Jiaming Chen
Skill-Aware Diffusion for Generalizable Robotic Manipulation
Jan 16, 2026Abstract:Robust generalization in robotic manipulation is crucial for robots to adapt flexibly to diverse environments. Existing methods usually improve generalization by scaling data and networks, but model tasks independently and overlook skill-level information. Observing that tasks within the same skill share similar motion patterns, we propose Skill-Aware Diffusion (SADiff), which explicitly incorporates skill-level information to improve generalization. SADiff learns skill-specific representations through a skill-aware encoding module with learnable skill tokens, and conditions a skill-constrained diffusion model to generate object-centric motion flow. A skill-retrieval transformation strategy further exploits skill-specific trajectory priors to refine the mapping from 2D motion flow to executable 3D actions. Furthermore, we introduce IsaacSkill, a high-fidelity dataset containing fundamental robotic skills for comprehensive evaluation and sim-to-real transfer. Experiments in simulation and real-world settings show that SADiff achieves good performance and generalization across various manipulation tasks. Code, data, and videos are available at https://sites.google.com/view/sa-diff.
Visionary: The World Model Carrier Built on WebGPU-Powered Gaussian Splatting Platform
Dec 09, 2025Abstract:Neural rendering, particularly 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS), has evolved rapidly and become a key component for building world models. However, existing viewer solutions remain fragmented, heavy, or constrained by legacy pipelines, resulting in high deployment friction and limited support for dynamic content and generative models. In this work, we present Visionary, an open, web-native platform for real-time various Gaussian Splatting and meshes rendering. Built on an efficient WebGPU renderer with per-frame ONNX inference, Visionary enables dynamic neural processing while maintaining a lightweight, "click-to-run" browser experience. It introduces a standardized Gaussian Generator contract, which not only supports standard 3DGS rendering but also allows plug-and-play algorithms to generate or update Gaussians each frame. Such inference also enables us to apply feedforward generative post-processing. The platform further offers a plug in three.js library with a concise TypeScript API for seamless integration into existing web applications. Experiments show that, under identical 3DGS assets, Visionary achieves superior rendering efficiency compared to current Web viewers due to GPU-based primitive sorting. It already supports multiple variants, including MLP-based 3DGS, 4DGS, neural avatars, and style transformation or enhancement networks. By unifying inference and rendering directly in the browser, Visionary significantly lowers the barrier to reproduction, comparison, and deployment of 3DGS-family methods, serving as a unified World Model Carrier for both reconstructive and generative paradigms.
VLM-SFD: VLM-Assisted Siamese Flow Diffusion Framework for Dual-Arm Cooperative Manipulation
Jun 16, 2025Abstract:Dual-arm cooperative manipulation holds great promise for tackling complex real-world tasks that demand seamless coordination and adaptive dynamics. Despite substantial progress in learning-based motion planning, most approaches struggle to generalize across diverse manipulation tasks and adapt to dynamic, unstructured environments, particularly in scenarios involving interactions between two objects such as assembly, tool use, and bimanual grasping. To address these challenges, we introduce a novel VLM-Assisted Siamese Flow Diffusion (VLM-SFD) framework for efficient imitation learning in dual-arm cooperative manipulation. The proposed VLM-SFD framework exhibits outstanding adaptability, significantly enhancing the ability to rapidly adapt and generalize to diverse real-world tasks from only a minimal number of human demonstrations. Specifically, we propose a Siamese Flow Diffusion Network (SFDNet) employs a dual-encoder-decoder Siamese architecture to embed two target objects into a shared latent space, while a diffusion-based conditioning process-conditioned by task instructions-generates two-stream object-centric motion flows that guide dual-arm coordination. We further design a dynamic task assignment strategy that seamlessly maps the predicted 2D motion flows into 3D space and incorporates a pre-trained vision-language model (VLM) to adaptively assign the optimal motion to each robotic arm over time. Experiments validate the effectiveness of the proposed method, demonstrating its ability to generalize to diverse manipulation tasks while maintaining high efficiency and adaptability. The code and demo videos are publicly available on our project website https://sites.google.com/view/vlm-sfd/.
Vision-Language Model Predictive Control for Manipulation Planning and Trajectory Generation
Apr 07, 2025



Abstract:Model Predictive Control (MPC) is a widely adopted control paradigm that leverages predictive models to estimate future system states and optimize control inputs accordingly. However, while MPC excels in planning and control, it lacks the capability for environmental perception, leading to failures in complex and unstructured scenarios. To address this limitation, we introduce Vision-Language Model Predictive Control (VLMPC), a robotic manipulation planning framework that integrates the perception power of vision-language models (VLMs) with MPC. VLMPC utilizes a conditional action sampling module that takes a goal image or language instruction as input and leverages VLM to generate candidate action sequences. These candidates are fed into a video prediction model that simulates future frames based on the actions. In addition, we propose an enhanced variant, Traj-VLMPC, which replaces video prediction with motion trajectory generation to reduce computational complexity while maintaining accuracy. Traj-VLMPC estimates motion dynamics conditioned on the candidate actions, offering a more efficient alternative for long-horizon tasks and real-time applications. Both VLMPC and Traj-VLMPC select the optimal action sequence using a VLM-based hierarchical cost function that captures both pixel-level and knowledge-level consistency between the current observation and the task input. We demonstrate that both approaches outperform existing state-of-the-art methods on public benchmarks and achieve excellent performance in various real-world robotic manipulation tasks. Code is available at https://github.com/PPjmchen/VLMPC.
SCASeg: Strip Cross-Attention for Efficient Semantic Segmentation
Nov 26, 2024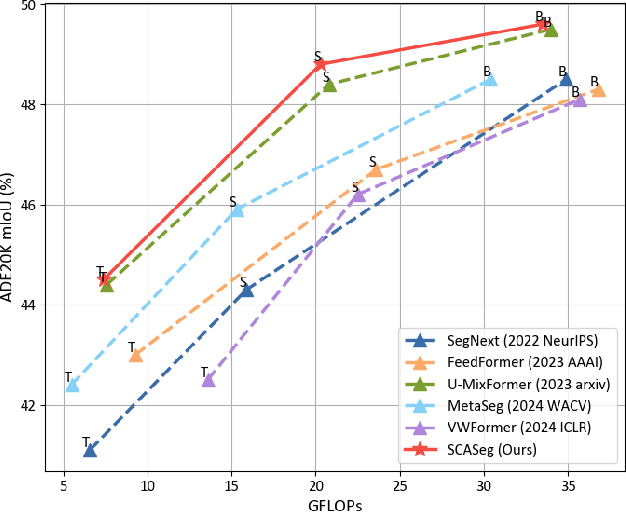

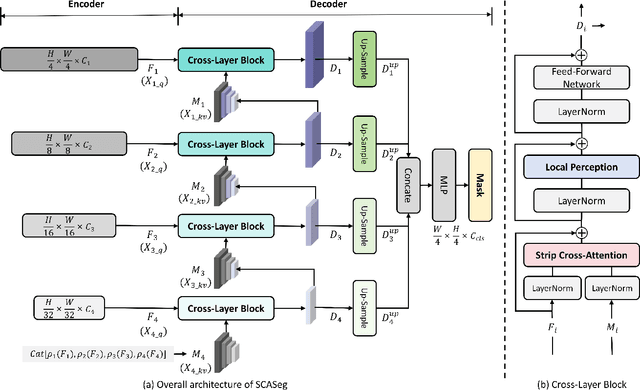

Abstract:The Vision Transformer (ViT) has achieved notable success in computer vision, with its variants extensively validated across various downstream tasks, including semantic segmentation. However, designed as general-purpose visual encoders, ViT backbones often overlook the specific needs of task decoders, revealing opportunities to design decoders tailored to efficient semantic segmentation. This paper proposes Strip Cross-Attention (SCASeg), an innovative decoder head explicitly designed for semantic segmentation. Instead of relying on the simple conventional skip connections, we employ lateral connections between the encoder and decoder stages, using encoder features as Queries for the cross-attention modules. Additionally, we introduce a Cross-Layer Block that blends hierarchical feature maps from different encoder and decoder stages to create a unified representation for Keys and Values. To further boost computational efficiency, SCASeg compresses queries and keys into strip-like patterns to optimize memory usage and inference speed over the traditional vanilla cross-attention. Moreover, the Cross-Layer Block incorporates the local perceptual strengths of convolution, enabling SCASeg to capture both global and local context dependencies across multiple layers. This approach facilitates effective feature interaction at different scales, improving the overall performance. Experiments show that the adaptable decoder of SCASeg produces competitive performance across different setups, surpassing leading segmentation architectures on all benchmark datasets, including ADE20K, Cityscapes, COCO-Stuff 164k, and Pascal VOC2012, even under varying computational limitations.
VLMPC: Vision-Language Model Predictive Control for Robotic Manipulation
Jul 13, 2024Abstract:Although Model Predictive Control (MPC) can effectively predict the future states of a system and thus is widely used in robotic manipulation tasks, it does not have the capability of environmental perception, leading to the failure in some complex scenarios. To address this issue, we introduce Vision-Language Model Predictive Control (VLMPC), a robotic manipulation framework which takes advantage of the powerful perception capability of vision language model (VLM) and integrates it with MPC. Specifically, we propose a conditional action sampling module which takes as input a goal image or a language instruction and leverages VLM to sample a set of candidate action sequences. Then, a lightweight action-conditioned video prediction model is designed to generate a set of future frames conditioned on the candidate action sequences. VLMPC produces the optimal action sequence with the assistance of VLM through a hierarchical cost function that formulates both pixel-level and knowledge-level consistence between the current observation and the goal image. We demonstrate that VLMPC outperforms the state-of-the-art methods on public benchmarks. More importantly, our method showcases excellent performance in various real-world tasks of robotic manipulation. Code is available at~\url{https://github.com/PPjmchen/VLMPC}.
Nowhere to Go: Benchmarking Multi-robot Collaboration in Target Trapping Environment
Aug 17, 2023Abstract:Collaboration is one of the most important factors in multi-robot systems. Considering certain real-world applications and to further promote its development, we propose a new benchmark to evaluate multi-robot collaboration in Target Trapping Environment (T2E). In T2E, two kinds of robots (called captor robot and target robot) share the same space. The captors aim to catch the target collaboratively, while the target will try to escape from the trap. Both the trapping and escaping process can use the environment layout to help achieve the corresponding objective, which requires high collaboration between robots and the utilization of the environment. For the benchmark, we present and evaluate multiple learning-based baselines in T2E, and provide insights into regimes of multi-robot collaboration. We also make our benchmark publicly available and encourage researchers from related robotics disciplines to propose, evaluate, and compare their solutions in this benchmark. Our project is released at https://github.com/Dr-Xiaogaren/T2E.
HAM: Hierarchical Attention Model with High Performance for 3D Visual Grounding
Oct 30, 2022



Abstract:This paper tackles an emerging and challenging vision-language task, namely 3D visual grounding on point clouds. Many recent works benefit from Transformer with the well-known attention mechanism, leading to a tremendous breakthrough for this task. However, we find that they realize the achievement by using various pre-training or multi-stage processing. To simplify the pipeline, we carefully investigate 3D visual grounding and summarize three fundamental problems about how to develop an end-to-end model with high performance for this task. To address these problems, we especially introduce a novel Hierarchical Attention Model (HAM), offering multi-granularity representation and efficient augmentation for both given texts and multi-modal visual inputs. Extensive experimental results demonstrate the superiority of our proposed HAM model. Specifically, HAM ranks first on the large-scale ScanRefer challenge, which outperforms all the existing methods by a significant margin. Codes will be released after acceptance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge