Zheng Ding
TreeGRPO: Tree-Advantage GRPO for Online RL Post-Training of Diffusion Models
Dec 09, 2025



Abstract:Reinforcement learning (RL) post-training is crucial for aligning generative models with human preferences, but its prohibitive computational cost remains a major barrier to widespread adoption. We introduce \textbf{TreeGRPO}, a novel RL framework that dramatically improves training efficiency by recasting the denoising process as a search tree. From shared initial noise samples, TreeGRPO strategically branches to generate multiple candidate trajectories while efficiently reusing their common prefixes. This tree-structured approach delivers three key advantages: (1) \emph{High sample efficiency}, achieving better performance under same training samples (2) \emph{Fine-grained credit assignment} via reward backpropagation that computes step-specific advantages, overcoming the uniform credit assignment limitation of trajectory-based methods, and (3) \emph{Amortized computation} where multi-child branching enables multiple policy updates per forward pass. Extensive experiments on both diffusion and flow-based models demonstrate that TreeGRPO achieves \textbf{2.4$\times$ faster training} while establishing a superior Pareto frontier in the efficiency-reward trade-off space. Our method consistently outperforms GRPO baselines across multiple benchmarks and reward models, providing a scalable and effective pathway for RL-based visual generative model alignment. The project website is available at treegrpo.github.io.
C3Editor: Achieving Controllable Consistency in 2D Model for 3D Editing
Oct 06, 2025Abstract:Existing 2D-lifting-based 3D editing methods often encounter challenges related to inconsistency, stemming from the lack of view-consistent 2D editing models and the difficulty of ensuring consistent editing across multiple views. To address these issues, we propose C3Editor, a controllable and consistent 2D-lifting-based 3D editing framework. Given an original 3D representation and a text-based editing prompt, our method selectively establishes a view-consistent 2D editing model to achieve superior 3D editing results. The process begins with the controlled selection of a ground truth (GT) view and its corresponding edited image as the optimization target, allowing for user-defined manual edits. Next, we fine-tune the 2D editing model within the GT view and across multiple views to align with the GT-edited image while ensuring multi-view consistency. To meet the distinct requirements of GT view fitting and multi-view consistency, we introduce separate LoRA modules for targeted fine-tuning. Our approach delivers more consistent and controllable 2D and 3D editing results than existing 2D-lifting-based methods, outperforming them in both qualitative and quantitative evaluations.
Explorative Inbetweening of Time and Space
Mar 21, 2024


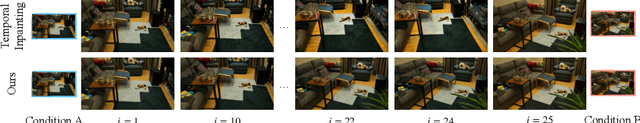
Abstract:We introduce bounded generation as a generalized task to control video generation to synthesize arbitrary camera and subject motion based only on a given start and end frame. Our objective is to fully leverage the inherent generalization capability of an image-to-video model without additional training or fine-tuning of the original model. This is achieved through the proposed new sampling strategy, which we call Time Reversal Fusion, that fuses the temporally forward and backward denoising paths conditioned on the start and end frame, respectively. The fused path results in a video that smoothly connects the two frames, generating inbetweening of faithful subject motion, novel views of static scenes, and seamless video looping when the two bounding frames are identical. We curate a diverse evaluation dataset of image pairs and compare against the closest existing methods. We find that Time Reversal Fusion outperforms related work on all subtasks, exhibiting the ability to generate complex motions and 3D-consistent views guided by bounded frames. See project page at https://time-reversal.github.io.
HOIDiffusion: Generating Realistic 3D Hand-Object Interaction Data
Mar 18, 2024



Abstract:3D hand-object interaction data is scarce due to the hardware constraints in scaling up the data collection process. In this paper, we propose HOIDiffusion for generating realistic and diverse 3D hand-object interaction data. Our model is a conditional diffusion model that takes both the 3D hand-object geometric structure and text description as inputs for image synthesis. This offers a more controllable and realistic synthesis as we can specify the structure and style inputs in a disentangled manner. HOIDiffusion is trained by leveraging a diffusion model pre-trained on large-scale natural images and a few 3D human demonstrations. Beyond controllable image synthesis, we adopt the generated 3D data for learning 6D object pose estimation and show its effectiveness in improving perception systems. Project page: https://mq-zhang1.github.io/HOIDiffusion
Restoration by Generation with Constrained Priors
Dec 28, 2023



Abstract:The inherent generative power of denoising diffusion models makes them well-suited for image restoration tasks where the objective is to find the optimal high-quality image within the generative space that closely resembles the input image. We propose a method to adapt a pretrained diffusion model for image restoration by simply adding noise to the input image to be restored and then denoise. Our method is based on the observation that the space of a generative model needs to be constrained. We impose this constraint by finetuning the generative model with a set of anchor images that capture the characteristics of the input image. With the constrained space, we can then leverage the sampling strategy used for generation to do image restoration. We evaluate against previous methods and show superior performances on multiple real-world restoration datasets in preserving identity and image quality. We also demonstrate an important and practical application on personalized restoration, where we use a personal album as the anchor images to constrain the generative space. This approach allows us to produce results that accurately preserve high-frequency details, which previous works are unable to do. Project webpage: https://gen2res.github.io.
TokenCompose: Grounding Diffusion with Token-level Supervision
Dec 06, 2023



Abstract:We present TokenCompose, a Latent Diffusion Model for text-to-image generation that achieves enhanced consistency between user-specified text prompts and model-generated images. Despite its tremendous success, the standard denoising process in the Latent Diffusion Model takes text prompts as conditions only, absent explicit constraint for the consistency between the text prompts and the image contents, leading to unsatisfactory results for composing multiple object categories. TokenCompose aims to improve multi-category instance composition by introducing the token-wise consistency terms between the image content and object segmentation maps in the finetuning stage. TokenCompose can be applied directly to the existing training pipeline of text-conditioned diffusion models without extra human labeling information. By finetuning Stable Diffusion, the model exhibits significant improvements in multi-category instance composition and enhanced photorealism for its generated images.
Dolfin: Diffusion Layout Transformers without Autoencoder
Oct 25, 2023



Abstract:In this paper, we introduce a novel generative model, Diffusion Layout Transformers without Autoencoder (Dolfin), which significantly improves the modeling capability with reduced complexity compared to existing methods. Dolfin employs a Transformer-based diffusion process to model layout generation. In addition to an efficient bi-directional (non-causal joint) sequence representation, we further propose an autoregressive diffusion model (Dolfin-AR) that is especially adept at capturing rich semantic correlations for the neighboring objects, such as alignment, size, and overlap. When evaluated against standard generative layout benchmarks, Dolfin notably improves performance across various metrics (fid, alignment, overlap, MaxIoU and DocSim scores), enhancing transparency and interoperability in the process. Moreover, Dolfin's applications extend beyond layout generation, making it suitable for modeling geometric structures, such as line segments. Our experiments present both qualitative and quantitative results to demonstrate the advantages of Dolfin.
Patched Denoising Diffusion Models For High-Resolution Image Synthesis
Aug 02, 2023



Abstract:We propose an effective denoising diffusion model for generating high-resolution images (e.g., 1024$\times$512), trained on small-size image patches (e.g., 64$\times$64). We name our algorithm Patch-DM, in which a new feature collage strategy is designed to avoid the boundary artifact when synthesizing large-size images. Feature collage systematically crops and combines partial features of the neighboring patches to predict the features of a shifted image patch, allowing the seamless generation of the entire image due to the overlap in the patch feature space. Patch-DM produces high-quality image synthesis results on our newly collected dataset of nature images (1024$\times$512), as well as on standard benchmarks of smaller sizes (256$\times$256), including LSUN-Bedroom, LSUN-Church, and FFHQ. We compare our method with previous patch-based generation methods and achieve state-of-the-art FID scores on all four datasets. Further, Patch-DM also reduces memory complexity compared to the classic diffusion models.
DiffusionRig: Learning Personalized Priors for Facial Appearance Editing
Apr 13, 2023


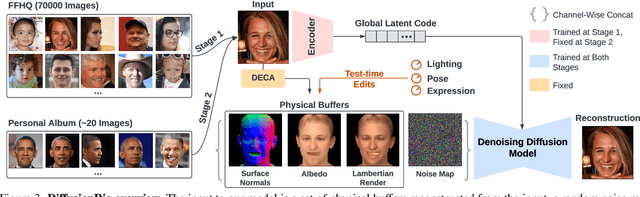
Abstract:We address the problem of learning person-specific facial priors from a small number (e.g., 20) of portrait photos of the same person. This enables us to edit this specific person's facial appearance, such as expression and lighting, while preserving their identity and high-frequency facial details. Key to our approach, which we dub DiffusionRig, is a diffusion model conditioned on, or "rigged by," crude 3D face models estimated from single in-the-wild images by an off-the-shelf estimator. On a high level, DiffusionRig learns to map simplistic renderings of 3D face models to realistic photos of a given person. Specifically, DiffusionRig is trained in two stages: It first learns generic facial priors from a large-scale face dataset and then person-specific priors from a small portrait photo collection of the person of interest. By learning the CGI-to-photo mapping with such personalized priors, DiffusionRig can "rig" the lighting, facial expression, head pose, etc. of a portrait photo, conditioned only on coarse 3D models while preserving this person's identity and other high-frequency characteristics. Qualitative and quantitative experiments show that DiffusionRig outperforms existing approaches in both identity preservation and photorealism. Please see the project website: https://diffusionrig.github.io for the supplemental material, video, code, and data.
Point Cloud Recognition with Position-to-Structure Attention Transformers
Oct 05, 2022



Abstract:In this paper, we present Position-to-Structure Attention Transformers (PS-Former), a Transformer-based algorithm for 3D point cloud recognition. PS-Former deals with the challenge in 3D point cloud representation where points are not positioned in a fixed grid structure and have limited feature description (only 3D coordinates ($x, y, z$) for scattered points). Existing Transformer-based architectures in this domain often require a pre-specified feature engineering step to extract point features. Here, we introduce two new aspects in PS-Former: 1) a learnable condensation layer that performs point downsampling and feature extraction; and 2) a Position-to-Structure Attention mechanism that recursively enriches the structural information with the position attention branch. Compared with the competing methods, while being generic with less heuristics feature designs, PS-Former demonstrates competitive experimental results on three 3D point cloud tasks including classification, part segmentation, and scene segmentation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge