Yuhang Yang
From Frames to Sequences: Temporally Consistent Human-Centric Dense Prediction
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:In this work, we focus on the challenge of temporally consistent human-centric dense prediction across video sequences. Existing models achieve strong per-frame accuracy but often flicker under motion, occlusion, and lighting changes, and they rarely have paired human video supervision for multiple dense tasks. We address this gap with a scalable synthetic data pipeline that generates photorealistic human frames and motion-aligned sequences with pixel-accurate depth, normals, and masks. Unlike prior static data synthetic pipelines, our pipeline provides both frame-level labels for spatial learning and sequence-level supervision for temporal learning. Building on this, we train a unified ViT-based dense predictor that (i) injects an explicit human geometric prior via CSE embeddings and (ii) improves geometry-feature reliability with a lightweight channel reweighting module after feature fusion. Our two-stage training strategy, combining static pretraining with dynamic sequence supervision, enables the model first to acquire robust spatial representations and then refine temporal consistency across motion-aligned sequences. Extensive experiments show that we achieve state-of-the-art performance on THuman2.1 and Hi4D and generalize effectively to in-the-wild videos.
TableGPT-R1: Advancing Tabular Reasoning Through Reinforcement Learning
Dec 23, 2025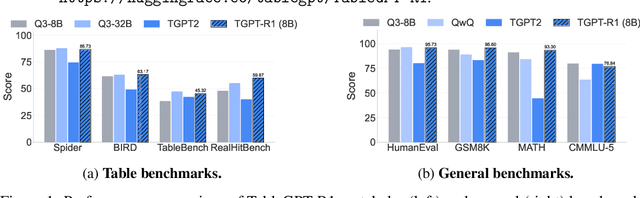
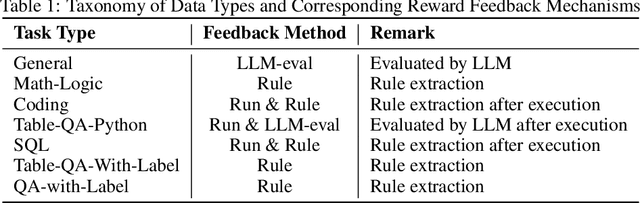
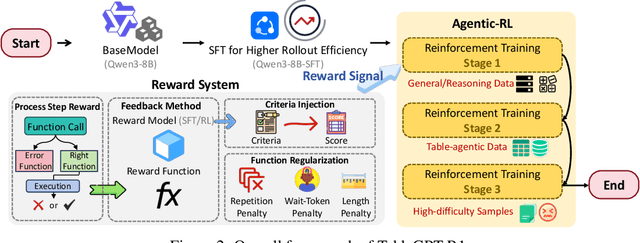
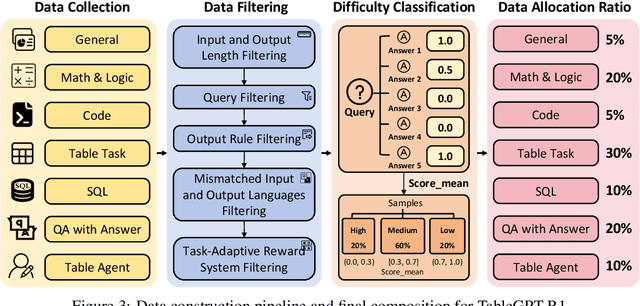
Abstract:Tabular data serves as the backbone of modern data analysis and scientific research. While Large Language Models (LLMs) fine-tuned via Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT) have significantly improved natural language interaction with such structured data, they often fall short in handling the complex, multi-step reasoning and robust code execution required for real-world table tasks. Reinforcement Learning (RL) offers a promising avenue to enhance these capabilities, yet its application in the tabular domain faces three critical hurdles: the scarcity of high-quality agentic trajectories with closed-loop code execution and environment feedback on diverse table structures, the extreme heterogeneity of feedback signals ranging from rigid SQL execution to open-ended data interpretation, and the risk of catastrophic forgetting of general knowledge during vertical specialization. To overcome these challenges and unlock advanced reasoning on complex tables, we introduce \textbf{TableGPT-R1}, a specialized tabular model built on a systematic RL framework. Our approach integrates a comprehensive data engineering pipeline that synthesizes difficulty-stratified agentic trajectories for both supervised alignment and RL rollouts, a task-adaptive reward system that combines rule-based verification with a criteria-injected reward model and incorporates process-level step reward shaping with behavioral regularization, and a multi-stage training framework that progressively stabilizes reasoning before specializing in table-specific tasks. Extensive evaluations demonstrate that TableGPT-R1 achieves state-of-the-art performance on authoritative benchmarks, significantly outperforming baseline models while retaining robust general capabilities. Our model is available at https://huggingface.co/tablegpt/TableGPT-R1.
RealHiTBench: A Comprehensive Realistic Hierarchical Table Benchmark for Evaluating LLM-Based Table Analysis
Jun 16, 2025Abstract:With the rapid advancement of Large Language Models (LLMs), there is an increasing need for challenging benchmarks to evaluate their capabilities in handling complex tabular data. However, existing benchmarks are either based on outdated data setups or focus solely on simple, flat table structures. In this paper, we introduce RealHiTBench, a comprehensive benchmark designed to evaluate the performance of both LLMs and Multimodal LLMs (MLLMs) across a variety of input formats for complex tabular data, including LaTeX, HTML, and PNG. RealHiTBench also includes a diverse collection of tables with intricate structures, spanning a wide range of task types. Our experimental results, using 25 state-of-the-art LLMs, demonstrate that RealHiTBench is indeed a challenging benchmark. Moreover, we also develop TreeThinker, a tree-based pipeline that organizes hierarchical headers into a tree structure for enhanced tabular reasoning, validating the importance of improving LLMs' perception of table hierarchies. We hope that our work will inspire further research on tabular data reasoning and the development of more robust models. The code and data are available at https://github.com/cspzyy/RealHiTBench.
DanceTogether! Identity-Preserving Multi-Person Interactive Video Generation
May 23, 2025Abstract:Controllable video generation (CVG) has advanced rapidly, yet current systems falter when more than one actor must move, interact, and exchange positions under noisy control signals. We address this gap with DanceTogether, the first end-to-end diffusion framework that turns a single reference image plus independent pose-mask streams into long, photorealistic videos while strictly preserving every identity. A novel MaskPoseAdapter binds "who" and "how" at every denoising step by fusing robust tracking masks with semantically rich-but noisy-pose heat-maps, eliminating the identity drift and appearance bleeding that plague frame-wise pipelines. To train and evaluate at scale, we introduce (i) PairFS-4K, 26 hours of dual-skater footage with 7,000+ distinct IDs, (ii) HumanRob-300, a one-hour humanoid-robot interaction set for rapid cross-domain transfer, and (iii) TogetherVideoBench, a three-track benchmark centered on the DanceTogEval-100 test suite covering dance, boxing, wrestling, yoga, and figure skating. On TogetherVideoBench, DanceTogether outperforms the prior arts by a significant margin. Moreover, we show that a one-hour fine-tune yields convincing human-robot videos, underscoring broad generalization to embodied-AI and HRI tasks. Extensive ablations confirm that persistent identity-action binding is critical to these gains. Together, our model, datasets, and benchmark lift CVG from single-subject choreography to compositionally controllable, multi-actor interaction, opening new avenues for digital production, simulation, and embodied intelligence. Our video demos and code are available at https://DanceTog.github.io/.
GRACE: Estimating Geometry-level 3D Human-Scene Contact from 2D Images
May 10, 2025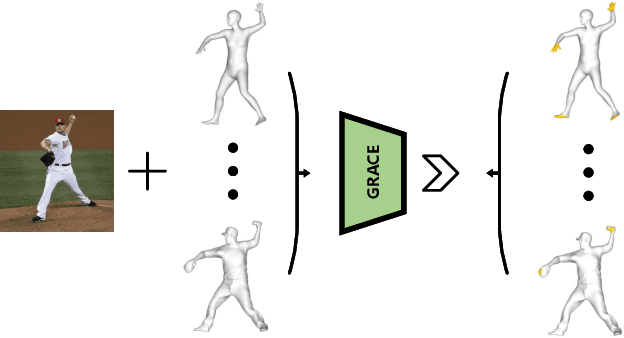
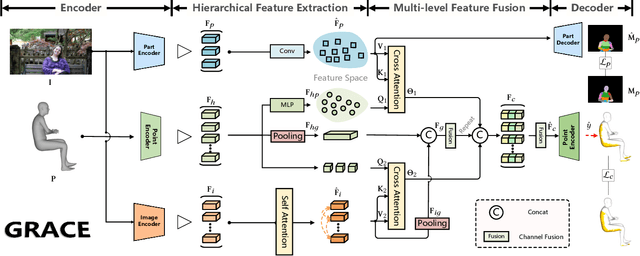
Abstract:Estimating the geometry level of human-scene contact aims to ground specific contact surface points at 3D human geometries, which provides a spatial prior and bridges the interaction between human and scene, supporting applications such as human behavior analysis, embodied AI, and AR/VR. To complete the task, existing approaches predominantly rely on parametric human models (e.g., SMPL), which establish correspondences between images and contact regions through fixed SMPL vertex sequences. This actually completes the mapping from image features to an ordered sequence. However, this approach lacks consideration of geometry, limiting its generalizability in distinct human geometries. In this paper, we introduce GRACE (Geometry-level Reasoning for 3D Human-scene Contact Estimation), a new paradigm for 3D human contact estimation. GRACE incorporates a point cloud encoder-decoder architecture along with a hierarchical feature extraction and fusion module, enabling the effective integration of 3D human geometric structures with 2D interaction semantics derived from images. Guided by visual cues, GRACE establishes an implicit mapping from geometric features to the vertex space of the 3D human mesh, thereby achieving accurate modeling of contact regions. This design ensures high prediction accuracy and endows the framework with strong generalization capability across diverse human geometries. Extensive experiments on multiple benchmark datasets demonstrate that GRACE achieves state-of-the-art performance in contact estimation, with additional results further validating its robust generalization to unstructured human point clouds.
SIGMAN:Scaling 3D Human Gaussian Generation with Millions of Assets
Apr 09, 2025Abstract:3D human digitization has long been a highly pursued yet challenging task. Existing methods aim to generate high-quality 3D digital humans from single or multiple views, but remain primarily constrained by current paradigms and the scarcity of 3D human assets. Specifically, recent approaches fall into several paradigms: optimization-based and feed-forward (both single-view regression and multi-view generation with reconstruction). However, they are limited by slow speed, low quality, cascade reasoning, and ambiguity in mapping low-dimensional planes to high-dimensional space due to occlusion and invisibility, respectively. Furthermore, existing 3D human assets remain small-scale, insufficient for large-scale training. To address these challenges, we propose a latent space generation paradigm for 3D human digitization, which involves compressing multi-view images into Gaussians via a UV-structured VAE, along with DiT-based conditional generation, we transform the ill-posed low-to-high-dimensional mapping problem into a learnable distribution shift, which also supports end-to-end inference. In addition, we employ the multi-view optimization approach combined with synthetic data to construct the HGS-1M dataset, which contains $1$ million 3D Gaussian assets to support the large-scale training. Experimental results demonstrate that our paradigm, powered by large-scale training, produces high-quality 3D human Gaussians with intricate textures, facial details, and loose clothing deformation.
VideoGen-Eval: Agent-based System for Video Generation Evaluation
Mar 30, 2025



Abstract:The rapid advancement of video generation has rendered existing evaluation systems inadequate for assessing state-of-the-art models, primarily due to simple prompts that cannot showcase the model's capabilities, fixed evaluation operators struggling with Out-of-Distribution (OOD) cases, and misalignment between computed metrics and human preferences. To bridge the gap, we propose VideoGen-Eval, an agent evaluation system that integrates LLM-based content structuring, MLLM-based content judgment, and patch tools designed for temporal-dense dimensions, to achieve a dynamic, flexible, and expandable video generation evaluation. Additionally, we introduce a video generation benchmark to evaluate existing cutting-edge models and verify the effectiveness of our evaluation system. It comprises 700 structured, content-rich prompts (both T2V and I2V) and over 12,000 videos generated by 20+ models, among them, 8 cutting-edge models are selected as quantitative evaluation for the agent and human. Extensive experiments validate that our proposed agent-based evaluation system demonstrates strong alignment with human preferences and reliably completes the evaluation, as well as the diversity and richness of the benchmark.
HERO: Human Reaction Generation from Videos
Mar 11, 2025Abstract:Human reaction generation represents a significant research domain for interactive AI, as humans constantly interact with their surroundings. Previous works focus mainly on synthesizing the reactive motion given a human motion sequence. This paradigm limits interaction categories to human-human interactions and ignores emotions that may influence reaction generation. In this work, we propose to generate 3D human reactions from RGB videos, which involves a wider range of interaction categories and naturally provides information about expressions that may reflect the subject's emotions. To cope with this task, we present HERO, a simple yet powerful framework for Human rEaction geneRation from videOs. HERO considers both global and frame-level local representations of the video to extract the interaction intention, and then uses the extracted interaction intention to guide the synthesis of the reaction. Besides, local visual representations are continuously injected into the model to maximize the exploitation of the dynamic properties inherent in videos. Furthermore, the ViMo dataset containing paired Video-Motion data is collected to support the task. In addition to human-human interactions, these video-motion pairs also cover animal-human interactions and scene-human interactions. Extensive experiments demonstrate the superiority of our methodology. The code and dataset will be publicly available at https://jackyu6.github.io/HERO.
Frequency-Based Alignment of EEG and Audio Signals Using Contrastive Learning and SincNet for Auditory Attention Detection
Mar 06, 2025Abstract:Humans exhibit a remarkable ability to focus auditory attention in complex acoustic environments, such as cocktail parties. Auditory attention detection (AAD) aims to identify the attended speaker by analyzing brain signals, such as electroencephalography (EEG) data. Existing AAD algorithms often leverage deep learning's powerful nonlinear modeling capabilities, few consider the neural mechanisms underlying auditory processing in the brain. In this paper, we propose SincAlignNet, a novel network based on an improved SincNet and contrastive learning, designed to align audio and EEG features for auditory attention detection. The SincNet component simulates the brain's processing of audio during auditory attention, while contrastive learning guides the model to learn the relationship between EEG signals and attended speech. During inference, we calculate the cosine similarity between EEG and audio features and also explore direct inference of the attended speaker using EEG data. Cross-trial evaluations results demonstrate that SincAlignNet outperforms state-of-the-art AAD methods on two publicly available datasets, KUL and DTU, achieving average accuracies of 78.3% and 92.2%, respectively, with a 1-second decision window. The model exhibits strong interpretability, revealing that the left and right temporal lobes are more active during both male and female speaker scenarios. Furthermore, we found that using data from only six electrodes near the temporal lobes maintains similar or even better performance compared to using 64 electrodes. These findings indicate that efficient low-density EEG online decoding is achievable, marking an important step toward the practical implementation of neuro-guided hearing aids in real-world applications. Code is available at: https://github.com/LiaoEuan/SincAlignNet.
DisPose: Disentangling Pose Guidance for Controllable Human Image Animation
Dec 13, 2024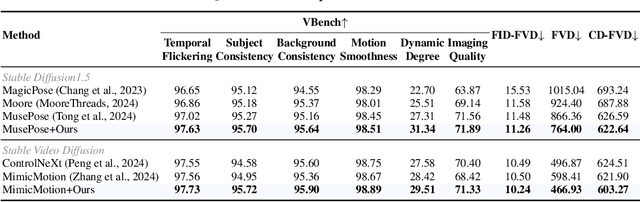
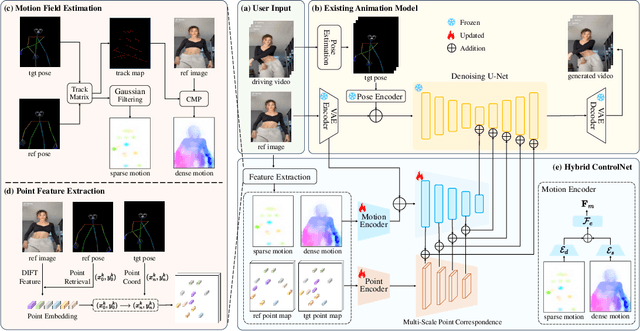
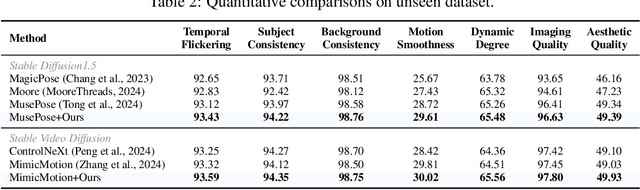

Abstract:Controllable human image animation aims to generate videos from reference images using driving videos. Due to the limited control signals provided by sparse guidance (e.g., skeleton pose), recent works have attempted to introduce additional dense conditions (e.g., depth map) to ensure motion alignment. However, such strict dense guidance impairs the quality of the generated video when the body shape of the reference character differs significantly from that of the driving video. In this paper, we present DisPose to mine more generalizable and effective control signals without additional dense input, which disentangles the sparse skeleton pose in human image animation into motion field guidance and keypoint correspondence. Specifically, we generate a dense motion field from a sparse motion field and the reference image, which provides region-level dense guidance while maintaining the generalization of the sparse pose control. We also extract diffusion features corresponding to pose keypoints from the reference image, and then these point features are transferred to the target pose to provide distinct identity information. To seamlessly integrate into existing models, we propose a plug-and-play hybrid ControlNet that improves the quality and consistency of generated videos while freezing the existing model parameters. Extensive qualitative and quantitative experiments demonstrate the superiority of DisPose compared to current methods. Code: \href{https://github.com/lihxxx/DisPose}{https://github.com/lihxxx/DisPose}.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge