Yuxiang Wang
End-to-End Semantic ID Generation for Generative Advertisement Recommendation
Feb 12, 2026Abstract:Generative Recommendation (GR) has excelled by framing recommendation as next-token prediction. This paradigm relies on Semantic IDs (SIDs) to tokenize large-scale items into discrete sequences. Existing GR approaches predominantly generate SIDs via Residual Quantization (RQ), where items are encoded into embeddings and then quantized to discrete SIDs. However, this paradigm suffers from inherent limitations: 1) Objective misalignment and semantic degradation stemming from the two-stage compression; 2) Error accumulation inherent in the structure of RQ. To address these limitations, we propose UniSID, a Unified SID generation framework for generative advertisement recommendation. Specifically, we jointly optimize embeddings and SIDs in an end-to-end manner from raw advertising data, enabling semantic information to flow directly into the SID space and thus addressing the inherent limitations of the two-stage cascading compression paradigm. To capture fine-grained semantics, a multi-granularity contrastive learning strategy is introduced to align distinct items across SID levels. Finally, a summary-based ad reconstruction mechanism is proposed to encourage SIDs to capture high-level semantic information that is not explicitly present in advertising contexts. Experiments demonstrate that UniSID consistently outperforms state-of-the-art SID generation methods, yielding up to a 4.62% improvement in Hit Rate metrics across downstream advertising scenarios compared to the strongest baseline.
FedMosaic: Federated Retrieval-Augmented Generation via Parametric Adapters
Feb 05, 2026Abstract:Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) enhances Large Language Models (LLMs) by grounding generation in external knowledge to improve factuality and reduce hallucinations. Yet most deployments assume a centralized corpus, which is infeasible in privacy aware domains where knowledge remains siloed. This motivates federated RAG (FedRAG), where a central LLM server collaborates with distributed silos without sharing raw documents. In context RAG violates this requirement by transmitting verbatim documents, whereas parametric RAG encodes documents into lightweight adapters that merge with a frozen LLM at inference, avoiding raw-text exchange. We adopt the parametric approach but face two unique challenges induced by FedRAG: high storage and communication from per-document adapters, and destructive aggregation caused by indiscriminately merging multiple adapters. We present FedMosaic, the first federated RAG framework built on parametric adapters. FedMosaic clusters semantically related documents into multi-document adapters with document-specific masks to reduce overhead while preserving specificity, and performs selective adapter aggregation to combine only relevance-aligned, nonconflicting adapters. Experiments show that FedMosaic achieves an average 10.9% higher accuracy than state-of-the-art methods in four categories, while lowering storage costs by 78.8% to 86.3% and communication costs by 91.4%, and never sharing raw documents.
QA-ReID: Quality-Aware Query-Adaptive Convolution Leveraging Fused Global and Structural Cues for Clothes-Changing ReID
Jan 27, 2026Abstract:Unlike conventional person re-identification (ReID), clothes-changing ReID (CC-ReID) presents severe challenges due to substantial appearance variations introduced by clothing changes. In this work, we propose the Quality-Aware Dual-Branch Matching (QA-ReID), which jointly leverages RGB-based features and parsing-based representations to model both global appearance and clothing-invariant structural cues. These heterogeneous features are adaptively fused through a multi-modal attention module. At the matching stage, we further design the Quality-Aware Query Adaptive Convolution (QAConv-QA), which incorporates pixel-level importance weighting and bidirectional consistency constraints to enhance robustness against clothing variations. Extensive experiments demonstrate that QA-ReID achieves state-of-the-art performance on multiple benchmarks, including PRCC, LTCC, and VC-Clothes, and significantly outperforms existing approaches under cross-clothing scenarios.
VoxPrivacy: A Benchmark for Evaluating Interactional Privacy of Speech Language Models
Jan 27, 2026Abstract:As Speech Language Models (SLMs) transition from personal devices to shared, multi-user environments such as smart homes, a new challenge emerges: the model is expected to distinguish between users to manage information flow appropriately. Without this capability, an SLM could reveal one user's confidential schedule to another, a privacy failure we term interactional privacy. Thus, the ability to generate speaker-aware responses becomes essential for SLM safe deployment. Current SLM benchmarks test dialogue ability but overlook speaker identity. Multi-speaker benchmarks check who said what without assessing whether SLMs adapt their responses. Privacy benchmarks focus on globally sensitive data (e.g., bank passwords) while neglecting contextual privacy-sensitive information (e.g., a user's private appointment). To address this gap, we introduce VoxPrivacy, the first benchmark designed to evaluate interactional privacy in SLMs. VoxPrivacy spans three tiers of increasing difficulty, from following direct secrecy commands to proactively protecting privacy. Our evaluation of nine SLMs on a 32-hour bilingual dataset reveals a widespread vulnerability: most open-source models perform close to random chance (around 50% accuracy) on conditional privacy decisions, while even strong closed-source systems fall short on proactive privacy inference. We further validate these findings on Real-VoxPrivacy, a human-recorded subset, confirming that failures observed on synthetic data persist in real speech. Finally, we demonstrate a viable path forward: by fine-tuning on a new 4,000-hour training set, we improve privacy-preserving abilities while maintaining robustness. To support future work, we release the VoxPrivacy benchmark, the large-scale training set, and the fine-tuned model to foster the development of safer and more context-aware SLMs.
Beyond Linearization: Attributed Table Graphs for Table Reasoning
Jan 13, 2026Abstract:Table reasoning, a task to answer questions by reasoning over data presented in tables, is an important topic due to the prevalence of knowledge stored in tabular formats. Recent solutions use Large Language Models (LLMs), exploiting the semantic understanding and reasoning capabilities of LLMs. A common paradigm of such solutions linearizes tables to form plain texts that are served as input to LLMs. This paradigm has critical issues. It loses table structures, lacks explicit reasoning paths for result explainability, and is subject to the "lost-in-the-middle" issue. To address these issues, we propose Table Graph Reasoner (TABGR), a training-free model that represents tables as an Attributed Table Graph (ATG). The ATG explicitly preserves row-column-cell structures while enabling graph-based reasoning for explainability. We further propose a Question-Guided Personalized PageRank (QG-PPR) mechanism to rerank tabular data and mitigate the lost-in-the-middle issue. Extensive experiments on two commonly used benchmarks show that TABGR consistently outperforms state-of-the-art models by up to 9.7% in accuracy. Our code will be made publicly available upon publication.
DevPiolt: Operation Recommendation for IoT Devices at Xiaomi Home
Nov 18, 2025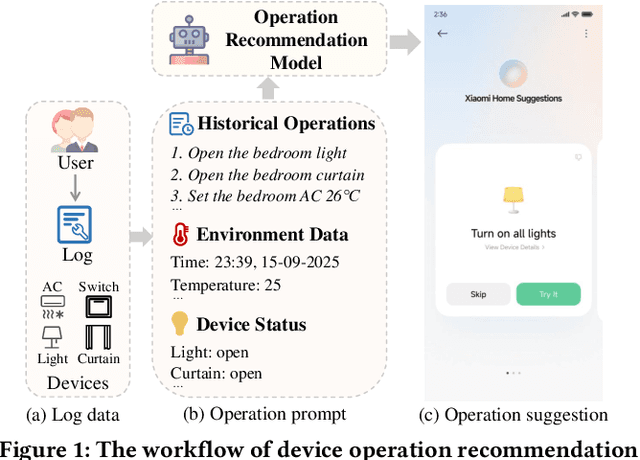
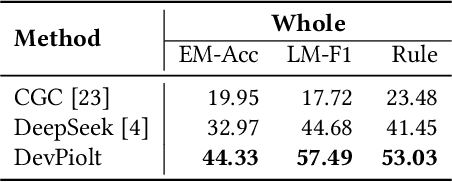
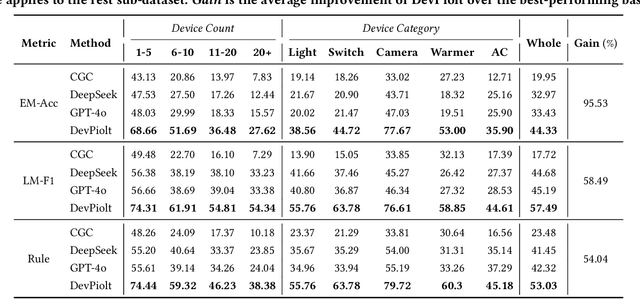
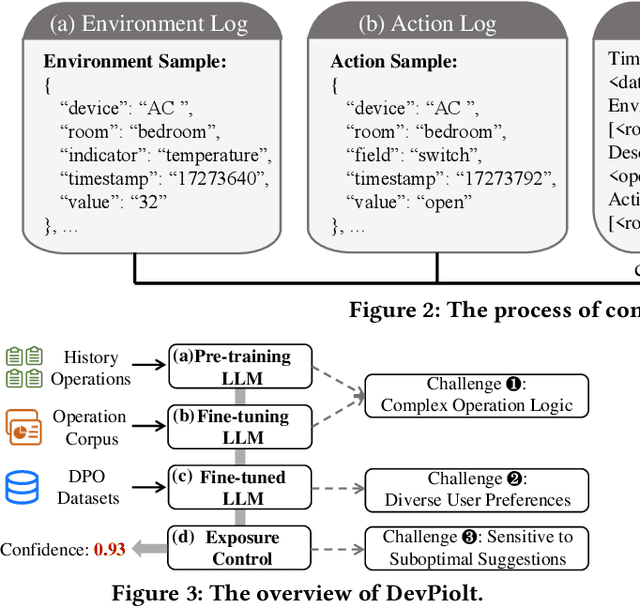
Abstract:Operation recommendation for IoT devices refers to generating personalized device operations for users based on their context, such as historical operations, environment information, and device status. This task is crucial for enhancing user satisfaction and corporate profits. Existing recommendation models struggle with complex operation logic, diverse user preferences, and sensitive to suboptimal suggestions, limiting their applicability to IoT device operations. To address these issues, we propose DevPiolt, a LLM-based recommendation model for IoT device operations. Specifically, we first equip the LLM with fundamental domain knowledge of IoT operations via continual pre-training and multi-task fine-tuning. Then, we employ direct preference optimization to align the fine-tuned LLM with specific user preferences. Finally, we design a confidence-based exposure control mechanism to avoid negative user experiences from low-quality recommendations. Extensive experiments show that DevPiolt significantly outperforms baselines on all datasets, with an average improvement of 69.5% across all metrics. DevPiolt has been practically deployed in Xiaomi Home app for one quarter, providing daily operation recommendations to 255,000 users. Online experiment results indicate a 21.6% increase in unique visitor device coverage and a 29.1% increase in page view acceptance rates.
DRWKV: Focusing on Object Edges for Low-Light Image Enhancement
Jul 24, 2025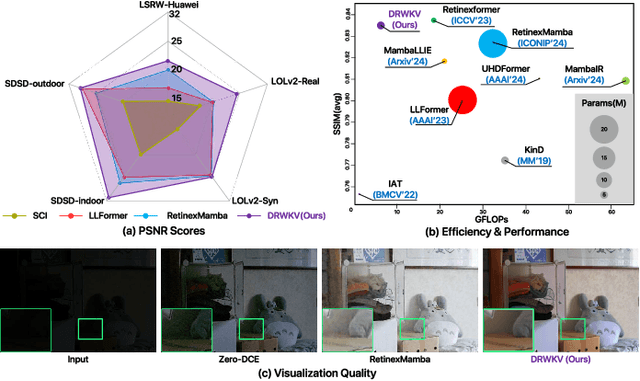
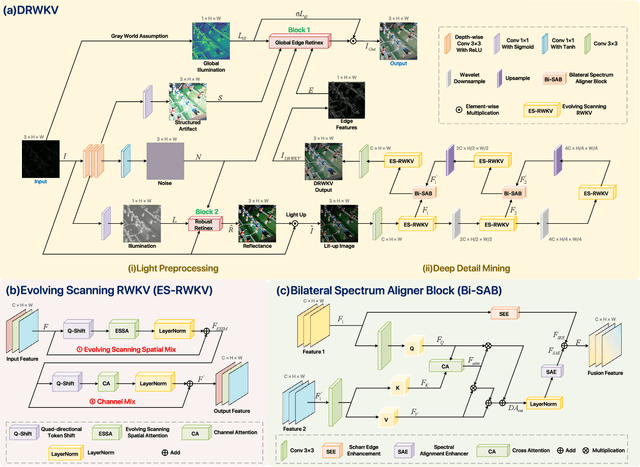
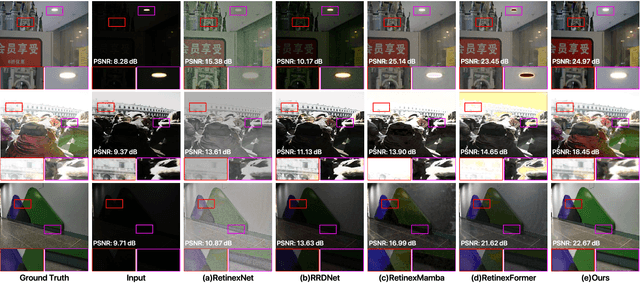

Abstract:Low-light image enhancement remains a challenging task, particularly in preserving object edge continuity and fine structural details under extreme illumination degradation. In this paper, we propose a novel model, DRWKV (Detailed Receptance Weighted Key Value), which integrates our proposed Global Edge Retinex (GER) theory, enabling effective decoupling of illumination and edge structures for enhanced edge fidelity. Secondly, we introduce Evolving WKV Attention, a spiral-scanning mechanism that captures spatial edge continuity and models irregular structures more effectively. Thirdly, we design the Bilateral Spectrum Aligner (Bi-SAB) and a tailored MS2-Loss to jointly align luminance and chrominance features, improving visual naturalness and mitigating artifacts. Extensive experiments on five LLIE benchmarks demonstrate that DRWKV achieves leading performance in PSNR, SSIM, and NIQE while maintaining low computational complexity. Furthermore, DRWKV enhances downstream performance in low-light multi-object tracking tasks, validating its generalization capabilities.
MGDFIS: Multi-scale Global-detail Feature Integration Strategy for Small Object Detection
Jun 15, 2025Abstract:Small object detection in UAV imagery is crucial for applications such as search-and-rescue, traffic monitoring, and environmental surveillance, but it is hampered by tiny object size, low signal-to-noise ratios, and limited feature extraction. Existing multi-scale fusion methods help, but add computational burden and blur fine details, making small object detection in cluttered scenes difficult. To overcome these challenges, we propose the Multi-scale Global-detail Feature Integration Strategy (MGDFIS), a unified fusion framework that tightly couples global context with local detail to boost detection performance while maintaining efficiency. MGDFIS comprises three synergistic modules: the FusionLock-TSS Attention Module, which marries token-statistics self-attention with DynamicTanh normalization to highlight spectral and spatial cues at minimal cost; the Global-detail Integration Module, which fuses multi-scale context via directional convolution and parallel attention while preserving subtle shape and texture variations; and the Dynamic Pixel Attention Module, which generates pixel-wise weighting maps to rebalance uneven foreground and background distributions and sharpen responses to true object regions. Extensive experiments on the VisDrone benchmark demonstrate that MGDFIS consistently outperforms state-of-the-art methods across diverse backbone architectures and detection frameworks, achieving superior precision and recall with low inference time. By striking an optimal balance between accuracy and resource usage, MGDFIS provides a practical solution for small-object detection on resource-constrained UAV platforms.
RAGSynth: Synthetic Data for Robust and Faithful RAG Component Optimization
May 16, 2025Abstract:RAG can enhance the performance of LLMs on knowledge-intensive tasks. Various RAG paradigms, including vanilla, planning-based, and iterative RAG, are built upon 2 cores: the retriever, which should robustly select relevant documents across complex queries, and the generator, which should faithfully synthesize responses. However, existing retrievers rely heavily on public knowledge and struggle with queries of varying logical complexity and clue completeness, while generators frequently face fidelity problems. In this work, we introduce RAGSynth, a framework that includes a data construction modeling and a corresponding synthetic data generation implementation, designed to optimize retriever robustness and generator fidelity. Additionally, we present SynthBench, a benchmark encompassing 8 domain-specific documents across 4 domains, featuring diverse query complexities, clue completeness, and fine-grained citation granularity. Leveraging RAGSynth, we generate a large-scale synthetic dataset, including single and multi-hop. Extensive experiments demonstrate that the synthetic data significantly improves the robustness of the retrievers and the fidelity of the generators. Additional evaluations confirm that RAGSynth can also generalize well across different domains. By integrating the optimized retrievers into various RAG paradigms, we consistently observe enhanced RAG system performance. We have open-sourced the implementation on https://github.com/EachSheep/RAGSynth.
Exploiting Text Semantics for Few and Zero Shot Node Classification on Text-attributed Graph
May 13, 2025



Abstract:Text-attributed graph (TAG) provides a text description for each graph node, and few- and zero-shot node classification on TAGs have many applications in fields such as academia and social networks. Existing work utilizes various graph-based augmentation techniques to train the node and text embeddings, while text-based augmentations are largely unexplored. In this paper, we propose Text Semantics Augmentation (TSA) to improve accuracy by introducing more text semantic supervision signals. Specifically, we design two augmentation techniques, i.e., positive semantics matching and negative semantics contrast, to provide more reference texts for each graph node or text description. Positive semantic matching retrieves texts with similar embeddings to match with a graph node. Negative semantic contrast adds a negative prompt to construct a text description with the opposite semantics, which is contrasted with the original node and text. We evaluate TSA on 5 datasets and compare with 13 state-of-the-art baselines. The results show that TSA consistently outperforms all baselines, and its accuracy improvements over the best-performing baseline are usually over 5%.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge