annotations encompassing indoor, outdoor, and simulated environments, for evaluating 3D spatial cognition in VLMs. Our results demonstrate that SpatialRGPT significantly enhances performance in spatial reasoning tasks, both with and without local region prompts. The model also exhibits strong generalization capabilities, effectively reasoning about complex spatial relations and functioning as a region-aware dense reward annotator for robotic tasks. Code, dataset, and benchmark will be released at https://www.anjiecheng.me/SpatialRGPT
A Construct-Optimize Approach to Sparse View Synthesis without Camera Pose
May 06, 2024Abstract:Novel view synthesis from a sparse set of input images is a challenging problem of great practical interest, especially when camera poses are absent or inaccurate. Direct optimization of camera poses and usage of estimated depths in neural radiance field algorithms usually do not produce good results because of the coupling between poses and depths, and inaccuracies in monocular depth estimation. In this paper, we leverage the recent 3D Gaussian splatting method to develop a novel construct-and-optimize method for sparse view synthesis without camera poses. Specifically, we construct a solution progressively by using monocular depth and projecting pixels back into the 3D world. During construction, we optimize the solution by detecting 2D correspondences between training views and the corresponding rendered images. We develop a unified differentiable pipeline for camera registration and adjustment of both camera poses and depths, followed by back-projection. We also introduce a novel notion of an expected surface in Gaussian splatting, which is critical to our optimization. These steps enable a coarse solution, which can then be low-pass filtered and refined using standard optimization methods. We demonstrate results on the Tanks and Temples and Static Hikes datasets with as few as three widely-spaced views, showing significantly better quality than competing methods, including those with approximate camera pose information. Moreover, our results improve with more views and outperform previous InstantNGP and Gaussian Splatting algorithms even when using half the dataset.
HOIDiffusion: Generating Realistic 3D Hand-Object Interaction Data
Mar 18, 2024



Abstract:3D hand-object interaction data is scarce due to the hardware constraints in scaling up the data collection process. In this paper, we propose HOIDiffusion for generating realistic and diverse 3D hand-object interaction data. Our model is a conditional diffusion model that takes both the 3D hand-object geometric structure and text description as inputs for image synthesis. This offers a more controllable and realistic synthesis as we can specify the structure and style inputs in a disentangled manner. HOIDiffusion is trained by leveraging a diffusion model pre-trained on large-scale natural images and a few 3D human demonstrations. Beyond controllable image synthesis, we adopt the generated 3D data for learning 6D object pose estimation and show its effectiveness in improving perception systems. Project page: https://mq-zhang1.github.io/HOIDiffusion
Learning Generalizable Feature Fields for Mobile Manipulation
Mar 12, 2024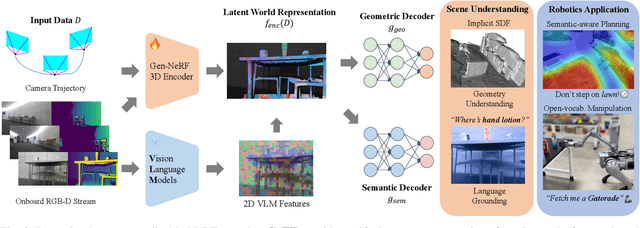
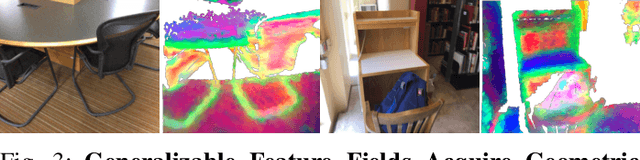
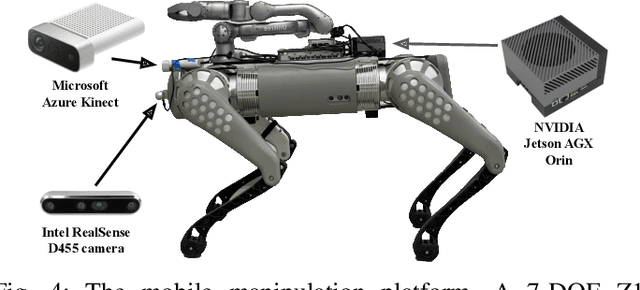
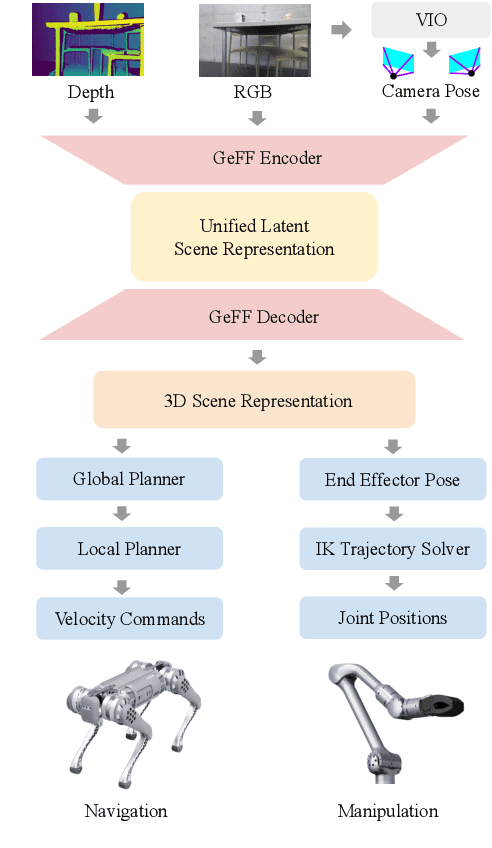
Abstract:An open problem in mobile manipulation is how to represent objects and scenes in a unified manner, so that robots can use it both for navigating in the environment and manipulating objects. The latter requires capturing intricate geometry while understanding fine-grained semantics, whereas the former involves capturing the complexity inherit to an expansive physical scale. In this work, we present GeFF (Generalizable Feature Fields), a scene-level generalizable neural feature field that acts as a unified representation for both navigation and manipulation that performs in real-time. To do so, we treat generative novel view synthesis as a pre-training task, and then align the resulting rich scene priors with natural language via CLIP feature distillation. We demonstrate the effectiveness of this approach by deploying GeFF on a quadrupedal robot equipped with a manipulator. We evaluate GeFF's ability to generalize to open-set objects as well as running time, when performing open-vocabulary mobile manipulation in dynamic scenes.
RGBD Objects in the Wild: Scaling Real-World 3D Object Learning from RGB-D Videos
Jan 24, 2024



Abstract:We introduce a new RGB-D object dataset captured in the wild called WildRGB-D. Unlike most existing real-world object-centric datasets which only come with RGB capturing, the direct capture of the depth channel allows better 3D annotations and broader downstream applications. WildRGB-D comprises large-scale category-level RGB-D object videos, which are taken using an iPhone to go around the objects in 360 degrees. It contains around 8500 recorded objects and nearly 20000 RGB-D videos across 46 common object categories. These videos are taken with diverse cluttered backgrounds with three setups to cover as many real-world scenarios as possible: (i) a single object in one video; (ii) multiple objects in one video; and (iii) an object with a static hand in one video. The dataset is annotated with object masks, real-world scale camera poses, and reconstructed aggregated point clouds from RGBD videos. We benchmark four tasks with WildRGB-D including novel view synthesis, camera pose estimation, object 6d pose estimation, and object surface reconstruction. Our experiments show that the large-scale capture of RGB-D objects provides a large potential to advance 3D object learning. Our project page is https://wildrgbd.github.io/.
COLMAP-Free 3D Gaussian Splatting
Dec 12, 2023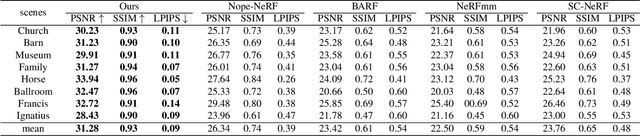
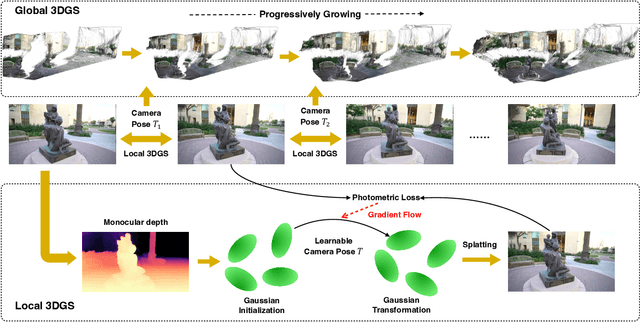
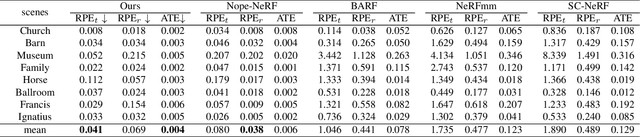
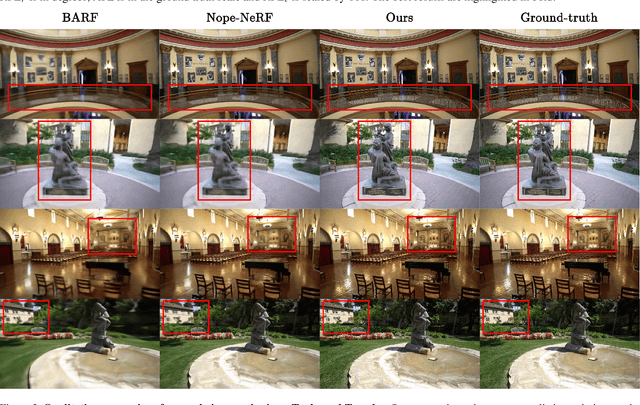
Abstract:While neural rendering has led to impressive advances in scene reconstruction and novel view synthesis, it relies heavily on accurately pre-computed camera poses. To relax this constraint, multiple efforts have been made to train Neural Radiance Fields (NeRFs) without pre-processed camera poses. However, the implicit representations of NeRFs provide extra challenges to optimize the 3D structure and camera poses at the same time. On the other hand, the recently proposed 3D Gaussian Splatting provides new opportunities given its explicit point cloud representations. This paper leverages both the explicit geometric representation and the continuity of the input video stream to perform novel view synthesis without any SfM preprocessing. We process the input frames in a sequential manner and progressively grow the 3D Gaussians set by taking one input frame at a time, without the need to pre-compute the camera poses. Our method significantly improves over previous approaches in view synthesis and camera pose estimation under large motion changes. Our project page is https://oasisyang.github.io/colmap-free-3dgs
3D Reconstruction with Generalizable Neural Fields using Scene Priors
Sep 29, 2023



Abstract:High-fidelity 3D scene reconstruction has been substantially advanced by recent progress in neural fields. However, most existing methods train a separate network from scratch for each individual scene. This is not scalable, inefficient, and unable to yield good results given limited views. While learning-based multi-view stereo methods alleviate this issue to some extent, their multi-view setting makes it less flexible to scale up and to broad applications. Instead, we introduce training generalizable Neural Fields incorporating scene Priors (NFPs). The NFP network maps any single-view RGB-D image into signed distance and radiance values. A complete scene can be reconstructed by merging individual frames in the volumetric space WITHOUT a fusion module, which provides better flexibility. The scene priors can be trained on large-scale datasets, allowing for fast adaptation to the reconstruction of a new scene with fewer views. NFP not only demonstrates SOTA scene reconstruction performance and efficiency, but it also supports single-image novel-view synthesis, which is underexplored in neural fields. More qualitative results are available at: https://oasisyang.github.io/neural-prior
FastPoseGait: A Toolbox and Benchmark for Efficient Pose-based Gait Recognition
Sep 02, 2023Abstract:We present FastPoseGait, an open-source toolbox for pose-based gait recognition based on PyTorch. Our toolbox supports a set of cutting-edge pose-based gait recognition algorithms and a variety of related benchmarks. Unlike other pose-based projects that focus on a single algorithm, FastPoseGait integrates several state-of-the-art (SOTA) algorithms under a unified framework, incorporating both the latest advancements and best practices to ease the comparison of effectiveness and efficiency. In addition, to promote future research on pose-based gait recognition, we provide numerous pre-trained models and detailed benchmark results, which offer valuable insights and serve as a reference for further investigations. By leveraging the highly modular structure and diverse methods offered by FastPoseGait, researchers can quickly delve into pose-based gait recognition and promote development in the field. In this paper, we outline various features of this toolbox, aiming that our toolbox and benchmarks can further foster collaboration, facilitate reproducibility, and encourage the development of innovative algorithms for pose-based gait recognition. FastPoseGait is available at https://github.com//BNU-IVC/FastPoseGait and is actively maintained. We will continue updating this report as we add new features.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge