Yuhao Lin
ZeroDexGrasp: Zero-Shot Task-Oriented Dexterous Grasp Synthesis with Prompt-Based Multi-Stage Semantic Reasoning
Nov 17, 2025Abstract:Task-oriented dexterous grasping holds broad application prospects in robotic manipulation and human-object interaction. However, most existing methods still struggle to generalize across diverse objects and task instructions, as they heavily rely on costly labeled data to ensure task-specific semantic alignment. In this study, we propose \textbf{ZeroDexGrasp}, a zero-shot task-oriented dexterous grasp synthesis framework integrating Multimodal Large Language Models with grasp refinement to generate human-like grasp poses that are well aligned with specific task objectives and object affordances. Specifically, ZeroDexGrasp employs prompt-based multi-stage semantic reasoning to infer initial grasp configurations and object contact information from task and object semantics, then exploits contact-guided grasp optimization to refine these poses for physical feasibility and task alignment. Experimental results demonstrate that ZeroDexGrasp enables high-quality zero-shot dexterous grasping on diverse unseen object categories and complex task requirements, advancing toward more generalizable and intelligent robotic grasping.
OmniDexGrasp: Generalizable Dexterous Grasping via Foundation Model and Force Feedback
Oct 27, 2025



Abstract:Enabling robots to dexterously grasp and manipulate objects based on human commands is a promising direction in robotics. However, existing approaches are challenging to generalize across diverse objects or tasks due to the limited scale of semantic dexterous grasp datasets. Foundation models offer a new way to enhance generalization, yet directly leveraging them to generate feasible robotic actions remains challenging due to the gap between abstract model knowledge and physical robot execution. To address these challenges, we propose OmniDexGrasp, a generalizable framework that achieves omni-capabilities in user prompting, dexterous embodiment, and grasping tasks by combining foundation models with the transfer and control strategies. OmniDexGrasp integrates three key modules: (i) foundation models are used to enhance generalization by generating human grasp images supporting omni-capability of user prompt and task; (ii) a human-image-to-robot-action transfer strategy converts human demonstrations into executable robot actions, enabling omni dexterous embodiment; (iii) force-aware adaptive grasp strategy ensures robust and stable grasp execution. Experiments in simulation and on real robots validate the effectiveness of OmniDexGrasp on diverse user prompts, grasp task and dexterous hands, and further results show its extensibility to dexterous manipulation tasks.
TypeTele: Releasing Dexterity in Teleoperation by Dexterous Manipulation Types
Jul 02, 2025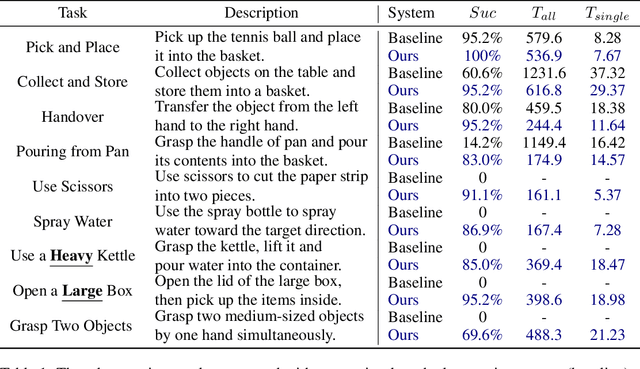

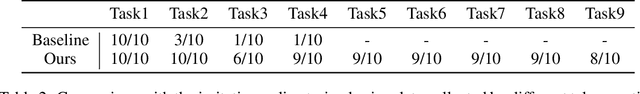
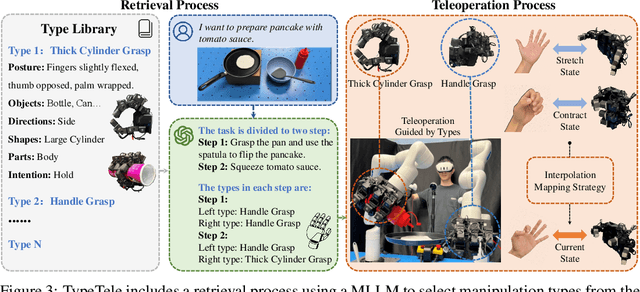
Abstract:Dexterous teleoperation plays a crucial role in robotic manipulation for real-world data collection and remote robot control. Previous dexterous teleoperation mostly relies on hand retargeting to closely mimic human hand postures. However, these approaches may fail to fully leverage the inherent dexterity of dexterous hands, which can execute unique actions through their structural advantages compared to human hands. To address this limitation, we propose TypeTele, a type-guided dexterous teleoperation system, which enables dexterous hands to perform actions that are not constrained by human motion patterns. This is achieved by introducing dexterous manipulation types into the teleoperation system, allowing operators to employ appropriate types to complete specific tasks. To support this system, we build an extensible dexterous manipulation type library to cover comprehensive dexterous postures used in manipulation tasks. During teleoperation, we employ a MLLM (Multi-modality Large Language Model)-assisted type retrieval module to identify the most suitable manipulation type based on the specific task and operator commands. Extensive experiments of real-world teleoperation and imitation learning demonstrate that the incorporation of manipulation types significantly takes full advantage of the dexterous robot's ability to perform diverse and complex tasks with higher success rates.
Guiding LLM-based Smart Contract Generation with Finite State Machine
May 13, 2025Abstract:Smart contract is a kind of self-executing code based on blockchain technology with a wide range of application scenarios, but the traditional generation method relies on manual coding and expert auditing, which has a high threshold and low efficiency. Although Large Language Models (LLMs) show great potential in programming tasks, they still face challenges in smart contract generation w.r.t. effectiveness and security. To solve these problems, we propose FSM-SCG, a smart contract generation framework based on finite state machine (FSM) and LLMs, which significantly improves the quality of the generated code by abstracting user requirements to generate FSM, guiding LLMs to generate smart contracts, and iteratively optimizing the code with the feedback of compilation and security checks. The experimental results show that FSM-SCG significantly improves the quality of smart contract generation. Compared to the best baseline, FSM-SCG improves the compilation success rate of generated smart contract code by at most 48%, and reduces the average vulnerability risk score by approximately 68%.
AffordDexGrasp: Open-set Language-guided Dexterous Grasp with Generalizable-Instructive Affordance
Mar 10, 2025Abstract:Language-guided robot dexterous generation enables robots to grasp and manipulate objects based on human commands. However, previous data-driven methods are hard to understand intention and execute grasping with unseen categories in the open set. In this work, we explore a new task, Open-set Language-guided Dexterous Grasp, and find that the main challenge is the huge gap between high-level human language semantics and low-level robot actions. To solve this problem, we propose an Affordance Dexterous Grasp (AffordDexGrasp) framework, with the insight of bridging the gap with a new generalizable-instructive affordance representation. This affordance can generalize to unseen categories by leveraging the object's local structure and category-agnostic semantic attributes, thereby effectively guiding dexterous grasp generation. Built upon the affordance, our framework introduces Affordacne Flow Matching (AFM) for affordance generation with language as input, and Grasp Flow Matching (GFM) for generating dexterous grasp with affordance as input. To evaluate our framework, we build an open-set table-top language-guided dexterous grasp dataset. Extensive experiments in the simulation and real worlds show that our framework surpasses all previous methods in open-set generalization.
TacCap: A Wearable FBG-Based Tactile Sensor for Seamless Human-to-Robot Skill Transfer
Mar 03, 2025Abstract:Tactile sensing is essential for dexterous manipulation, yet large-scale human demonstration datasets lack tactile feedback, limiting their effectiveness in skill transfer to robots. To address this, we introduce TacCap, a wearable Fiber Bragg Grating (FBG)-based tactile sensor designed for seamless human-to-robot transfer. TacCap is lightweight, durable, and immune to electromagnetic interference, making it ideal for real-world data collection. We detail its design and fabrication, evaluate its sensitivity, repeatability, and cross-sensor consistency, and assess its effectiveness through grasp stability prediction and ablation studies. Our results demonstrate that TacCap enables transferable tactile data collection, bridging the gap between human demonstrations and robotic execution. To support further research and development, we open-source our hardware design and software.
Categorical Keypoint Positional Embedding for Robust Animal Re-Identification
Dec 01, 2024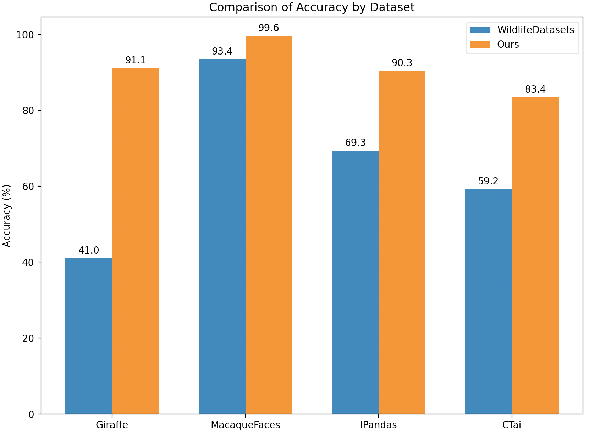
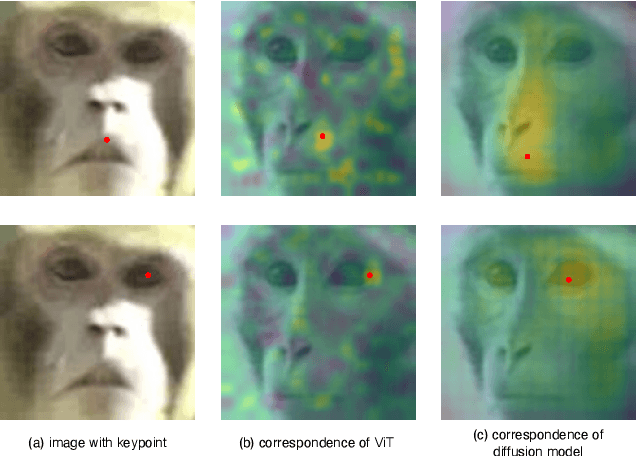
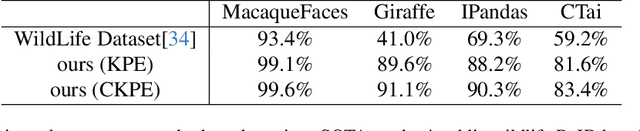

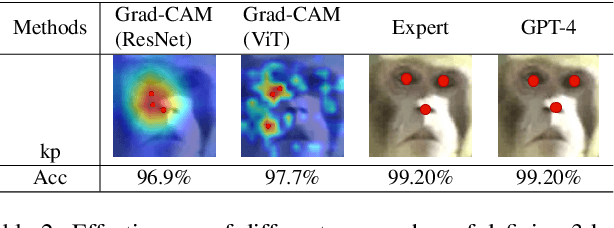
Abstract:Animal re-identification (ReID) has become an indispensable tool in ecological research, playing a critical role in tracking population dynamics, analyzing behavioral patterns, and assessing ecological impacts, all of which are vital for informed conservation strategies. Unlike human ReID, animal ReID faces significant challenges due to the high variability in animal poses, diverse environmental conditions, and the inability to directly apply pre-trained models to animal data, making the identification process across species more complex. This work introduces an innovative keypoint propagation mechanism, which utilizes a single annotated image and a pre-trained diffusion model to propagate keypoints across an entire dataset, significantly reducing the cost of manual annotation. Additionally, we enhance the Vision Transformer (ViT) by implementing Keypoint Positional Encoding (KPE) and Categorical Keypoint Positional Embedding (CKPE), enabling the ViT to learn more robust and semantically-aware representations. This provides more comprehensive and detailed keypoint representations, leading to more accurate and efficient re-identification. Our extensive experimental evaluations demonstrate that this approach significantly outperforms existing state-of-the-art methods across four wildlife datasets. The code will be publicly released.
A Simple-but-effective Baseline for Training-free Class-Agnostic Counting
Mar 03, 2024Abstract:Class-Agnostic Counting (CAC) seeks to accurately count objects in a given image with only a few reference examples. While previous methods achieving this relied on additional training, recent efforts have shown that it's possible to accomplish this without training by utilizing pre-existing foundation models, particularly the Segment Anything Model (SAM), for counting via instance-level segmentation. Although promising, current training-free methods still lag behind their training-based counterparts in terms of performance. In this research, we present a straightforward training-free solution that effectively bridges this performance gap, serving as a strong baseline. The primary contribution of our work lies in the discovery of four key technologies that can enhance performance. Specifically, we suggest employing a superpixel algorithm to generate more precise initial point prompts, utilizing an image encoder with richer semantic knowledge to replace the SAM encoder for representing candidate objects, and adopting a multiscale mechanism and a transductive prototype scheme to update the representation of reference examples. By combining these four technologies, our approach achieves significant improvements over existing training-free methods and delivers performance on par with training-based ones.
Semantic Role Labeling Guided Out-of-distribution Detection
May 29, 2023Abstract:Identifying unexpected domain-shifted instances in natural language processing is crucial in real-world applications. Previous works identify the OOD instance by leveraging a single global feature embedding to represent the sentence, which cannot characterize subtle OOD patterns well. Another major challenge current OOD methods face is learning effective low-dimensional sentence representations to identify the hard OOD instances that are semantically similar to the ID data. In this paper, we propose a new unsupervised OOD detection method, namely Semantic Role Labeling Guided Out-of-distribution Detection (SRLOOD), that separates, extracts, and learns the semantic role labeling (SRL) guided fine-grained local feature representations from different arguments of a sentence and the global feature representations of the full sentence using a margin-based contrastive loss. A novel self-supervised approach is also introduced to enhance such global-local feature learning by predicting the SRL extracted role. The resulting model achieves SOTA performance on four OOD benchmarks, indicating the effectiveness of our approach. Codes will be available upon acceptance.
Masked and Adaptive Transformer for Exemplar Based Image Translation
Mar 30, 2023Abstract:We present a novel framework for exemplar based image translation. Recent advanced methods for this task mainly focus on establishing cross-domain semantic correspondence, which sequentially dominates image generation in the manner of local style control. Unfortunately, cross-domain semantic matching is challenging; and matching errors ultimately degrade the quality of generated images. To overcome this challenge, we improve the accuracy of matching on the one hand, and diminish the role of matching in image generation on the other hand. To achieve the former, we propose a masked and adaptive transformer (MAT) for learning accurate cross-domain correspondence, and executing context-aware feature augmentation. To achieve the latter, we use source features of the input and global style codes of the exemplar, as supplementary information, for decoding an image. Besides, we devise a novel contrastive style learning method, for acquire quality-discriminative style representations, which in turn benefit high-quality image generation. Experimental results show that our method, dubbed MATEBIT, performs considerably better than state-of-the-art methods, in diverse image translation tasks. The codes are available at \url{https://github.com/AiArt-HDU/MATEBIT}.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge