Zhiyang Chen
ERNIE 5.0 Technical Report
Feb 04, 2026Abstract:In this report, we introduce ERNIE 5.0, a natively autoregressive foundation model desinged for unified multimodal understanding and generation across text, image, video, and audio. All modalities are trained from scratch under a unified next-group-of-tokens prediction objective, based on an ultra-sparse mixture-of-experts (MoE) architecture with modality-agnostic expert routing. To address practical challenges in large-scale deployment under diverse resource constraints, ERNIE 5.0 adopts a novel elastic training paradigm. Within a single pre-training run, the model learns a family of sub-models with varying depths, expert capacities, and routing sparsity, enabling flexible trade-offs among performance, model size, and inference latency in memory- or time-constrained scenarios. Moreover, we systematically address the challenges of scaling reinforcement learning to unified foundation models, thereby guaranteeing efficient and stable post-training under ultra-sparse MoE architectures and diverse multimodal settings. Extensive experiments demonstrate that ERNIE 5.0 achieves strong and balanced performance across multiple modalities. To the best of our knowledge, among publicly disclosed models, ERNIE 5.0 represents the first production-scale realization of a trillion-parameter unified autoregressive model that supports both multimodal understanding and generation. To facilitate further research, we present detailed visualizations of modality-agnostic expert routing in the unified model, alongside comprehensive empirical analysis of elastic training, aiming to offer profound insights to the community.
Minimum-Cost Network Flow with Dual Predictions
Jan 28, 2026Abstract:Recent work has shown that machine-learned predictions can provably improve the performance of classic algorithms. In this work, we propose the first minimum-cost network flow algorithm augmented with a dual prediction. Our method is based on a classic minimum-cost flow algorithm, namely $\varepsilon$-relaxation. We provide time complexity bounds in terms of the infinity norm prediction error, which is both consistent and robust. We also prove sample complexity bounds for PAC-learning the prediction. We empirically validate our theoretical results on two applications of minimum-cost flow, i.e., traffic networks and chip escape routing, in which we learn a fixed prediction, and a feature-based neural network model to infer the prediction, respectively. Experimental results illustrate $12.74\times$ and $1.64\times$ average speedup on two applications.
MiMo-V2-Flash Technical Report
Jan 08, 2026Abstract:We present MiMo-V2-Flash, a Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) model with 309B total parameters and 15B active parameters, designed for fast, strong reasoning and agentic capabilities. MiMo-V2-Flash adopts a hybrid attention architecture that interleaves Sliding Window Attention (SWA) with global attention, with a 128-token sliding window under a 5:1 hybrid ratio. The model is pre-trained on 27 trillion tokens with Multi-Token Prediction (MTP), employing a native 32k context length and subsequently extended to 256k. To efficiently scale post-training compute, MiMo-V2-Flash introduces a novel Multi-Teacher On-Policy Distillation (MOPD) paradigm. In this framework, domain-specialized teachers (e.g., trained via large-scale reinforcement learning) provide dense and token-level reward, enabling the student model to perfectly master teacher expertise. MiMo-V2-Flash rivals top-tier open-weight models such as DeepSeek-V3.2 and Kimi-K2, despite using only 1/2 and 1/3 of their total parameters, respectively. During inference, by repurposing MTP as a draft model for speculative decoding, MiMo-V2-Flash achieves up to 3.6 acceptance length and 2.6x decoding speedup with three MTP layers. We open-source both the model weights and the three-layer MTP weights to foster open research and community collaboration.
Empowering DINO Representations for Underwater Instance Segmentation via Aligner and Prompter
Nov 11, 2025Abstract:Underwater instance segmentation (UIS), integrating pixel-level understanding and instance-level discrimination, is a pivotal technology in marine resource exploration and ecological protection. In recent years, large-scale pretrained visual foundation models, exemplified by DINO, have advanced rapidly and demonstrated remarkable performance on complex downstream tasks. In this paper, we demonstrate that DINO can serve as an effective feature learner for UIS, and we introduce DiveSeg, a novel framework built upon two insightful components: (1) The AquaStyle Aligner, designed to embed underwater color style features into the DINO fine-tuning process, facilitating better adaptation to the underwater domain. (2) The ObjectPrior Prompter, which incorporates binary segmentation-based prompts to deliver object-level priors, provides essential guidance for instance segmentation task that requires both object- and instance-level reasoning. We conduct thorough experiments on the popular UIIS and USIS10K datasets, and the results show that DiveSeg achieves the state-of-the-art performance. Code: https://github.com/ettof/Diveseg.
From Seeing to Predicting: A Vision-Language Framework for Trajectory Forecasting and Controlled Video Generation
Oct 01, 2025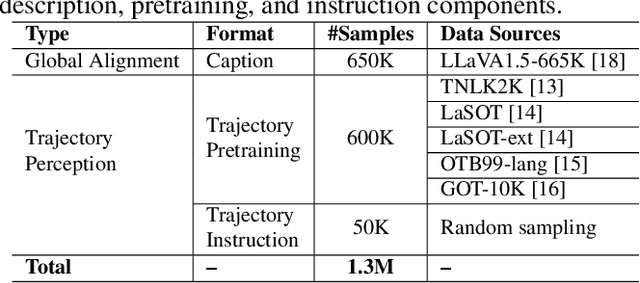
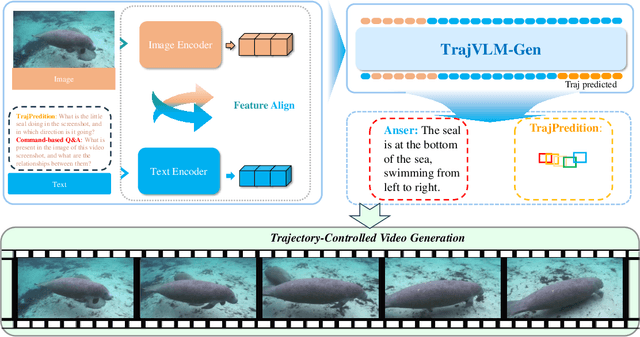
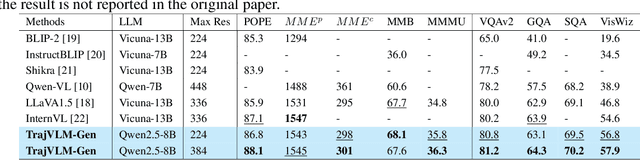
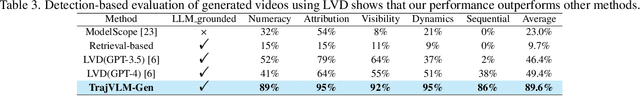
Abstract:Current video generation models produce physically inconsistent motion that violates real-world dynamics. We propose TrajVLM-Gen, a two-stage framework for physics-aware image-to-video generation. First, we employ a Vision Language Model to predict coarse-grained motion trajectories that maintain consistency with real-world physics. Second, these trajectories guide video generation through attention-based mechanisms for fine-grained motion refinement. We build a trajectory prediction dataset based on video tracking data with realistic motion patterns. Experiments on UCF-101 and MSR-VTT demonstrate that TrajVLM-Gen outperforms existing methods, achieving competitive FVD scores of 545 on UCF-101 and 539 on MSR-VTT.
InfLVG: Reinforce Inference-Time Consistent Long Video Generation with GRPO
May 23, 2025Abstract:Recent advances in text-to-video generation, particularly with autoregressive models, have enabled the synthesis of high-quality videos depicting individual scenes. However, extending these models to generate long, cross-scene videos remains a significant challenge. As the context length grows during autoregressive decoding, computational costs rise sharply, and the model's ability to maintain consistency and adhere to evolving textual prompts deteriorates. We introduce InfLVG, an inference-time framework that enables coherent long video generation without requiring additional long-form video data. InfLVG leverages a learnable context selection policy, optimized via Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO), to dynamically identify and retain the most semantically relevant context throughout the generation process. Instead of accumulating the entire generation history, the policy ranks and selects the top-$K$ most contextually relevant tokens, allowing the model to maintain a fixed computational budget while preserving content consistency and prompt alignment. To optimize the policy, we design a hybrid reward function that jointly captures semantic alignment, cross-scene consistency, and artifact reduction. To benchmark performance, we introduce the Cross-scene Video Benchmark (CsVBench) along with an Event Prompt Set (EPS) that simulates complex multi-scene transitions involving shared subjects and varied actions/backgrounds. Experimental results show that InfLVG can extend video length by up to 9$\times$, achieving strong consistency and semantic fidelity across scenes. Our code is available at https://github.com/MAPLE-AIGC/InfLVG.
SLOT: Sample-specific Language Model Optimization at Test-time
May 18, 2025Abstract:We propose SLOT (Sample-specific Language Model Optimization at Test-time), a novel and parameter-efficient test-time inference approach that enhances a language model's ability to more accurately respond to individual prompts. Existing Large Language Models (LLMs) often struggle with complex instructions, leading to poor performances on those not well represented among general samples. To address this, SLOT conducts few optimization steps at test-time to update a light-weight sample-specific parameter vector. It is added to the final hidden layer before the output head, and enables efficient adaptation by caching the last layer features during per-sample optimization. By minimizing the cross-entropy loss on the input prompt only, SLOT helps the model better aligned with and follow each given instruction. In experiments, we demonstrate that our method outperforms the compared models across multiple benchmarks and LLMs. For example, Qwen2.5-7B with SLOT achieves an accuracy gain of 8.6% on GSM8K from 57.54% to 66.19%, while DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Llama-70B with SLOT achieves a SOTA accuracy of 68.69% on GPQA among 70B-level models. Our code is available at https://github.com/maple-research-lab/SLOT.
RAGSynth: Synthetic Data for Robust and Faithful RAG Component Optimization
May 16, 2025Abstract:RAG can enhance the performance of LLMs on knowledge-intensive tasks. Various RAG paradigms, including vanilla, planning-based, and iterative RAG, are built upon 2 cores: the retriever, which should robustly select relevant documents across complex queries, and the generator, which should faithfully synthesize responses. However, existing retrievers rely heavily on public knowledge and struggle with queries of varying logical complexity and clue completeness, while generators frequently face fidelity problems. In this work, we introduce RAGSynth, a framework that includes a data construction modeling and a corresponding synthetic data generation implementation, designed to optimize retriever robustness and generator fidelity. Additionally, we present SynthBench, a benchmark encompassing 8 domain-specific documents across 4 domains, featuring diverse query complexities, clue completeness, and fine-grained citation granularity. Leveraging RAGSynth, we generate a large-scale synthetic dataset, including single and multi-hop. Extensive experiments demonstrate that the synthetic data significantly improves the robustness of the retrievers and the fidelity of the generators. Additional evaluations confirm that RAGSynth can also generalize well across different domains. By integrating the optimized retrievers into various RAG paradigms, we consistently observe enhanced RAG system performance. We have open-sourced the implementation on https://github.com/EachSheep/RAGSynth.
Reinforcing the Diffusion Chain of Lateral Thought with Diffusion Language Models
May 15, 2025Abstract:We introduce the \emph{Diffusion Chain of Lateral Thought (DCoLT)}, a reasoning framework for diffusion language models. DCoLT treats each intermediate step in the reverse diffusion process as a latent "thinking" action and optimizes the entire reasoning trajectory to maximize the reward on the correctness of the final answer with outcome-based Reinforcement Learning (RL). Unlike traditional Chain-of-Thought (CoT) methods that follow a causal, linear thinking process, DCoLT allows bidirectional, non-linear reasoning with no strict rule on grammatical correctness amid its intermediate steps of thought. We implement DCoLT on two representative Diffusion Language Models (DLMs). First, we choose SEDD as a representative continuous-time discrete diffusion model, where its concrete score derives a probabilistic policy to maximize the RL reward over the entire sequence of intermediate diffusion steps. We further consider the discrete-time masked diffusion language model -- LLaDA, and find that the order to predict and unmask tokens plays an essential role to optimize its RL action resulting from the ranking-based Unmasking Policy Module (UPM) defined by the Plackett-Luce model. Experiments on both math and code generation tasks show that using only public data and 16 H800 GPUs, DCoLT-reinforced DLMs outperform other DLMs trained by SFT or RL or even both. Notably, DCoLT-reinforced LLaDA boosts its reasoning accuracy by +9.8%, +5.7%, +11.4%, +19.5% on GSM8K, MATH, MBPP, and HumanEval.
The 1st Solution for 4th PVUW MeViS Challenge: Unleashing the Potential of Large Multimodal Models for Referring Video Segmentation
Apr 07, 2025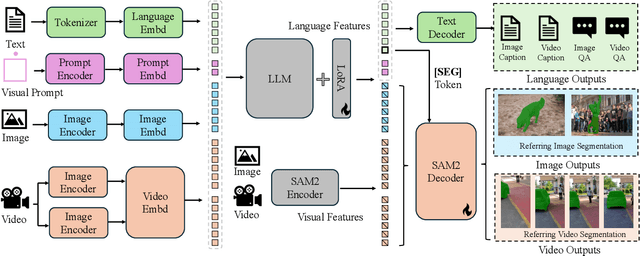
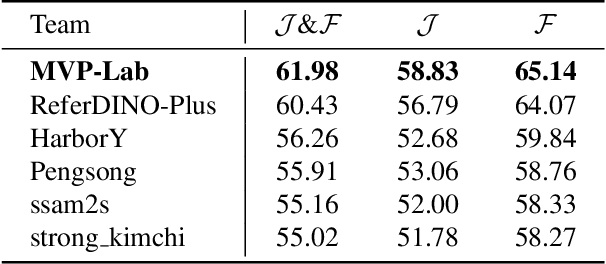
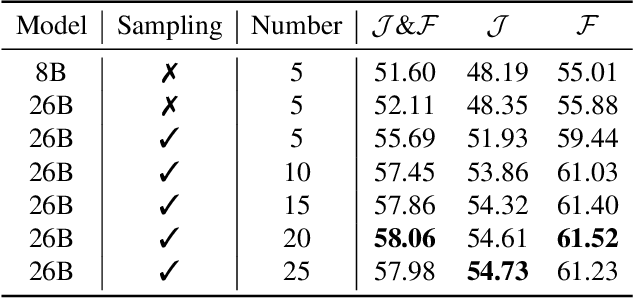
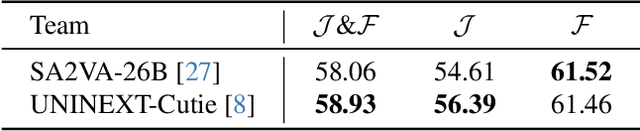
Abstract:Motion expression video segmentation is designed to segment objects in accordance with the input motion expressions. In contrast to the conventional Referring Video Object Segmentation (RVOS), it places emphasis on motion as well as multi-object expressions, making it more arduous. Recently, Large Multimodal Models (LMMs) have begun to shine in RVOS due to their powerful vision-language perception capabilities. In this work, we propose a simple and effective inference optimization method to fully unleash the potential of LMMs in referring video segmentation. Firstly, we use Sa2VA as our baseline, which is a unified LMM for dense grounded understanding of both images and videos. Secondly, we uniformly sample the video frames during the inference process to enhance the model's understanding of the entire video. Finally, we integrate the results of multiple expert models to mitigate the erroneous predictions of a single model. Our solution achieved 61.98% J&F on the MeViS test set and ranked 1st place in the 4th PVUW Challenge MeViS Track at CVPR 2025.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge