Yuxin Hong
AniME: Adaptive Multi-Agent Planning for Long Animation Generation
Aug 27, 2025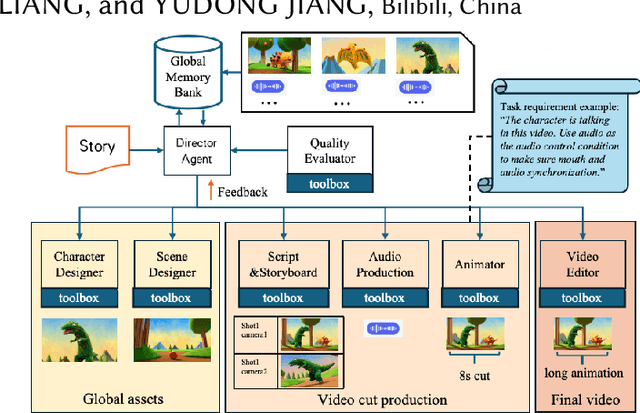
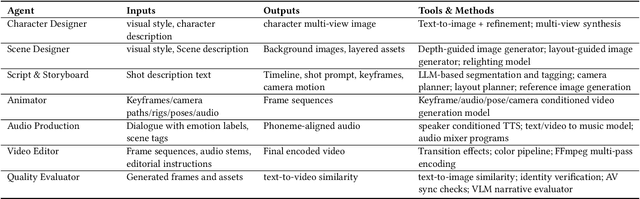

Abstract:We present AniME, a director-oriented multi-agent system for automated long-form anime production, covering the full workflow from a story to the final video. The director agent keeps a global memory for the whole workflow, and coordinates several downstream specialized agents. By integrating customized Model Context Protocol (MCP) with downstream model instruction, the specialized agent adaptively selects control conditions for diverse sub-tasks. AniME produces cinematic animation with consistent characters and synchronized audio visual elements, offering a scalable solution for AI-driven anime creation.
Evolution-aware VAriance (EVA) Coreset Selection for Medical Image Classification
Jun 09, 2024



Abstract:In the medical field, managing high-dimensional massive medical imaging data and performing reliable medical analysis from it is a critical challenge, especially in resource-limited environments such as remote medical facilities and mobile devices. This necessitates effective dataset compression techniques to reduce storage, transmission, and computational cost. However, existing coreset selection methods are primarily designed for natural image datasets, and exhibit doubtful effectiveness when applied to medical image datasets due to challenges such as intra-class variation and inter-class similarity. In this paper, we propose a novel coreset selection strategy termed as Evolution-aware VAriance (EVA), which captures the evolutionary process of model training through a dual-window approach and reflects the fluctuation of sample importance more precisely through variance measurement. Extensive experiments on medical image datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of our strategy over previous SOTA methods, especially at high compression rates. EVA achieves 98.27% accuracy with only 10% training data, compared to 97.20% for the full training set. None of the compared baseline methods can exceed Random at 5% selection rate, while EVA outperforms Random by 5.61%, showcasing its potential for efficient medical image analysis.
The Ninth NTIRE 2024 Efficient Super-Resolution Challenge Report
Apr 16, 2024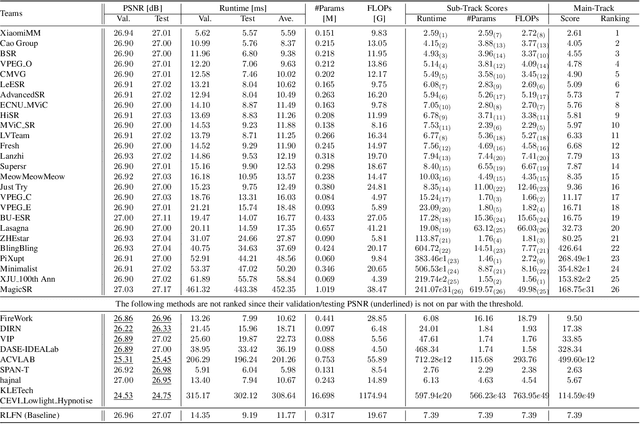
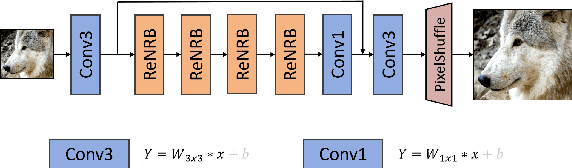
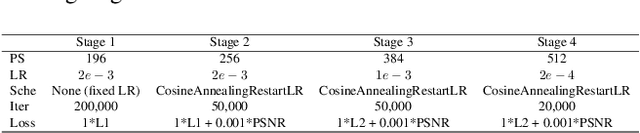
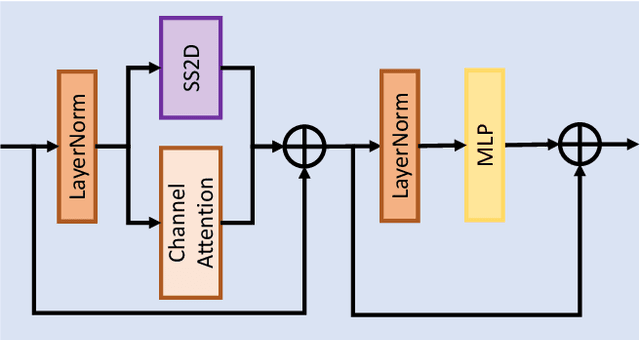
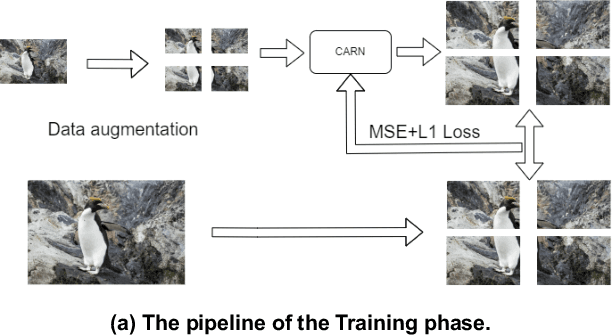
Abstract:This paper provides a comprehensive review of the NTIRE 2024 challenge, focusing on efficient single-image super-resolution (ESR) solutions and their outcomes. The task of this challenge is to super-resolve an input image with a magnification factor of x4 based on pairs of low and corresponding high-resolution images. The primary objective is to develop networks that optimize various aspects such as runtime, parameters, and FLOPs, while still maintaining a peak signal-to-noise ratio (PSNR) of approximately 26.90 dB on the DIV2K_LSDIR_valid dataset and 26.99 dB on the DIV2K_LSDIR_test dataset. In addition, this challenge has 4 tracks including the main track (overall performance), sub-track 1 (runtime), sub-track 2 (FLOPs), and sub-track 3 (parameters). In the main track, all three metrics (ie runtime, FLOPs, and parameter count) were considered. The ranking of the main track is calculated based on a weighted sum-up of the scores of all other sub-tracks. In sub-track 1, the practical runtime performance of the submissions was evaluated, and the corresponding score was used to determine the ranking. In sub-track 2, the number of FLOPs was considered. The score calculated based on the corresponding FLOPs was used to determine the ranking. In sub-track 3, the number of parameters was considered. The score calculated based on the corresponding parameters was used to determine the ranking. RLFN is set as the baseline for efficiency measurement. The challenge had 262 registered participants, and 34 teams made valid submissions. They gauge the state-of-the-art in efficient single-image super-resolution. To facilitate the reproducibility of the challenge and enable other researchers to build upon these findings, the code and the pre-trained model of validated solutions are made publicly available at https://github.com/Amazingren/NTIRE2024_ESR/.
NTIRE 2024 Challenge on Image Super-Resolution ($\times$4): Methods and Results
Apr 15, 2024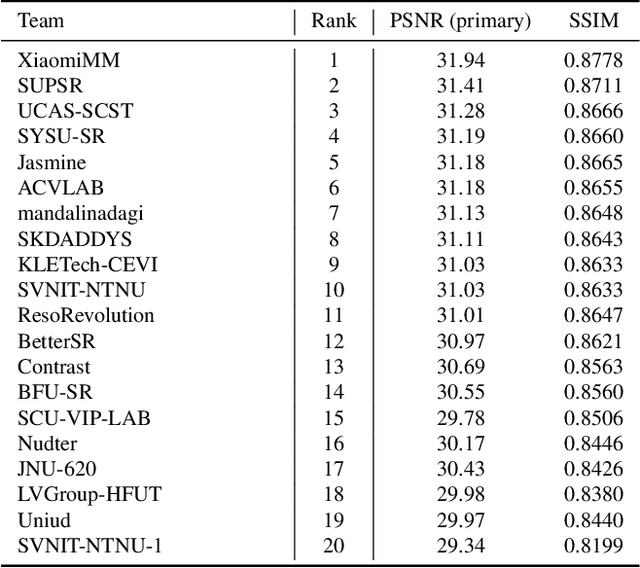
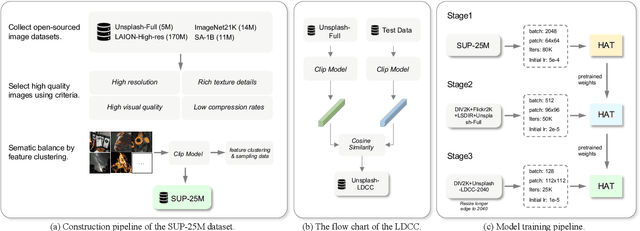
Abstract:This paper reviews the NTIRE 2024 challenge on image super-resolution ($\times$4), highlighting the solutions proposed and the outcomes obtained. The challenge involves generating corresponding high-resolution (HR) images, magnified by a factor of four, from low-resolution (LR) inputs using prior information. The LR images originate from bicubic downsampling degradation. The aim of the challenge is to obtain designs/solutions with the most advanced SR performance, with no constraints on computational resources (e.g., model size and FLOPs) or training data. The track of this challenge assesses performance with the PSNR metric on the DIV2K testing dataset. The competition attracted 199 registrants, with 20 teams submitting valid entries. This collective endeavour not only pushes the boundaries of performance in single-image SR but also offers a comprehensive overview of current trends in this field.
Self-supervised Amodal Video Object Segmentation
Oct 23, 2022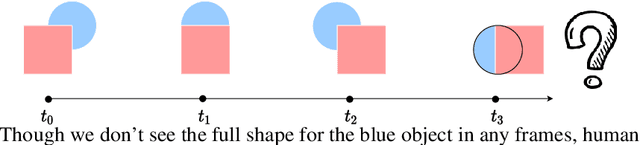
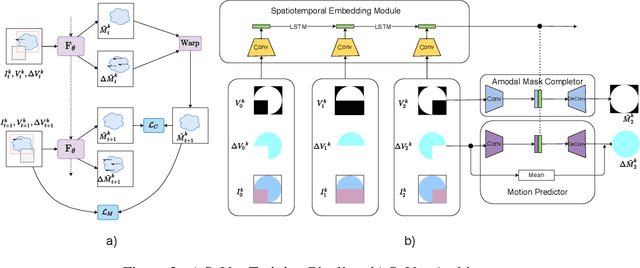
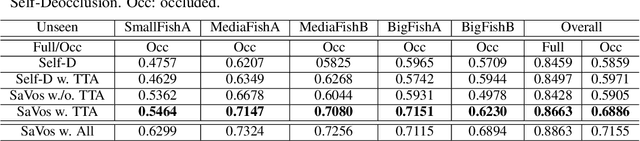
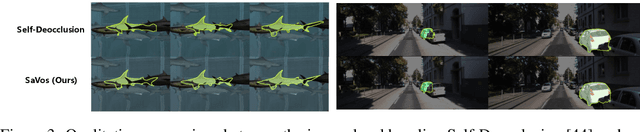
Abstract:Amodal perception requires inferring the full shape of an object that is partially occluded. This task is particularly challenging on two levels: (1) it requires more information than what is contained in the instant retina or imaging sensor, (2) it is difficult to obtain enough well-annotated amodal labels for supervision. To this end, this paper develops a new framework of Self-supervised amodal Video object segmentation (SaVos). Our method efficiently leverages the visual information of video temporal sequences to infer the amodal mask of objects. The key intuition is that the occluded part of an object can be explained away if that part is visible in other frames, possibly deformed as long as the deformation can be reasonably learned. Accordingly, we derive a novel self-supervised learning paradigm that efficiently utilizes the visible object parts as the supervision to guide the training on videos. In addition to learning type prior to complete masks for known types, SaVos also learns the spatiotemporal prior, which is also useful for the amodal task and could generalize to unseen types. The proposed framework achieves the state-of-the-art performance on the synthetic amodal segmentation benchmark FISHBOWL and the real world benchmark KINS-Video-Car. Further, it lends itself well to being transferred to novel distributions using test-time adaptation, outperforming existing models even after the transfer to a new distribution.
QS-Craft: Learning to Quantize, Scrabble and Craft for Conditional Human Motion Animation
Mar 22, 2022



Abstract:This paper studies the task of conditional Human Motion Animation (cHMA). Given a source image and a driving video, the model should animate the new frame sequence, in which the person in the source image should perform a similar motion as the pose sequence from the driving video. Despite the success of Generative Adversarial Network (GANs) methods in image and video synthesis, it is still very challenging to conduct cHMA due to the difficulty in efficiently utilizing the conditional guided information such as images or poses, and generating images of good visual quality. To this end, this paper proposes a novel model of learning to Quantize, Scrabble, and Craft (QS-Craft) for conditional human motion animation. The key novelties come from the newly introduced three key steps: quantize, scrabble and craft. Particularly, our QS-Craft employs transformer in its structure to utilize the attention architectures. The guided information is represented as a pose coordinate sequence extracted from the driving videos. Extensive experiments on human motion datasets validate the efficacy of our model.
The Image Local Autoregressive Transformer
Jun 04, 2021



Abstract:Recently, AutoRegressive (AR) models for the whole image generation empowered by transformers have achieved comparable or even better performance to Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs). Unfortunately, directly applying such AR models to edit/change local image regions, may suffer from the problems of missing global information, slow inference speed, and information leakage of local guidance. To address these limitations, we propose a novel model -- image Local Autoregressive Transformer (iLAT), to better facilitate the locally guided image synthesis. Our iLAT learns the novel local discrete representations, by the newly proposed local autoregressive (LA) transformer of the attention mask and convolution mechanism. Thus iLAT can efficiently synthesize the local image regions by key guidance information. Our iLAT is evaluated on various locally guided image syntheses, such as pose-guided person image synthesis and face editing. Both the quantitative and qualitative results show the efficacy of our model.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge