Xiaodan Shao
Two-stage Multi-beam Training for Multiuser Millimeter-Wave Communications
Jan 07, 2026Abstract:In this letter, we study an efficient multi-beam training method for multiuser millimeter-wave communication systems. Unlike the conventional single-beam training method that relies on exhaustive search, multi-beam training design faces a key challenge in balancing the trade-off between beam training overhead and success beam-identification rate, exacerbated by severe inter-beam interference. To tackle this challenge, we propose a new two-stage multi-beam training method with two distinct multi-beam patterns to enable fast and accurate user angle identification. Specifically, in the first stage, the antenna array is divided into sparse subarrays to generate multiple beams (with high array gains), for identifying candidate user angles. In the second stage, the array is redivided into dense subarrays to generate flexibly steered wide beams, for which a cross-validation method is employed to effectively resolve the remaining angular ambiguity in the first stage. Last, numerical results demonstrate that the proposed method significantly improves the success beam-identification rate compared to existing multi-beam training methods, while retaining or even reducing the required beam training overhead.
Intelligent Reflecting Surfaces for Integrated Sensing and Communications: A Survey
Nov 14, 2025
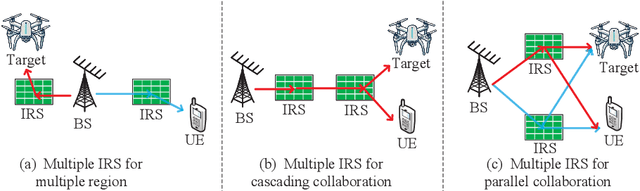
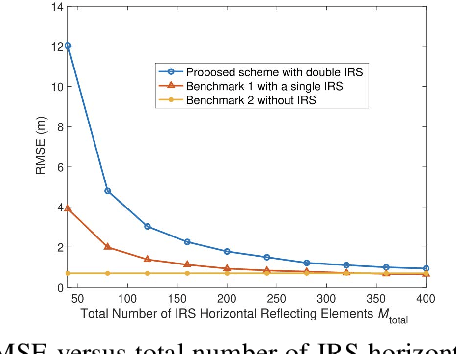
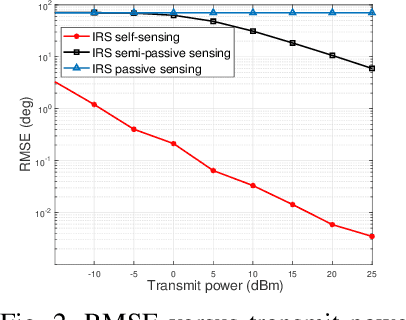
Abstract:The rapid development of sixth-generation (6G) wireless networks requires seamless integration of communication and sensing to support ubiquitous intelligence and real-time, high-reliability applications. Integrated sensing and communication (ISAC) has emerged as a key solution for achieving this convergence, offering joint utilization of spectral, hardware, and computing resources. However, realizing high-performance ISAC remains challenging due to environmental line-of-sight (LoS) blockage, limited spatial resolution, and the inherent coverage asymmetry and resource coupling between sensing and communication. Intelligent reflecting surfaces (IRSs), featuring low-cost, energy-efficient, and programmable electromagnetic reconfiguration, provide a promising solution to overcome these limitations. This article presents a comprehensive overview of IRS-aided wireless sensing and ISAC technologies, including IRS architectures, target detection and estimation techniques, beamforming designs, and performance metrics. It further explores IRS-enabled new opportunities for more efficient performance balancing, coexistence, and networking in ISAC systems, focuses on current design bottlenecks, and outlines future research directions. This article aims to offer a unified design framework that guides the development of practical and scalable IRS-aided ISAC systems for the next-generation wireless network.
AI Signal Processing Paradigm for Movable Antenna: From Geometric Optimization to Electromagnetic Reconfigurability
Oct 22, 2025Abstract:As 6G wireless communication systems evolve toward intelligence and high reconfigurability, the limitations of traditional fixed antenna (TFA) has become increasingly prominent, with geometrically movable antenna (GMA) and electromagnetically reconfigurable antenna (ERA) emerging as key technologies to break through this bottleneck. GMA activates spatial degrees of freedom (DoF) by dynamically adjusting antenna positions, ERA regulates radiation characteristics using tunable metamaterials, thereby introducing DoF in the electromagnetic domain. However, the ``geometric-electromagnetic dual reconfiguration" paradigm formed by their integration poses severe challenges of high-dimensional hybrid optimization to signal processing. To address this issue, we integrate the geometric optimization of GMA and the electromagnetic reconfiguration of ERA for the first time, propose a unified modeling framework for movable and reconfigurable antenna (MARA), investigate the channel modeling and spectral efficiency (SE) optimization for GMA, ERA, and MARA. Besides, we systematically review artificial intelligence (AI)-based solutions, focusing on analyzing the advantages of AI over traditional algorithms in high-dimensional non-convex optimization computations. This paper fills the gap in existing literature regarding the lack of a comprehensive review on the AI-driven signal processing paradigm under geometric-electromagnetic dual reconfiguration and provides theoretical support for the design and optimization of 6G wireless systems with high SE and flexibility.
Polarized 6D Movable Antenna for Wireless Communication: Channel Modeling and Optimization
Jun 04, 2025Abstract:In this paper, we propose a novel polarized six-dimensional movable antenna (P-6DMA) to enhance the performance of wireless communication cost-effectively. Specifically, the P-6DMA enables polarforming by adaptively tuning the antenna's polarization electrically as well as controls the antenna's rotation mechanically, thereby exploiting both polarization and spatial diversity to reconfigure wireless channels for improving communication performance. First, we model the P-6DMA channel in terms of transceiver antenna polarforming vectors and antenna rotations. We then propose a new two-timescale transmission protocol to maximize the weighted sum-rate for a P-6DMA-enhanced multiuser system. Specifically, antenna rotations at the base station (BS) are first optimized based on the statistical channel state information (CSI) of all users, which varies at a much slower rate compared to their instantaneous CSI. Then, transceiver polarforming vectors are designed to cater to the instantaneous CSI under the optimized BS antennas' rotations. Under the polarforming phase shift and amplitude constraints, a new polarforming and rotation joint design problem is efficiently addressed by a low-complexity algorithm based on penalty dual decomposition, where the polarforming coefficients are updated in parallel to reduce computational time. Simulation results demonstrate the significant performance advantages of polarforming, antenna rotation, and their joint design in comparison with various benchmarks without polarforming or antenna rotation adaptation.
Directional Sparsity Based Statistical Channel Estimation for 6D Movable Antenna Communications
May 21, 2025Abstract:Six-dimensional movable antenna (6DMA) is an innovative and transformative technology to improve wireless network capacity by adjusting the 3D positions and 3D rotations of antennas/surfaces (sub-arrays) based on the channel spatial distribution. For optimization of the antenna positions and rotations, the acquisition of statistical channel state information (CSI) is essential for 6DMA systems. In this paper, we unveil for the first time a new \textbf{\textit{directional sparsity}} property of the 6DMA channels between the base station (BS) and the distributed users, where each user has significant channel gains only with a (small) subset of 6DMA position-rotation pairs, which can receive direct/reflected signals from the user. By exploiting this property, a covariance-based algorithm is proposed for estimating the statistical CSI in terms of the average channel power at a small number of 6DMA positions and rotations. Based on such limited channel power estimation, the average channel powers for all possible 6DMA positions and rotations in the BS movement region are reconstructed by further estimating the multi-path average power and direction-of-arrival (DOA) vectors of all users. Simulation results show that the proposed directional sparsity-based algorithm can achieve higher channel power estimation accuracy than existing benchmark schemes, while requiring a lower pilot overhead.
Intelligent Polarforming Antenna Enhanced Sensing and Communication: Modeling and Optimization
May 12, 2025Abstract:In this paper, we propose a novel intelligent polarforming antenna (IPA) to achieve cost-effective wireless sensing and communication. Specifically, the IPA can enable polarforming by adaptively controlling the antenna's polarization electrically as well as its position/rotation mechanically, so as to effectively exploit polarization and spatial diversity to reconfigure wireless channels for improving sensing and communication performance. We study an IPA-enhanced integrated sensing and communication (ISAC) system that utilizes user location sensing to facilitate communication between an IPA-equipped base station (BS) and IPA-equipped users. First, we model the IPA channel in terms of transceiver antenna polarforming vectors and antenna positions/rotations. We then propose a two-timescale ISAC protocol, where in the slow timescale, user localization is first performed, followed by the optimization of the BS antennas' positions and rotations based on the sensed user locations; subsequently, in the fast timescale, transceiver polarforming is adapted to cater to the instantaneous channel state information (CSI), with the optimized BS antennas' positions and rotations. We propose a new polarforming-based user localization method that uses a structured time-domain pattern of pilot-polarforming vectors to extract the common stable components in the IPA channel across different polarizations based on the parallel factor (PARAFAC) tensor model. Moreover, we maximize the achievable average sum-rate of users by jointly optimizing the fast-timescale transceiver polarforming, including phase shifts and amplitude variations, along with the slow-timescale antenna rotations and positions at the BS. Simulation results validate the effectiveness of polarforming-based localization algorithm and demonstrate the performance advantages of polarforming, antenna placement, and their joint design.
Hybrid-Field 6D Movable Antenna for Terahertz Communications: Channel Modeling and Estimation
May 07, 2025Abstract:In this work, we study a six-dimensional movable antenna (6DMA)-enhanced Terahertz (THz) network that supports a large number of users with a few antennas by controlling the three-dimensional (3D) positions and 3D rotations of antenna surfaces/subarrays at the base station (BS). However, the short wavelength of THz signals combined with a large 6DMA movement range extends the near-field region. As a result, a user can be in the far-field region relative to the antennas on one 6DMA surface, while simultaneously residing in the near-field region relative to other 6DMA surfaces. Moreover, 6DMA THz channel estimation suffers from increased computational complexity and pilot overhead due to uneven power distribution across the large number of candidate position-rotation pairs, as well as the limited number of radio frequency (RF) chains in THz bands. To address these issues, we propose an efficient hybrid-field generalized 6DMA THz channel model, which accounts for planar wave propagation within individual 6DMA surfaces and spherical waves among different 6DMA surfaces. Furthermore, we propose a low-overhead channel estimation algorithm that leverages directional sparsity to construct a complete channel map for all potential antenna position-rotation pairs. Numerical results show that the proposed hybrid-field channel model achieves a sum rate close to that of the ground-truth near-field channel model and confirm that the channel estimation method yields accurate results with low complexity.
Statistical Channel Based Low-Complexity Rotation and Position Optimization for 6D Movable Antennas Enabled Wireless Communication
Apr 29, 2025Abstract:Six-dimensional movable antenna (6DMA) is a promising technology to fully exploit spatial variation in wireless channels by allowing flexible adjustment of three-dimensional (3D) positions and rotations of antennas at the transceiver. In this paper, we investigate the practical low-complexity design of 6DMA-enabled communication systems, including transmission protocol, statistical channel information (SCI) acquisition, and joint position and rotation optimization of 6DMA surfaces based on the SCI of users. Specifically, an orthogonal matching pursuit (OMP)-based algorithm is proposed for the estimation of SCI of users at all possible position-rotation pairs of 6DMA surfaces based on the channel measurements at a small subset of position-rotation pairs. Then, the average sum logarithmic rate of all users is maximized by jointly designing the positions and rotations of 6DMA surfaces based on their SCI acquired. Different from prior works on 6DMA which adopt alternating optimization to design 6DMA positions/rotations with iterations, we propose a new sequential optimization approach that first determines 6DMA rotations and then finds their feasible positions to realize the optimized rotations subject to practical antenna placement constraints. Simulation results show that the proposed sequential optimization significantly reduces the computational complexity of conventional alternating optimization, while achieving comparable communication performance. It is also shown that the proposed SCI-based 6DMA design can effectively enhance the communication throughput of wireless networks over existing fixed (position and rotation) antenna arrays, yet with a practically appealing low-complexity implementation.
Rotatable Antennas for Integrated Sensing and Communications
Mar 13, 2025Abstract:In this letter, we propose to deploy rotatable antennas (RAs) at the base station (BS) to enhance both communication and sensing (C&S) performances, by exploiting a new spatial degree-of-freedom (DoF) offered by array rotation. Specifically, we formulate a multi-objective optimization problem to simultaneously maximize the sum-rate of multiple communication users and minimize the Cram\'er-Rao bound (CRB) for target angle estimation, by jointly optimizing the transmit beamforming vectors and the array rotation angle at the BS. To solve this problem, we first equivalently decompose it into two subproblems, corresponding to an inner problem for beamforming optimization and an outer problem for array rotation optimization. Although these two subproblems are non-convex, we obtain their high-quality solutions by applying the block coordinate descent (BCD) technique and one-dimensional exhaustive search, respectively. Moreover, we show that for the communication-only case, RAs provide an additional rotation gain to improve communication performance; while for the sensing-only case, the equivalent spatial aperture can be enlarged by RAs for achieving higher sensing accuracy. Finally, numerical results are presented to showcase the performance gains of RAs over fixed-rotation antennas in integrated sensing and communications (ISAC).
A Tutorial on Movable Antennas for Wireless Networks
Feb 25, 2025



Abstract:Movable antenna (MA) has been recognized as a promising technology to enhance the performance of wireless communication and sensing by enabling antenna movement. Such a significant paradigm shift from conventional fixed antennas (FAs) to MAs offers tremendous new opportunities towards realizing more versatile, adaptive and efficient next-generation wireless networks such as 6G. In this paper, we provide a comprehensive tutorial on the fundamentals and advancements in the area of MA-empowered wireless networks. First, we overview the historical development and contemporary applications of MA technologies. Next, to characterize the continuous variation in wireless channels with respect to antenna position and/or orientation, we present new field-response channel models tailored for MAs, which are applicable to narrowband and wideband systems as well as far-field and near-field propagation conditions. Subsequently, we review the state-of-the-art architectures for implementing MAs and discuss their practical constraints. A general optimization framework is then formulated to fully exploit the spatial degrees of freedom (DoFs) in antenna movement for performance enhancement in wireless systems. In particular, we delve into two major design issues for MA systems. First, we address the intricate antenna movement optimization problem for various communication and/or sensing systems to maximize the performance gains achievable by MAs. Second, we deal with the challenging channel acquisition issue in MA systems for reconstructing the channel mapping between arbitrary antenna positions inside the transmitter and receiver regions. Moreover, we show existing prototypes developed for MA-aided communication/sensing and the experimental results based on them. Finally, the extension of MA design to other wireless systems and its synergy with other emerging wireless technologies are discussed.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge