Xirui Tang
Research on the Online Update Method for Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) Model with Incremental Learning
Jan 13, 2025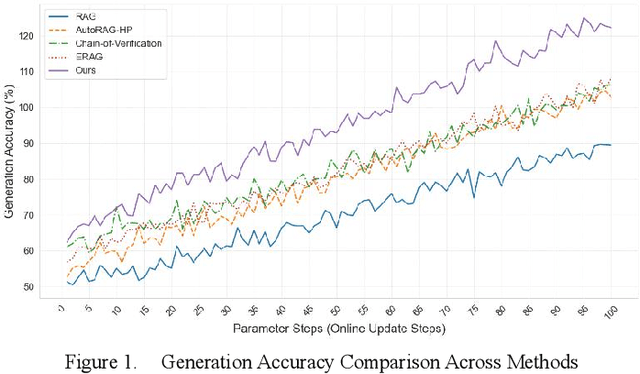
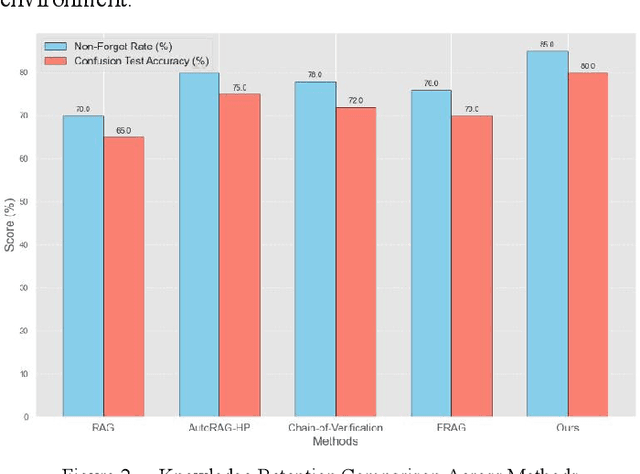
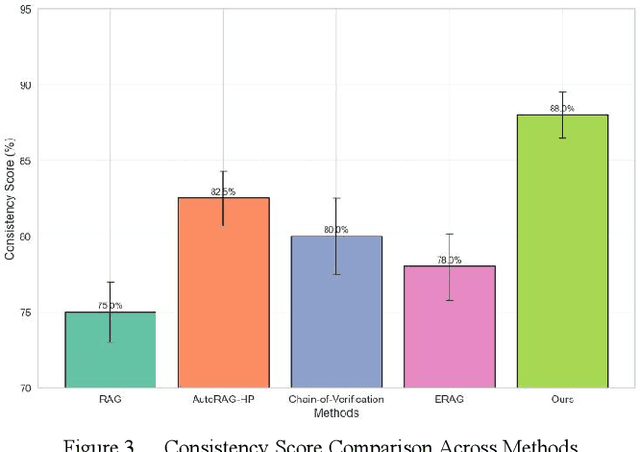
Abstract:In the contemporary context of rapid advancements in information technology and the exponential growth of data volume, language models are confronted with significant challenges in effectively navigating the dynamic and ever-evolving information landscape to update and adapt to novel knowledge in real time. In this work, an online update method is proposed, which is based on the existing Retrieval Enhanced Generation (RAG) model with multiple innovation mechanisms. Firstly, the dynamic memory is used to capture the emerging data samples, and then gradually integrate them into the core model through a tunable knowledge distillation strategy. At the same time, hierarchical indexing and multi-layer gating mechanism are introduced into the retrieval module to ensure that the retrieved content is more targeted and accurate. Finally, a multi-stage network structure is established for different types of inputs in the generation stage, and cross-attention matching and screening are carried out on the intermediate representations of each stage to ensure the effective integration and iterative update of new and old knowledge. Experimental results show that the proposed method is better than the existing mainstream comparison models in terms of knowledge retention and inference accuracy.
Improved Adaboost Algorithm for Web Advertisement Click Prediction Based on Long Short-Term Memory Networks
Aug 08, 2024
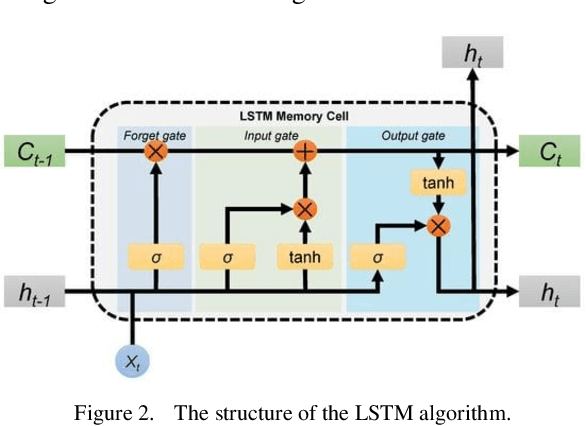
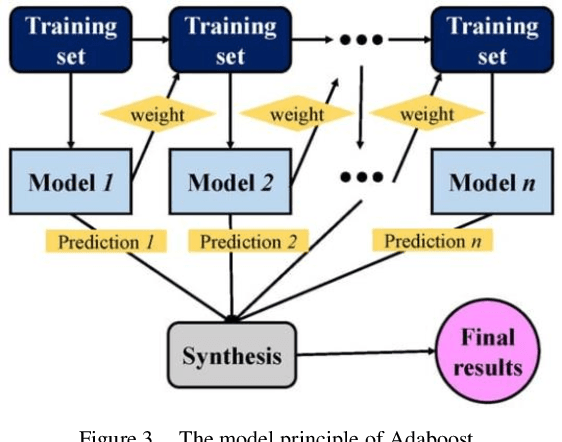
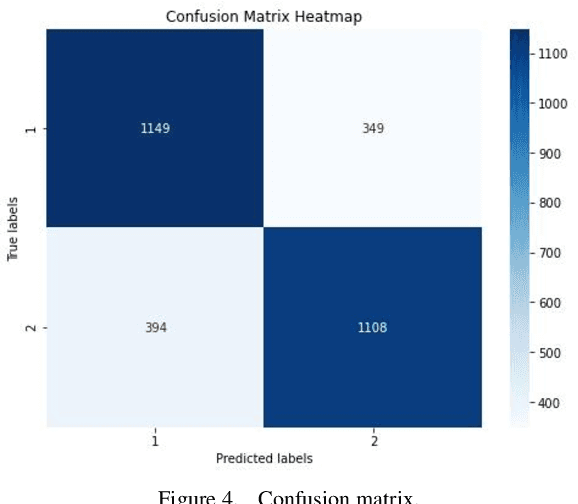
Abstract:This paper explores an improved Adaboost algorithm based on Long Short-Term Memory Networks (LSTMs), which aims to improve the prediction accuracy of user clicks on web page advertisements. By comparing it with several common machine learning algorithms, the paper analyses the advantages of the new model in ad click prediction. It is shown that the improved algorithm proposed in this paper performs well in user ad click prediction with an accuracy of 92%, which is an improvement of 13.6% compared to the highest of 78.4% among the other three base models. This significant improvement indicates that the algorithm is more capable of capturing user behavioural characteristics and time series patterns. In addition, this paper evaluates the model's performance on other performance metrics, including accuracy, recall, and F1 score. The results show that the improved Adaboost algorithm based on LSTM is significantly ahead of the traditional model in all these metrics, which further validates its effectiveness and superiority. Especially when facing complex and dynamically changing user behaviours, the model is able to better adapt and make accurate predictions. In order to ensure the practicality and reliability of the model, this study also focuses on the accuracy difference between the training set and the test set. After validation, the accuracy of the proposed model on these two datasets only differs by 1.7%, which is a small difference indicating that the model has good generalisation ability and can be effectively applied to real-world scenarios.
Regression prediction algorithm for energy consumption regression in cloud computing based on horned lizard algorithm optimised convolutional neural network-bidirectional gated recurrent unit
Jul 26, 2024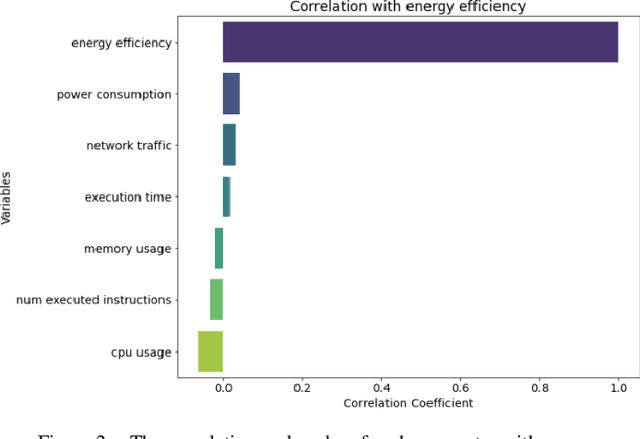
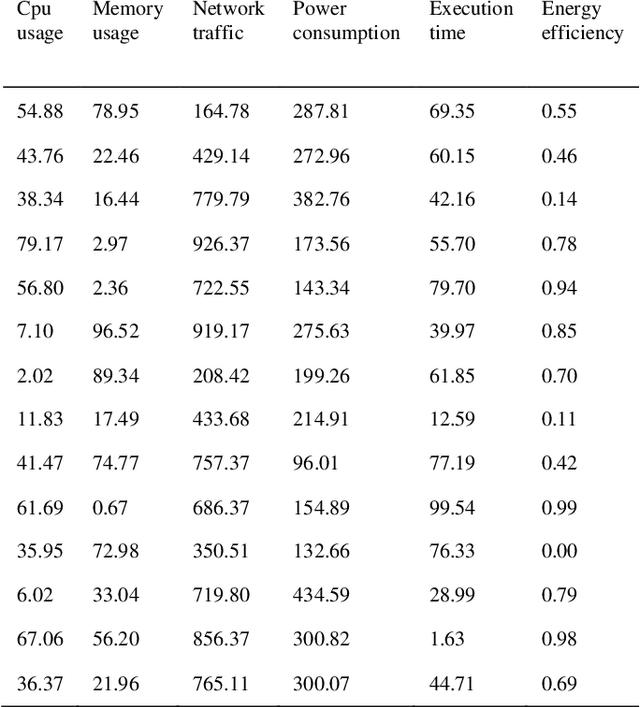
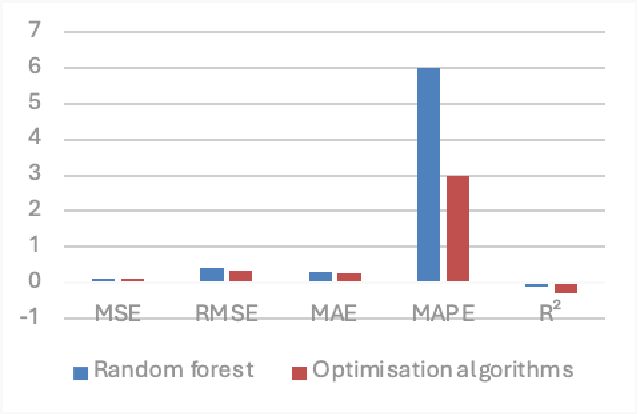
Abstract:For this paper, a prediction study of cloud computing energy consumption was conducted by optimising the data regression algorithm based on the horned lizard optimisation algorithm for Convolutional Neural Networks-Bi-Directional Gated Recurrent Units. Firstly, through Spearman correlation analysis of CPU, usage, memory usage, network traffic, power consumption, number of instructions executed, execution time and energy efficiency, we found that power consumption has the highest degree of positive correlation with energy efficiency, while CPU usage has the highest degree of negative correlation with energy efficiency. In our experiments, we introduced a random forest model and an optimisation model based on the horned lizard optimisation algorithm for testing, and the results show that the optimisation algorithm has better prediction results compared to the random forest model. Specifically, the mean square error (MSE) of the optimisation algorithm is 0.01 smaller than that of the random forest model, and the mean absolute error (MAE) is 0.01 smaller than that of the random forest.3 The results of the combined metrics show that the optimisation algorithm performs more accurately and reliably in predicting energy efficiency. This research result provides new ideas and methods to improve the energy efficiency of cloud computing systems. This research not only expands the scope of application in the field of cloud computing, but also provides a strong support for improving the energy use efficiency of the system.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge