Kaiyuan Liu
MCGA: A Multi-task Classical Chinese Literary Genre Audio Corpus
Jan 14, 2026Abstract:With the rapid advancement of Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs), their potential has garnered significant attention in Chinese Classical Studies (CCS). While existing research has primarily focused on text and visual modalities, the audio corpus within this domain remains largely underexplored. To bridge this gap, we propose the Multi-task Classical Chinese Literary Genre Audio Corpus (MCGA). It encompasses a diverse range of literary genres across six tasks: Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR), Speech-to-Text Translation (S2TT), Speech Emotion Captioning (SEC), Spoken Question Answering (SQA), Speech Understanding (SU), and Speech Reasoning (SR). Through the evaluation of ten MLLMs, our experimental results demonstrate that current models still face substantial challenges when processed on the MCGA test set. Furthermore, we introduce an evaluation metric for SEC and a metric to measure the consistency between the speech and text capabilities of MLLMs. We release MCGA and our code to the public to facilitate the development of MLLMs with more robust multidimensional audio capabilities in CCS. MCGA Corpus: https://github.com/yxduir/MCGA
Distribution-Aligned Sequence Distillation for Superior Long-CoT Reasoning
Jan 14, 2026Abstract:In this report, we introduce DASD-4B-Thinking, a lightweight yet highly capable, fully open-source reasoning model. It achieves SOTA performance among open-source models of comparable scale across challenging benchmarks in mathematics, scientific reasoning, and code generation -- even outperforming several larger models. We begin by critically reexamining a widely adopted distillation paradigm in the community: SFT on teacher-generated responses, also known as sequence-level distillation. Although a series of recent works following this scheme have demonstrated remarkable efficiency and strong empirical performance, they are primarily grounded in the SFT perspective. Consequently, these approaches focus predominantly on designing heuristic rules for SFT data filtering, while largely overlooking the core principle of distillation itself -- enabling the student model to learn the teacher's full output distribution so as to inherit its generalization capability. Specifically, we identify three critical limitations in current practice: i) Inadequate representation of the teacher's sequence-level distribution; ii) Misalignment between the teacher's output distribution and the student's learning capacity; and iii) Exposure bias arising from teacher-forced training versus autoregressive inference. In summary, these shortcomings reflect a systemic absence of explicit teacher-student interaction throughout the distillation process, leaving the essence of distillation underexploited. To address these issues, we propose several methodological innovations that collectively form an enhanced sequence-level distillation training pipeline. Remarkably, DASD-4B-Thinking obtains competitive results using only 448K training samples -- an order of magnitude fewer than those employed by most existing open-source efforts. To support community research, we publicly release our models and the training dataset.
Where Did This Sentence Come From? Tracing Provenance in LLM Reasoning Distillation
Dec 24, 2025Abstract:Reasoning distillation has attracted increasing attention. It typically leverages a large teacher model to generate reasoning paths, which are then used to fine-tune a student model so that it mimics the teacher's behavior in training contexts. However, previous approaches have lacked a detailed analysis of the origins of the distilled model's capabilities. It remains unclear whether the student can maintain consistent behaviors with the teacher in novel test-time contexts, or whether it regresses to its original output patterns, raising concerns about the generalization of distillation models. To analyse this question, we introduce a cross-model Reasoning Distillation Provenance Tracing framework. For each action (e.g., a sentence) produced by the distilled model, we obtain the predictive probabilities assigned by the teacher, the original student, and the distilled model under the same context. By comparing these probabilities, we classify each action into different categories. By systematically disentangling the provenance of each action, we experimentally demonstrate that, in test-time contexts, the distilled model can indeed generate teacher-originated actions, which correlate with and plausibly explain observed performance on distilled model. Building on this analysis, we further propose a teacher-guided data selection method. Unlike prior approach that rely on heuristics, our method directly compares teacher-student divergences on the training data, providing a principled selection criterion. We validate the effectiveness of our approach across multiple representative teacher models and diverse student models. The results highlight the utility of our provenance-tracing framework and underscore its promise for reasoning distillation. We hope to share Reasoning Distillation Provenance Tracing and our insights into reasoning distillation with the community.
FrontierCS: Evolving Challenges for Evolving Intelligence
Dec 17, 2025



Abstract:We introduce FrontierCS, a benchmark of 156 open-ended problems across diverse areas of computer science, designed and reviewed by experts, including CS PhDs and top-tier competitive programming participants and problem setters. Unlike existing benchmarks that focus on tasks with known optimal solutions, FrontierCS targets problems where the optimal solution is unknown, but the quality of a solution can be objectively evaluated. Models solve these tasks by implementing executable programs rather than outputting a direct answer. FrontierCS includes algorithmic problems, which are often NP-hard variants of competitive programming problems with objective partial scoring, and research problems with the same property. For each problem we provide an expert reference solution and an automatic evaluator. Combining open-ended design, measurable progress, and expert curation, FrontierCS provides a benchmark at the frontier of computer-science difficulty. Empirically, we find that frontier reasoning models still lag far behind human experts on both the algorithmic and research tracks, that increasing reasoning budgets alone does not close this gap, and that models often over-optimize for generating merely workable code instead of discovering high-quality algorithms and system designs.
CCFQA: A Benchmark for Cross-Lingual and Cross-Modal Speech and Text Factuality Evaluation
Aug 10, 2025Abstract:As Large Language Models (LLMs) are increasingly popularized in the multilingual world, ensuring hallucination-free factuality becomes markedly crucial. However, existing benchmarks for evaluating the reliability of Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) predominantly focus on textual or visual modalities with a primary emphasis on English, which creates a gap in evaluation when processing multilingual input, especially in speech. To bridge this gap, we propose a novel \textbf{C}ross-lingual and \textbf{C}ross-modal \textbf{F}actuality benchmark (\textbf{CCFQA}). Specifically, the CCFQA benchmark contains parallel speech-text factual questions across 8 languages, designed to systematically evaluate MLLMs' cross-lingual and cross-modal factuality capabilities. Our experimental results demonstrate that current MLLMs still face substantial challenges on the CCFQA benchmark. Furthermore, we propose a few-shot transfer learning strategy that effectively transfers the Question Answering (QA) capabilities of LLMs in English to multilingual Spoken Question Answering (SQA) tasks, achieving competitive performance with GPT-4o-mini-Audio using just 5-shot training. We release CCFQA as a foundational research resource to promote the development of MLLMs with more robust and reliable speech understanding capabilities. Our code and dataset are available at https://github.com/yxduir/ccfqa.
Efficient Reasoning Through Suppression of Self-Affirmation Reflections in Large Reasoning Models
Jun 14, 2025
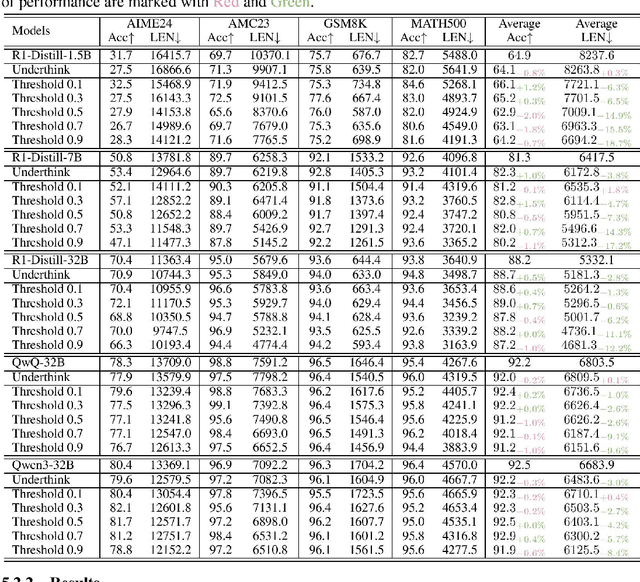
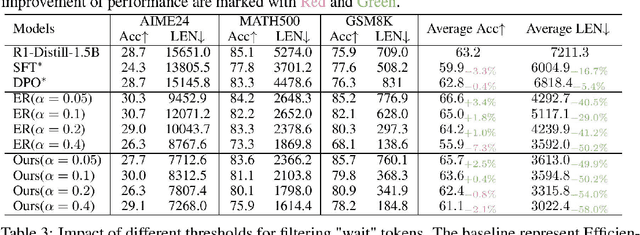
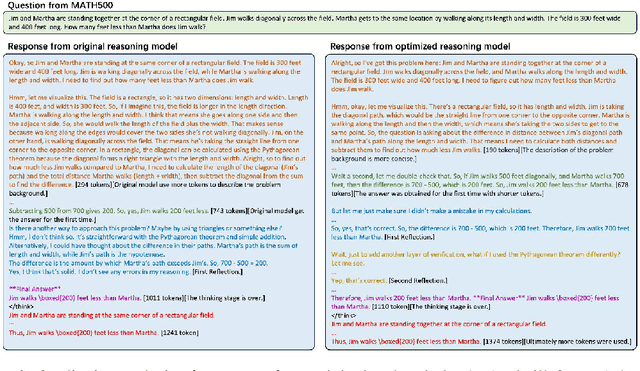
Abstract:While recent advances in large reasoning models have demonstrated remarkable performance, efficient reasoning remains critical due to the rapid growth of output length. Existing optimization approaches highlights a tendency toward "overthinking", yet lack fine-grained analysis. In this work, we focus on Self-Affirmation Reflections: redundant reflective steps that affirm prior content and often occurs after the already correct reasoning steps. Observations of both original and optimized reasoning models reveal pervasive self-affirmation reflections. Notably, these reflections sometimes lead to longer outputs in optimized models than their original counterparts. Through detailed analysis, we uncover an intriguing pattern: compared to other reflections, the leading words (i.e., the first word of sentences) in self-affirmation reflections exhibit a distinct probability bias. Motivated by this insight, we can locate self-affirmation reflections and conduct a train-free experiment demonstrating that suppressing self-affirmation reflections reduces output length without degrading accuracy across multiple models (R1-Distill-Models, QwQ-32B, and Qwen3-32B). Furthermore, we also improve current train-based method by explicitly suppressing such reflections. In our experiments, we achieve length compression of 18.7\% in train-free settings and 50.2\% in train-based settings for R1-Distill-Qwen-1.5B. Moreover, our improvements are simple yet practical and can be directly applied to existing inference frameworks, such as vLLM. We believe that our findings will provide community insights for achieving more precise length compression and step-level efficient reasoning.
LiveCodeBench Pro: How Do Olympiad Medalists Judge LLMs in Competitive Programming?
Jun 13, 2025Abstract:Recent reports claim that large language models (LLMs) now outperform elite humans in competitive programming. Drawing on knowledge from a group of medalists in international algorithmic contests, we revisit this claim, examining how LLMs differ from human experts and where limitations still remain. We introduce LiveCodeBench Pro, a benchmark composed of problems from Codeforces, ICPC, and IOI that are continuously updated to reduce the likelihood of data contamination. A team of Olympiad medalists annotates every problem for algorithmic categories and conducts a line-by-line analysis of failed model-generated submissions. Using this new data and benchmark, we find that frontier models still have significant limitations: without external tools, the best model achieves only 53% pass@1 on medium-difficulty problems and 0% on hard problems, domains where expert humans still excel. We also find that LLMs succeed at implementation-heavy problems but struggle with nuanced algorithmic reasoning and complex case analysis, often generating confidently incorrect justifications. High performance appears largely driven by implementation precision and tool augmentation, not superior reasoning. LiveCodeBench Pro thus highlights the significant gap to human grandmaster levels, while offering fine-grained diagnostics to steer future improvements in code-centric LLM reasoning.
GeoCAD: Local Geometry-Controllable CAD Generation
Jun 12, 2025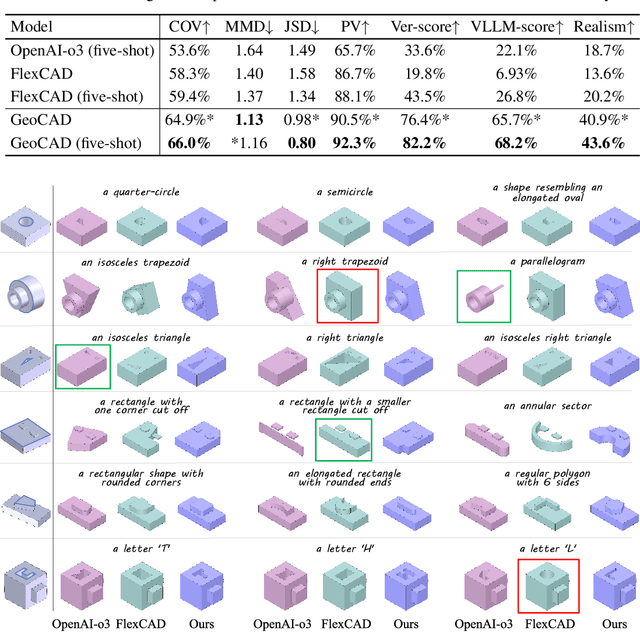
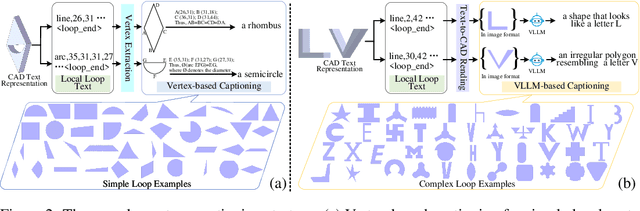
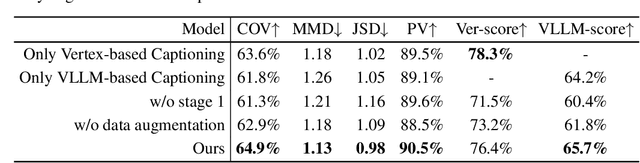

Abstract:Local geometry-controllable computer-aided design (CAD) generation aims to modify local parts of CAD models automatically, enhancing design efficiency. It also ensures that the shapes of newly generated local parts follow user-specific geometric instructions (e.g., an isosceles right triangle or a rectangle with one corner cut off). However, existing methods encounter challenges in achieving this goal. Specifically, they either lack the ability to follow textual instructions or are unable to focus on the local parts. To address this limitation, we introduce GeoCAD, a user-friendly and local geometry-controllable CAD generation method. Specifically, we first propose a complementary captioning strategy to generate geometric instructions for local parts. This strategy involves vertex-based and VLLM-based captioning for systematically annotating simple and complex parts, respectively. In this way, we caption $\sim$221k different local parts in total. In the training stage, given a CAD model, we randomly mask a local part. Then, using its geometric instruction and the remaining parts as input, we prompt large language models (LLMs) to predict the masked part. During inference, users can specify any local part for modification while adhering to a variety of predefined geometric instructions. Extensive experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of GeoCAD in generation quality, validity and text-to-CAD consistency. Code will be available at https://github.com/Zhanwei-Z/GeoCAD.
ProjectEval: A Benchmark for Programming Agents Automated Evaluation on Project-Level Code Generation
Mar 10, 2025



Abstract:Recently, LLM agents have made rapid progress in improving their programming capabilities. However, existing benchmarks lack the ability to automatically evaluate from users' perspective, and also lack the explainability of the results of LLM agents' code generation capabilities. Thus, we introduce ProjectEval, a new benchmark for LLM agents project-level code generation's automated evaluation by simulating user interaction. ProjectEval is constructed by LLM with human reviewing. It has three different level inputs of natural languages or code skeletons. ProjectEval can evaluate the generated projects by user interaction simulation for execution, and by code similarity through existing objective indicators. Through ProjectEval, we find that systematic engineering project code, overall understanding of the project and comprehensive analysis capability are the keys for LLM agents to achieve practical projects. Our findings and benchmark provide valuable insights for developing more effective programming agents that can be deployed in future real-world production.
Moyun: A Diffusion-Based Model for Style-Specific Chinese Calligraphy Generation
Oct 10, 2024



Abstract:Although Chinese calligraphy generation has achieved style transfer, generating calligraphy by specifying the calligrapher, font, and character style remains challenging. To address this, we propose a new Chinese calligraphy generation model 'Moyun' , which replaces the Unet in the Diffusion model with Vision Mamba and introduces the TripleLabel control mechanism to achieve controllable calligraphy generation. The model was tested on our large-scale dataset 'Mobao' of over 1.9 million images, and the results demonstrate that 'Moyun' can effectively control the generation process and produce calligraphy in the specified style. Even for calligraphy the calligrapher has not written, 'Moyun' can generate calligraphy that matches the style of the calligrapher.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge