Zhanwei Zhang
Careful Queries, Credible Results: Teaching RAG Models Advanced Web Search Tools with Reinforcement Learning
Aug 11, 2025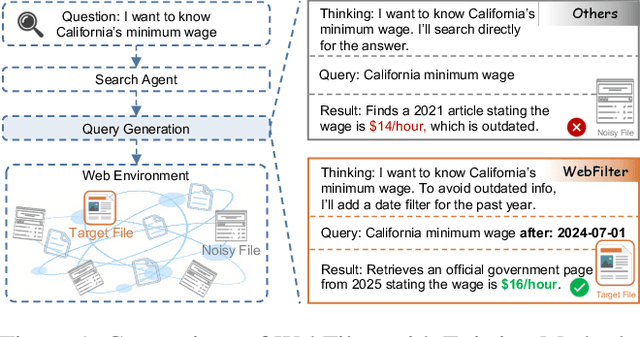
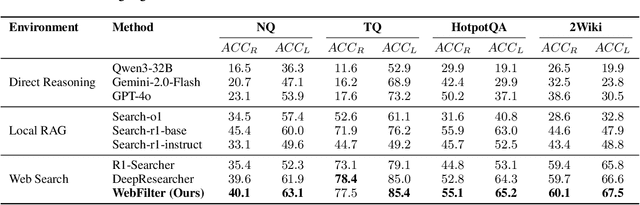
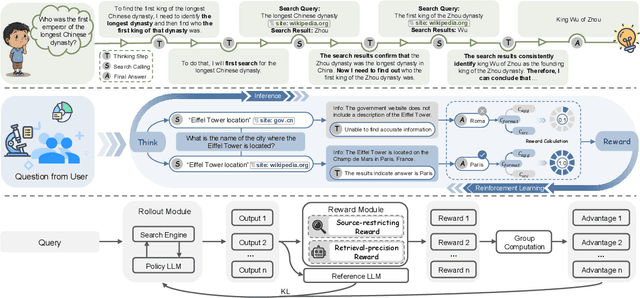
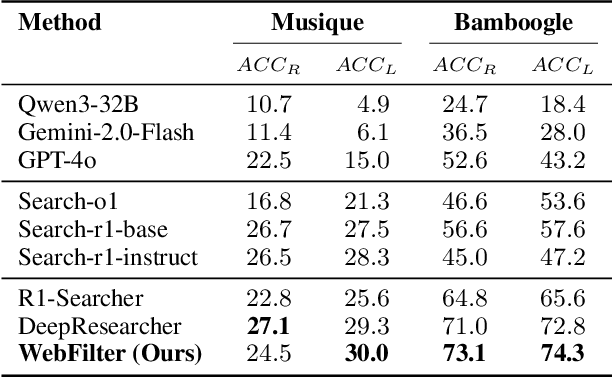
Abstract:Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) enhances large language models (LLMs) by integrating up-to-date external knowledge, yet real-world web environments present unique challenges. These limitations manifest as two key challenges: pervasive misinformation in the web environment, which introduces unreliable or misleading content that can degrade retrieval accuracy, and the underutilization of web tools, which, if effectively employed, could enhance query precision and help mitigate this noise, ultimately improving the retrieval results in RAG systems. To address these issues, we propose WebFilter, a novel RAG framework that generates source-restricted queries and filters out unreliable content. This approach combines a retrieval filtering mechanism with a behavior- and outcome-driven reward strategy, optimizing both query formulation and retrieval outcomes. Extensive experiments demonstrate that WebFilter improves answer quality and retrieval precision, outperforming existing RAG methods on both in-domain and out-of-domain benchmarks.
Efficient Reasoning Through Suppression of Self-Affirmation Reflections in Large Reasoning Models
Jun 14, 2025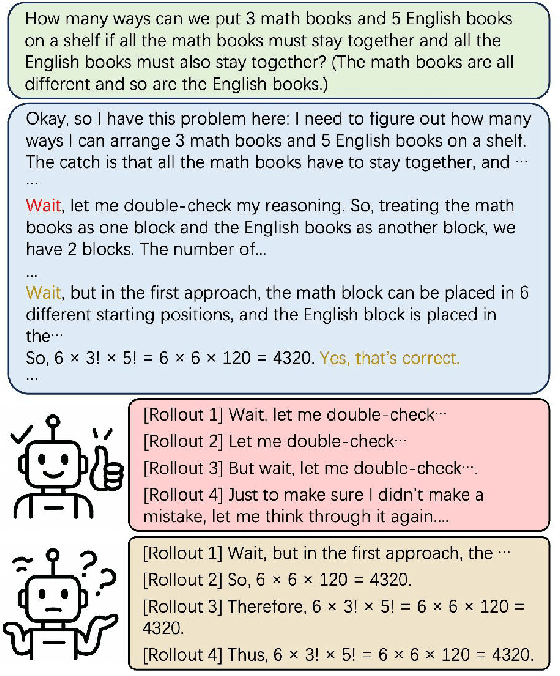
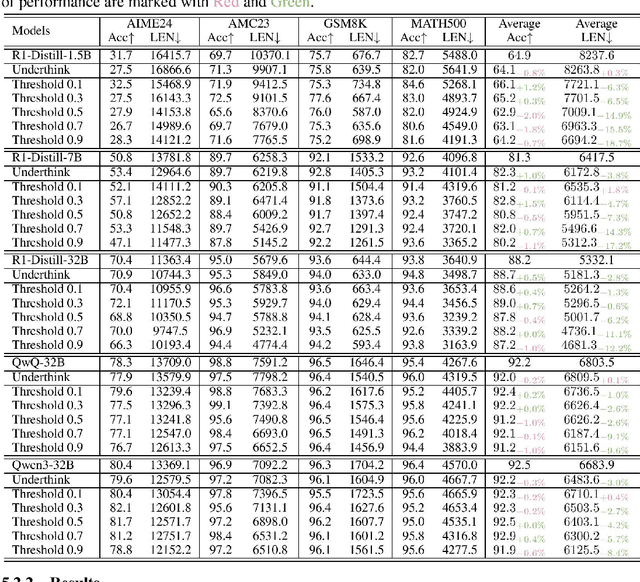
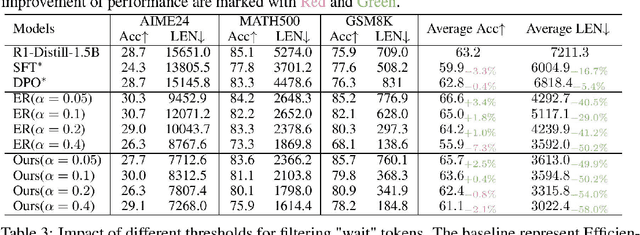
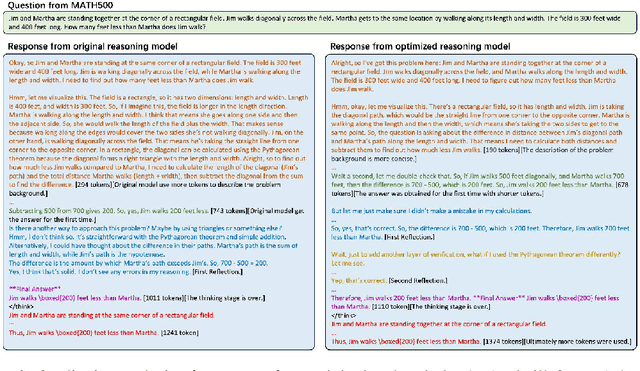
Abstract:While recent advances in large reasoning models have demonstrated remarkable performance, efficient reasoning remains critical due to the rapid growth of output length. Existing optimization approaches highlights a tendency toward "overthinking", yet lack fine-grained analysis. In this work, we focus on Self-Affirmation Reflections: redundant reflective steps that affirm prior content and often occurs after the already correct reasoning steps. Observations of both original and optimized reasoning models reveal pervasive self-affirmation reflections. Notably, these reflections sometimes lead to longer outputs in optimized models than their original counterparts. Through detailed analysis, we uncover an intriguing pattern: compared to other reflections, the leading words (i.e., the first word of sentences) in self-affirmation reflections exhibit a distinct probability bias. Motivated by this insight, we can locate self-affirmation reflections and conduct a train-free experiment demonstrating that suppressing self-affirmation reflections reduces output length without degrading accuracy across multiple models (R1-Distill-Models, QwQ-32B, and Qwen3-32B). Furthermore, we also improve current train-based method by explicitly suppressing such reflections. In our experiments, we achieve length compression of 18.7\% in train-free settings and 50.2\% in train-based settings for R1-Distill-Qwen-1.5B. Moreover, our improvements are simple yet practical and can be directly applied to existing inference frameworks, such as vLLM. We believe that our findings will provide community insights for achieving more precise length compression and step-level efficient reasoning.
GeoCAD: Local Geometry-Controllable CAD Generation
Jun 12, 2025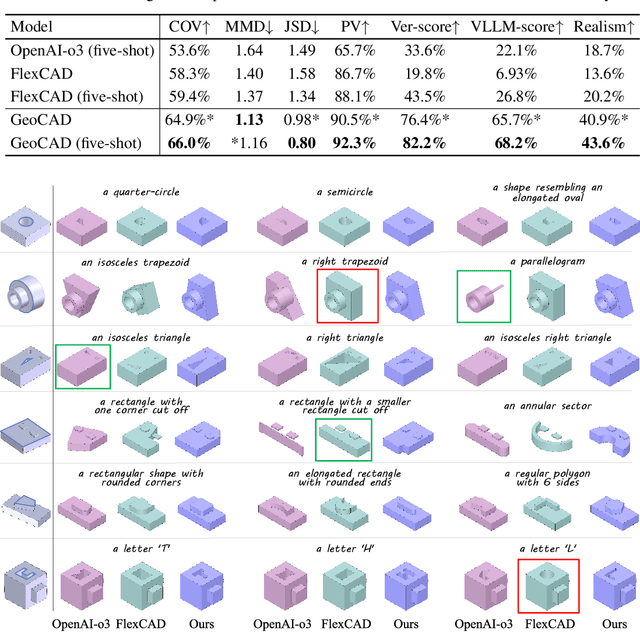
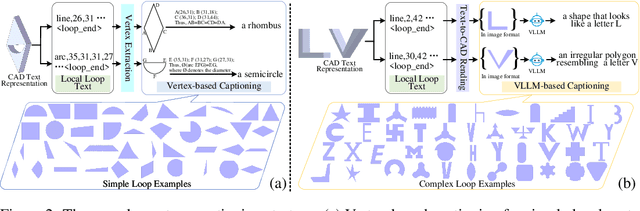
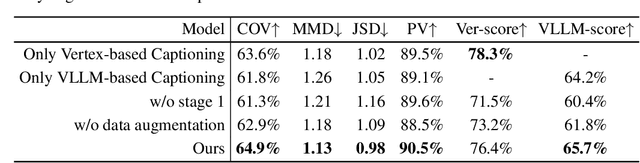

Abstract:Local geometry-controllable computer-aided design (CAD) generation aims to modify local parts of CAD models automatically, enhancing design efficiency. It also ensures that the shapes of newly generated local parts follow user-specific geometric instructions (e.g., an isosceles right triangle or a rectangle with one corner cut off). However, existing methods encounter challenges in achieving this goal. Specifically, they either lack the ability to follow textual instructions or are unable to focus on the local parts. To address this limitation, we introduce GeoCAD, a user-friendly and local geometry-controllable CAD generation method. Specifically, we first propose a complementary captioning strategy to generate geometric instructions for local parts. This strategy involves vertex-based and VLLM-based captioning for systematically annotating simple and complex parts, respectively. In this way, we caption $\sim$221k different local parts in total. In the training stage, given a CAD model, we randomly mask a local part. Then, using its geometric instruction and the remaining parts as input, we prompt large language models (LLMs) to predict the masked part. During inference, users can specify any local part for modification while adhering to a variety of predefined geometric instructions. Extensive experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of GeoCAD in generation quality, validity and text-to-CAD consistency. Code will be available at https://github.com/Zhanwei-Z/GeoCAD.
G2LTraj: A Global-to-Local Generation Approach for Trajectory Prediction
Apr 30, 2024



Abstract:Predicting future trajectories of traffic agents accurately holds substantial importance in various applications such as autonomous driving. Previous methods commonly infer all future steps of an agent either recursively or simultaneously. However, the recursive strategy suffers from the accumulated error, while the simultaneous strategy overlooks the constraints among future steps, resulting in kinematically infeasible predictions. To address these issues, in this paper, we propose G2LTraj, a plug-and-play global-to-local generation approach for trajectory prediction. Specifically, we generate a series of global key steps that uniformly cover the entire future time range. Subsequently, the local intermediate steps between the adjacent key steps are recursively filled in. In this way, we prevent the accumulated error from propagating beyond the adjacent key steps. Moreover, to boost the kinematical feasibility, we not only introduce the spatial constraints among key steps but also strengthen the temporal constraints among the intermediate steps. Finally, to ensure the optimal granularity of key steps, we design a selectable granularity strategy that caters to each predicted trajectory. Our G2LTraj significantly improves the performance of seven existing trajectory predictors across the ETH, UCY and nuScenes datasets. Experimental results demonstrate its effectiveness. Code will be available at https://github.com/Zhanwei-Z/G2LTraj.
Pseudo Label Refinery for Unsupervised Domain Adaptation on Cross-dataset 3D Object Detection
Apr 30, 2024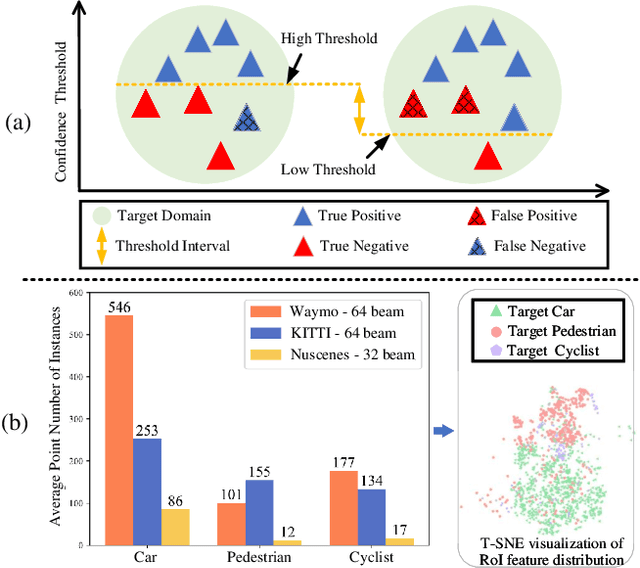
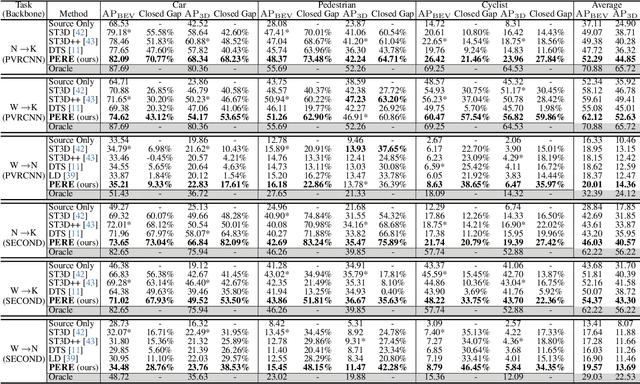
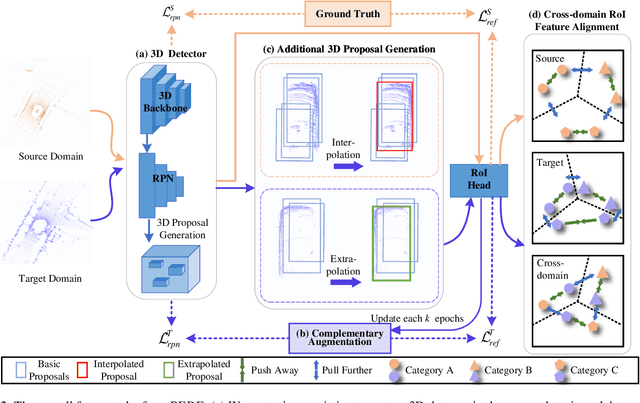
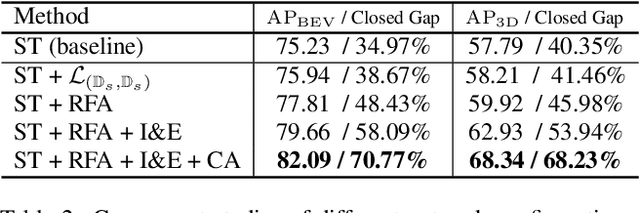
Abstract:Recent self-training techniques have shown notable improvements in unsupervised domain adaptation for 3D object detection (3D UDA). These techniques typically select pseudo labels, i.e., 3D boxes, to supervise models for the target domain. However, this selection process inevitably introduces unreliable 3D boxes, in which 3D points cannot be definitively assigned as foreground or background. Previous techniques mitigate this by reweighting these boxes as pseudo labels, but these boxes can still poison the training process. To resolve this problem, in this paper, we propose a novel pseudo label refinery framework. Specifically, in the selection process, to improve the reliability of pseudo boxes, we propose a complementary augmentation strategy. This strategy involves either removing all points within an unreliable box or replacing it with a high-confidence box. Moreover, the point numbers of instances in high-beam datasets are considerably higher than those in low-beam datasets, also degrading the quality of pseudo labels during the training process. We alleviate this issue by generating additional proposals and aligning RoI features across different domains. Experimental results demonstrate that our method effectively enhances the quality of pseudo labels and consistently surpasses the state-of-the-art methods on six autonomous driving benchmarks. Code will be available at https://github.com/Zhanwei-Z/PERE.
UniHDA: Towards Universal Hybrid Domain Adaptation of Image Generators
Jan 23, 2024

Abstract:Generative domain adaptation has achieved remarkable progress, enabling us to adapt a pre-trained generator to a new target domain. However, existing methods simply adapt the generator to a single target domain and are limited to a single modality, either text-driven or image-driven. Moreover, they are prone to overfitting domain-specific attributes, which inevitably compromises cross-domain consistency. In this paper, we propose UniHDA, a unified and versatile framework for generative hybrid domain adaptation with multi-modal references from multiple domains. We use CLIP encoder to project multi-modal references into a unified embedding space and then linear interpolate the direction vectors from multiple target domains to achieve hybrid domain adaptation. To ensure the cross-domain consistency, we propose a novel cross-domain spatial structure (CSS) loss that maintains detailed spatial structure information between source and target generator. Experiments show that the adapted generator can synthesise realistic images with various attribute compositions. Additionally, our framework is versatile to multiple generators, \eg, StyleGAN2 and Diffusion Models.
A Duet Recommendation Algorithm Based on Jointly Local and Global Representation Learning
Dec 03, 2020



Abstract:Knowledge graph (KG), as the side information, is widely utilized to learn the semantic representations of item/user for recommendation system. The traditional recommendation algorithms usually just depend on user-item interactions, but ignore the inherent web information describing the item/user, which could be formulated by the knowledge graph embedding (KGE) methods to significantly improve applications' performance. In this paper, we propose a knowledge-aware-based recommendation algorithm to capture the local and global representation learning from heterogeneous information. Specifically, the local model and global model can naturally depict the inner patterns in the content-based heterogeneous information and interactive behaviors among the users and items. Based on the method that local and global representations are learned jointly by graph convolutional networks with attention mechanism, the final recommendation probability is calculated by a fully-connected neural network. Extensive experiments are conducted on two real-world datasets to verify the proposed algorithm's validation. The evaluation results indicate that the proposed algorithm surpasses state-of-arts by $10.0\%$, $5.1\%$, $2.5\%$ and $1.8\%$ in metrics of MAE, RMSE, AUC and F1-score at least, respectively. The significant improvements reveal the capacity of our proposal to recommend user/item effectively.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge