Chuanzhi Xu
FedVideoMAE: Efficient Privacy-Preserving Federated Video Moderation
Dec 21, 2025



Abstract:The rapid growth of short-form video platforms increases the need for privacy-preserving moderation, as cloud-based pipelines expose raw videos to privacy risks, high bandwidth costs, and inference latency. To address these challenges, we propose an on-device federated learning framework for video violence detection that integrates self-supervised VideoMAE representations, LoRA-based parameter-efficient adaptation, and defense-in-depth privacy protection. Our approach reduces the trainable parameter count to 5.5M (~3.5% of a 156M backbone) and incorporates DP-SGD with configurable privacy budgets and secure aggregation. Experiments on RWF-2000 with 40 clients achieve 77.25% accuracy without privacy protection and 65-66% under strong differential privacy, while reducing communication cost by $28.3\times$ compared to full-model federated learning. The code is available at: {https://github.com/zyt-599/FedVideoMAE}
DRWKV: Focusing on Object Edges for Low-Light Image Enhancement
Jul 24, 2025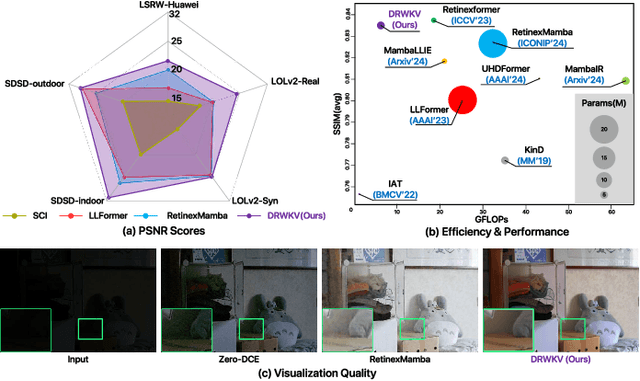
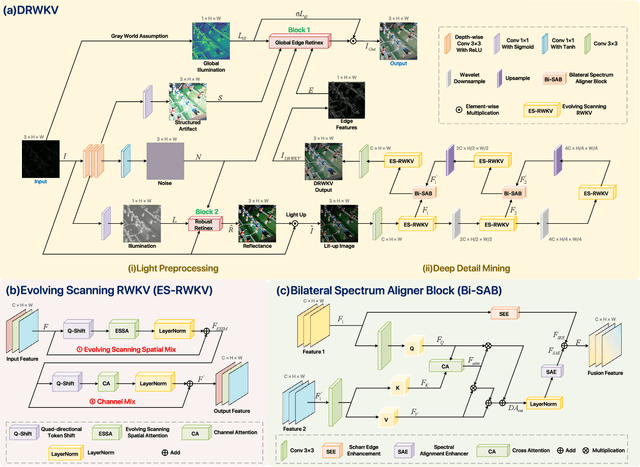
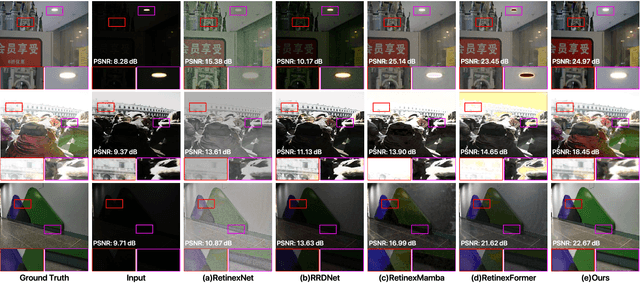

Abstract:Low-light image enhancement remains a challenging task, particularly in preserving object edge continuity and fine structural details under extreme illumination degradation. In this paper, we propose a novel model, DRWKV (Detailed Receptance Weighted Key Value), which integrates our proposed Global Edge Retinex (GER) theory, enabling effective decoupling of illumination and edge structures for enhanced edge fidelity. Secondly, we introduce Evolving WKV Attention, a spiral-scanning mechanism that captures spatial edge continuity and models irregular structures more effectively. Thirdly, we design the Bilateral Spectrum Aligner (Bi-SAB) and a tailored MS2-Loss to jointly align luminance and chrominance features, improving visual naturalness and mitigating artifacts. Extensive experiments on five LLIE benchmarks demonstrate that DRWKV achieves leading performance in PSNR, SSIM, and NIQE while maintaining low computational complexity. Furthermore, DRWKV enhances downstream performance in low-light multi-object tracking tasks, validating its generalization capabilities.
MGDFIS: Multi-scale Global-detail Feature Integration Strategy for Small Object Detection
Jun 15, 2025Abstract:Small object detection in UAV imagery is crucial for applications such as search-and-rescue, traffic monitoring, and environmental surveillance, but it is hampered by tiny object size, low signal-to-noise ratios, and limited feature extraction. Existing multi-scale fusion methods help, but add computational burden and blur fine details, making small object detection in cluttered scenes difficult. To overcome these challenges, we propose the Multi-scale Global-detail Feature Integration Strategy (MGDFIS), a unified fusion framework that tightly couples global context with local detail to boost detection performance while maintaining efficiency. MGDFIS comprises three synergistic modules: the FusionLock-TSS Attention Module, which marries token-statistics self-attention with DynamicTanh normalization to highlight spectral and spatial cues at minimal cost; the Global-detail Integration Module, which fuses multi-scale context via directional convolution and parallel attention while preserving subtle shape and texture variations; and the Dynamic Pixel Attention Module, which generates pixel-wise weighting maps to rebalance uneven foreground and background distributions and sharpen responses to true object regions. Extensive experiments on the VisDrone benchmark demonstrate that MGDFIS consistently outperforms state-of-the-art methods across diverse backbone architectures and detection frameworks, achieving superior precision and recall with low inference time. By striking an optimal balance between accuracy and resource usage, MGDFIS provides a practical solution for small-object detection on resource-constrained UAV platforms.
A Survey of 3D Reconstruction with Event Cameras: From Event-based Geometry to Neural 3D Rendering
May 13, 2025Abstract:Event cameras have emerged as promising sensors for 3D reconstruction due to their ability to capture per-pixel brightness changes asynchronously. Unlike conventional frame-based cameras, they produce sparse and temporally rich data streams, which enable more accurate 3D reconstruction and open up the possibility of performing reconstruction in extreme environments such as high-speed motion, low light, or high dynamic range scenes. In this survey, we provide the first comprehensive review focused exclusively on 3D reconstruction using event cameras. The survey categorises existing works into three major types based on input modality - stereo, monocular, and multimodal systems, and further classifies them by reconstruction approach, including geometry-based, deep learning-based, and recent neural rendering techniques such as Neural Radiance Fields and 3D Gaussian Splatting. Methods with a similar research focus were organised chronologically into the most subdivided groups. We also summarise public datasets relevant to event-based 3D reconstruction. Finally, we highlight current research limitations in data availability, evaluation, representation, and dynamic scene handling, and outline promising future research directions. This survey aims to serve as a comprehensive reference and a roadmap for future developments in event-driven 3D reconstruction.
A Survey on Event-driven 3D Reconstruction: Development under Different Categories
Mar 26, 2025


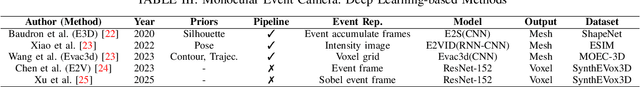
Abstract:Event cameras have gained increasing attention for 3D reconstruction due to their high temporal resolution, low latency, and high dynamic range. They capture per-pixel brightness changes asynchronously, allowing accurate reconstruction under fast motion and challenging lighting conditions. In this survey, we provide a comprehensive review of event-driven 3D reconstruction methods, including stereo, monocular, and multimodal systems. We further categorize recent developments based on geometric, learning-based, and hybrid approaches. Emerging trends, such as neural radiance fields and 3D Gaussian splatting with event data, are also covered. The related works are structured chronologically to illustrate the innovations and progression within the field. To support future research, we also highlight key research gaps and future research directions in dataset, experiment, evaluation, event representation, etc.
Towards End-to-End Neuromorphic Voxel-based 3D Object Reconstruction Without Physical Priors
Jan 01, 2025

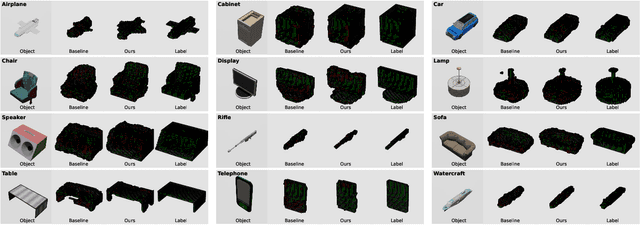

Abstract:Neuromorphic cameras, also known as event cameras, are asynchronous brightness-change sensors that can capture extremely fast motion without suffering from motion blur, making them particularly promising for 3D reconstruction in extreme environments. However, existing research on 3D reconstruction using monocular neuromorphic cameras is limited, and most of the methods rely on estimating physical priors and employ complex multi-step pipelines. In this work, we propose an end-to-end method for dense voxel 3D reconstruction using neuromorphic cameras that eliminates the need to estimate physical priors. Our method incorporates a novel event representation to enhance edge features, enabling the proposed feature-enhancement model to learn more effectively. Additionally, we introduced Optimal Binarization Threshold Selection Principle as a guideline for future related work, using the optimal reconstruction results achieved with threshold optimization as the benchmark. Our method achieves a 54.6% improvement in reconstruction accuracy compared to the baseline method.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge