Xiao Zhao
HybridOcc: NeRF Enhanced Transformer-based Multi-Camera 3D Occupancy Prediction
Aug 17, 2024



Abstract:Vision-based 3D semantic scene completion (SSC) describes autonomous driving scenes through 3D volume representations. However, the occlusion of invisible voxels by scene surfaces poses challenges to current SSC methods in hallucinating refined 3D geometry. This paper proposes HybridOcc, a hybrid 3D volume query proposal method generated by Transformer framework and NeRF representation and refined in a coarse-to-fine SSC prediction framework. HybridOcc aggregates contextual features through the Transformer paradigm based on hybrid query proposals while combining it with NeRF representation to obtain depth supervision. The Transformer branch contains multiple scales and uses spatial cross-attention for 2D to 3D transformation. The newly designed NeRF branch implicitly infers scene occupancy through volume rendering, including visible and invisible voxels, and explicitly captures scene depth rather than generating RGB color. Furthermore, we present an innovative occupancy-aware ray sampling method to orient the SSC task instead of focusing on the scene surface, further improving the overall performance. Extensive experiments on nuScenes and SemanticKITTI datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of our HybridOcc on the SSC task.
MaskBEV: Towards A Unified Framework for BEV Detection and Map Segmentation
Aug 17, 2024
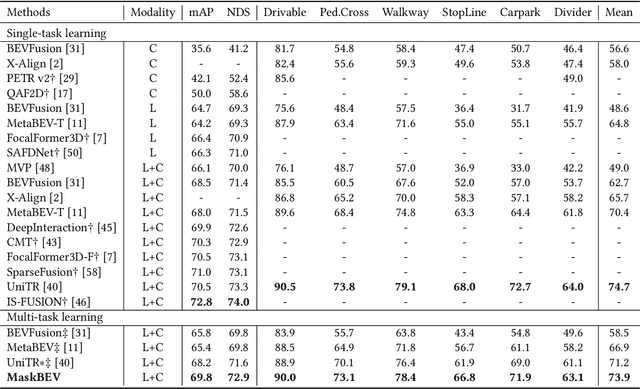

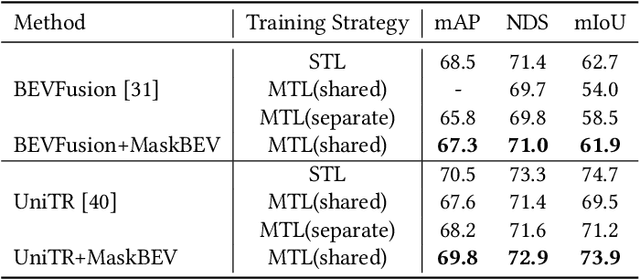
Abstract:Accurate and robust multimodal multi-task perception is crucial for modern autonomous driving systems. However, current multimodal perception research follows independent paradigms designed for specific perception tasks, leading to a lack of complementary learning among tasks and decreased performance in multi-task learning (MTL) due to joint training. In this paper, we propose MaskBEV, a masked attention-based MTL paradigm that unifies 3D object detection and bird's eye view (BEV) map segmentation. MaskBEV introduces a task-agnostic Transformer decoder to process these diverse tasks, enabling MTL to be completed in a unified decoder without requiring additional design of specific task heads. To fully exploit the complementary information between BEV map segmentation and 3D object detection tasks in BEV space, we propose spatial modulation and scene-level context aggregation strategies. These strategies consider the inherent dependencies between BEV segmentation and 3D detection, naturally boosting MTL performance. Extensive experiments on nuScenes dataset show that compared with previous state-of-the-art MTL methods, MaskBEV achieves 1.3 NDS improvement in 3D object detection and 2.7 mIoU improvement in BEV map segmentation, while also demonstrating slightly leading inference speed.
Correlation-Decoupled Knowledge Distillation for Multimodal Sentiment Analysis with Incomplete Modalities
Apr 25, 2024



Abstract:Multimodal sentiment analysis (MSA) aims to understand human sentiment through multimodal data. Most MSA efforts are based on the assumption of modality completeness. However, in real-world applications, some practical factors cause uncertain modality missingness, which drastically degrades the model's performance. To this end, we propose a Correlation-decoupled Knowledge Distillation (CorrKD) framework for the MSA task under uncertain missing modalities. Specifically, we present a sample-level contrastive distillation mechanism that transfers comprehensive knowledge containing cross-sample correlations to reconstruct missing semantics. Moreover, a category-guided prototype distillation mechanism is introduced to capture cross-category correlations using category prototypes to align feature distributions and generate favorable joint representations. Eventually, we design a response-disentangled consistency distillation strategy to optimize the sentiment decision boundaries of the student network through response disentanglement and mutual information maximization. Comprehensive experiments on three datasets indicate that our framework can achieve favorable improvements compared with several baselines.
CPR-Coach: Recognizing Composite Error Actions based on Single-class Training
Sep 21, 2023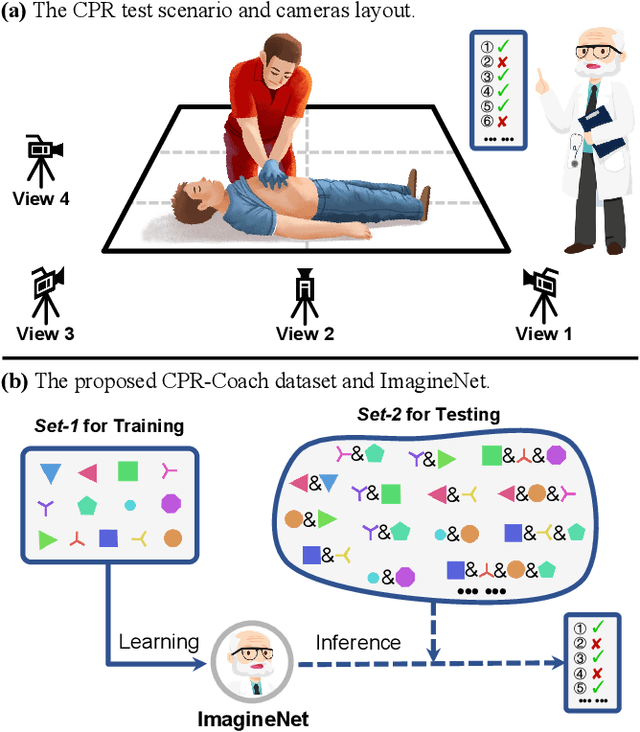
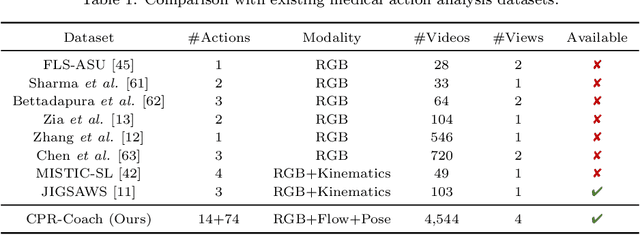
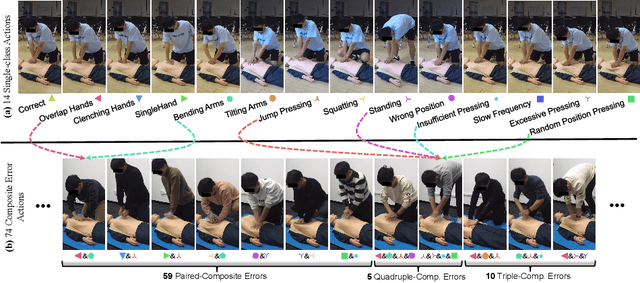
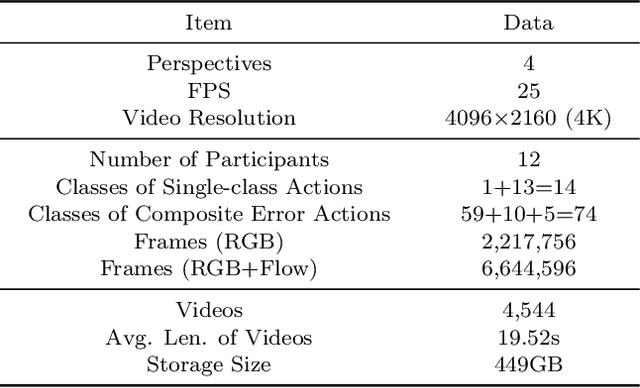
Abstract:The fine-grained medical action analysis task has received considerable attention from pattern recognition communities recently, but it faces the problems of data and algorithm shortage. Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation (CPR) is an essential skill in emergency treatment. Currently, the assessment of CPR skills mainly depends on dummies and trainers, leading to high training costs and low efficiency. For the first time, this paper constructs a vision-based system to complete error action recognition and skill assessment in CPR. Specifically, we define 13 types of single-error actions and 74 types of composite error actions during external cardiac compression and then develop a video dataset named CPR-Coach. By taking the CPR-Coach as a benchmark, this paper thoroughly investigates and compares the performance of existing action recognition models based on different data modalities. To solve the unavoidable Single-class Training & Multi-class Testing problem, we propose a humancognition-inspired framework named ImagineNet to improve the model's multierror recognition performance under restricted supervision. Extensive experiments verify the effectiveness of the framework. We hope this work could advance research toward fine-grained medical action analysis and skill assessment. The CPR-Coach dataset and the code of ImagineNet are publicly available on Github.
Context De-confounded Emotion Recognition
Mar 26, 2023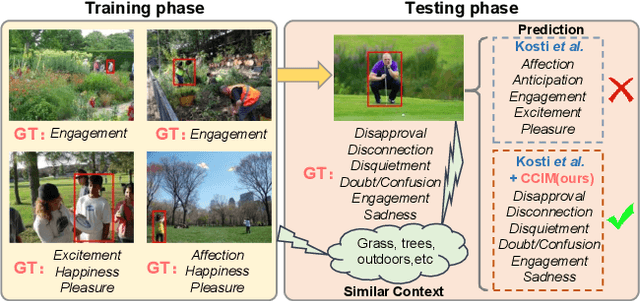
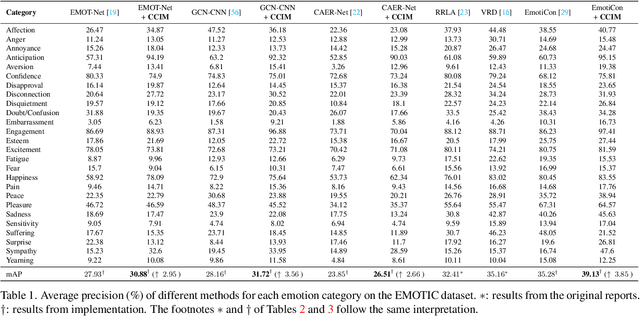
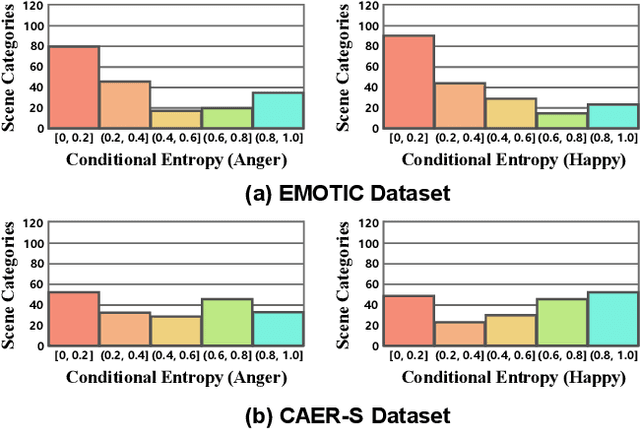
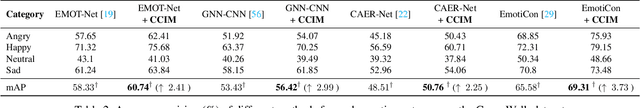
Abstract:Context-Aware Emotion Recognition (CAER) is a crucial and challenging task that aims to perceive the emotional states of the target person with contextual information. Recent approaches invariably focus on designing sophisticated architectures or mechanisms to extract seemingly meaningful representations from subjects and contexts. However, a long-overlooked issue is that a context bias in existing datasets leads to a significantly unbalanced distribution of emotional states among different context scenarios. Concretely, the harmful bias is a confounder that misleads existing models to learn spurious correlations based on conventional likelihood estimation, significantly limiting the models' performance. To tackle the issue, this paper provides a causality-based perspective to disentangle the models from the impact of such bias, and formulate the causalities among variables in the CAER task via a tailored causal graph. Then, we propose a Contextual Causal Intervention Module (CCIM) based on the backdoor adjustment to de-confound the confounder and exploit the true causal effect for model training. CCIM is plug-in and model-agnostic, which improves diverse state-of-the-art approaches by considerable margins. Extensive experiments on three benchmark datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of our CCIM and the significance of causal insight.
Trajectory and Transmit Power Optimization for IRS-Assisted UAV Communication under Malicious Jamming
Jan 14, 2022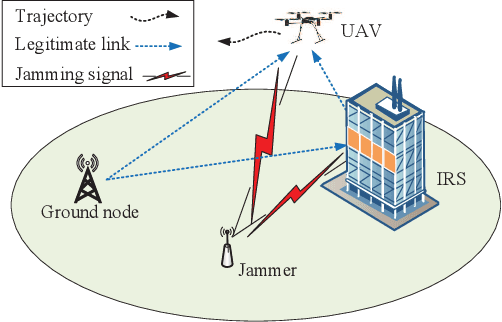
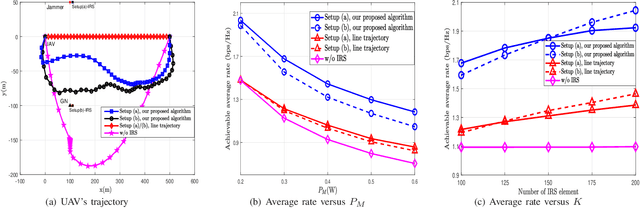
Abstract:In this letter, we investigate an unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) communication system, where an intelligent reflecting surface (IRS) is deployed to assist in the transmission from a ground node (GN) to the UAV in the presence of a jammer. We aim to maximize the average rate of the UAV communication by jointly optimizing the GN's transmit power, the IRS's passive beamforming and the UAV's trajectory. However, the formulated problem is difficult to solve due to the non-convex objective function and the coupled optimization variables. Thus, to tackle it, we propose an alternating optimization (AO) based algorithm by exploiting the successive convex approximation (SCA) and semidefinite relaxation (SDR) techniques. Simulation results show that the proposed algorithm can significantly improve the average rate compared with the benchmark algorithms. Moreover, it also shows that when the jamming power is large and the number of IRS elements is relatively small, deploying the IRS near the jammer outperforms deploying it near the GN, and vice versa.
A Comparative Study for Non-rigid Image Registration and Rigid Image Registration
Jan 12, 2020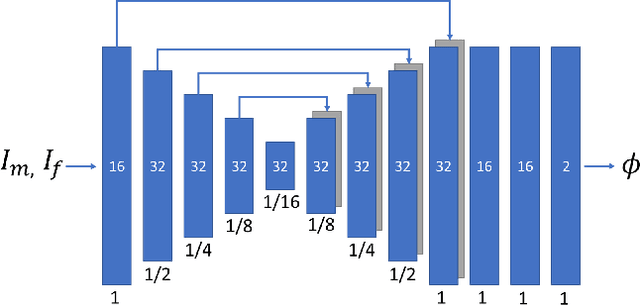
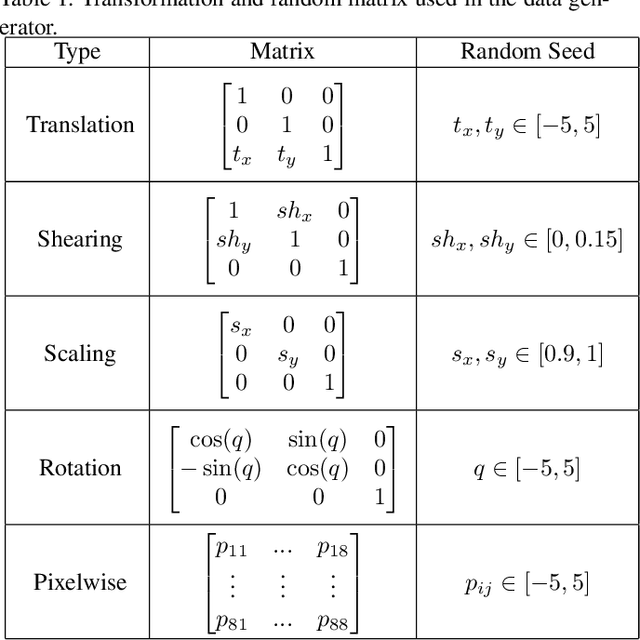
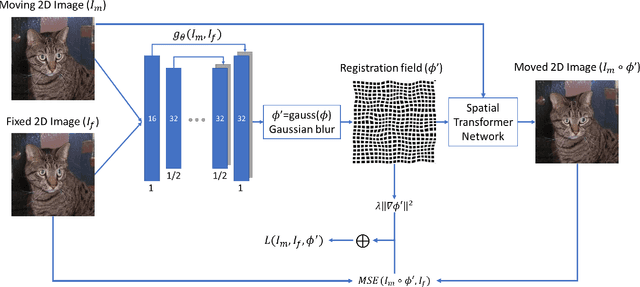
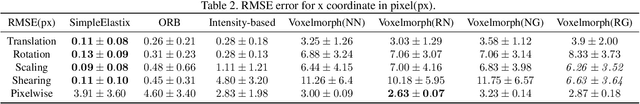
Abstract:Image registration algorithms can be generally categorized into two groups: non-rigid and rigid. Recently, many deep learning-based algorithms employ a neural net to characterize non-rigid image registration function. However, do they always perform better? In this study, we compare the state-of-art deep learning-based non-rigid registration approach with rigid registration approach. The data is generated from Kaggle Dog vs Cat Competition \url{https://www.kaggle.com/c/dogs-vs-cats/} and we test the algorithms' performance on rigid transformation including translation, rotation, scaling, shearing and pixelwise non-rigid transformation. The Voxelmorph is trained on rigidset and nonrigidset separately for comparison and we also add a gaussian blur layer to its original architecture to improve registration performance. The best quantitative results in both root-mean-square error (RMSE) and mean absolute error (MAE) metrics for rigid registration are produced by SimpleElastix and non-rigid registration by Voxelmorph. We select representative samples for visual assessment.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge