Guo-Jun Qi
FADPNet: Frequency-Aware Dual-Path Network for Face Super-Resolution
Jun 17, 2025Abstract:Face super-resolution (FSR) under limited computational costs remains an open problem. Existing approaches typically treat all facial pixels equally, resulting in suboptimal allocation of computational resources and degraded FSR performance. CNN is relatively sensitive to high-frequency facial features, such as component contours and facial outlines. Meanwhile, Mamba excels at capturing low-frequency features like facial color and fine-grained texture, and does so with lower complexity than Transformers. Motivated by these observations, we propose FADPNet, a Frequency-Aware Dual-Path Network that decomposes facial features into low- and high-frequency components and processes them via dedicated branches. For low-frequency regions, we introduce a Mamba-based Low-Frequency Enhancement Block (LFEB), which combines state-space attention with squeeze-and-excitation operations to extract low-frequency global interactions and emphasize informative channels. For high-frequency regions, we design a CNN-based Deep Position-Aware Attention (DPA) module to enhance spatially-dependent structural details, complemented by a lightweight High-Frequency Refinement (HFR) module that further refines frequency-specific representations. Through the above designs, our method achieves an excellent balance between FSR quality and model efficiency, outperforming existing approaches.
S2AFormer: Strip Self-Attention for Efficient Vision Transformer
May 28, 2025Abstract:Vision Transformer (ViT) has made significant advancements in computer vision, thanks to its token mixer's sophisticated ability to capture global dependencies between all tokens. However, the quadratic growth in computational demands as the number of tokens increases limits its practical efficiency. Although recent methods have combined the strengths of convolutions and self-attention to achieve better trade-offs, the expensive pairwise token affinity and complex matrix operations inherent in self-attention remain a bottleneck. To address this challenge, we propose S2AFormer, an efficient Vision Transformer architecture featuring novel Strip Self-Attention (SSA). We design simple yet effective Hybrid Perception Blocks (HPBs) to effectively integrate the local perception capabilities of CNNs with the global context modeling of Transformer's attention mechanisms. A key innovation of SSA lies in its reducing the spatial dimensions of $K$ and $V$ while compressing the channel dimensions of $Q$ and $K$. This design significantly reduces computational overhead while preserving accuracy, striking an optimal balance between efficiency and effectiveness. We evaluate the robustness and efficiency of S2AFormer through extensive experiments on multiple vision benchmarks, including ImageNet-1k for image classification, ADE20k for semantic segmentation, and COCO for object detection and instance segmentation. Results demonstrate that S2AFormer achieves significant accuracy gains with superior efficiency in both GPU and non-GPU environments, making it a strong candidate for efficient vision Transformers.
Reinforcing the Diffusion Chain of Lateral Thought with Diffusion Language Models
May 15, 2025Abstract:We introduce the \emph{Diffusion Chain of Lateral Thought (DCoLT)}, a reasoning framework for diffusion language models. DCoLT treats each intermediate step in the reverse diffusion process as a latent "thinking" action and optimizes the entire reasoning trajectory to maximize the reward on the correctness of the final answer with outcome-based Reinforcement Learning (RL). Unlike traditional Chain-of-Thought (CoT) methods that follow a causal, linear thinking process, DCoLT allows bidirectional, non-linear reasoning with no strict rule on grammatical correctness amid its intermediate steps of thought. We implement DCoLT on two representative Diffusion Language Models (DLMs). First, we choose SEDD as a representative continuous-time discrete diffusion model, where its concrete score derives a probabilistic policy to maximize the RL reward over the entire sequence of intermediate diffusion steps. We further consider the discrete-time masked diffusion language model -- LLaDA, and find that the order to predict and unmask tokens plays an essential role to optimize its RL action resulting from the ranking-based Unmasking Policy Module (UPM) defined by the Plackett-Luce model. Experiments on both math and code generation tasks show that using only public data and 16 H800 GPUs, DCoLT-reinforced DLMs outperform other DLMs trained by SFT or RL or even both. Notably, DCoLT-reinforced LLaDA boosts its reasoning accuracy by +9.8%, +5.7%, +11.4%, +19.5% on GSM8K, MATH, MBPP, and HumanEval.
Self-Guidance: Boosting Flow and Diffusion Generation on Their Own
Dec 08, 2024



Abstract:Proper guidance strategies are essential to get optimal generation results without re-training diffusion and flow-based text-to-image models. However, existing guidances either require specific training or strong inductive biases of neural network architectures, potentially limiting their applications. To address these issues, in this paper, we introduce Self-Guidance (SG), a strong diffusion guidance that neither needs specific training nor requires certain forms of neural network architectures. Different from previous approaches, the Self-Guidance calculates the guidance vectors by measuring the difference between the velocities of two successive diffusion timesteps. Therefore, SG can be readily applied for both conditional and unconditional models with flexible network architectures. We conduct intensive experiments on both text-to-image generation and text-to-video generations across flexible architectures including UNet-based models and diffusion transformer-based models. On current state-of-the-art diffusion models such as Stable Diffusion 3.5 and FLUX, SG significantly boosts the image generation performance in terms of FID, and Human Preference Scores. Moreover, we find that SG has a surprisingly positive effect on the generation of high-quality human bodies such as hands, faces, and arms, showing strong potential to overcome traditional challenges on human body generations with minimal effort. We will release our implementation of SG on SD 3.5 and FLUX models along with this paper.
Schedule On the Fly: Diffusion Time Prediction for Faster and Better Image Generation
Dec 02, 2024



Abstract:Diffusion and flow models have achieved remarkable successes in various applications such as text-to-image generation. However, these models typically rely on the same predetermined denoising schedules during inference for each prompt, which potentially limits the inference efficiency as well as the flexibility when handling different prompts. In this paper, we argue that the optimal noise schedule should adapt to each inference instance, and introduce the Time Prediction Diffusion Model (TPDM) to accomplish this. TPDM employs a plug-and-play Time Prediction Module (TPM) that predicts the next noise level based on current latent features at each denoising step. We train the TPM using reinforcement learning, aiming to maximize a reward that discounts the final image quality by the number of denoising steps. With such an adaptive scheduler, TPDM not only generates high-quality images that are aligned closely with human preferences but also adjusts the number of denoising steps and time on the fly, enhancing both performance and efficiency. We train TPDMs on multiple diffusion model benchmarks. With Stable Diffusion 3 Medium architecture, TPDM achieves an aesthetic score of 5.44 and a human preference score (HPS) of 29.59, while using around 50% fewer denoising steps to achieve better performance. We will release our best model alongside this paper.
SCASeg: Strip Cross-Attention for Efficient Semantic Segmentation
Nov 26, 2024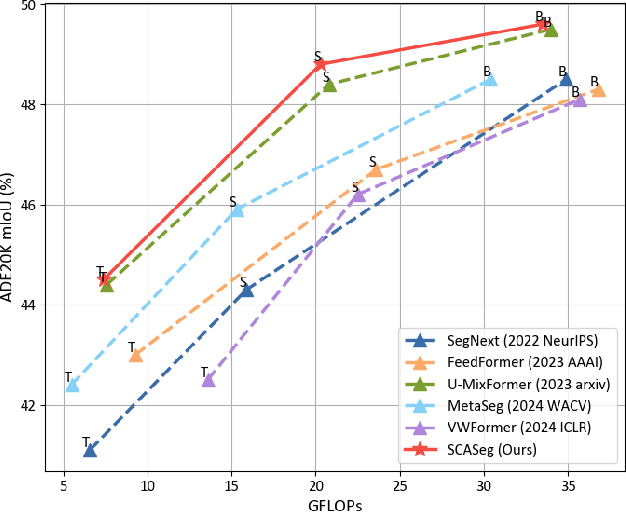

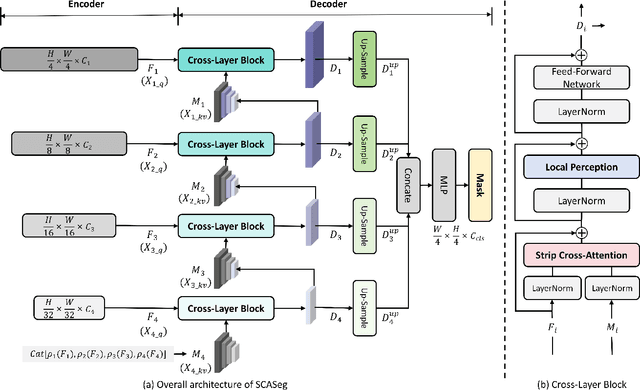

Abstract:The Vision Transformer (ViT) has achieved notable success in computer vision, with its variants extensively validated across various downstream tasks, including semantic segmentation. However, designed as general-purpose visual encoders, ViT backbones often overlook the specific needs of task decoders, revealing opportunities to design decoders tailored to efficient semantic segmentation. This paper proposes Strip Cross-Attention (SCASeg), an innovative decoder head explicitly designed for semantic segmentation. Instead of relying on the simple conventional skip connections, we employ lateral connections between the encoder and decoder stages, using encoder features as Queries for the cross-attention modules. Additionally, we introduce a Cross-Layer Block that blends hierarchical feature maps from different encoder and decoder stages to create a unified representation for Keys and Values. To further boost computational efficiency, SCASeg compresses queries and keys into strip-like patterns to optimize memory usage and inference speed over the traditional vanilla cross-attention. Moreover, the Cross-Layer Block incorporates the local perceptual strengths of convolution, enabling SCASeg to capture both global and local context dependencies across multiple layers. This approach facilitates effective feature interaction at different scales, improving the overall performance. Experiments show that the adaptable decoder of SCASeg produces competitive performance across different setups, surpassing leading segmentation architectures on all benchmark datasets, including ADE20K, Cityscapes, COCO-Stuff 164k, and Pascal VOC2012, even under varying computational limitations.
Openstory++: A Large-scale Dataset and Benchmark for Instance-aware Open-domain Visual Storytelling
Aug 07, 2024



Abstract:Recent image generation models excel at creating high-quality images from brief captions. However, they fail to maintain consistency of multiple instances across images when encountering lengthy contexts. This inconsistency is largely due to in existing training datasets the absence of granular instance feature labeling in existing training datasets. To tackle these issues, we introduce Openstory++, a large-scale dataset combining additional instance-level annotations with both images and text. Furthermore, we develop a training methodology that emphasizes entity-centric image-text generation, ensuring that the models learn to effectively interweave visual and textual information. Specifically, Openstory++ streamlines the process of keyframe extraction from open-domain videos, employing vision-language models to generate captions that are then polished by a large language model for narrative continuity. It surpasses previous datasets by offering a more expansive open-domain resource, which incorporates automated captioning, high-resolution imagery tailored for instance count, and extensive frame sequences for temporal consistency. Additionally, we present Cohere-Bench, a pioneering benchmark framework for evaluating the image generation tasks when long multimodal context is provided, including the ability to keep the background, style, instances in the given context coherent. Compared to existing benchmarks, our work fills critical gaps in multi-modal generation, propelling the development of models that can adeptly generate and interpret complex narratives in open-domain environments. Experiments conducted within Cohere-Bench confirm the superiority of Openstory++ in nurturing high-quality visual storytelling models, enhancing their ability to address open-domain generation tasks. More details can be found at https://openstorypp.github.io/
Multi-Condition Latent Diffusion Network for Scene-Aware Neural Human Motion Prediction
May 30, 2024



Abstract:Inferring 3D human motion is fundamental in many applications, including understanding human activity and analyzing one's intention. While many fruitful efforts have been made to human motion prediction, most approaches focus on pose-driven prediction and inferring human motion in isolation from the contextual environment, thus leaving the body location movement in the scene behind. However, real-world human movements are goal-directed and highly influenced by the spatial layout of their surrounding scenes. In this paper, instead of planning future human motion in a 'dark' room, we propose a Multi-Condition Latent Diffusion network (MCLD) that reformulates the human motion prediction task as a multi-condition joint inference problem based on the given historical 3D body motion and the current 3D scene contexts. Specifically, instead of directly modeling joint distribution over the raw motion sequences, MCLD performs a conditional diffusion process within the latent embedding space, characterizing the cross-modal mapping from the past body movement and current scene context condition embeddings to the future human motion embedding. Extensive experiments on large-scale human motion prediction datasets demonstrate that our MCLD achieves significant improvements over the state-of-the-art methods on both realistic and diverse predictions.
Towards Open Domain Text-Driven Synthesis of Multi-Person Motions
May 28, 2024Abstract:This work aims to generate natural and diverse group motions of multiple humans from textual descriptions. While single-person text-to-motion generation is extensively studied, it remains challenging to synthesize motions for more than one or two subjects from in-the-wild prompts, mainly due to the lack of available datasets. In this work, we curate human pose and motion datasets by estimating pose information from large-scale image and video datasets. Our models use a transformer-based diffusion framework that accommodates multiple datasets with any number of subjects or frames. Experiments explore both generation of multi-person static poses and generation of multi-person motion sequences. To our knowledge, our method is the first to generate multi-subject motion sequences with high diversity and fidelity from a large variety of textual prompts.
PoseAnimate: Zero-shot high fidelity pose controllable character animation
Apr 30, 2024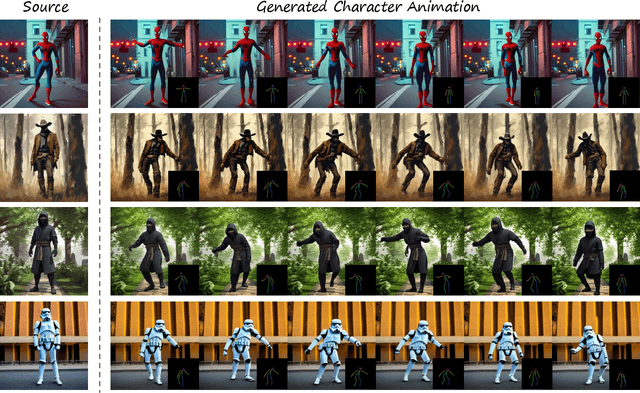
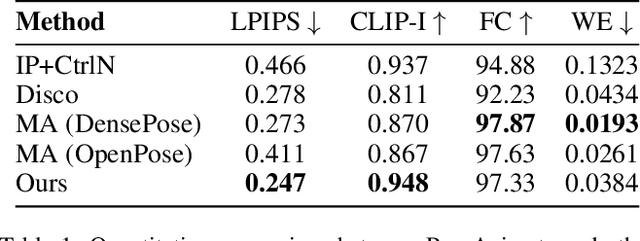
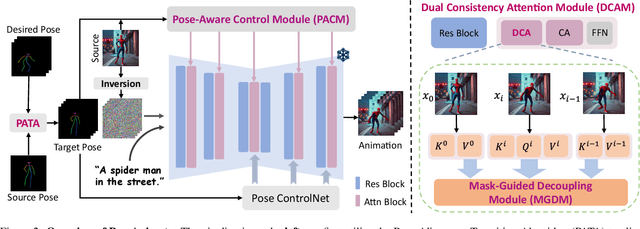
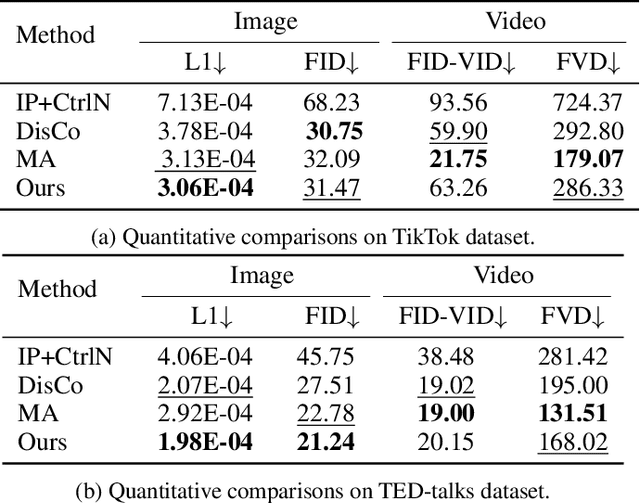
Abstract:Image-to-video(I2V) generation aims to create a video sequence from a single image, which requires high temporal coherence and visual fidelity with the source image.However, existing approaches suffer from character appearance inconsistency and poor preservation of fine details. Moreover, they require a large amount of video data for training, which can be computationally demanding.To address these limitations,we propose PoseAnimate, a novel zero-shot I2V framework for character animation.PoseAnimate contains three key components: 1) Pose-Aware Control Module (PACM) incorporates diverse pose signals into conditional embeddings, to preserve character-independent content and maintain precise alignment of actions.2) Dual Consistency Attention Module (DCAM) enhances temporal consistency, and retains character identity and intricate background details.3) Mask-Guided Decoupling Module (MGDM) refines distinct feature perception, improving animation fidelity by decoupling the character and background.We also propose a Pose Alignment Transition Algorithm (PATA) to ensure smooth action transition.Extensive experiment results demonstrate that our approach outperforms the state-of-the-art training-based methods in terms of character consistency and detail fidelity. Moreover, it maintains a high level of temporal coherence throughout the generated animations.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge