Hongchen Luo
University of Science and Technology of China, China
IIB-LPO: Latent Policy Optimization via Iterative Information Bottleneck
Jan 09, 2026Abstract:Recent advances in Reinforcement Learning with Verifiable Rewards (RLVR) for Large Language Model (LLM) reasoning have been hindered by a persistent challenge: exploration collapse. The semantic homogeneity of random rollouts often traps models in narrow, over-optimized behaviors. While existing methods leverage policy entropy to encourage exploration, they face inherent limitations. Global entropy regularization is susceptible to reward hacking, which can induce meaningless verbosity, whereas local token-selective updates struggle with the strong inductive bias of pre-trained models. To address this, we propose Latent Policy Optimization via Iterative Information Bottleneck (IIB-LPO), a novel approach that shifts exploration from statistical perturbation of token distributions to topological branching of reasoning trajectories. IIB-LPO triggers latent branching at high-entropy states to diversify reasoning paths and employs the Information Bottleneck principle both as a trajectory filter and a self-reward mechanism, ensuring concise and informative exploration. Empirical results across four mathematical reasoning benchmarks demonstrate that IIB-LPO achieves state-of-the-art performance, surpassing prior methods by margins of up to 5.3% in accuracy and 7.4% in diversity metrics.
Boosting the Generalization and Reasoning of Vision Language Models with Curriculum Reinforcement Learning
Mar 10, 2025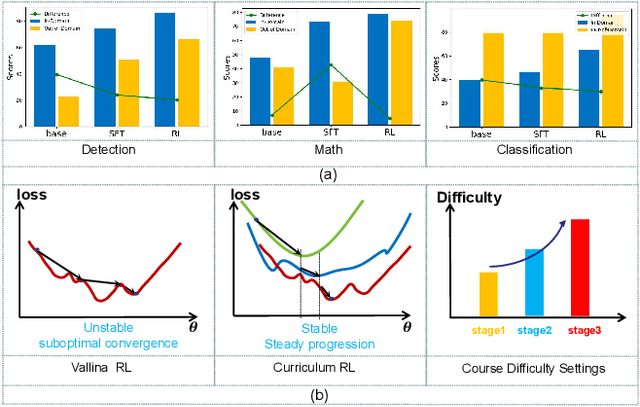
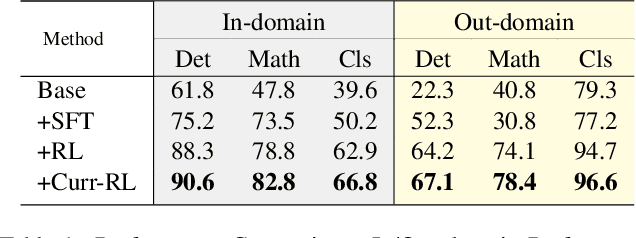
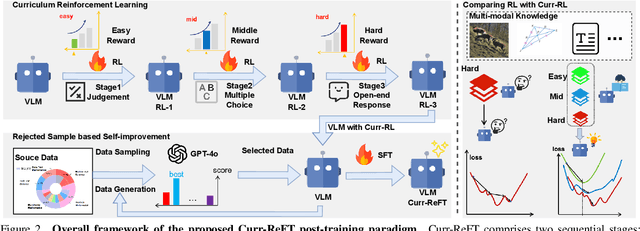
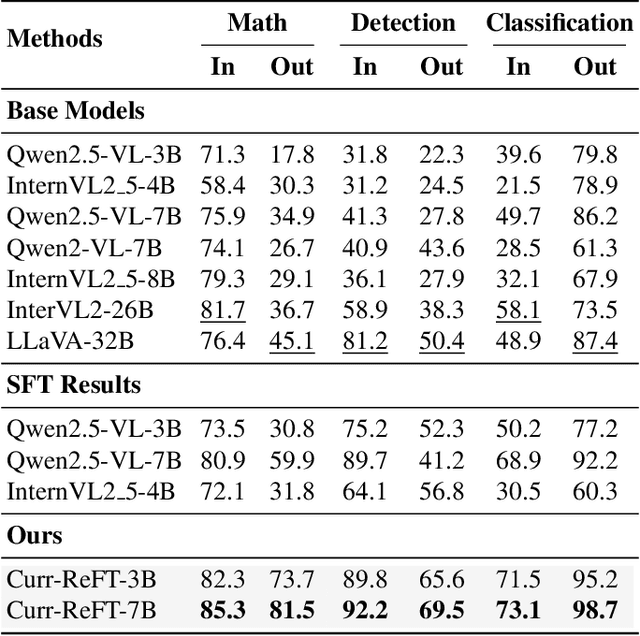
Abstract:While state-of-the-art vision-language models (VLMs) have demonstrated remarkable capabilities in complex visual-text tasks, their success heavily relies on massive model scaling, limiting their practical deployment. Small-scale VLMs offer a more practical alternative but face significant challenges when trained with traditional supervised fine-tuning (SFT), particularly in two aspects: out-of-domain (OOD) generalization and reasoning abilities, which significantly lags behind the contemporary Large language models (LLMs). To address these challenges, we propose Curriculum Reinforcement Finetuning (Curr-ReFT), a novel post-training paradigm specifically designed for small-scale VLMs. Inspired by the success of reinforcement learning in LLMs, Curr-ReFT comprises two sequential stages: (1) Curriculum Reinforcement Learning, which ensures steady progression of model capabilities through difficulty-aware reward design, transitioning from basic visual perception to complex reasoning tasks; and (2) Rejected Sampling-based Self-improvement, which maintains the fundamental capabilities of VLMs through selective learning from high-quality multimodal and language examples. Extensive experiments demonstrate that models trained with Curr-ReFT paradigm achieve state-of-the-art performance across various visual tasks in both in-domain and out-of-domain settings. Moreover, our Curr-ReFT enhanced 3B model matches the performance of 32B-parameter models, demonstrating that efficient training paradigms can effectively bridge the gap between small and large models.
GREAT: Geometry-Intention Collaborative Inference for Open-Vocabulary 3D Object Affordance Grounding
Nov 29, 2024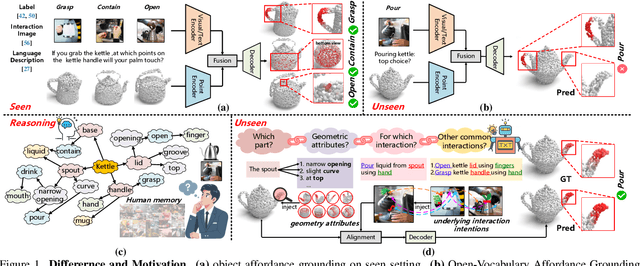
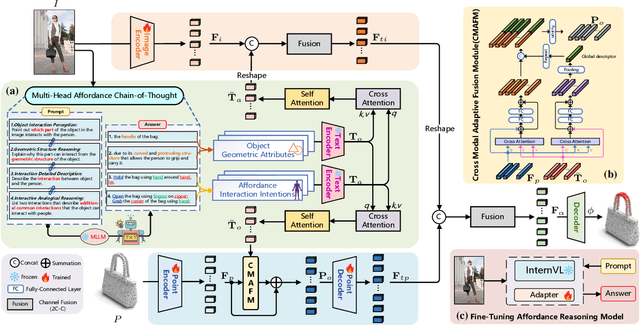
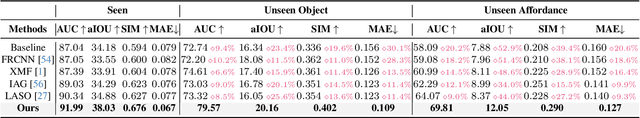
Abstract:Open-Vocabulary 3D object affordance grounding aims to anticipate ``action possibilities'' regions on 3D objects with arbitrary instructions, which is crucial for robots to generically perceive real scenarios and respond to operational changes. Existing methods focus on combining images or languages that depict interactions with 3D geometries to introduce external interaction priors. However, they are still vulnerable to a limited semantic space by failing to leverage implied invariant geometries and potential interaction intentions. Normally, humans address complex tasks through multi-step reasoning and respond to diverse situations by leveraging associative and analogical thinking. In light of this, we propose GREAT (GeometRy-intEntion collAboraTive inference) for Open-Vocabulary 3D Object Affordance Grounding, a novel framework that mines the object invariant geometry attributes and performs analogically reason in potential interaction scenarios to form affordance knowledge, fully combining the knowledge with both geometries and visual contents to ground 3D object affordance. Besides, we introduce the Point Image Affordance Dataset v2 (PIADv2), the largest 3D object affordance dataset at present to support the task. Extensive experiments demonstrate the effectiveness and superiority of GREAT. Code and dataset are available at project.
Leverage Task Context for Object Affordance Ranking
Nov 25, 2024Abstract:Intelligent agents accomplish different tasks by utilizing various objects based on their affordance, but how to select appropriate objects according to task context is not well-explored. Current studies treat objects within the affordance category as equivalent, ignoring that object affordances vary in priority with different task contexts, hindering accurate decision-making in complex environments. To enable agents to develop a deeper understanding of the objects required to perform tasks, we propose to leverage task context for object affordance ranking, i.e., given image of a complex scene and the textual description of the affordance and task context, revealing task-object relationships and clarifying the priority rank of detected objects. To this end, we propose a novel Context-embed Group Ranking Framework with task relation mining module and graph group update module to deeply integrate task context and perform global relative relationship transmission. Due to the lack of such data, we construct the first large-scale task-oriented affordance ranking dataset with 25 common tasks, over 50k images and more than 661k objects. Experimental results demonstrate the feasibility of the task context based affordance learning paradigm and the superiority of our model over state-of-the-art models in the fields of saliency ranking and multimodal object detection. The source code and dataset will be made available to the public.
Visual-Geometric Collaborative Guidance for Affordance Learning
Oct 15, 2024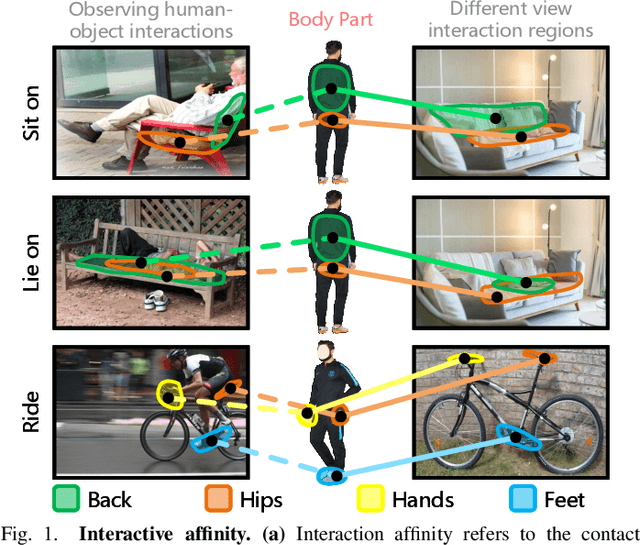
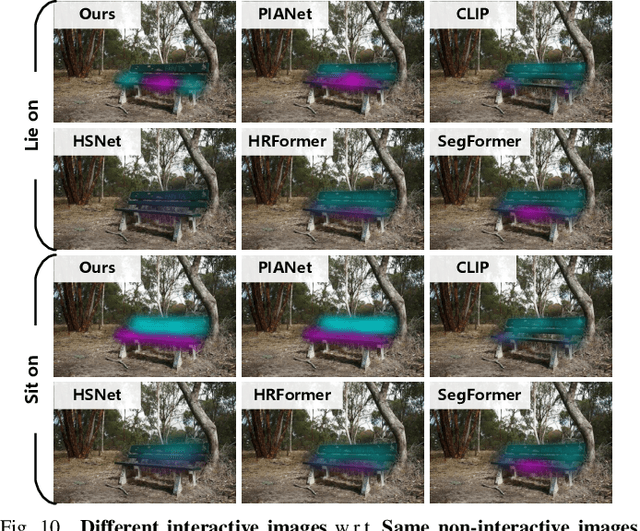

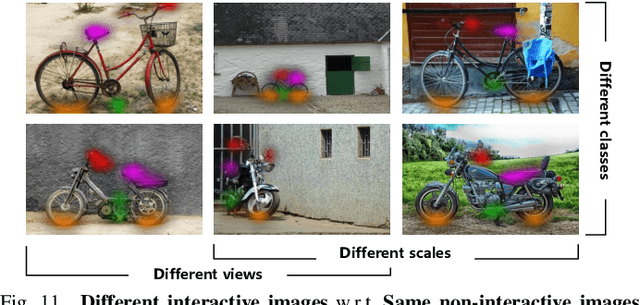
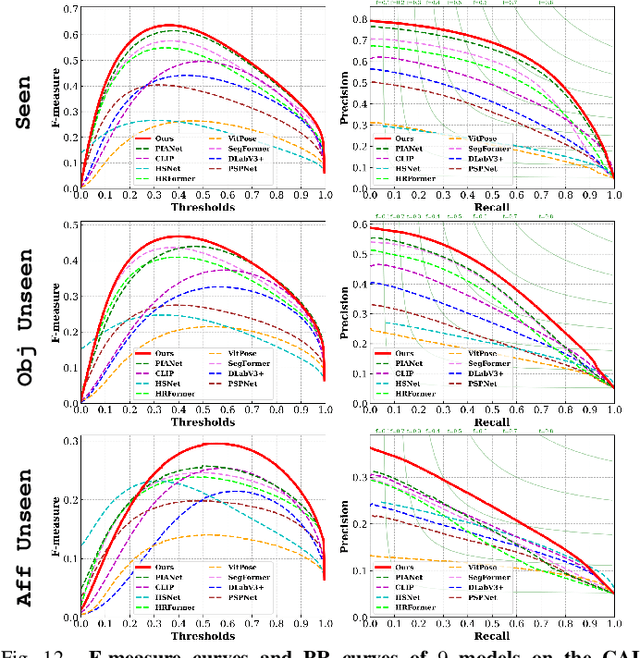
Abstract:Perceiving potential ``action possibilities'' (\ie, affordance) regions of images and learning interactive functionalities of objects from human demonstration is a challenging task due to the diversity of human-object interactions. Prevailing affordance learning algorithms often adopt the label assignment paradigm and presume that there is a unique relationship between functional region and affordance label, yielding poor performance when adapting to unseen environments with large appearance variations. In this paper, we propose to leverage interactive affinity for affordance learning, \ie extracting interactive affinity from human-object interaction and transferring it to non-interactive objects. Interactive affinity, which represents the contacts between different parts of the human body and local regions of the target object, can provide inherent cues of interconnectivity between humans and objects, thereby reducing the ambiguity of the perceived action possibilities. To this end, we propose a visual-geometric collaborative guided affordance learning network that incorporates visual and geometric cues to excavate interactive affinity from human-object interactions jointly. Besides, a contact-driven affordance learning (CAL) dataset is constructed by collecting and labeling over 55,047 images. Experimental results demonstrate that our method outperforms the representative models regarding objective metrics and visual quality. Project: \href{https://github.com/lhc1224/VCR-Net}{github.com/lhc1224/VCR-Net}.
VMAD: Visual-enhanced Multimodal Large Language Model for Zero-Shot Anomaly Detection
Sep 30, 2024Abstract:Zero-shot anomaly detection (ZSAD) recognizes and localizes anomalies in previously unseen objects by establishing feature mapping between textual prompts and inspection images, demonstrating excellent research value in flexible industrial manufacturing. However, existing ZSAD methods are limited by closed-world settings, struggling to unseen defects with predefined prompts. Recently, adapting Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) for Industrial Anomaly Detection (IAD) presents a viable solution. Unlike fixed-prompt methods, MLLMs exhibit a generative paradigm with open-ended text interpretation, enabling more adaptive anomaly analysis. However, this adaption faces inherent challenges as anomalies often manifest in fine-grained regions and exhibit minimal visual discrepancies from normal samples. To address these challenges, we propose a novel framework VMAD (Visual-enhanced MLLM Anomaly Detection) that enhances MLLM with visual-based IAD knowledge and fine-grained perception, simultaneously providing precise detection and comprehensive analysis of anomalies. Specifically, we design a Defect-Sensitive Structure Learning scheme that transfers patch-similarities cues from visual branch to our MLLM for improved anomaly discrimination. Besides, we introduce a novel visual projector, Locality-enhanced Token Compression, which mines multi-level features in local contexts to enhance fine-grained detection. Furthermore, we introduce the Real Industrial Anomaly Detection (RIAD), a comprehensive IAD dataset with detailed anomaly descriptions and analyses, offering a valuable resource for MLLM-based IAD development. Extensive experiments on zero-shot benchmarks, including MVTec-AD, Visa, WFDD, and RIAD datasets, demonstrate our superior performance over state-of-the-art methods. The code and dataset will be available soon.
Grounding 3D Scene Affordance From Egocentric Interactions
Sep 29, 2024
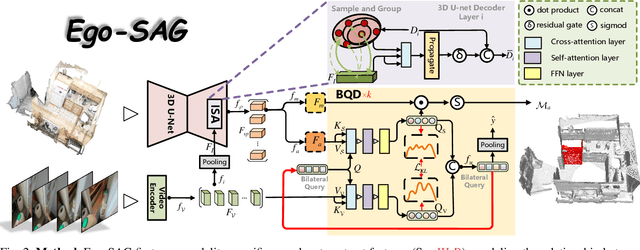
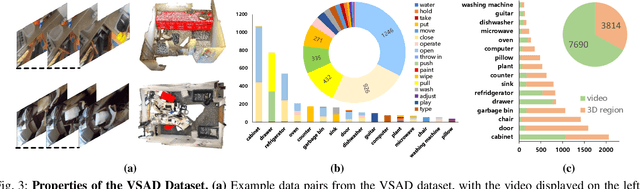

Abstract:Grounding 3D scene affordance aims to locate interactive regions in 3D environments, which is crucial for embodied agents to interact intelligently with their surroundings. Most existing approaches achieve this by mapping semantics to 3D instances based on static geometric structure and visual appearance. This passive strategy limits the agent's ability to actively perceive and engage with the environment, making it reliant on predefined semantic instructions. In contrast, humans develop complex interaction skills by observing and imitating how others interact with their surroundings. To empower the model with such abilities, we introduce a novel task: grounding 3D scene affordance from egocentric interactions, where the goal is to identify the corresponding affordance regions in a 3D scene based on an egocentric video of an interaction. This task faces the challenges of spatial complexity and alignment complexity across multiple sources. To address these challenges, we propose the Egocentric Interaction-driven 3D Scene Affordance Grounding (Ego-SAG) framework, which utilizes interaction intent to guide the model in focusing on interaction-relevant sub-regions and aligns affordance features from different sources through a bidirectional query decoder mechanism. Furthermore, we introduce the Egocentric Video-3D Scene Affordance Dataset (VSAD), covering a wide range of common interaction types and diverse 3D environments to support this task. Extensive experiments on VSAD validate both the feasibility of the proposed task and the effectiveness of our approach.
PEAR: Phrase-Based Hand-Object Interaction Anticipation
Jul 31, 2024Abstract:First-person hand-object interaction anticipation aims to predict the interaction process over a forthcoming period based on current scenes and prompts. This capability is crucial for embodied intelligence and human-robot collaboration. The complete interaction process involves both pre-contact interaction intention (i.e., hand motion trends and interaction hotspots) and post-contact interaction manipulation (i.e., manipulation trajectories and hand poses with contact). Existing research typically anticipates only interaction intention while neglecting manipulation, resulting in incomplete predictions and an increased likelihood of intention errors due to the lack of manipulation constraints. To address this, we propose a novel model, PEAR (Phrase-Based Hand-Object Interaction Anticipation), which jointly anticipates interaction intention and manipulation. To handle uncertainties in the interaction process, we employ a twofold approach. Firstly, we perform cross-alignment of verbs, nouns, and images to reduce the diversity of hand movement patterns and object functional attributes, thereby mitigating intention uncertainty. Secondly, we establish bidirectional constraints between intention and manipulation using dynamic integration and residual connections, ensuring consistency among elements and thus overcoming manipulation uncertainty. To rigorously evaluate the performance of the proposed model, we collect a new task-relevant dataset, EGO-HOIP, with comprehensive annotations. Extensive experimental results demonstrate the superiority of our method.
Bidirectional Progressive Transformer for Interaction Intention Anticipation
May 09, 2024Abstract:Interaction intention anticipation aims to jointly predict future hand trajectories and interaction hotspots. Existing research often treated trajectory forecasting and interaction hotspots prediction as separate tasks or solely considered the impact of trajectories on interaction hotspots, which led to the accumulation of prediction errors over time. However, a deeper inherent connection exists between hand trajectories and interaction hotspots, which allows for continuous mutual correction between them. Building upon this relationship, a novel Bidirectional prOgressive Transformer (BOT), which introduces a Bidirectional Progressive mechanism into the anticipation of interaction intention is established. Initially, BOT maximizes the utilization of spatial information from the last observation frame through the Spatial-Temporal Reconstruction Module, mitigating conflicts arising from changes of view in first-person videos. Subsequently, based on two independent prediction branches, a Bidirectional Progressive Enhancement Module is introduced to mutually improve the prediction of hand trajectories and interaction hotspots over time to minimize error accumulation. Finally, acknowledging the intrinsic randomness in human natural behavior, we employ a Trajectory Stochastic Unit and a C-VAE to introduce appropriate uncertainty to trajectories and interaction hotspots, respectively. Our method achieves state-of-the-art results on three benchmark datasets Epic-Kitchens-100, EGO4D, and EGTEA Gaze+, demonstrating superior in complex scenarios.
Intention-driven Ego-to-Exo Video Generation
Mar 17, 2024



Abstract:Ego-to-exo video generation refers to generating the corresponding exocentric video according to the egocentric video, providing valuable applications in AR/VR and embodied AI. Benefiting from advancements in diffusion model techniques, notable progress has been achieved in video generation. However, existing methods build upon the spatiotemporal consistency assumptions between adjacent frames, which cannot be satisfied in the ego-to-exo scenarios due to drastic changes in views. To this end, this paper proposes an Intention-Driven Ego-to-exo video generation framework (IDE) that leverages action intention consisting of human movement and action description as view-independent representation to guide video generation, preserving the consistency of content and motion. Specifically, the egocentric head trajectory is first estimated through multi-view stereo matching. Then, cross-view feature perception module is introduced to establish correspondences between exo- and ego- views, guiding the trajectory transformation module to infer human full-body movement from the head trajectory. Meanwhile, we present an action description unit that maps the action semantics into the feature space consistent with the exocentric image. Finally, the inferred human movement and high-level action descriptions jointly guide the generation of exocentric motion and interaction content (i.e., corresponding optical flow and occlusion maps) in the backward process of the diffusion model, ultimately warping them into the corresponding exocentric video. We conduct extensive experiments on the relevant dataset with diverse exo-ego video pairs, and our IDE outperforms state-of-the-art models in both subjective and objective assessments, demonstrating its efficacy in ego-to-exo video generation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge