Na Sun
A Multi-Mode Structured Light 3D Imaging System with Multi-Source Information Fusion for Underwater Pipeline Detection
Dec 12, 2025



Abstract:Underwater pipelines are highly susceptible to corrosion, which not only shorten their service life but also pose significant safety risks. Compared with manual inspection, the intelligent real-time imaging system for underwater pipeline detection has become a more reliable and practical solution. Among various underwater imaging techniques, structured light 3D imaging can restore the sufficient spatial detail for precise defect characterization. Therefore, this paper develops a multi-mode underwater structured light 3D imaging system for pipeline detection (UW-SLD system) based on multi-source information fusion. First, a rapid distortion correction (FDC) method is employed for efficient underwater image rectification. To overcome the challenges of extrinsic calibration among underwater sensors, a factor graph-based parameter optimization method is proposed to estimate the transformation matrix between the structured light and acoustic sensors. Furthermore, a multi-mode 3D imaging strategy is introduced to adapt to the geometric variability of underwater pipelines. Given the presence of numerous disturbances in underwater environments, a multi-source information fusion strategy and an adaptive extended Kalman filter (AEKF) are designed to ensure stable pose estimation and high-accuracy measurements. In particular, an edge detection-based ICP (ED-ICP) algorithm is proposed. This algorithm integrates pipeline edge detection network with enhanced point cloud registration to achieve robust and high-fidelity reconstruction of defect structures even under variable motion conditions. Extensive experiments are conducted under different operation modes, velocities, and depths. The results demonstrate that the developed system achieves superior accuracy, adaptability and robustness, providing a solid foundation for autonomous underwater pipeline detection.
Research on the Online Update Method for Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) Model with Incremental Learning
Jan 13, 2025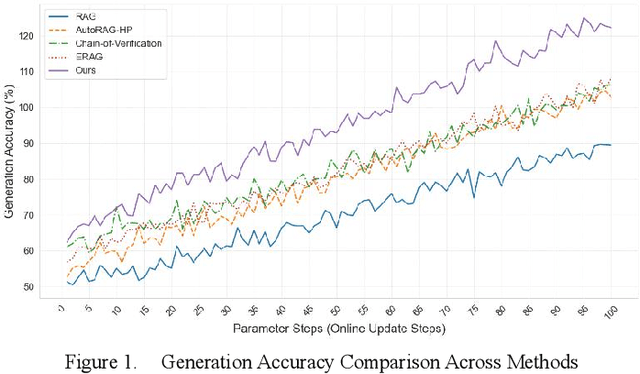
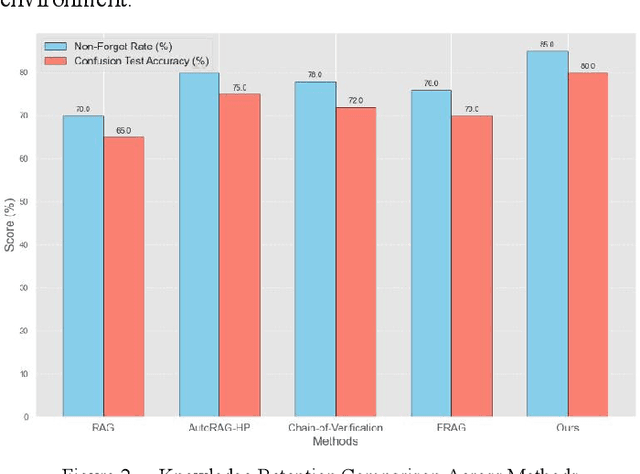
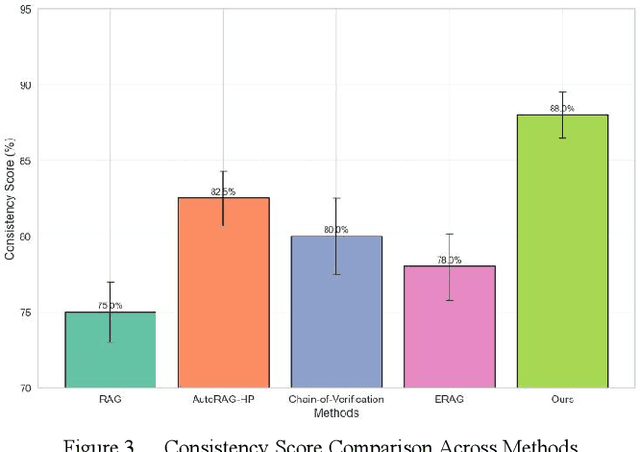
Abstract:In the contemporary context of rapid advancements in information technology and the exponential growth of data volume, language models are confronted with significant challenges in effectively navigating the dynamic and ever-evolving information landscape to update and adapt to novel knowledge in real time. In this work, an online update method is proposed, which is based on the existing Retrieval Enhanced Generation (RAG) model with multiple innovation mechanisms. Firstly, the dynamic memory is used to capture the emerging data samples, and then gradually integrate them into the core model through a tunable knowledge distillation strategy. At the same time, hierarchical indexing and multi-layer gating mechanism are introduced into the retrieval module to ensure that the retrieved content is more targeted and accurate. Finally, a multi-stage network structure is established for different types of inputs in the generation stage, and cross-attention matching and screening are carried out on the intermediate representations of each stage to ensure the effective integration and iterative update of new and old knowledge. Experimental results show that the proposed method is better than the existing mainstream comparison models in terms of knowledge retention and inference accuracy.
Boundary Peeling: Outlier Detection Method Using One-Class Peeling
Sep 11, 2023



Abstract:Unsupervised outlier detection constitutes a crucial phase within data analysis and remains a dynamic realm of research. A good outlier detection algorithm should be computationally efficient, robust to tuning parameter selection, and perform consistently well across diverse underlying data distributions. We introduce One-Class Boundary Peeling, an unsupervised outlier detection algorithm. One-class Boundary Peeling uses the average signed distance from iteratively-peeled, flexible boundaries generated by one-class support vector machines. One-class Boundary Peeling has robust hyperparameter settings and, for increased flexibility, can be cast as an ensemble method. In synthetic data simulations One-Class Boundary Peeling outperforms all state of the art methods when no outliers are present while maintaining comparable or superior performance in the presence of outliers, as compared to benchmark methods. One-Class Boundary Peeling performs competitively in terms of correct classification, AUC, and processing time using common benchmark data sets.
Depth Ranging Performance Evaluation and Improvement for RGB-D Cameras on Field-Based High-Throughput Phenotyping Robots
Nov 02, 2020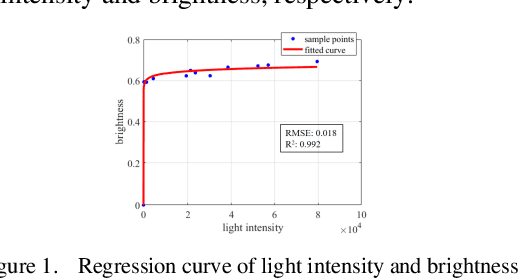


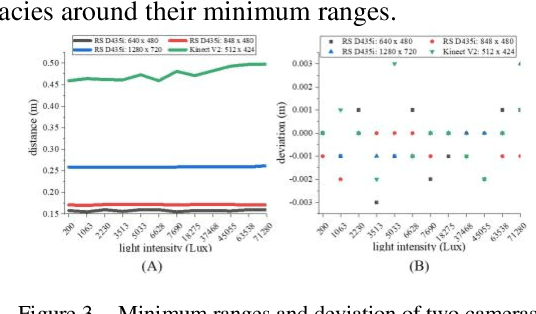
Abstract:RGB-D cameras have been successfully used for indoor High-ThroughpuT Phenotyping (HTTP). However, their capability and feasibility for in-field HTTP still need to be evaluated, due to the noise and disturbances generated by unstable illumination, specular reflection, and diffuse reflection, etc. To solve these problems, we evaluated the depth-ranging performances of two consumer-level RGB-D cameras (RealSense D435i and Kinect V2) under in-field HTTP scenarios, and proposed a strategy to compensate the depth measurement error. For performance evaluation, we focused on determining their optimal ranging areas for different crop organs. Based on the evaluation results, we proposed a brightness-and-distance-based Support Vector Regression Strategy, to compensate the ranging error. Furthermore, we analyzed the depth filling rate of two RGB-D cameras under different lighting intensities. Experimental results showed that: 1) For RealSense D435i, its effective ranging area is [0.160, 1.400] m, and in-field filling rate is approximately 90%. 2) For Kinect V2, it has a high ranging accuracy in the [0.497, 1.200] m, but its in-field filling rate is less than 24.9%. 3) Our error compensation model can effectively reduce the influences of lighting intensity and target distance. The maximum MSE and minimum R2 of this model are 0.029 and 0.867, respectively. To sum up, RealSense D435i has better ranging performances than Kinect V2 on in-field HTTP.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge