Hengyu Zhang
RSMA-Assited and Transceiver-Coordinated ICI Management for MIMO-OFDM System
Dec 19, 2025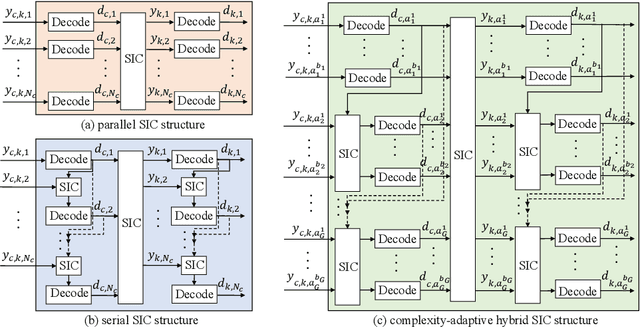
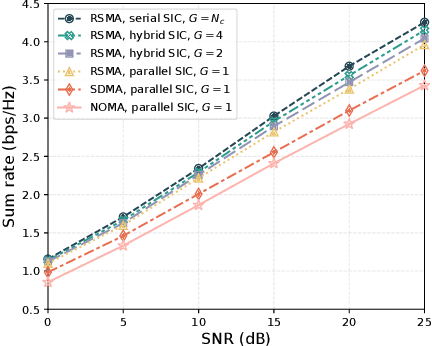
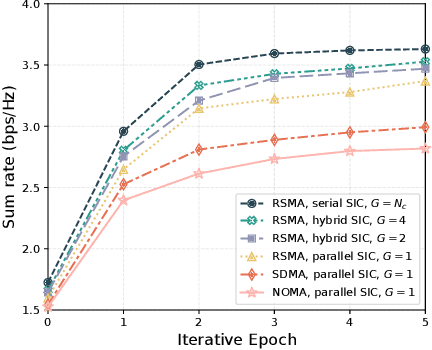
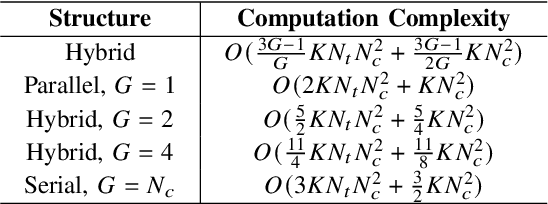
Abstract:High-mobility scenarios are becoming increasingly critical in next-generation communication systems. While multiple-input multiple-output orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (MIMO-OFDM) stands as a prominent technology, its performance in such scenarios is fundamentally limited by Doppler-induced inter-carrier interference (ICI). Rate splitting multiple access (RSMA), recognized as a key multiple access technique for future communications, demonstrates superior interference management capabilities that we leverage to address this challenge. In specific, we propose a novel RSMA-assisted and transceiver-coordinated transmission scheme for ICI management in MIMO-OFDM system: (1) At the receiver side, we develop a hybrid successive interference cancellation (SIC) architecture with dynamic subcarrier clustering, which enables parallel intra-cluster and serial inter-cluster processing to balance complexity and performance. (2) At the transmitter~side, we design a matched hybrid precoding through formulated sum-rate maximization, solved via our proposed augmented boundary-compressed particle swarm optimization (ABC-PSO) algorithm for analog phase optimization and weighted minimum mean-square error (WMMSE)-based digital precoding iteration. Simulation results show that our scheme brings effective ICI suppression and enhanced system capacity with controlled complexity.
From User Interface to Agent Interface: Efficiency Optimization of UI Representations for LLM Agents
Dec 15, 2025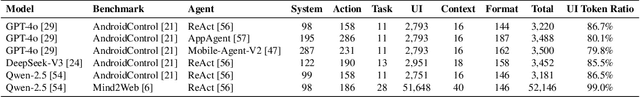
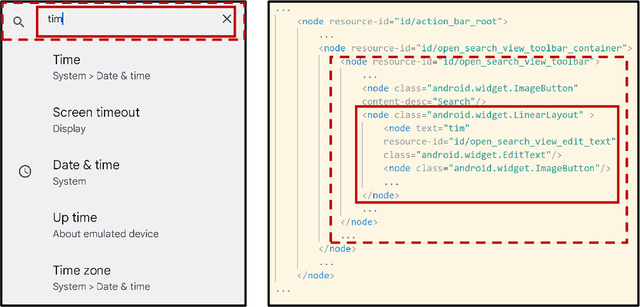
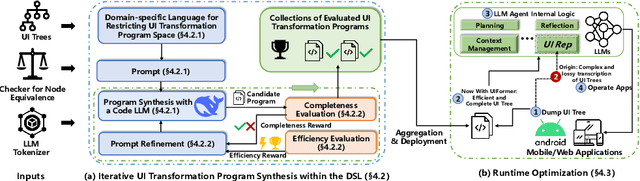
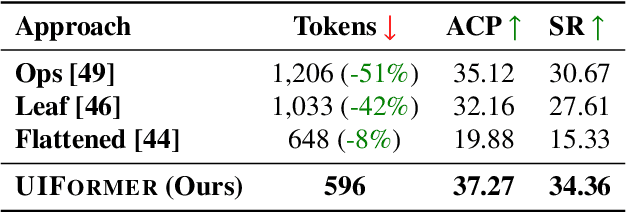
Abstract:While Large Language Model (LLM) agents show great potential for automated UI navigation such as automated UI testing and AI assistants, their efficiency has been largely overlooked. Our motivating study reveals that inefficient UI representation creates a critical performance bottleneck. However, UI representation optimization, formulated as the task of automatically generating programs that transform UI representations, faces two unique challenges. First, the lack of Boolean oracles, which traditional program synthesis uses to decisively validate semantic correctness, poses a fundamental challenge to co-optimization of token efficiency and completeness. Second, the need to process large, complex UI trees as input while generating long, compositional transformation programs, making the search space vast and error-prone. Toward addressing the preceding limitations, we present UIFormer, the first automated optimization framework that synthesizes UI transformation programs by conducting constraint-based optimization with structured decomposition of the complex synthesis task. First, UIFormer restricts the program space using a domain-specific language (DSL) that captures UI-specific operations. Second, UIFormer conducts LLM-based iterative refinement with correctness and efficiency rewards, providing guidance for achieving the efficiency-completeness co-optimization. UIFormer operates as a lightweight plugin that applies transformation programs for seamless integration with existing LLM agents, requiring minimal modifications to their core logic. Evaluations across three UI navigation benchmarks spanning Android and Web platforms with five LLMs demonstrate that UIFormer achieves 48.7% to 55.8% token reduction with minimal runtime overhead while maintaining or improving agent performance. Real-world industry deployment at WeChat further validates the practical impact of UIFormer.
Beamforming-Codebook-Aware Channel Knowledge Map Construction for Multi-Antenna Systems
May 22, 2025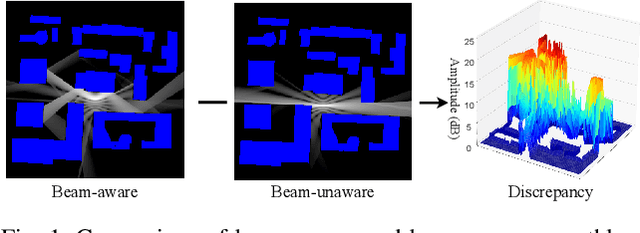
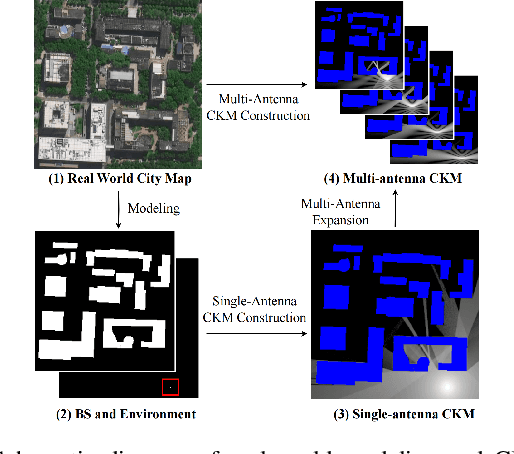
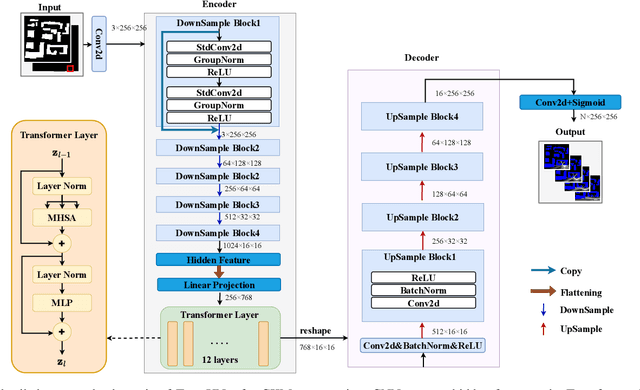
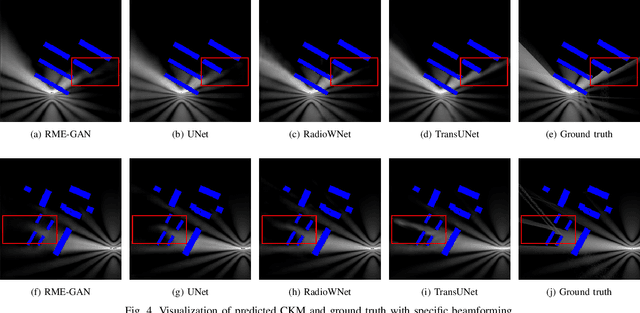
Abstract:Channel knowledge map (CKM) has emerged as a crucial technology for next-generation communication, enabling the construction of high-fidelity mappings between spatial environments and channel parameters via electromagnetic information analysis. Traditional CKM construction methods like ray tracing are computationally intensive. Recent studies utilizing neural networks (NNs) have achieved efficient CKM generation with reduced computational complexity and real-time processing capabilities. Nevertheless, existing research predominantly focuses on single-antenna systems, failing to address the beamforming requirements inherent to MIMO configurations. Given that appropriate precoding vector selection in MIMO systems can substantially enhance user communication rates, this paper presents a TransUNet-based framework for constructing CKM, which effectively incorporates discrete Fourier transform (DFT) precoding vectors. The proposed architecture combines a UNet backbone for multiscale feature extraction with a Transformer module to capture global dependencies among encoded linear vectors. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed method outperforms state-of-the-art (SOTA) deep learning (DL) approaches, yielding a 17\% improvement in RMSE compared to RadioWNet. The code is publicly accessible at https://github.com/github-whh/TransUNet.
Adaptive Coordinators and Prompts on Heterogeneous Graphs for Cross-Domain Recommendations
Oct 15, 2024


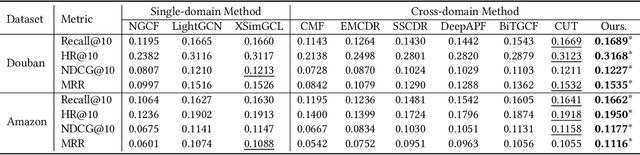
Abstract:In the online digital world, users frequently engage with diverse items across multiple domains (e.g., e-commerce platforms, streaming services, and social media networks), forming complex heterogeneous interaction graphs. Leveraging this multi-domain information can undoubtedly enhance the performance of recommendation systems by providing more comprehensive user insights and alleviating data sparsity in individual domains. However, integrating multi-domain knowledge for the cross-domain recommendation is very hard due to inherent disparities in user behavior and item characteristics and the risk of negative transfer, where irrelevant or conflicting information from the source domains adversely impacts the target domain's performance. To address these challenges, we offer HAGO, a novel framework with $\textbf{H}$eterogeneous $\textbf{A}$daptive $\textbf{G}$raph co$\textbf{O}$rdinators, which dynamically integrate multi-domain graphs into a cohesive structure by adaptively adjusting the connections between coordinators and multi-domain graph nodes, thereby enhancing beneficial inter-domain interactions while mitigating negative transfer effects. Additionally, we develop a universal multi-domain graph pre-training strategy alongside HAGO to collaboratively learn high-quality node representations across domains. To effectively transfer the learned multi-domain knowledge to the target domain, we design an effective graph prompting method, which incorporates pre-trained embeddings with learnable prompts for the recommendation task. Our framework is compatible with various graph-based models and pre-training techniques, demonstrating broad applicability and effectiveness. Further experimental results show that our solutions outperform state-of-the-art methods in multi-domain recommendation scenarios and highlight their potential for real-world applications.
Moyun: A Diffusion-Based Model for Style-Specific Chinese Calligraphy Generation
Oct 10, 2024



Abstract:Although Chinese calligraphy generation has achieved style transfer, generating calligraphy by specifying the calligrapher, font, and character style remains challenging. To address this, we propose a new Chinese calligraphy generation model 'Moyun' , which replaces the Unet in the Diffusion model with Vision Mamba and introduces the TripleLabel control mechanism to achieve controllable calligraphy generation. The model was tested on our large-scale dataset 'Mobao' of over 1.9 million images, and the results demonstrate that 'Moyun' can effectively control the generation process and produce calligraphy in the specified style. Even for calligraphy the calligrapher has not written, 'Moyun' can generate calligraphy that matches the style of the calligrapher.
Universal Modem Generation with Inherent Adaptability to Variant Underwater Acoustic Channels: a Data-Driven Perspective
Sep 21, 2024



Abstract:In underwater acoustic (UWA) communication, orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) is commonly employed to mitigate the inter-symbol interference (ISI) caused by delay spread. However, path-specific Doppler effects in UWA channels could result in significant inter-carrier interference (ICI) in the OFDM system. To address this problem, we introduce a multi-resolution convolutional neural network (CNN) named UWAModNet in this paper, designed to optimize the modem structure, specifically modulation and demodulation matrices. Based on a trade-off between the minimum and the average equivalent sub-channel rate, we propose an optimization criterion suitable to evaluate the performance of our learned modem. Additionally, a two-stage training strategy is developed to achieve quasi-optimal results. Simulations indicate that the learned modem outperforms zero-padded OFDM (ZP-OFDM) in terms of equivalent sub-channel rate and bit error rate, even under more severe Doppler effects during testing compared to training.
SinkLoRA: Enhanced Efficiency and Chat Capabilities for Long-Context Large Language Models
Jun 09, 2024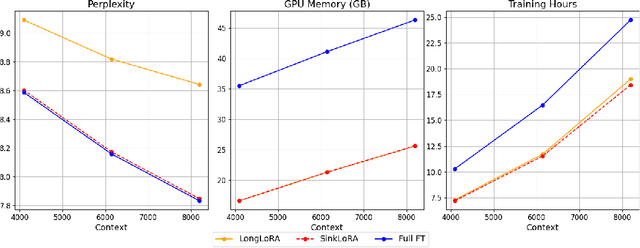
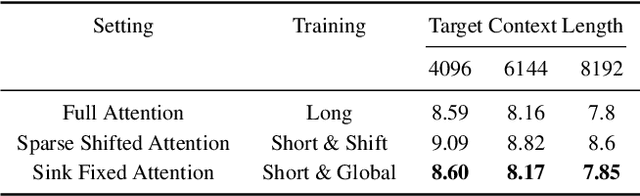
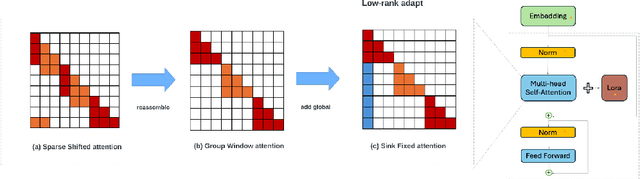
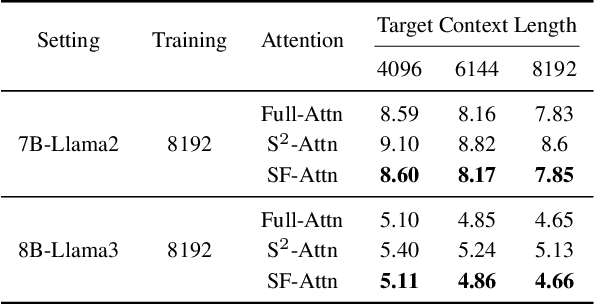
Abstract:Extending the functionality of the Transformer model to accommodate longer sequence lengths has become a critical challenge. This extension is crucial not only for improving tasks such as language translation and long-context processing but also for enabling novel applications like chatbots, code generation, and multimedia content creation. The primary obstacle is the self-attention mechanism, which scales quadratically with sequence length in terms of computation time and memory requirements. LongLoRA proposed shifted sparse attention (S\(^2\)-Attn), effectively enabling context extension and leading to non-trivial computation savings with similar performance to fine-tuning with vanilla attention. However, LongLoRA is still not as efficient as vanilla attention, reaching only 39\% of the perplexity improvement compared to full attention. This inefficiency is due to the cyclic shift applied within different attention head patterns, causing either chaos in the attention head structure or unnecessary information exchange between token groups. To address these issues, We propose \textbf{SinkLoRA}, which features better work partitioning. Specifically, (1) we developed SF-Attn with a segmentation and reassembly algorithm to proportionally return cyclically shifted groups of attention heads to their un-shifted state together with global attention of "sink attention tokens", achieving 92\% of the perplexity improvement compared to full attention after fine tuning, and (2) applied a SOTA KV cache compression algorithm H$_2$O to accelerate inference. Furthermore, We conducted supervised fine-tuning with SinkLoRA using a self collected LongAlpaca-plus dataset. All our code, models, datasets, and demos are available at \url{https://github.com/Dexter-GT-86/SinkLoRA}.
Deep Pattern Network for Click-Through Rate Prediction
Apr 17, 2024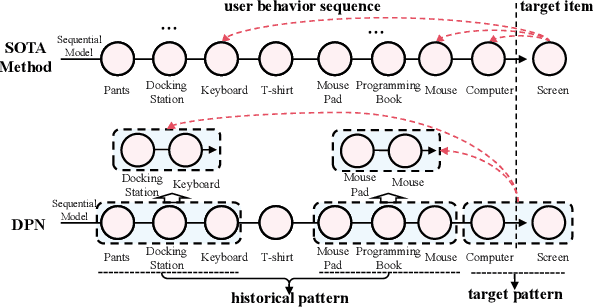
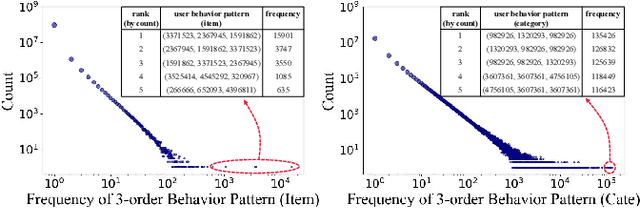
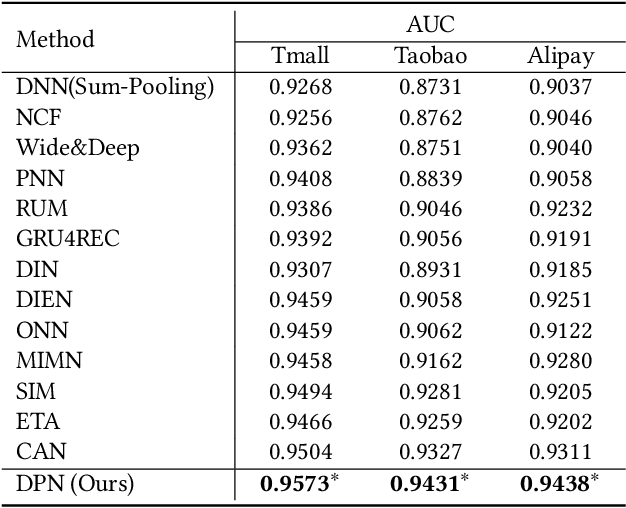
Abstract:Click-through rate (CTR) prediction tasks play a pivotal role in real-world applications, particularly in recommendation systems and online advertising. A significant research branch in this domain focuses on user behavior modeling. Current research predominantly centers on modeling co-occurrence relationships between the target item and items previously interacted with by users in their historical data. However, this focus neglects the intricate modeling of user behavior patterns. In reality, the abundance of user interaction records encompasses diverse behavior patterns, indicative of a spectrum of habitual paradigms. These patterns harbor substantial potential to significantly enhance CTR prediction performance. To harness the informational potential within user behavior patterns, we extend Target Attention (TA) to Target Pattern Attention (TPA) to model pattern-level dependencies. Furthermore, three critical challenges demand attention: the inclusion of unrelated items within behavior patterns, data sparsity in behavior patterns, and computational complexity arising from numerous patterns. To address these challenges, we introduce the Deep Pattern Network (DPN), designed to comprehensively leverage information from user behavior patterns. DPN efficiently retrieves target-related user behavior patterns using a target-aware attention mechanism. Additionally, it contributes to refining user behavior patterns through a pre-training paradigm based on self-supervised learning while promoting dependency learning within sparse patterns. Our comprehensive experiments, conducted across three public datasets, substantiate the superior performance and broad compatibility of DPN.
Modem Optimization of High-Mobility Scenarios: A Deep-Learning-Inspired Approach
Mar 21, 2024



Abstract:The next generation wireless communication networks are required to support high-mobility scenarios, such as reliable data transmission for high-speed railways. Nevertheless, widely utilized multi-carrier modulation, the orthogonal frequency division multiplex (OFDM), cannot deal with the severe Doppler spread brought by high mobility. To address this problem, some new modulation schemes, e.g. orthogonal time frequency space and affine frequency division multiplexing, have been proposed with different design criteria from OFDM, which promote reliability with the cost of extremely high implementation complexity. On the other hand, end-to-end systems achieve excellent gains by exploiting neural networks to replace traditional transmitters and receivers, but have to retrain and update continually with channel varying. In this paper, we propose the Modem Network (ModNet) to design a novel modem scheme. Compared with end-to-end systems, channels are directly fed into the network and we can directly get a modem scheme through ModNet. Then, the Tri-Phase training strategy is proposed, which mainly utilizes the siamese structure to unify the learned modem scheme without retraining frequently faced up with time-varying channels. Simulation results show the proposed modem scheme outperforms OFDM systems under different highmobility channel statistics.
Time-aligned Exposure-enhanced Model for Click-Through Rate Prediction
Aug 19, 2023



Abstract:Click-Through Rate (CTR) prediction, crucial in applications like recommender systems and online advertising, involves ranking items based on the likelihood of user clicks. User behavior sequence modeling has marked progress in CTR prediction, which extracts users' latent interests from their historical behavior sequences to facilitate accurate CTR prediction. Recent research explores using implicit feedback sequences, like unclicked records, to extract diverse user interests. However, these methods encounter key challenges: 1) temporal misalignment due to disparate sequence time ranges and 2) the lack of fine-grained interaction among feedback sequences. To address these challenges, we propose a novel framework called TEM4CTR, which ensures temporal alignment among sequences while leveraging auxiliary feedback information to enhance click behavior at the item level through a representation projection mechanism. Moreover, this projection-based information transfer module can effectively alleviate the negative impact of irrelevant or even potentially detrimental components of the auxiliary feedback information on the learning process of click behavior. Comprehensive experiments on public and industrial datasets confirm the superiority and effectiveness of TEM4CTR, showcasing the significance of temporal alignment in multi-feedback modeling.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge